Prerequisites
| Requirement | Description |
|---|---|
| Jenkins server | Running on http://localhost:8080 |
| SSH client | Installed on your local machine |
jenkins-cli.jar | Downloaded from your Jenkins server (Manage → Jenkins CLI) |
1. Discovering the Jenkins SSH Endpoint
Jenkins exposes its CLI over SSH on a configurable port. To find the SSH endpoint before enabling it, query the/login endpoint:
By default, the SSH server is disabled in Jenkins, so you won’t see the
X-SSH-Endpoint header until it’s enabled.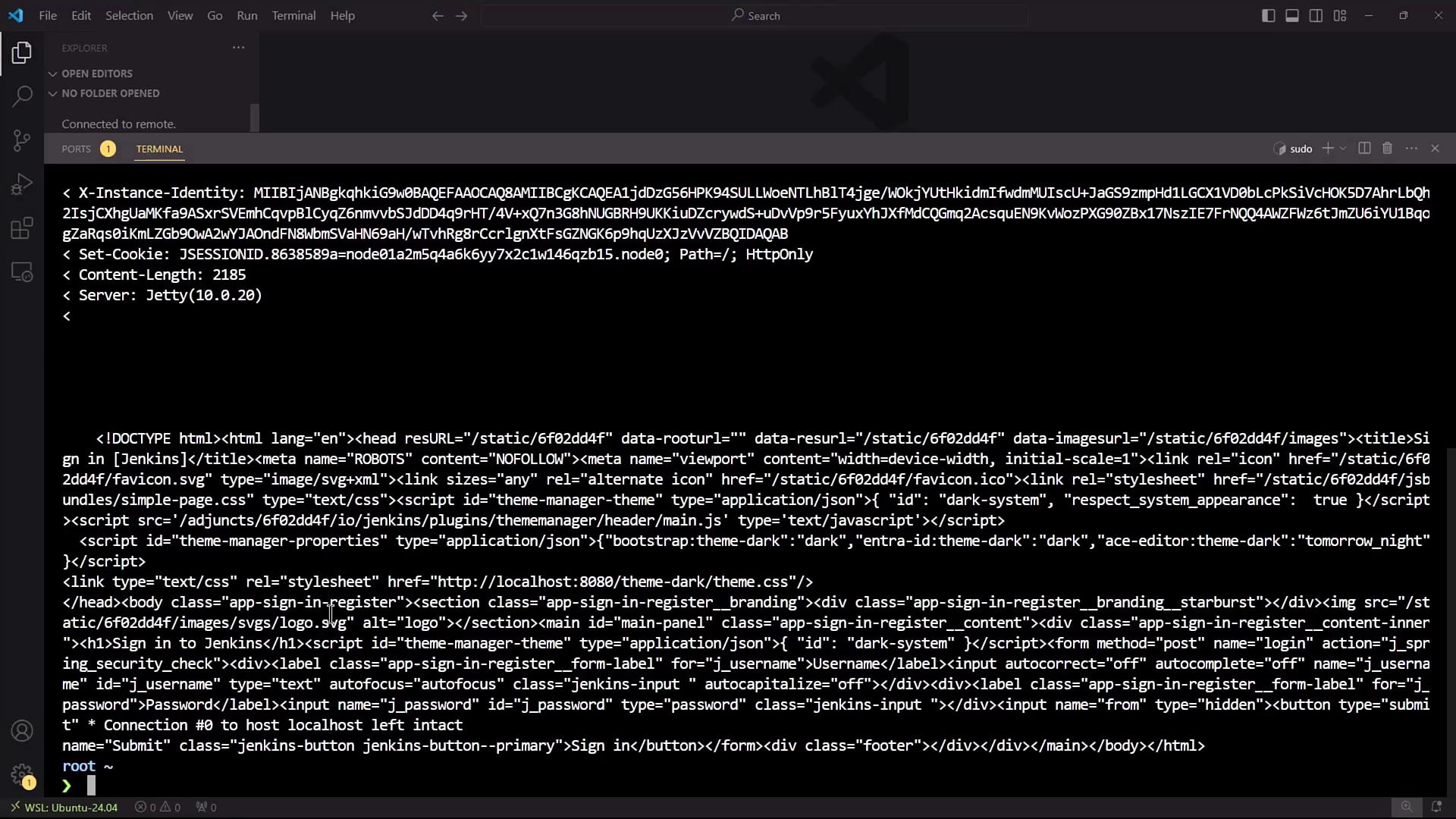
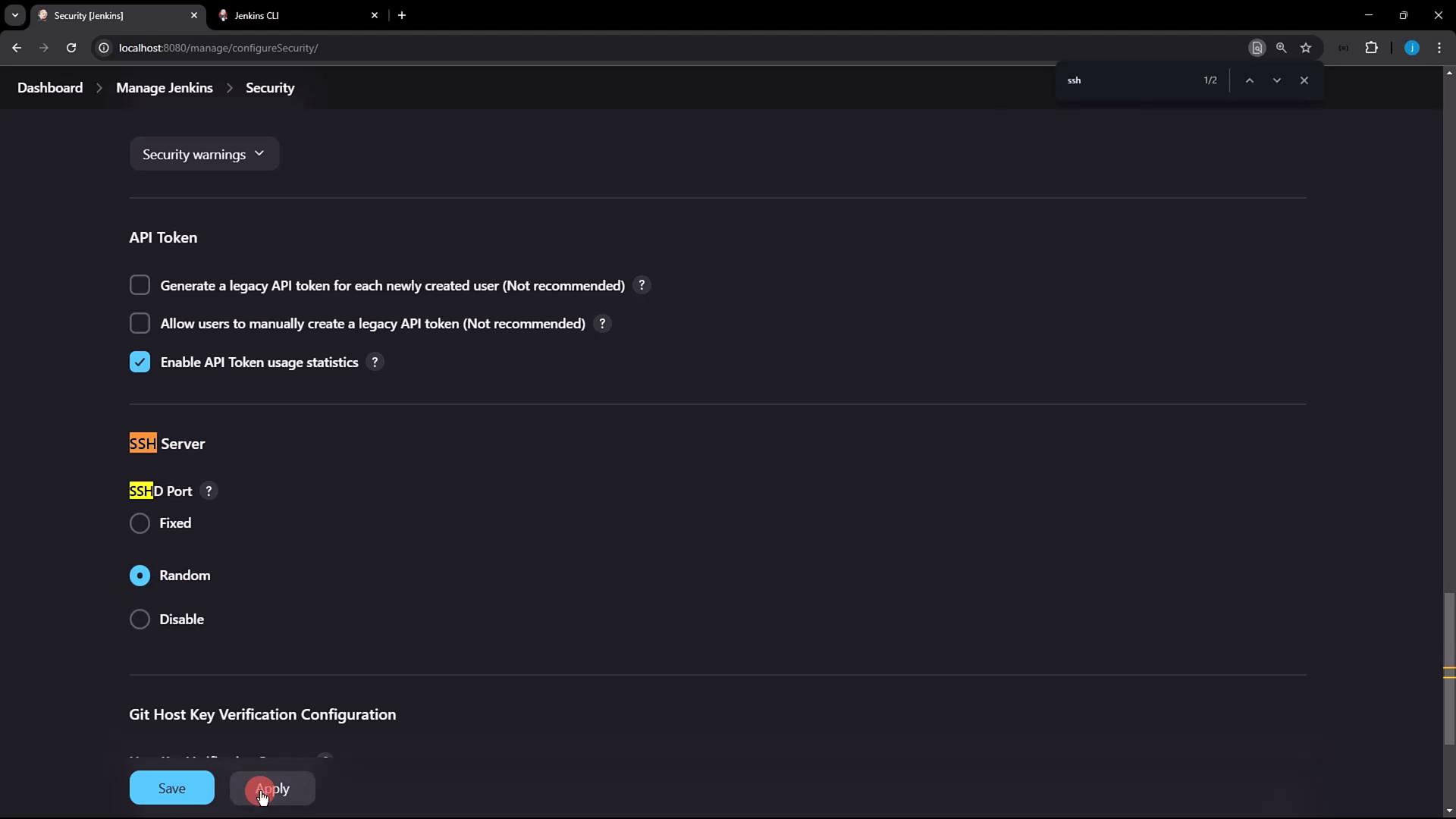
2. Enabling the Jenkins SSH Server
- In Jenkins, go to Manage Jenkins → Configure Global Security.
- Locate the SSH Server section and enable the SSH port. You can select Random or enter a fixed port (e.g.,
2222). - Click Apply to save changes.
