Use Case: Ride-Sharing or Delivery Applications
Consider a ride-sharing or delivery application—comparable to Uber or DoorDash. Such applications require efficient management of high volumes of real-time data, including:- User profiles and session states.
- Driver location updates and statuses.
- Ride or delivery requests and matching logs.
- Dynamic pricing calculations for rapid updates.
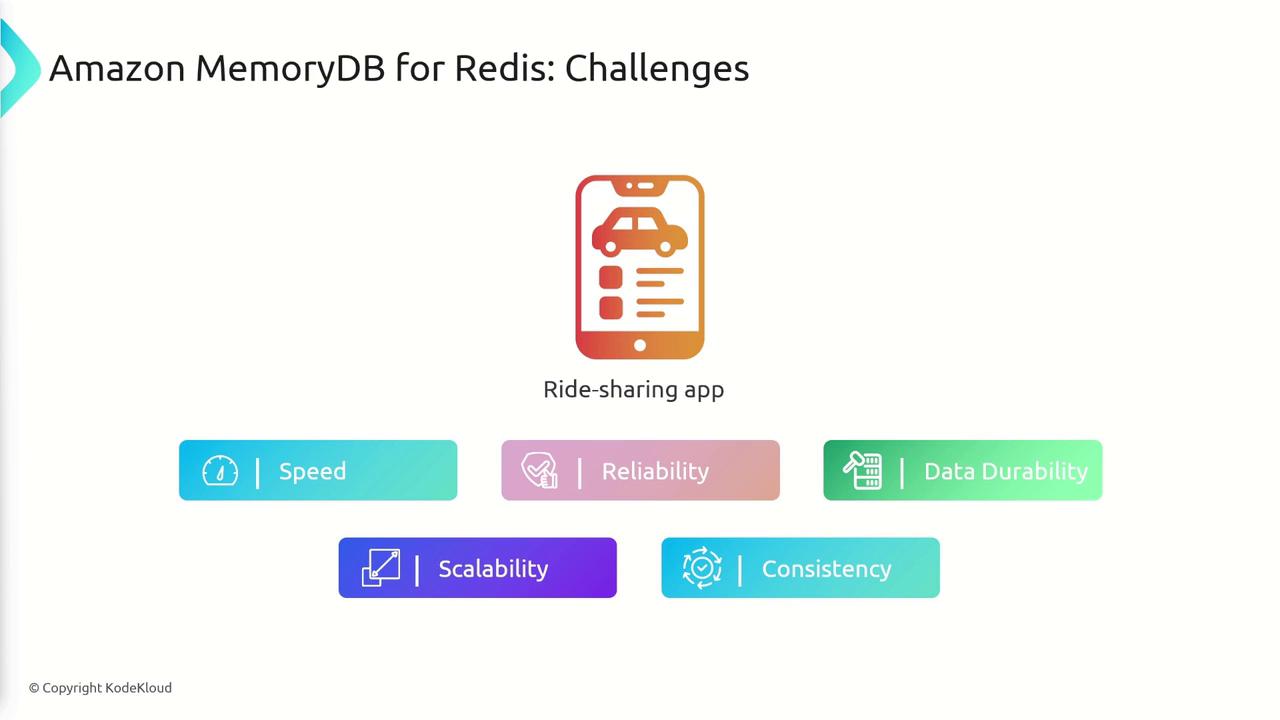
How MemoryDB Addresses These Challenges
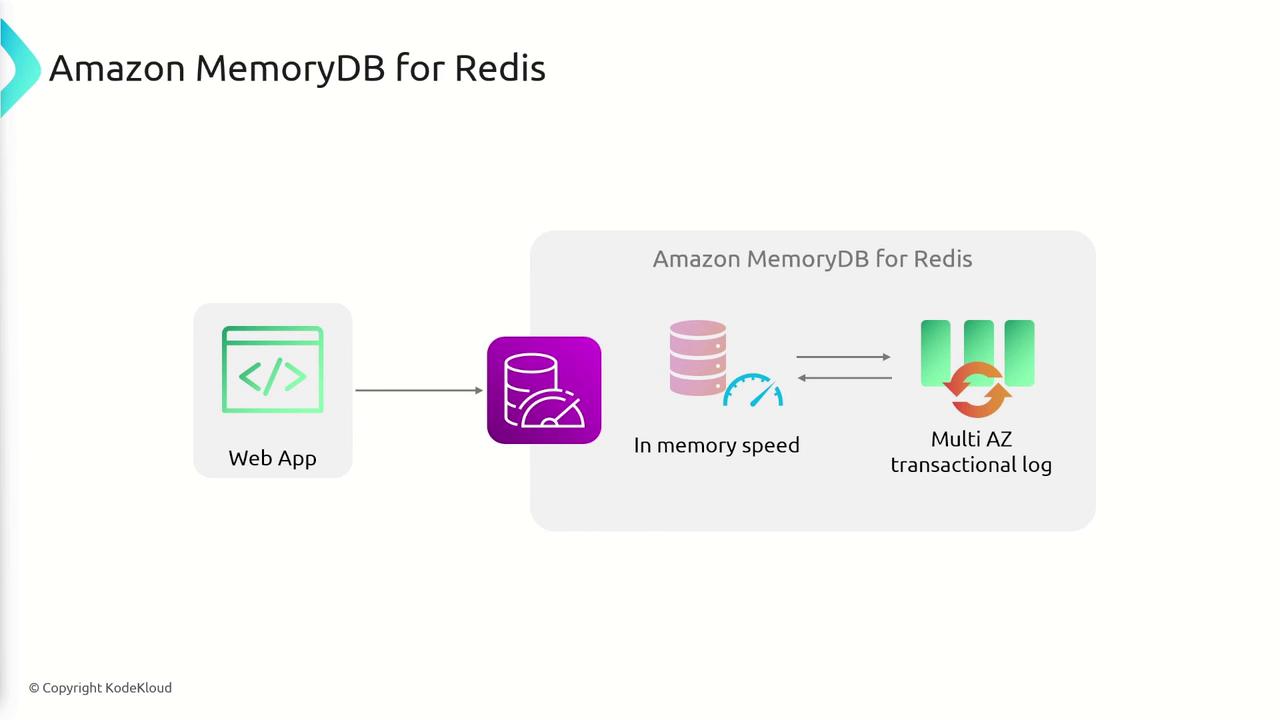
MemoryDB is an in-memory database that provides extremely low latency for read and write operations—ideal for real-time updates like driver location tracking and ride allocation. Its core features include:- High Availability: Utilizing multi-AZ replication and automatic failover, MemoryDB ensures continuous operation even if an entire data center fails.
- Data Durability: By synchronously replicating data across multiple Availability Zones (AZs), MemoryDB combines the speed of in-memory storage with the durability of disk-based systems.
- Scalability: MemoryDB dynamically scales in response to changing demand, making it perfect for peak traffic periods during holidays or special events.
- Strong Consistency: It guarantees that all users access the most recent data, an essential capability for time-sensitive decision-making.

