In this guide, you’ll learn how to convert a Declarative Pipeline into a fully Scripted Pipeline for the solar-system repository on the features/advanced-demo branch. We’ll cover tool setup, environment configuration, caching, timestamps, and concurrency control.
1. Review the Existing Declarative Pipeline The current pipeline installs Node.js, sets environment variables, and caches npm dependencies:
pipeline { agent { tools { nodejs 'nodejs-22-6-0' } } environment { SONAR_SCANNER_HOME = tool 'sonarqube-scanner-610' GITEA_TOKEN = credentials( 'gitea-api-token' ) } options { disableResume() disableConcurrentBuilds( abortPrevious : true ) } stages { stage( 'Installing Dependencies' ) { agent any options { timestamps() } steps { cache( maxCacheSize : 550 , caches : [ arbitraryFileCache( cacheName : 'npm-dependency-cache' , cacheValidityDecidingFile : 'package-lock.json' ) ]) { sh 'node -v' sh 'npm install --no-audit' stash( includes : 'node_modules' ) } } } } }
2. Create and Push the Scripted Branch git checkout -b pipeline/scripted git push -u origin pipeline/scripted
Pushing this branch triggers a new build in Jenkins.
3. Define the Scripted Pipeline Wrap all steps inside a node block and configure tools, environment, and build properties:
node { // 1. Tool setup: install Node.js and update PATH env . NODEJS_HOME = tool 'nodejs-22-6-0' env . PATH = " ${ env.NODEJS_HOME } /bin: ${ env.PATH } " // 2. Prevent concurrent builds and resume properties([ disableConcurrentBuilds( abortPrevious : true ), disableResume() ]) stage( 'Checkout' ) { checkout scm } // 3. Timestamp wrapper for better logs wrap([$ class : 'TimestamperBuildWrapper' ]) { stage( 'Installing Dependencies' ) { // 4. Cache npm modules across builds cache( maxCacheSize : 550 , caches : [ arbitraryFileCache( cacheName : 'npm-dependency-cache' , cacheValidityDecidingFile : 'package-lock.json' ) ]) { sh 'node -v' sh 'npm install --no-audit' stash( includes : 'node_modules' ) } } } }
Caching node_modules speeds up CI by restoring dependencies from the cache on subsequent runs, reducing network overhead.
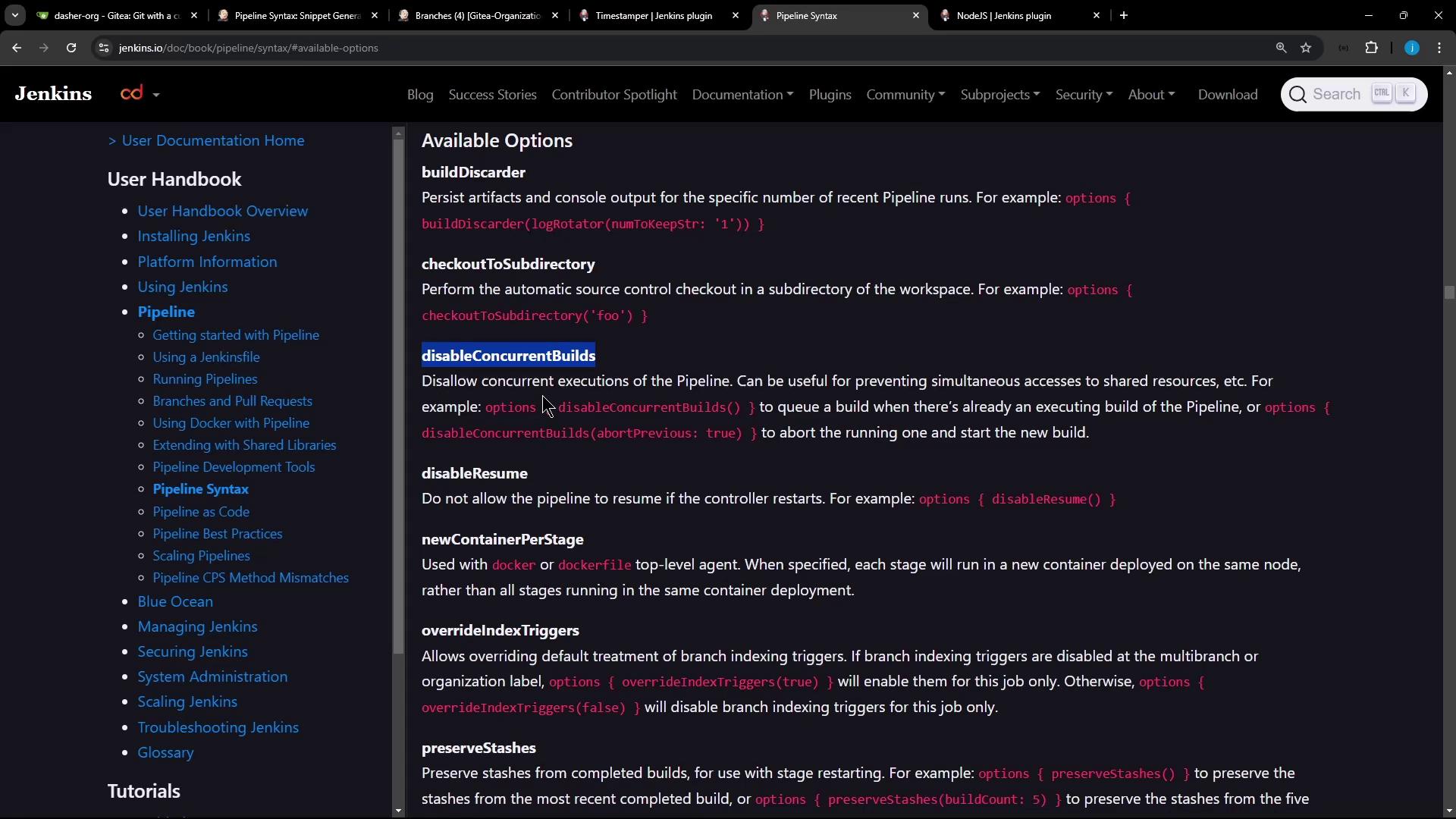
4. Check Pipeline Syntax Reference If you need to explore other Scripted Pipeline constructs, consult the official syntax guide.
// Example: wrap([$class: 'TimestamperBuildWrapper']) { ... } // Visit: https://www.jenkins.io/doc/book/pipeline/syntax/
5. Validate First and Subsequent Runs On the first run , the cache is empty:
> node -v v22.6.0 > npm install --no-audit added 365 packages in 3s
On subsequent runs , the cache is restored for faster installs:
[Cache ...] Restoring cache... > node -v v22.6.0 > npm install --no-audit up to date in 1s
6. Ensure Concurrency Control Start two builds in quick succession; the earlier build will be aborted to honor abortPrevious: true.
Aborting previous builds can interrupt cleanup tasks. Ensure your pipeline handles partial states and rollbacks correctly.
Table: Key Pipeline Options Option Purpose disableConcurrentBuilds(abortPrevious: true)Prevents parallel runs by aborting earlier builds on the same branch disableResume()Disables resume from checkpoints to simplify workflow wrap([$class: 'TimestamperBuildWrapper'])Adds timestamps to console output cache(...)Reuses files between builds to speed up dependency installation
Links and References