If you choose a fixed port, make sure it’s open in your firewall and not in use by another service.
curl command:
3. Generating and Registering Your SSH Key
3.1 Generate an SSH Key Pair
If you don’t already have an SSH key, generate one:~/.ssh/id_rsa) and leave the passphrase empty if you prefer. Then display your public key:
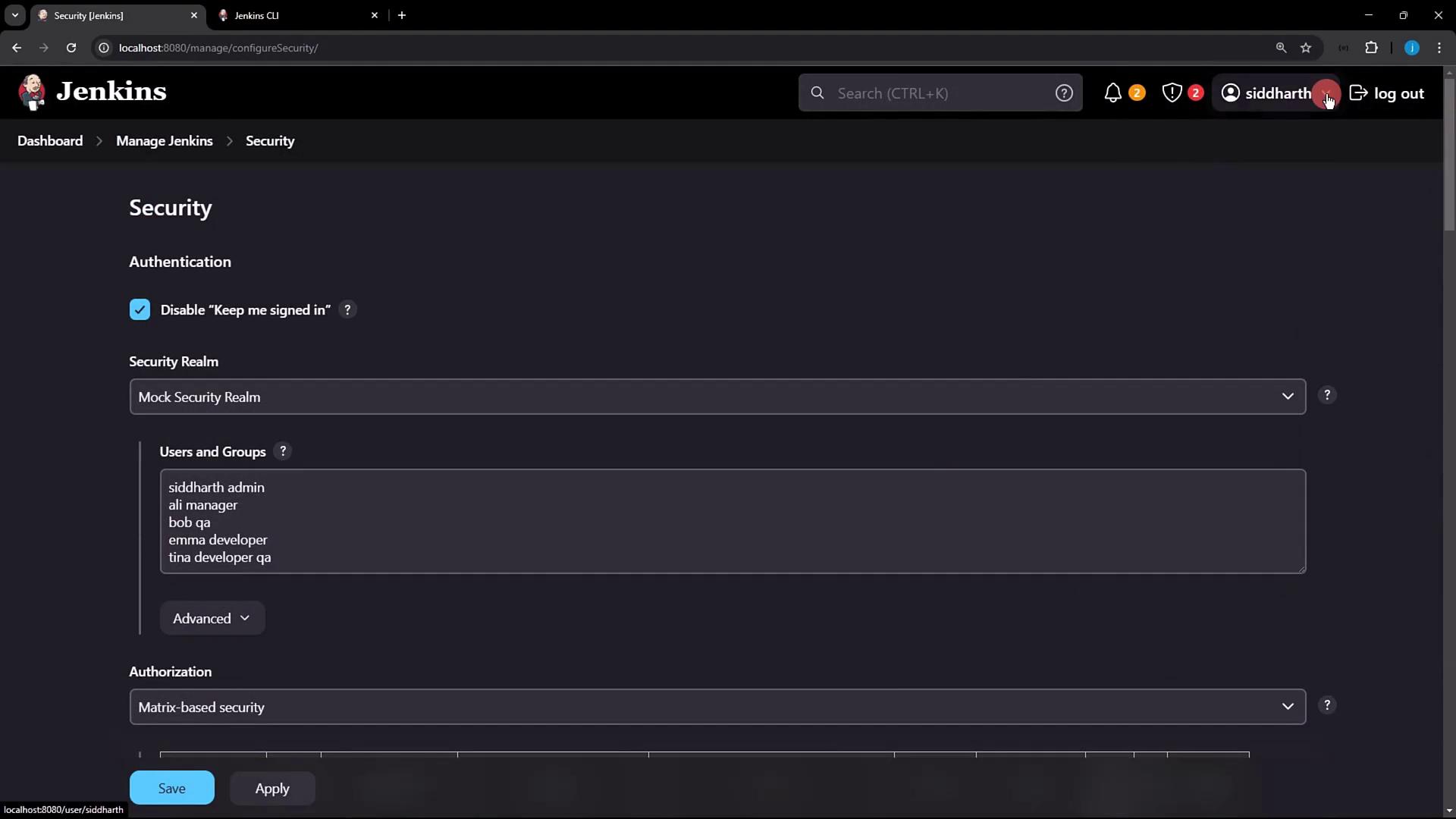
3.2 Add Your Public Key in Jenkins
- Click your Jenkins user name (e.g., siddharth) → Configure.