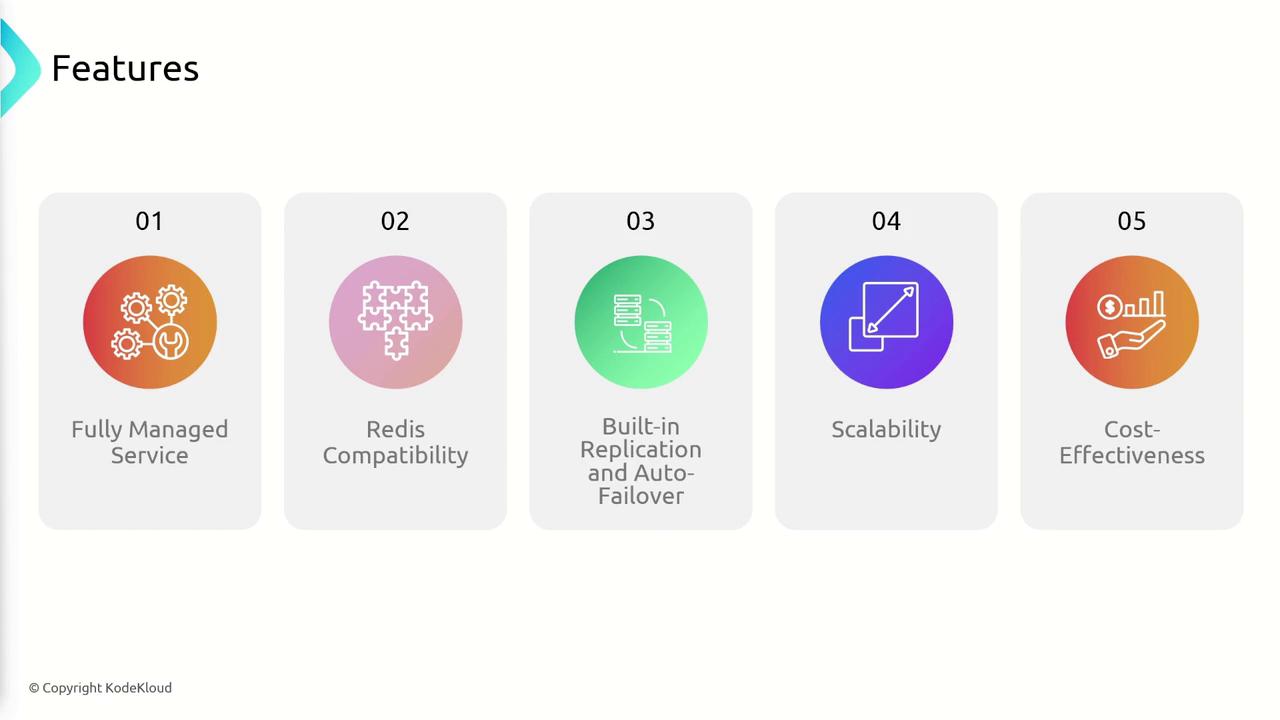
Fully Managed Service
MemoryDB is offered as a fully managed service by AWS. AWS handles all the heavy lifting—including provisioning, patching, and ongoing management—so you can focus on building your application. Key benefits include:- Redis Compatibility: Seamlessly run your existing Redis applications.
- Automatic Replication: Data is replicated across multiple AZs, enhancing durability and availability.
