Creating an IAM User
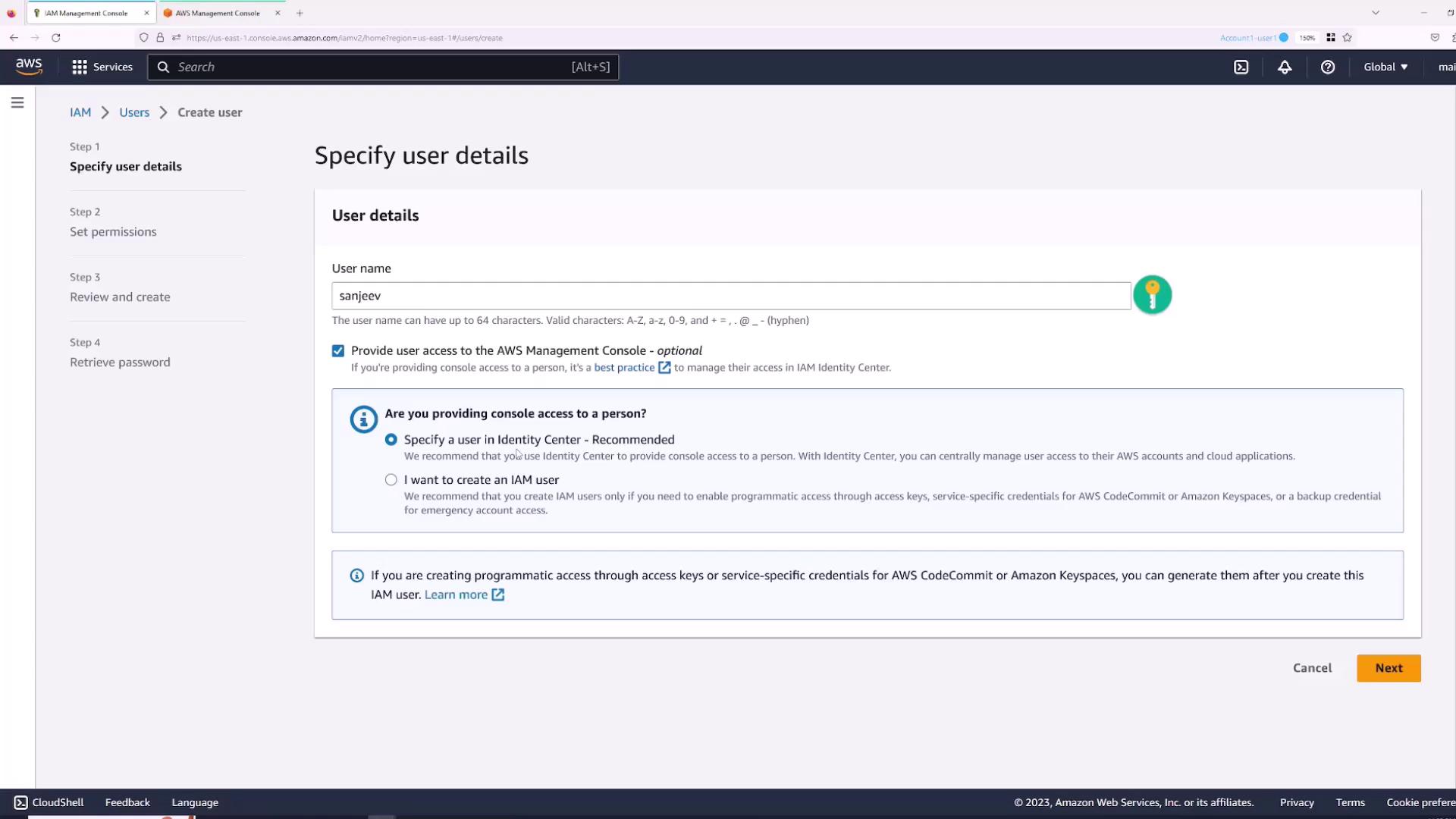
Follow these steps to create an IAM user:- Navigate to the Users section.
- Click Add Users.
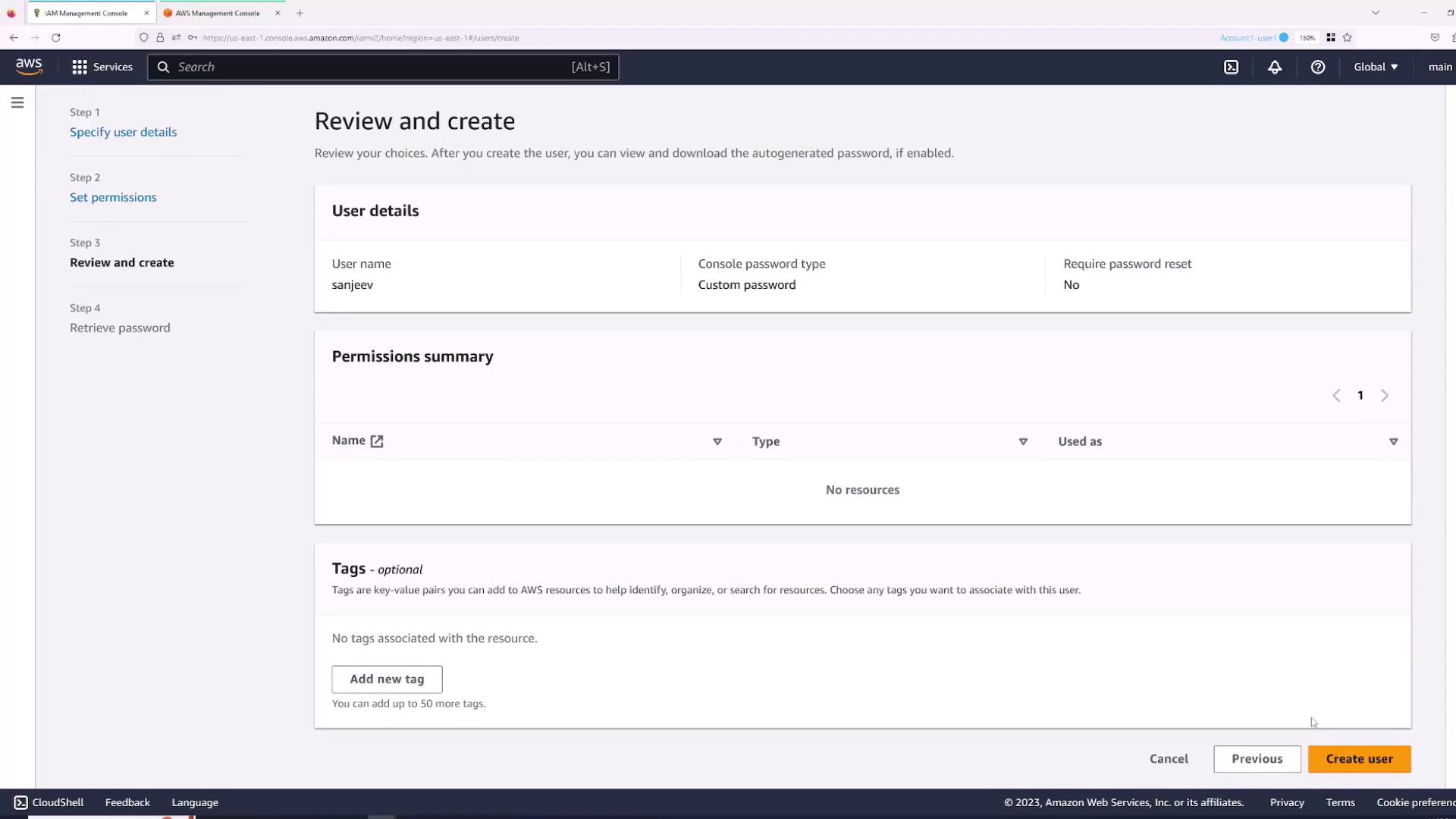
- Enter a username (for example, “Sanjeev”) and select the checkbox for “Provide user access to AWS Management Console”.
- Choose whether to auto-generate a password or set one manually. For this demonstration, specify the password and disable the “users must create a new password at next sign-in” option.
- Click Next.