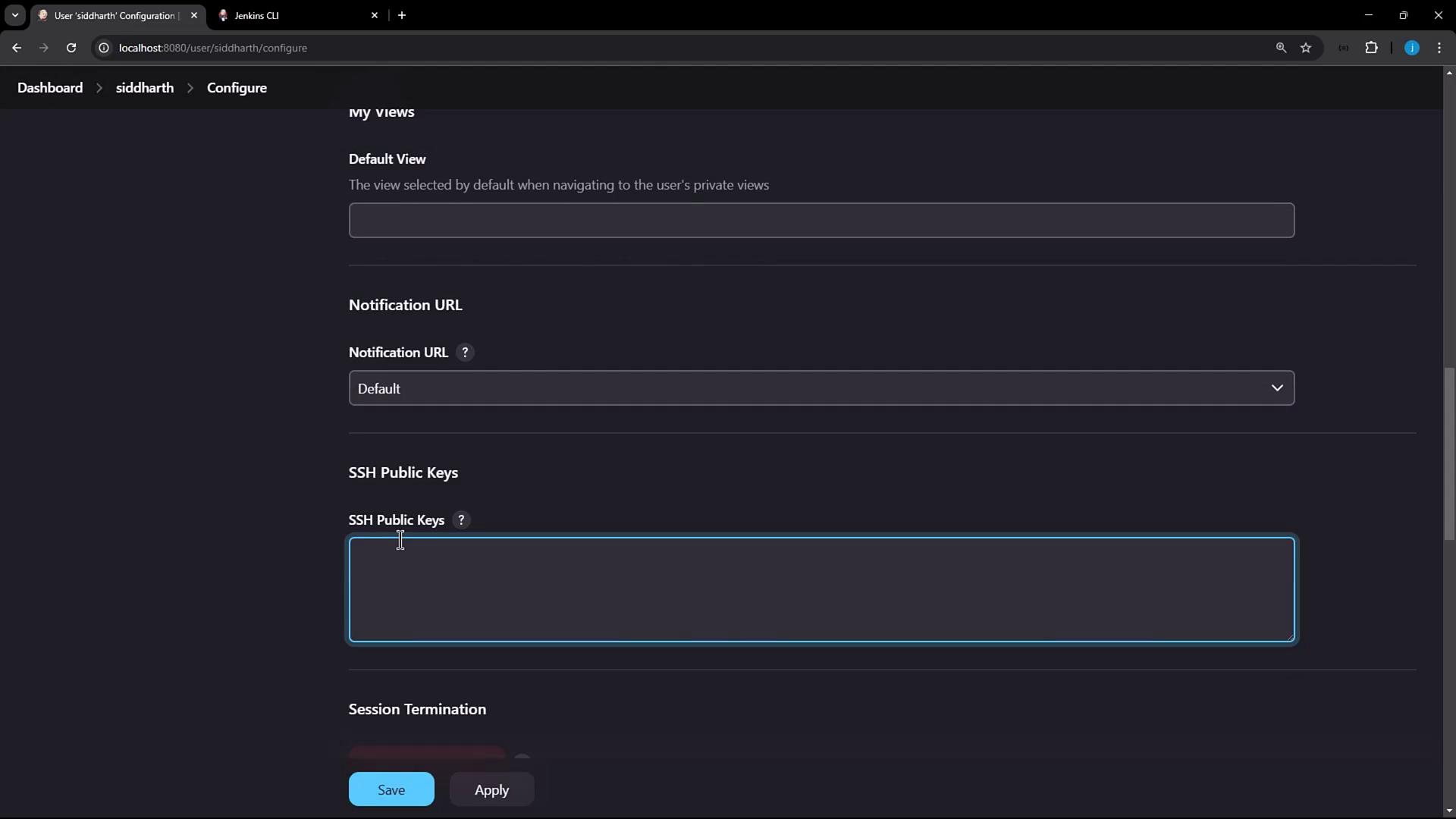
- Scroll to the SSH Public Keys section.
- Paste the contents of
~/.ssh/id_rsa.pubinto the text box. - Click Apply.
4. Connecting to Jenkins via SSH
Now that your public key is registered, connect to Jenkins over SSH and run CLI commands. Replace4397 with the port reported by X-SSH-Endpoint:
5. Using SSH Mode with the Jenkins CLI JAR
You can also invoke SSH mode directly viajenkins-cli.jar. For full details, see the Jenkins CLI documentation.
Authentication Methods Comparison
| Method | Port/Protocol | Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| HTTP Basic Auth | 8080 (HTTP) | Minimal |
| SSH Key Auth | Custom (SSH) | Moderate |