- Auto-Failover: Minimize downtime with automatic failover during unexpected failures.
- Dynamic Scaling: Adjust your database, compute, and memory resources without experiencing downtime.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces the need for separate caching layers, lowering management and operational expenses.
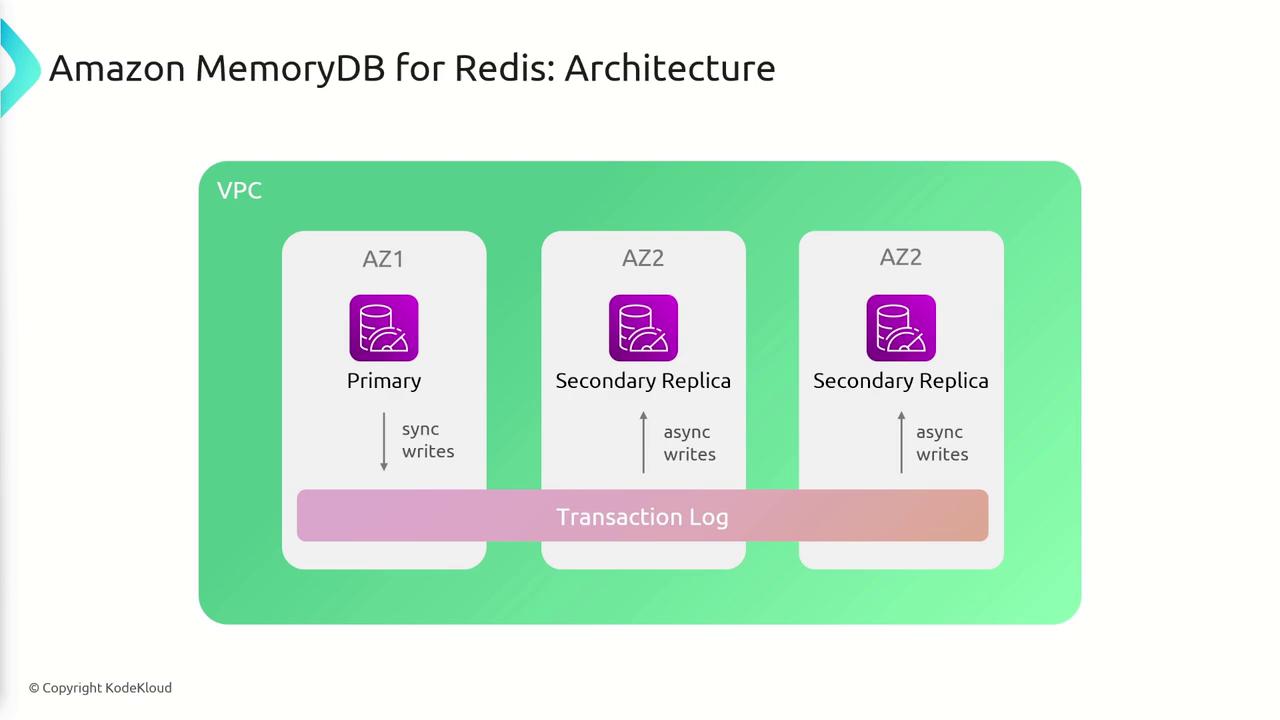
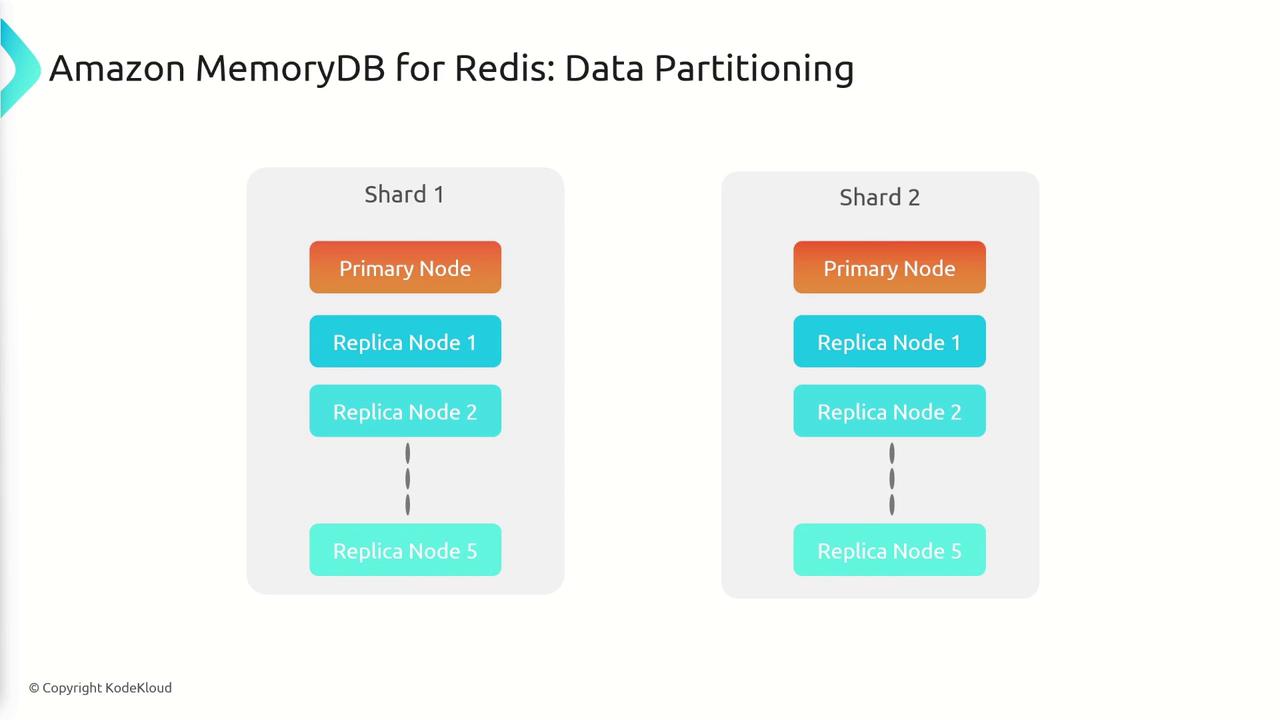
