What Is Pipeline Durability?
Pipeline durability in Jenkins controls how pipeline state is written to disk so that builds can recover after a crash or restart. Choosing the right durability level helps you balance:- Resilience: Ability to resume an in-progress build.
- Performance: Disk I/O overhead when recording pipeline checkpoints.
Durability Levels
| Level | Description |
|---|---|
| MAX_SURVIVABILITY | Writes state after every step. Safest but introduces the most disk I/O overhead. |
| PERFORMANCE_OPTIMIZED | Minimizes disk writes for faster execution. Builds cannot resume on unclean shutdown. |
| SURVIVABLE_NON_ATOMIC | Compromise between state safety and performance. |
Use MAX_SURVIVABILITY for critical pipelines that must resume after crashes, and PERFORMANCE_OPTIMIZED when speed is more important than resumability.
Configuring Durability Settings
You can override the default durability level at three scopes:- Global (all pipelines)
- Branch (multibranch projects)
- Per-Pipeline (individual job)
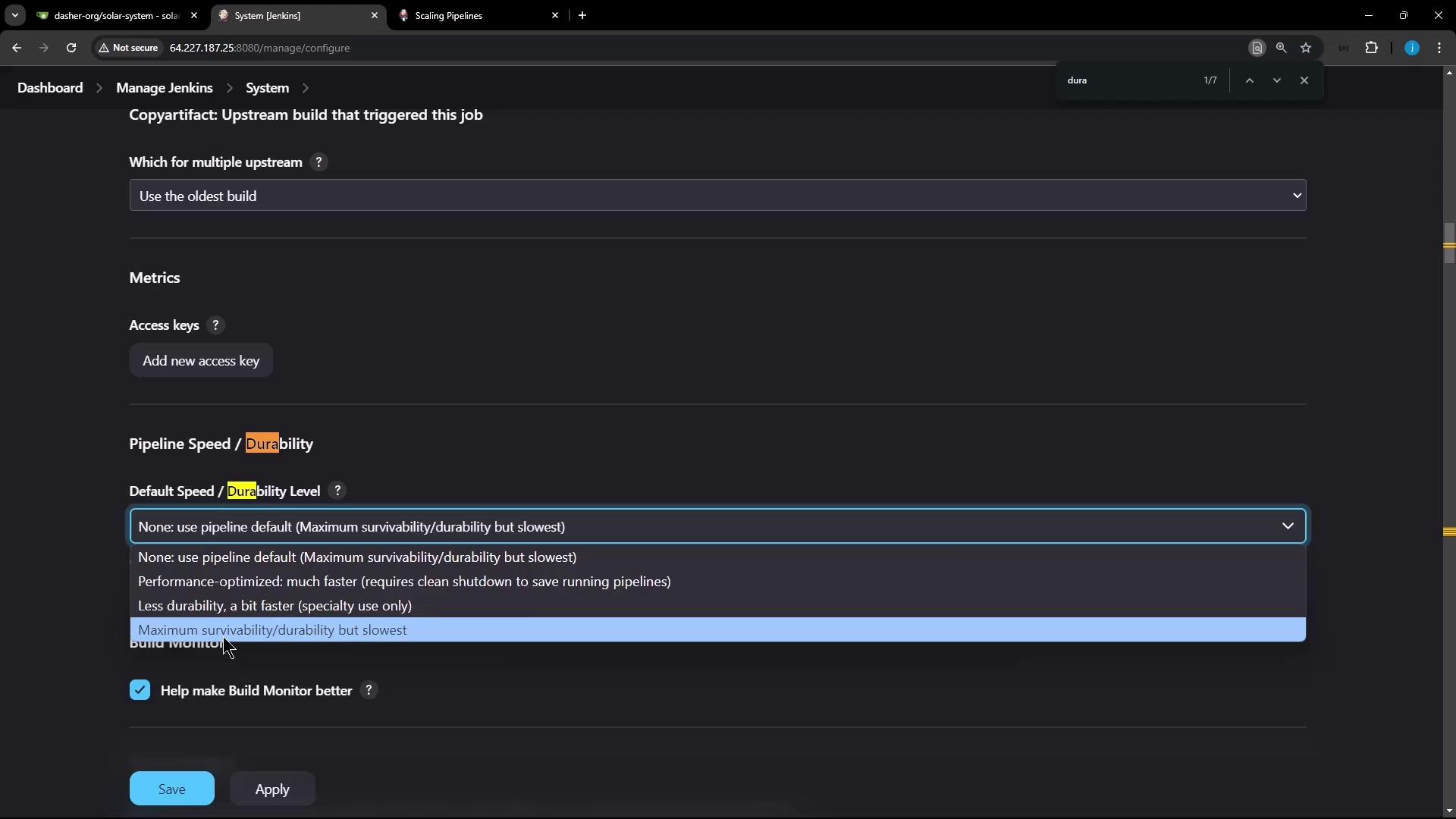
1. Global Configuration
To set the default durability level for every pipeline:- Navigate to Manage Jenkins → Configure System.
