Setting Up the .ebextensions Folder
When working with EB extensions, you must create a folder named .ebextensions in the root of your project directory. All configuration files placed inside this folder must use the.config file extension. While the filename itself has no impact on functionality, it is best practice to choose descriptive names that clarify the file’s purpose.
For example, in our Elastic Beanstalk demonstration, the application source code includes two configuration files:
- network-load-balancer.config: Modifies the configuration of the load balancer in the environment.
- environment-variables.config: Sets environment variables on the EC2 instances hosting the application.
Example: Including HTML Files
Below is an example of an HTML file included in the application. Remember, any file included in your application must follow the correct format:Configuring a Network Load Balancer
The network-load-balancer.config file changes the default load balancer from an application load balancer to a network load balancer. Consider the following YAML snippet:Setting Environment Variables
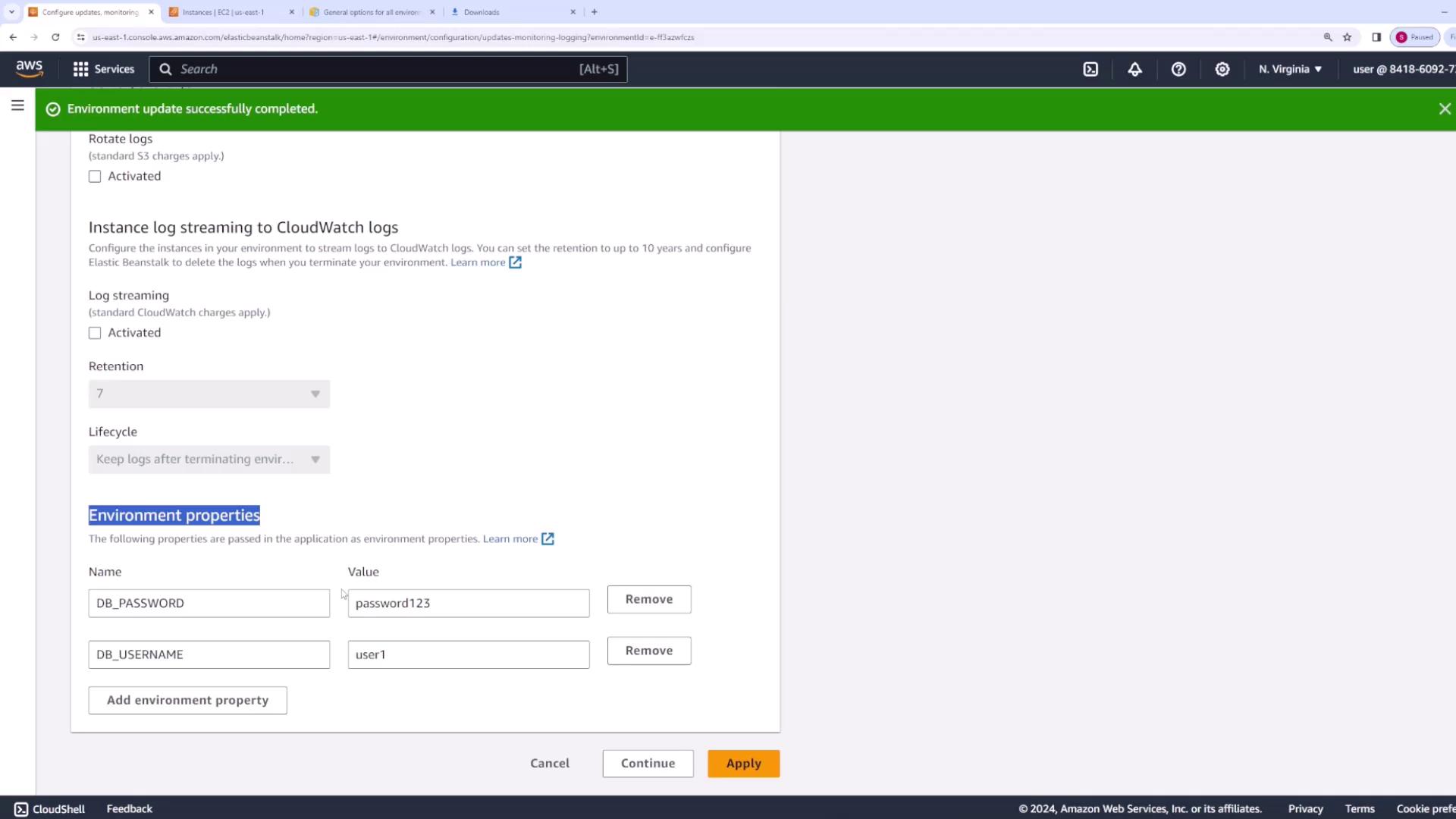
Similarly, the environment-variables.config file is used to set environment variables that your application may require. For instance, the snippet below sets the database username and password:After configuring your environment, package your application source code into a ZIP file. In this demonstration, the package is named “version three” to indicate the updated configuration. When you upload the package, Elastic Beanstalk automatically reads and applies the configuration settings.
Verifying Updates in the AWS Console
To confirm that the environment variables and other settings have been applied:- Open your application’s web console.
- Navigate to the configuration section under “Updates, Monitoring, and Logging.”
- Scroll down to “Platform Software” and review the “Environment Properties” that were set by your EB extensions.