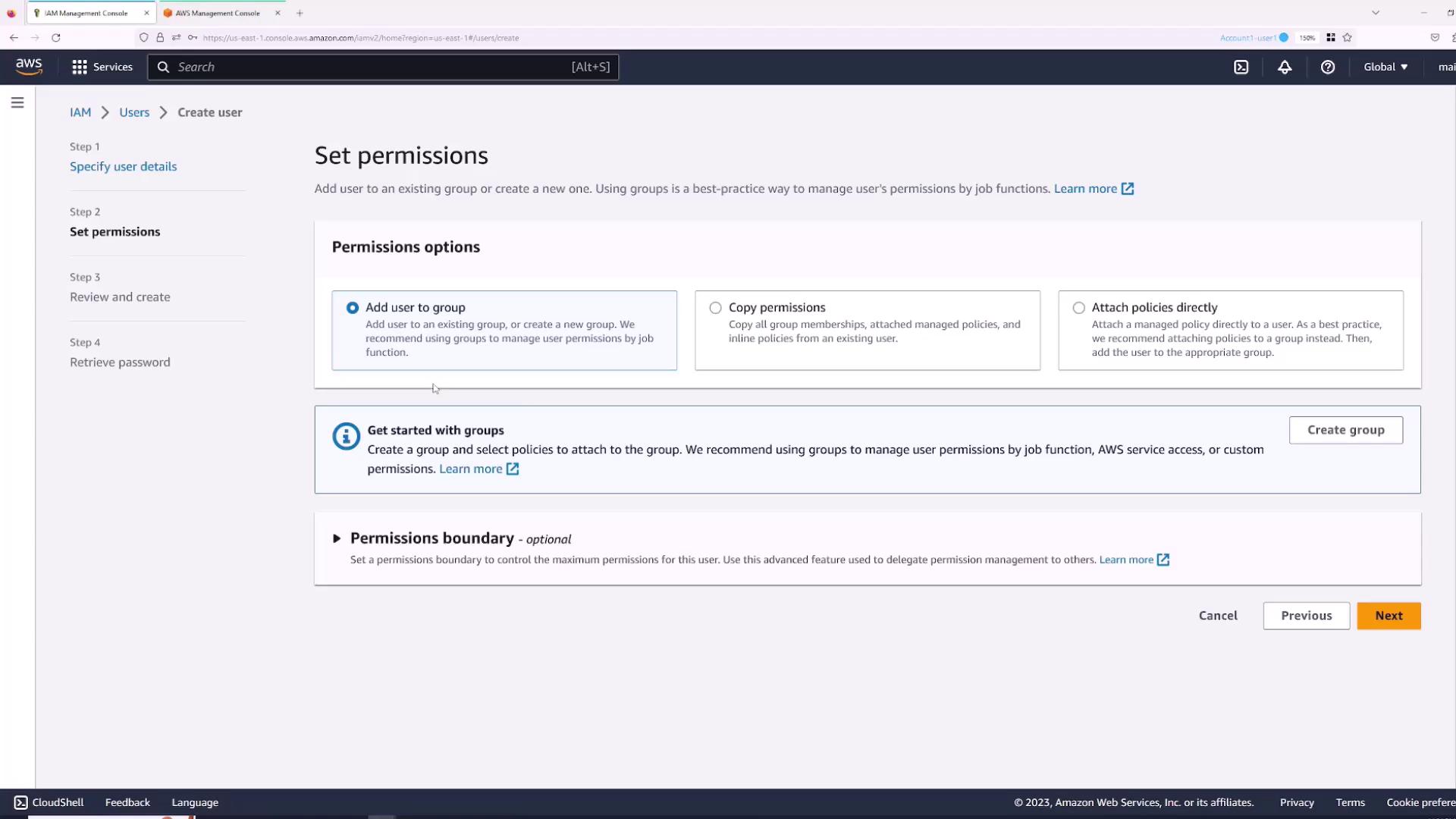
Setting User Permissions
By default, a new IAM user receives no permissions. You can provide permissions by:- Adding the user to an existing group.
- Copying permissions from another user.
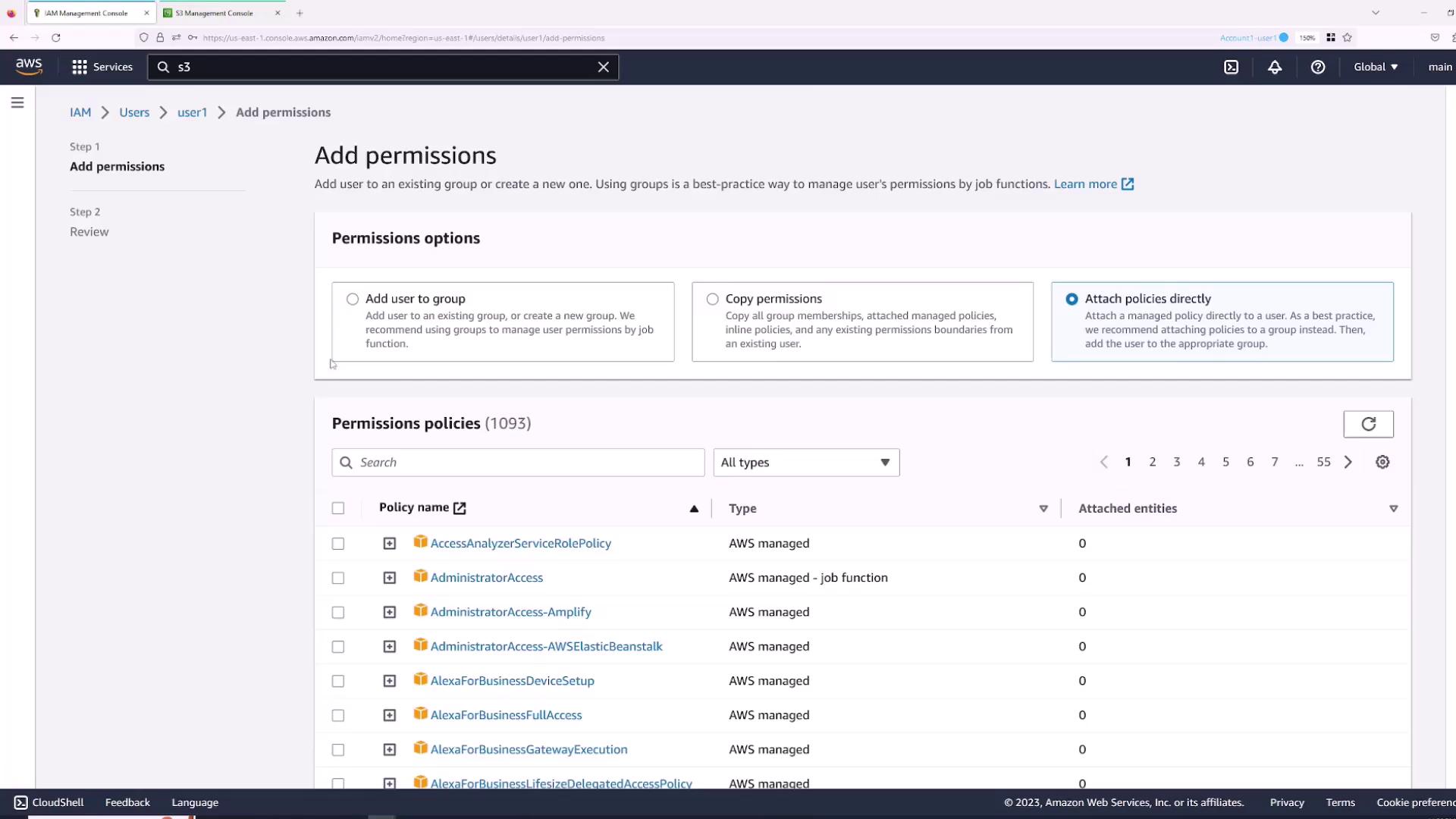
- Attaching policies directly.