Architecture Overview
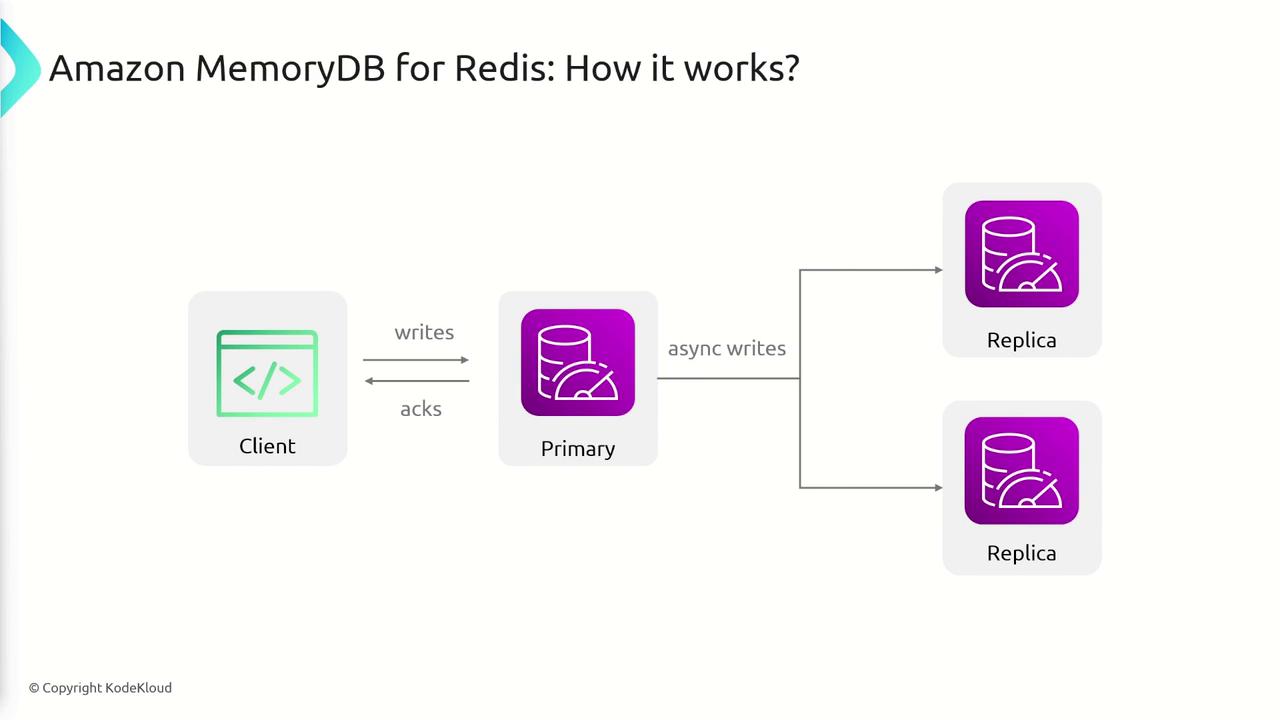
MemoryDB’s architecture is designed around a primary instance with secondary replicas. The workflow includes the following steps:- Writing Data: Data is initially written to the primary node.
- On-Disk Storage and Replication: After writing to the primary, an on-disk storage mechanism saves the data, while a distributed transaction log ensures durability and manages replication.
