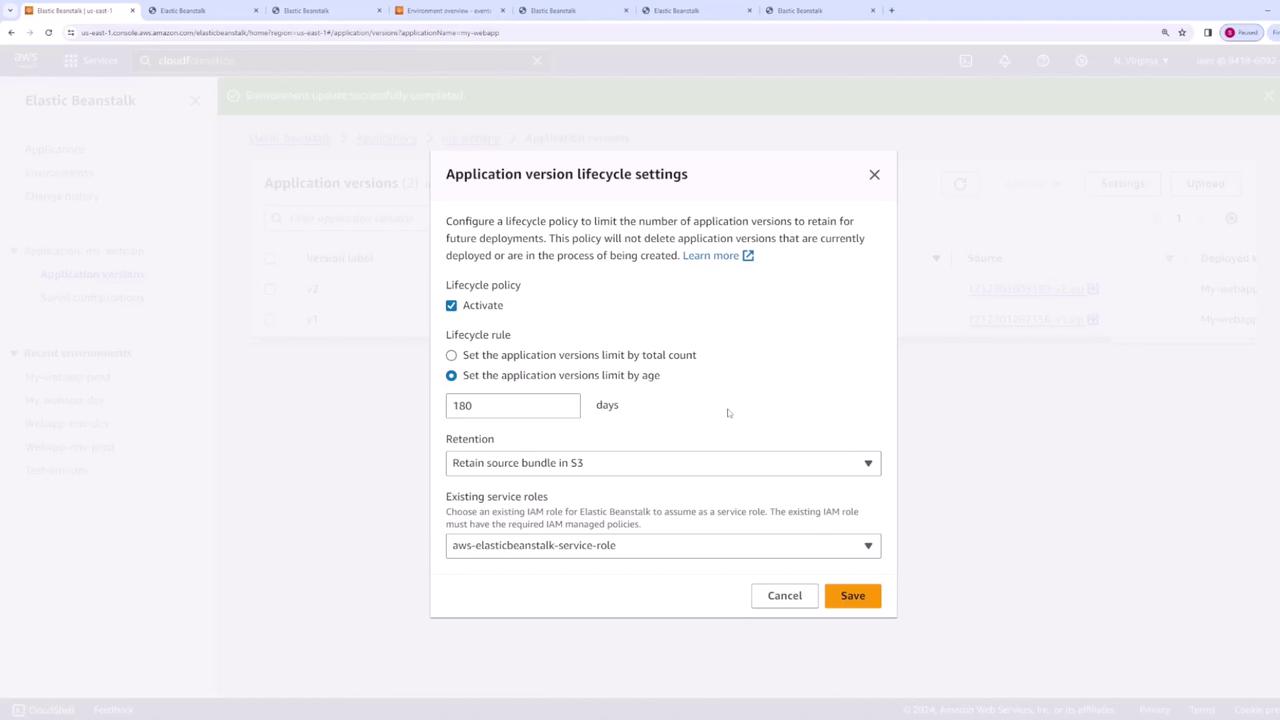
Configuring Lifecycle Policies
To set up a lifecycle policy, follow these steps:- Select your application (e.g., your web app) from the Elastic Beanstalk console.
- Navigate to Application Versions.
- Click on Settings to enable the lifecycle policy.
-
Retention Period:
Specify a duration (for example, 180 days). Versions older than the defined period will be automatically removed. -
Version Limit:
Set a maximum number of versions (for example, 200). When a new version is added that exceeds this limit (i.e., the 201st version), the oldest version will be deleted, maintaining only the most recent 200 versions.
For enhanced version control and resource management, carefully choose between a fixed retention period and a version limit based on your project’s requirements.
Understanding Amazon S3 Integration
When a version of your code is uploaded to Elastic Beanstalk, it is stored in an Amazon S3 bucket. To verify this storage, log in to the S3 console and locate the bucket associated with your environment (for example, “Elastic Beanstalk US East One”). Within this bucket, you will see your application versions stored as zip files. The image below illustrates the Amazon S3 bucket interface, which shows the zip files along with details such as last modified dates, sizes, and storage classes.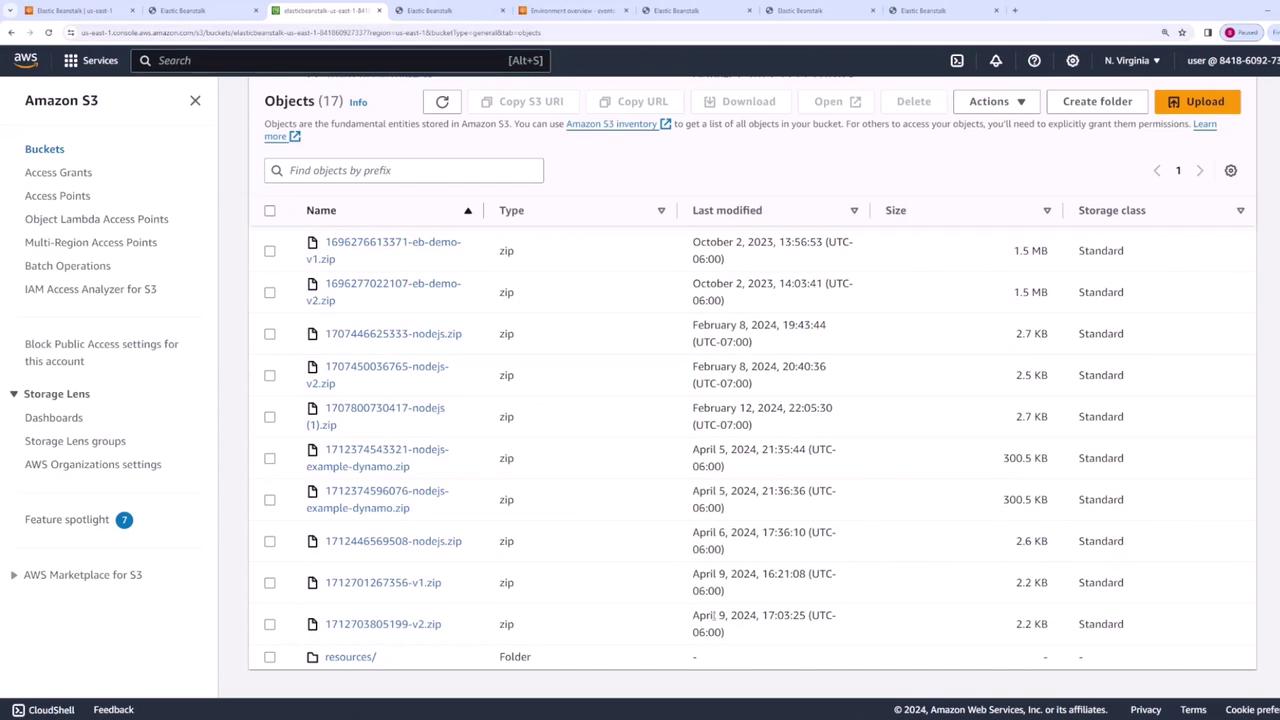
S3 File Management Options
When setting up a lifecycle policy, you have two options regarding associated files in S3:-
Retain Files in S3:
Even if a version is deleted from Elastic Beanstalk, its corresponding file remains in S3. This option is useful if you need to revert to an older version at any point. -
Delete Files from S3:
Choosing this option means that deleting a version from Elastic Beanstalk will also remove its associated file from S3 to maintain a clean storage environment.
Ensure that you understand the implications of deleting files from S3. If you might need to rollback to an earlier version, consider retaining the files even after deletion from Elastic Beanstalk.