Logging in as an IAM User
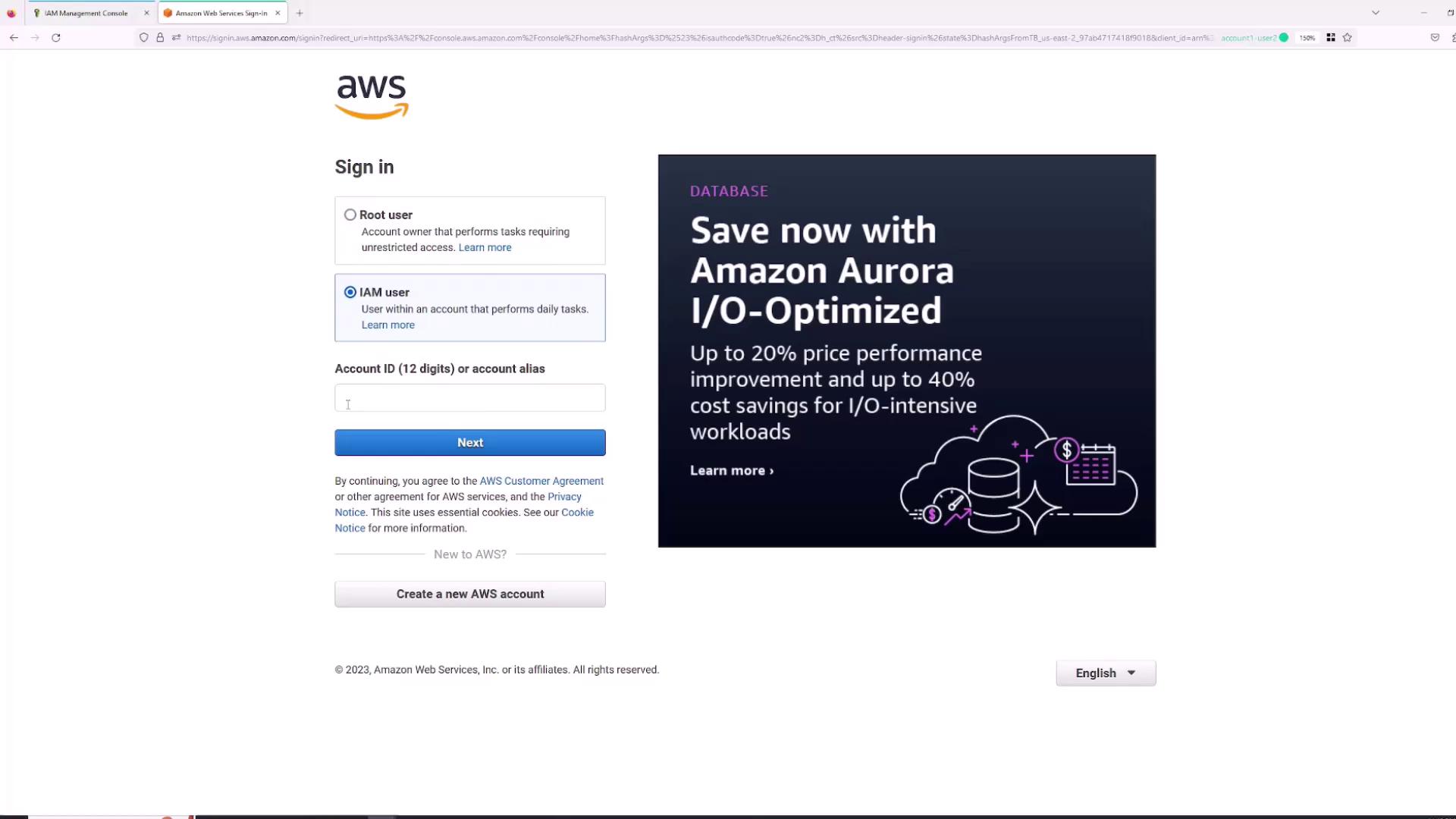
To log in as the newly created IAM user “Sanjeev”:- Open a new browser tab or an incognito window.
- Select the “IAM user” sign-in option (not the “root user” sign-in).
- Enter your AWS Account ID. You can find this by clicking your account name in the root session and copying the account ID.
- Enter the username (“Sanjeev”) and the previously specified password.