- Transaction Log: Each write operation is recorded in a transaction log stored across multiple AZs before being made available to clients. This log enables replicas to asynchronously update, offering an eventually consistent system.
Comparing MemoryDB with ElastiCache
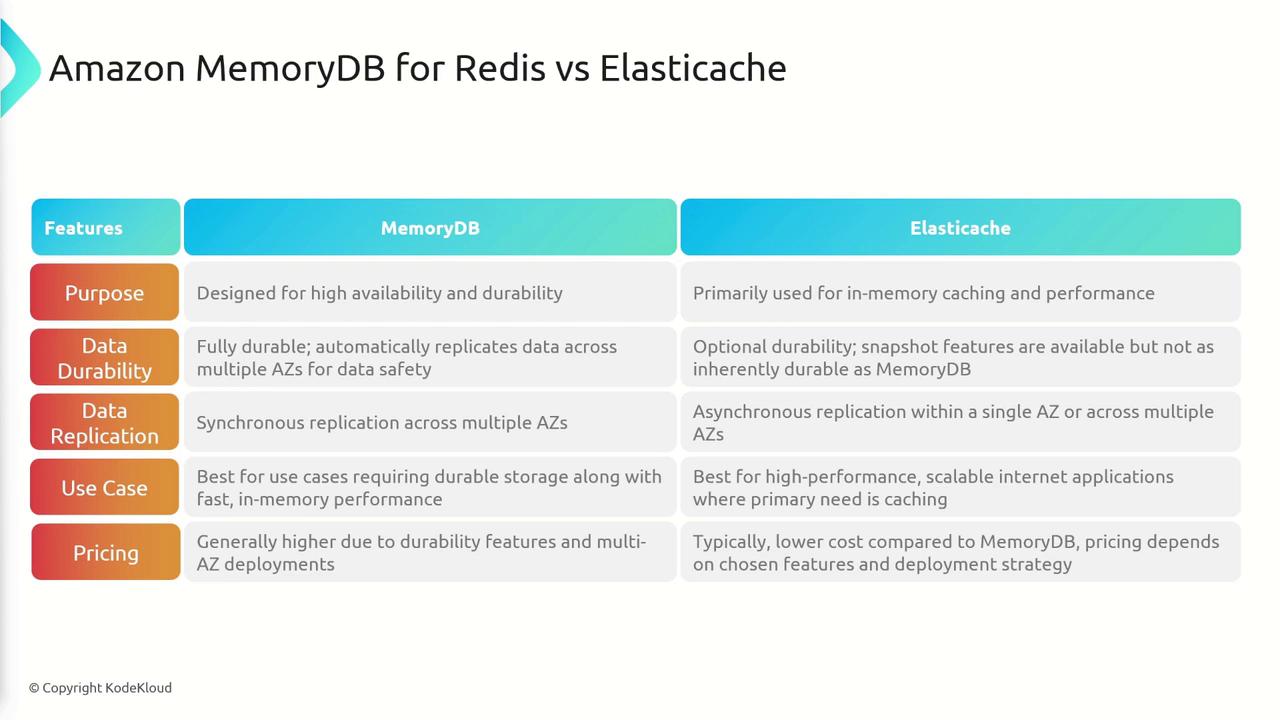
Both MemoryDB and ElastiCache are in-memory caching services, but they serve different purposes. The following table outlines the key differences:| Feature | MemoryDB | ElastiCache |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | High availability and data durability | In-memory caching to boost performance |
| Data Durability | Full durability with multi-AZ replication | Optional durability with snapshot features |
| Replication | Synchronous replication across multiple AZs | Typically asynchronous (single or multi-AZ) |
| Use Cases | Scenarios where data persistence is critical | Scenarios focused on enhancing performance |
| Pricing | Generally higher due to robust features | More cost-effective with a focus on caching |
MemoryDB not only enhances data durability and availability but also integrates seamlessly with your existing Redis applications, making it an attractive option for mission-critical applications.