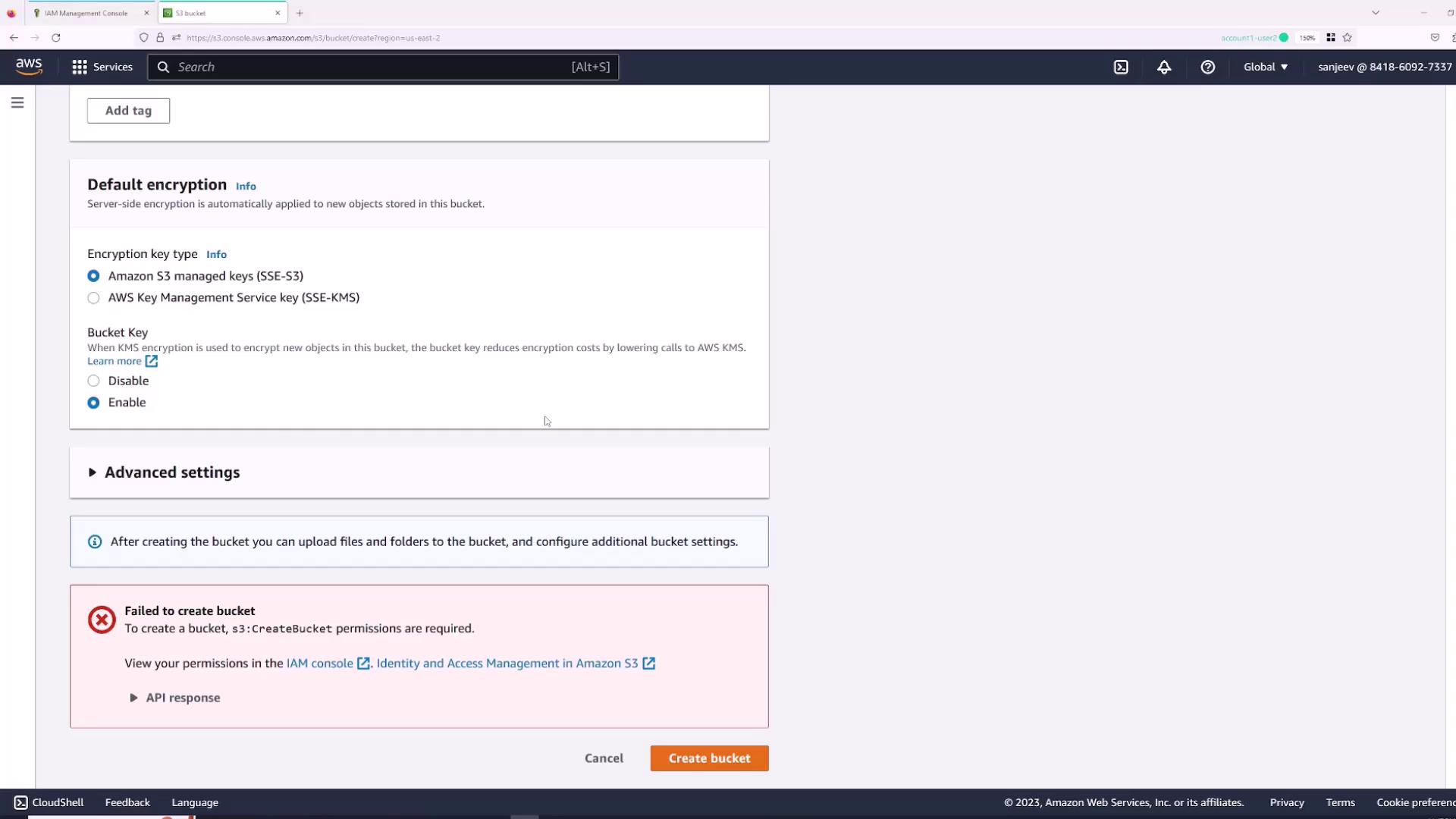
Granting Permissions via the Root User
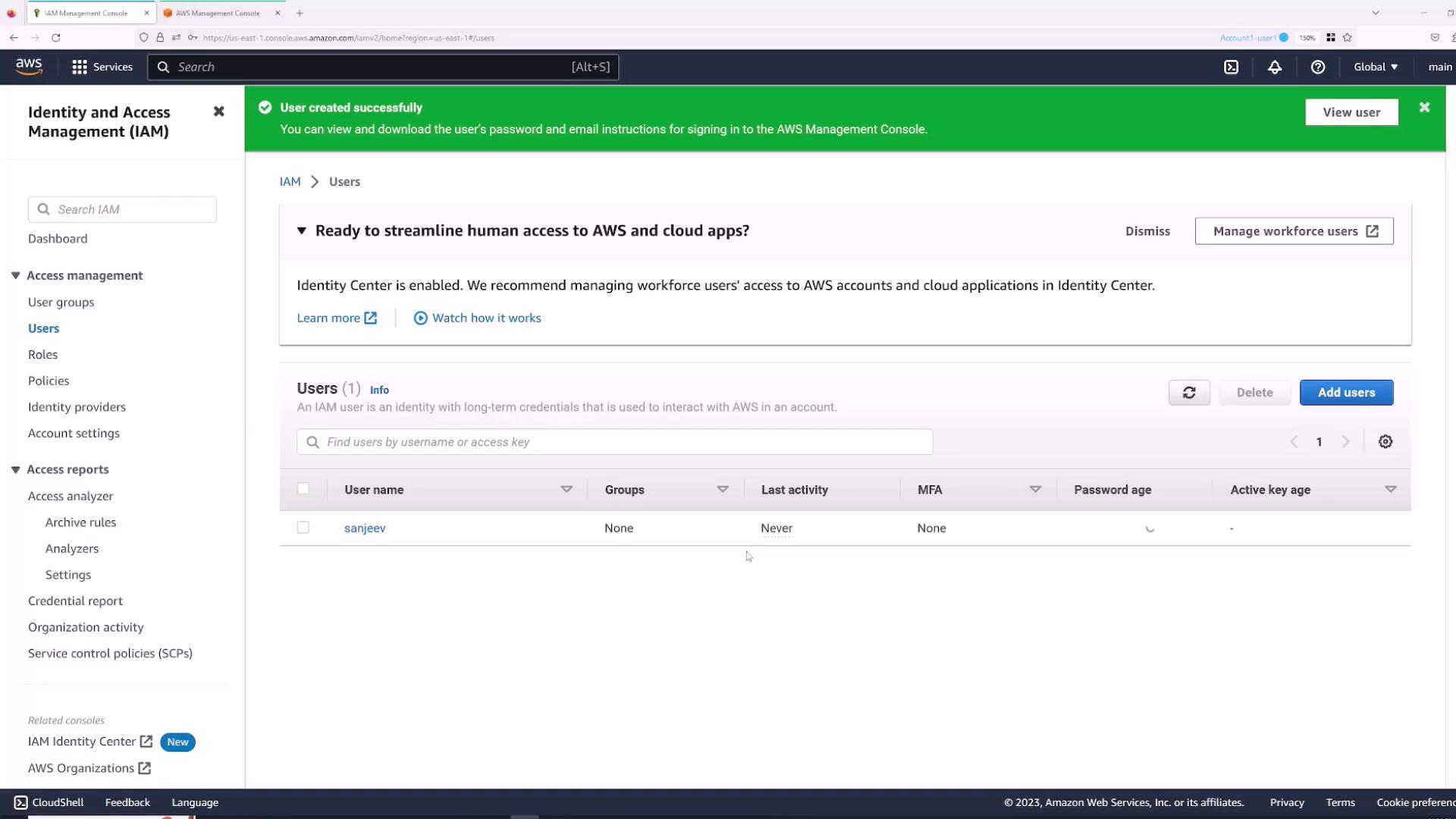
Since the IAM user “Sanjeev” lacks permissions, you must use the root account to grant the required policies:- Switch back to the root user session.
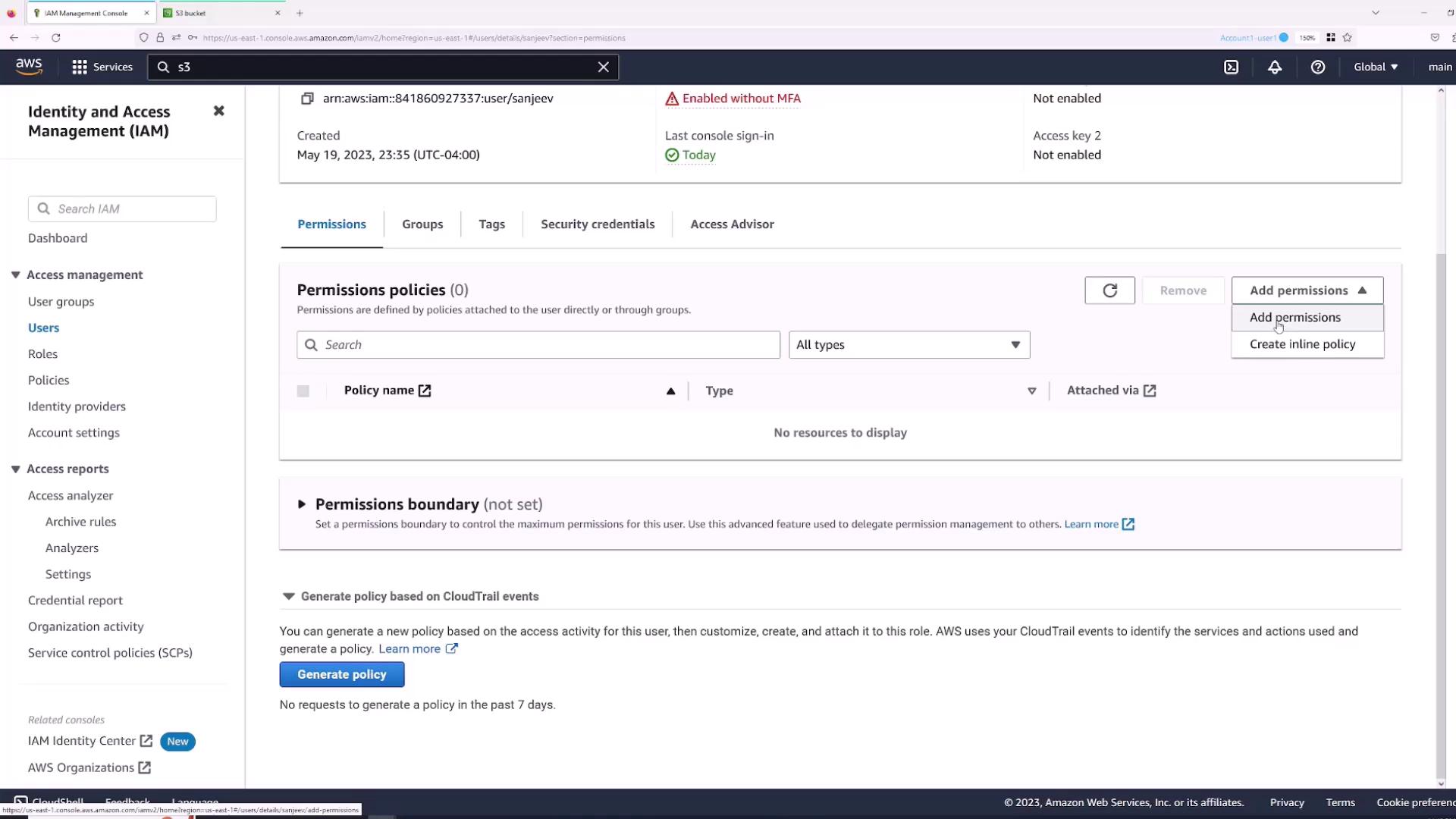
- In the IAM console, open the Users section and select the “Sanjeev” user.
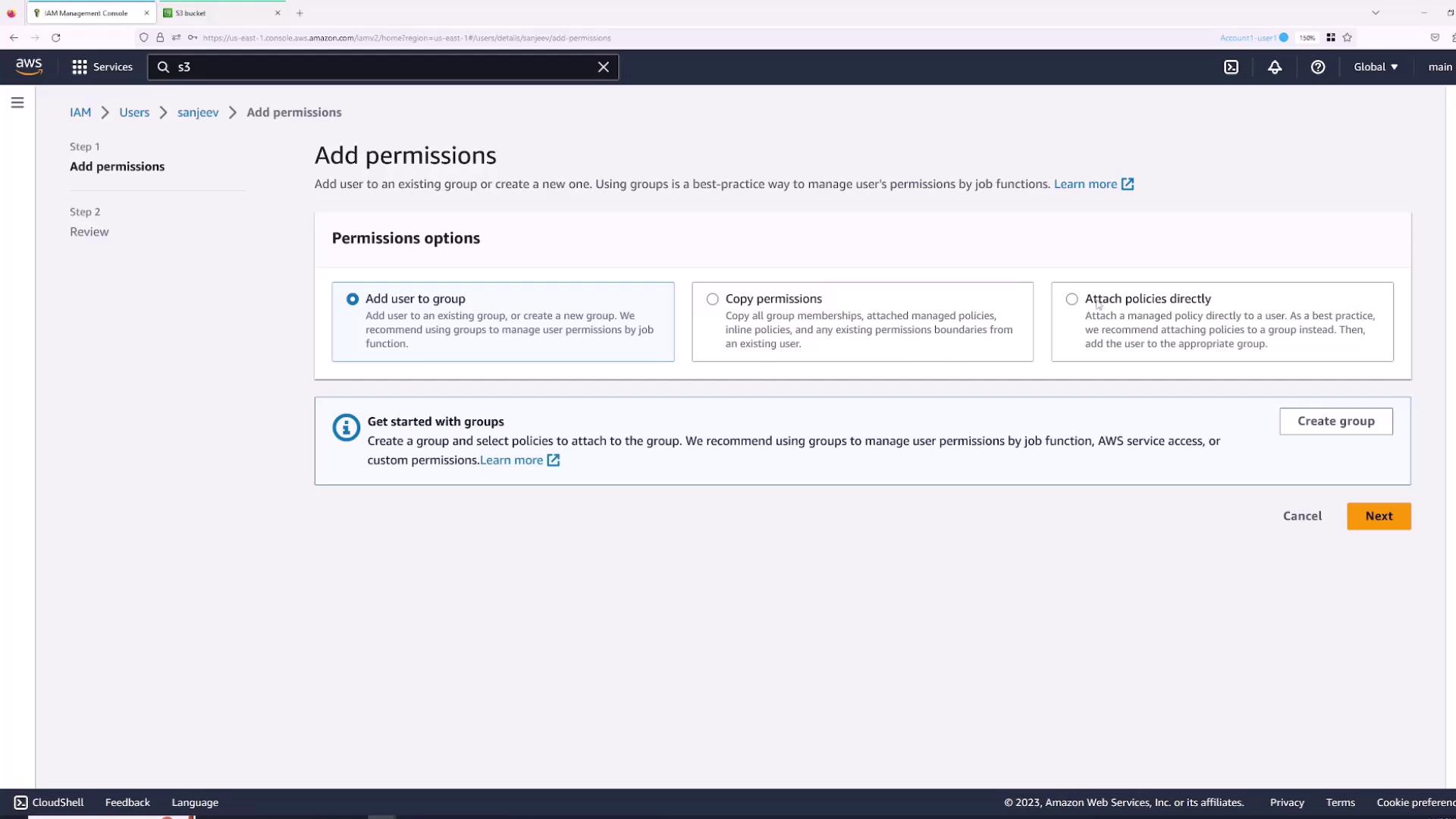
- Navigate to the Permissions tab and click Add permissions.
- Choose “Attach policies directly” and select the AWS managed policy “AdministratorAccess” for full access.
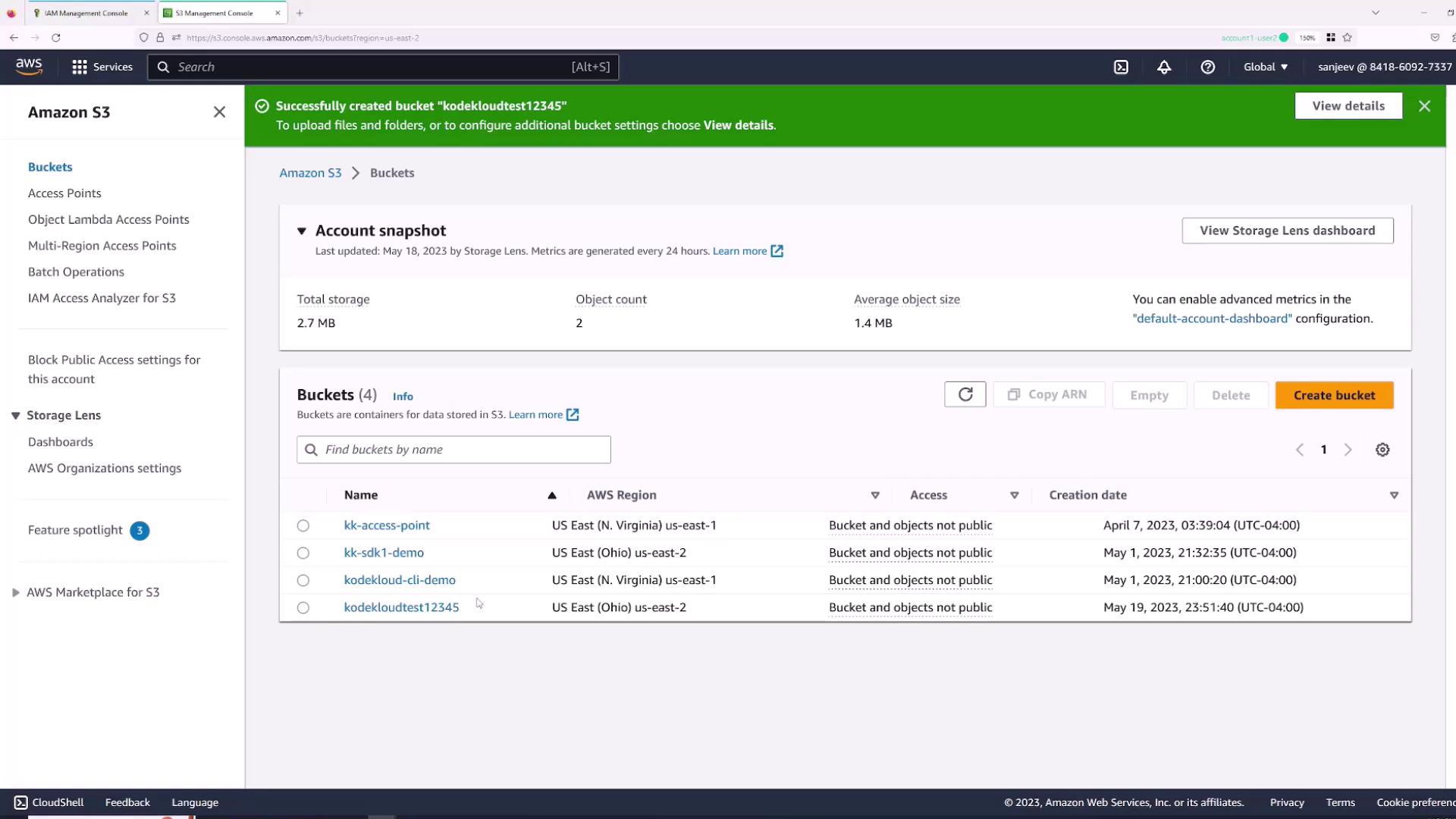
Managing Permissions with Groups
For organizations with multiple employees requiring similar permissions, using AWS groups simplifies permission management. Instead of assigning permissions individually, create groups and attach the necessary policies.- Optionally, remove any existing direct permissions from the “Sanjeev” user.
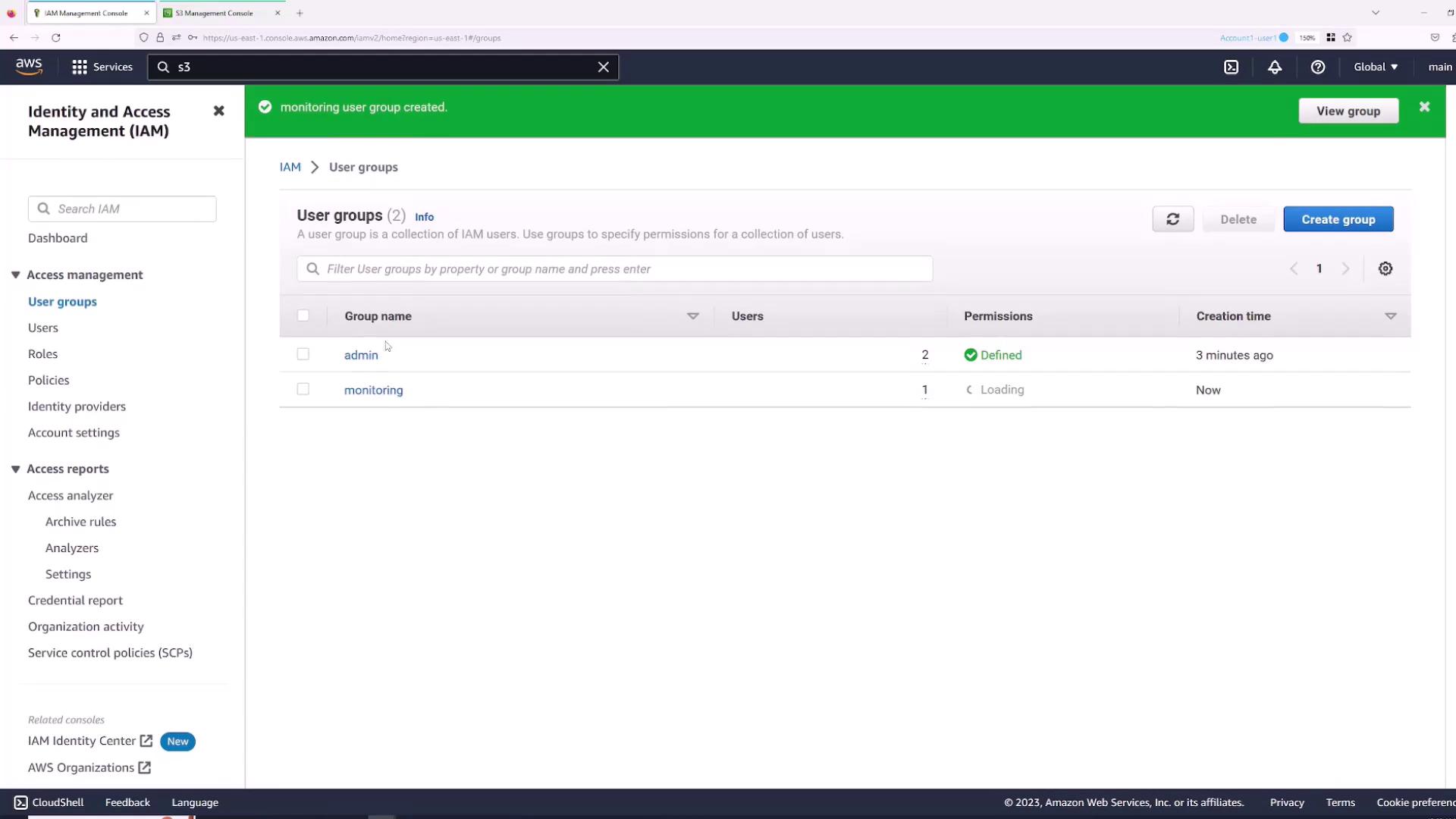
- Create a new group (e.g., “Admin”) and add users who require administrative access.
- Attach the “AdministratorAccess” policy to this group and create the group.

Using Roles for Temporary Permissions
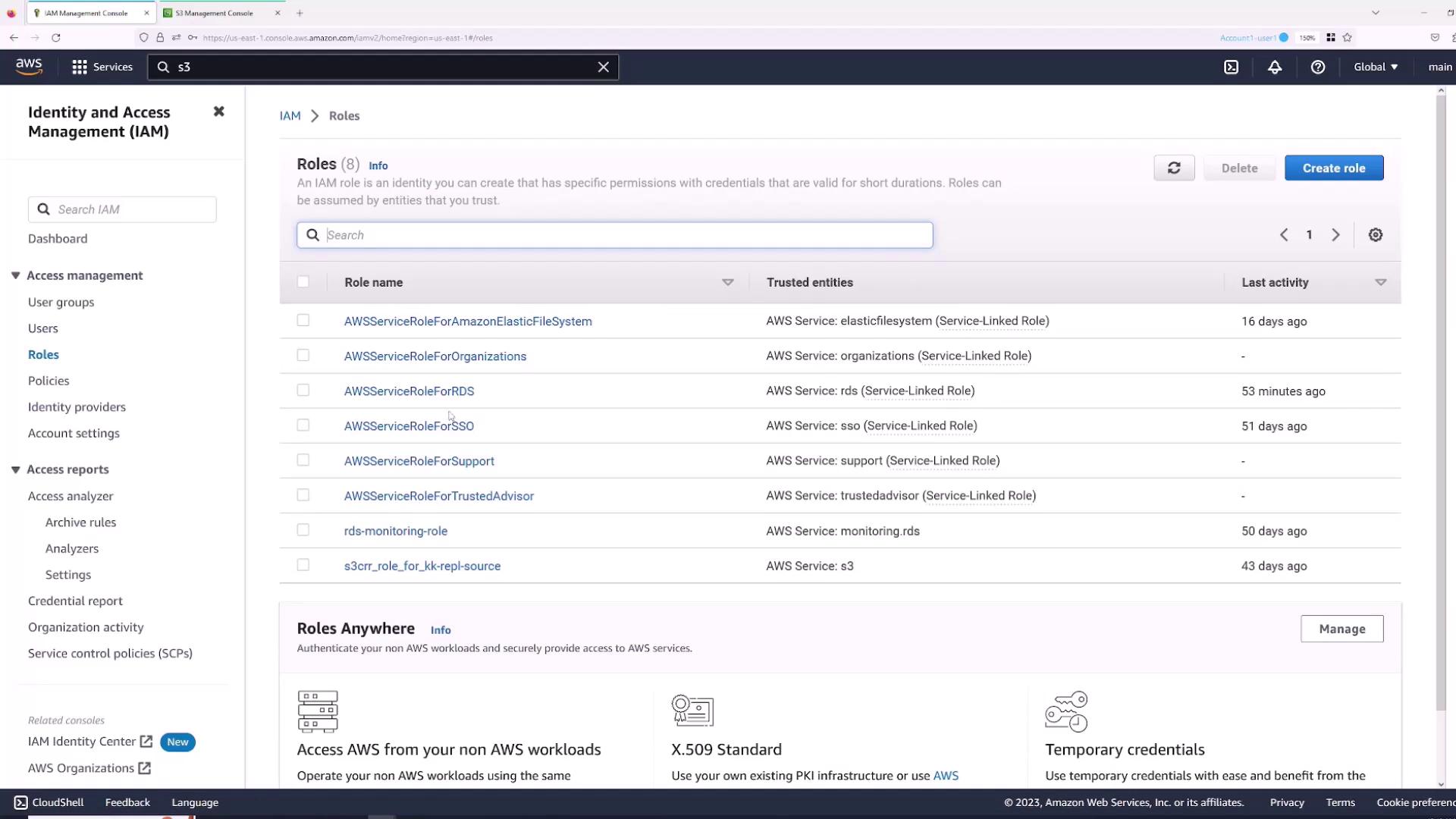
AWS IAM roles allow users or services to assume temporary permissions. For example, a user with read-only access can temporarily assume a role with enhanced permissions to modify S3 buckets. To create a role:- Open the Roles section in the IAM console.
- Click Create Role.
- Select “AWS account” if the role will be assumed within your account.
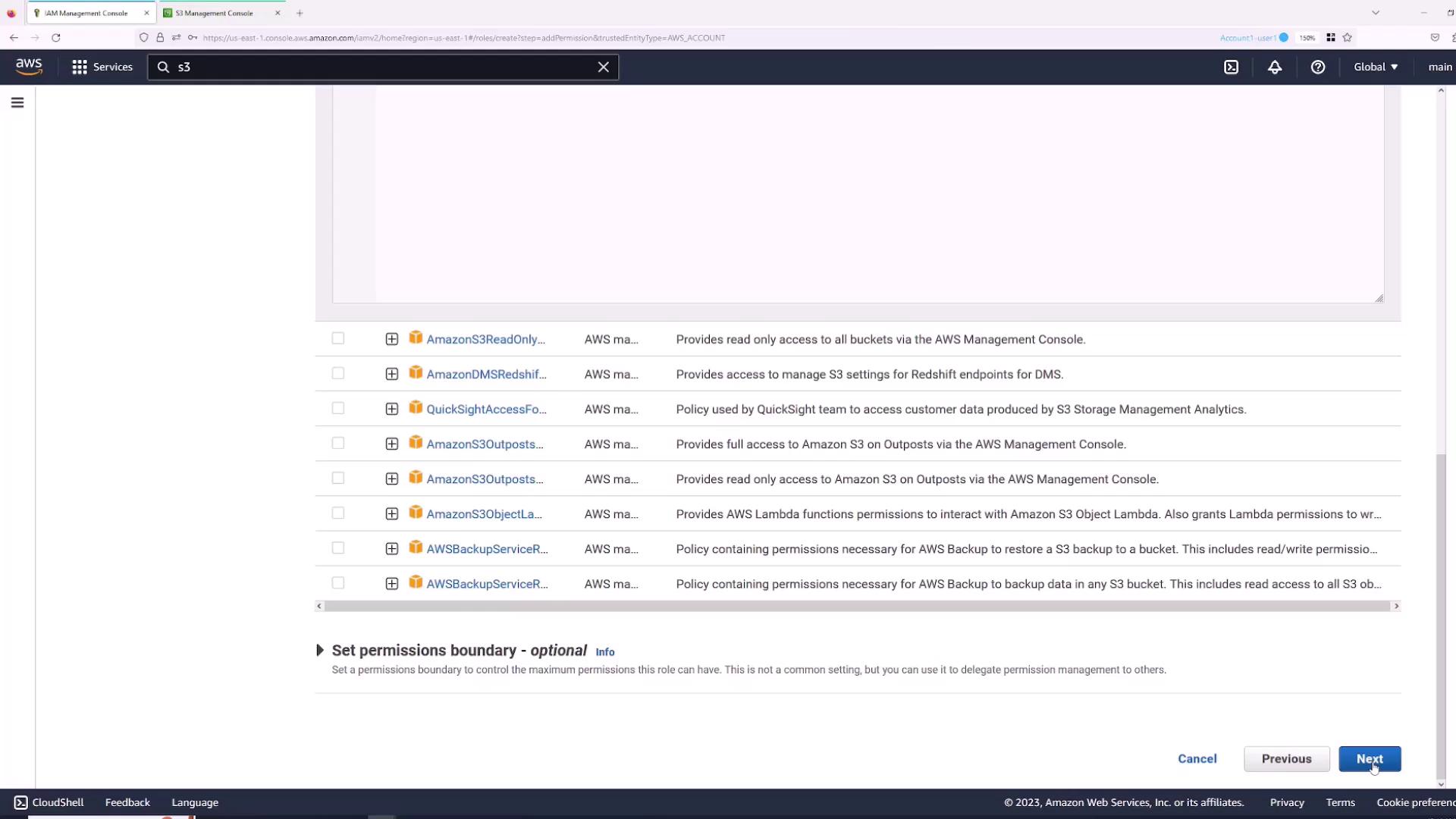
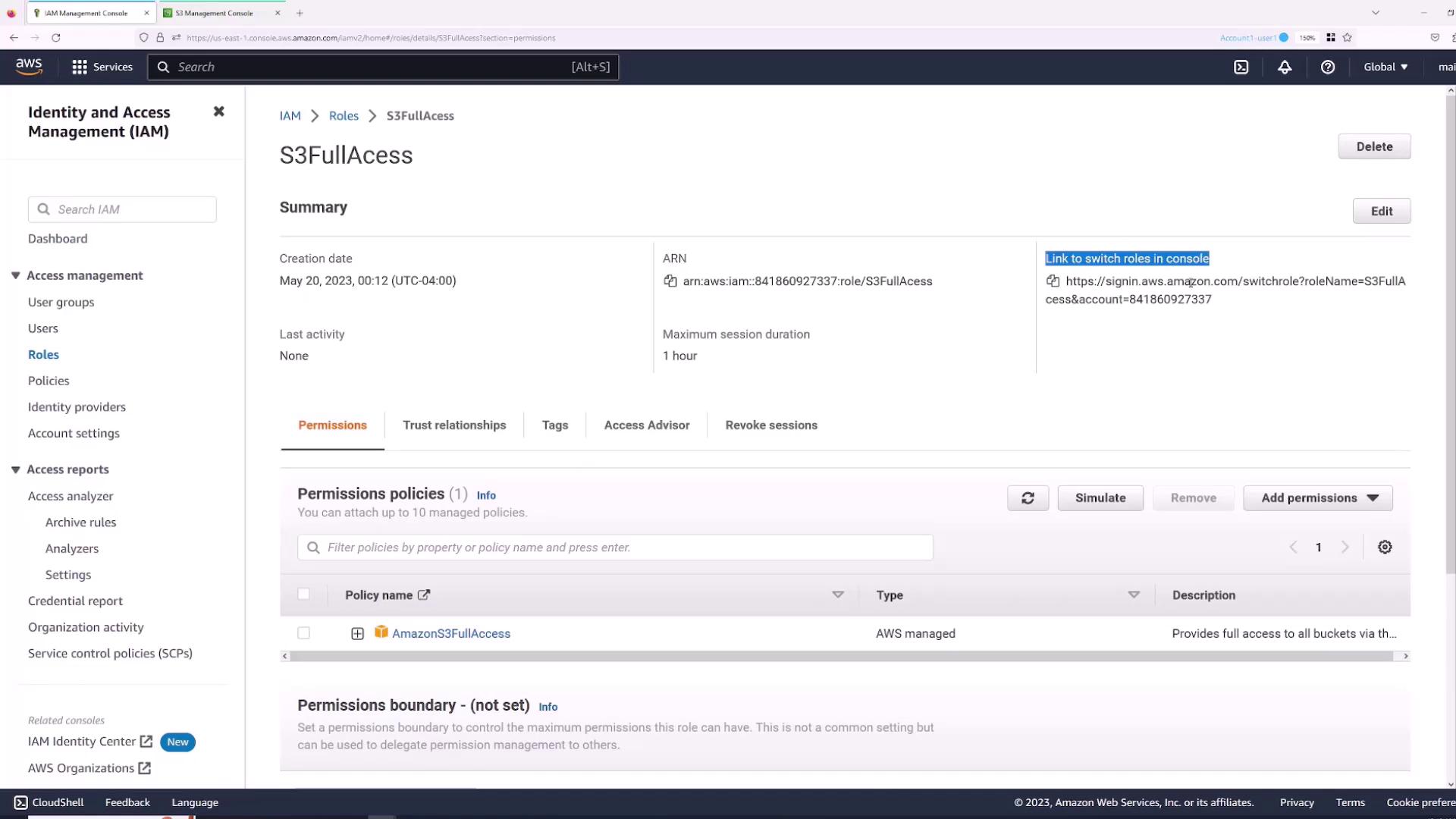
- Click Next, then attach the required permissions, such as the AWS managed “S3FullAccess” policy.
- Name the role (for example, “S3FullAccess”) and complete the creation process.
Restricting Role Assumption to Specific Users
To ensure that only designated users (e.g., “Sanjeev”) can assume the S3FullAccess role, attach an inline policy to that user:- In the IAM console, navigate to the “Sanjeev” user.
- Click Add Permissions and select Create Inline Policy.
- For the service, choose STS, and under actions, select AssumeRole.
- Specify the role’s ARN. Use the provided interface to add the ARN by entering the role name.
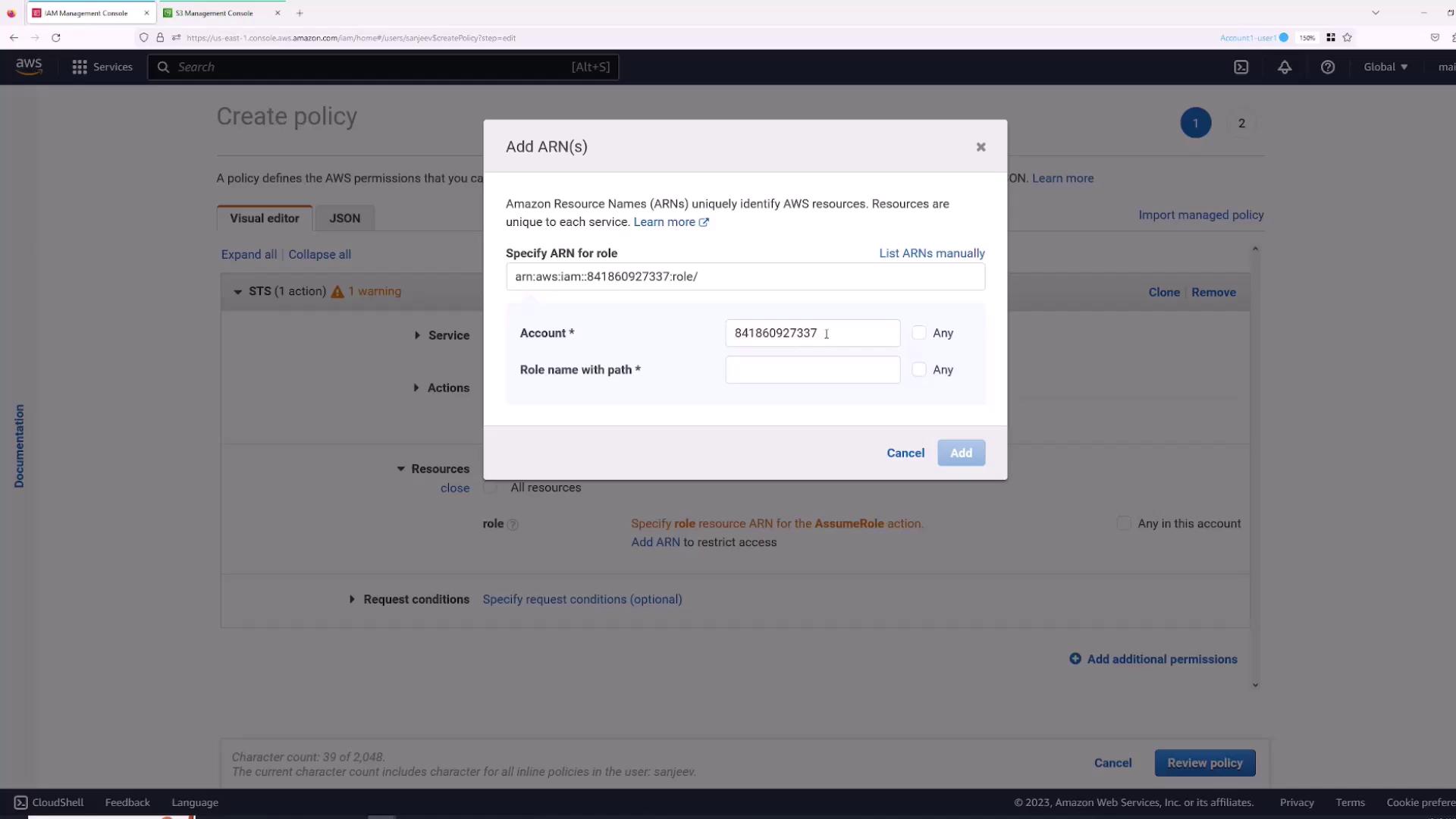
- Review and create the policy, naming it (for example, “AssumeS3Access”). The resulting policy will look similar to:
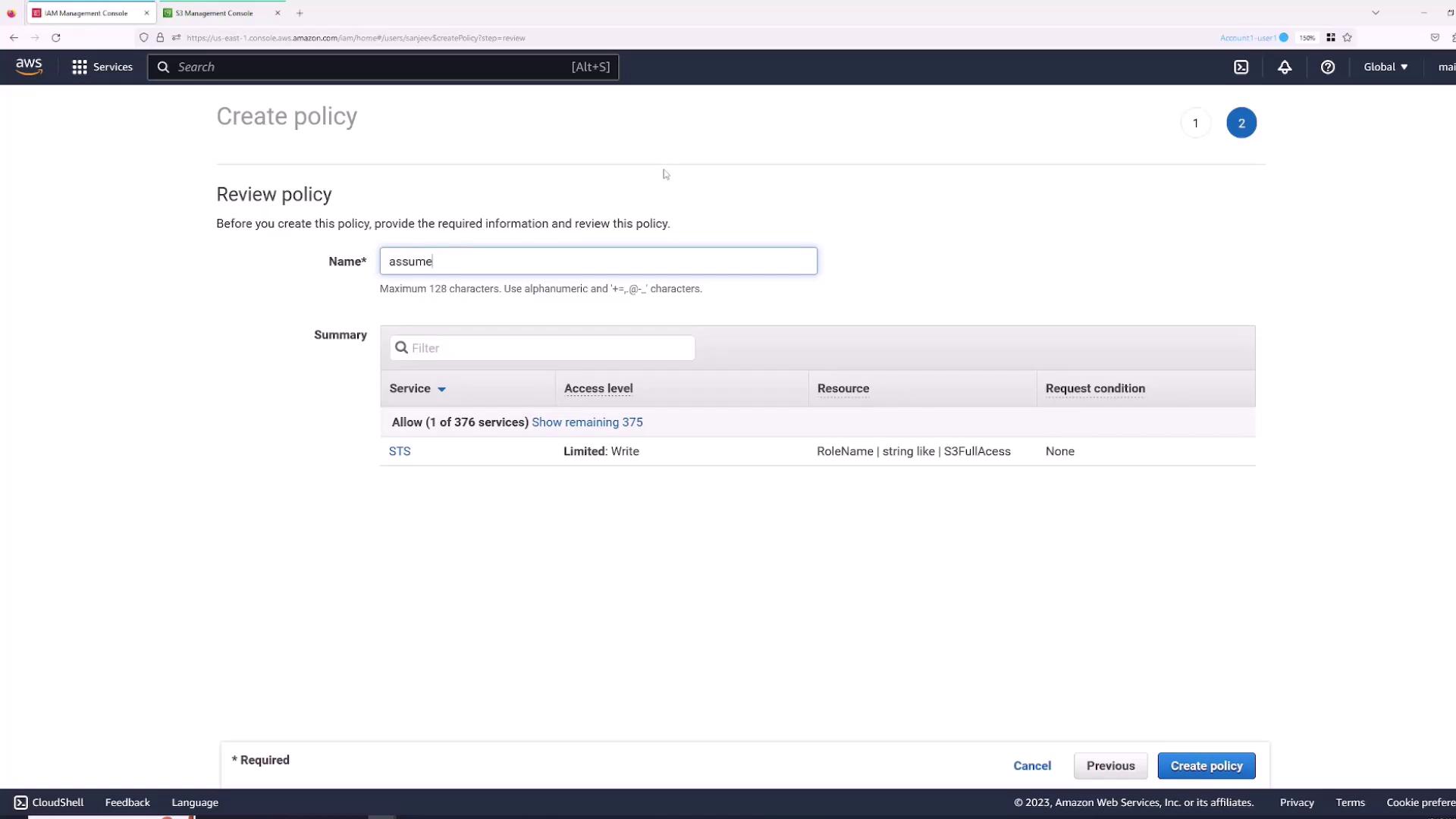
- Go to the Roles section and select the “S3FullAccess” role.
- Click the Switch Role link.
- Paste the provided URL in the “Sanjeev” session. The switch role page will auto-fill the AWS account, role name, and let you set a display name (e.g., “S3 role”) along with a color.
- Click Switch Role.

Summary
In this guide, we covered how to:- Create IAM users and provide access to the AWS Management Console.
- Grant permissions directly and through groups to efficiently manage multiple users.
- Utilize IAM roles for temporary permission elevation.
- Secure role assumption using precise AWS STS policies.