- Search for “Pipeline Speed/Durability.”
- Choose your preferred default level.
2. Branch-Level (Multibranch Projects)
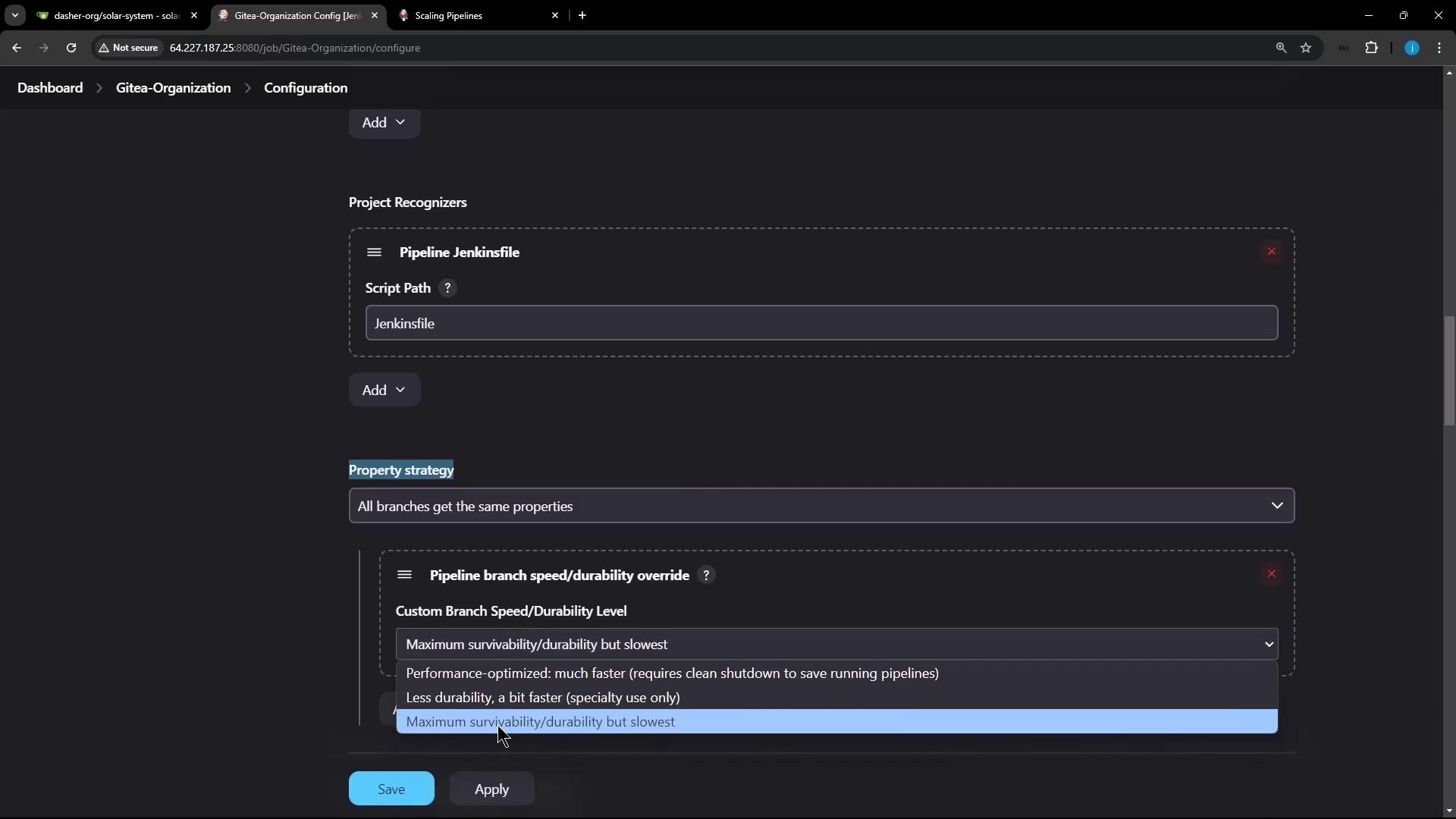
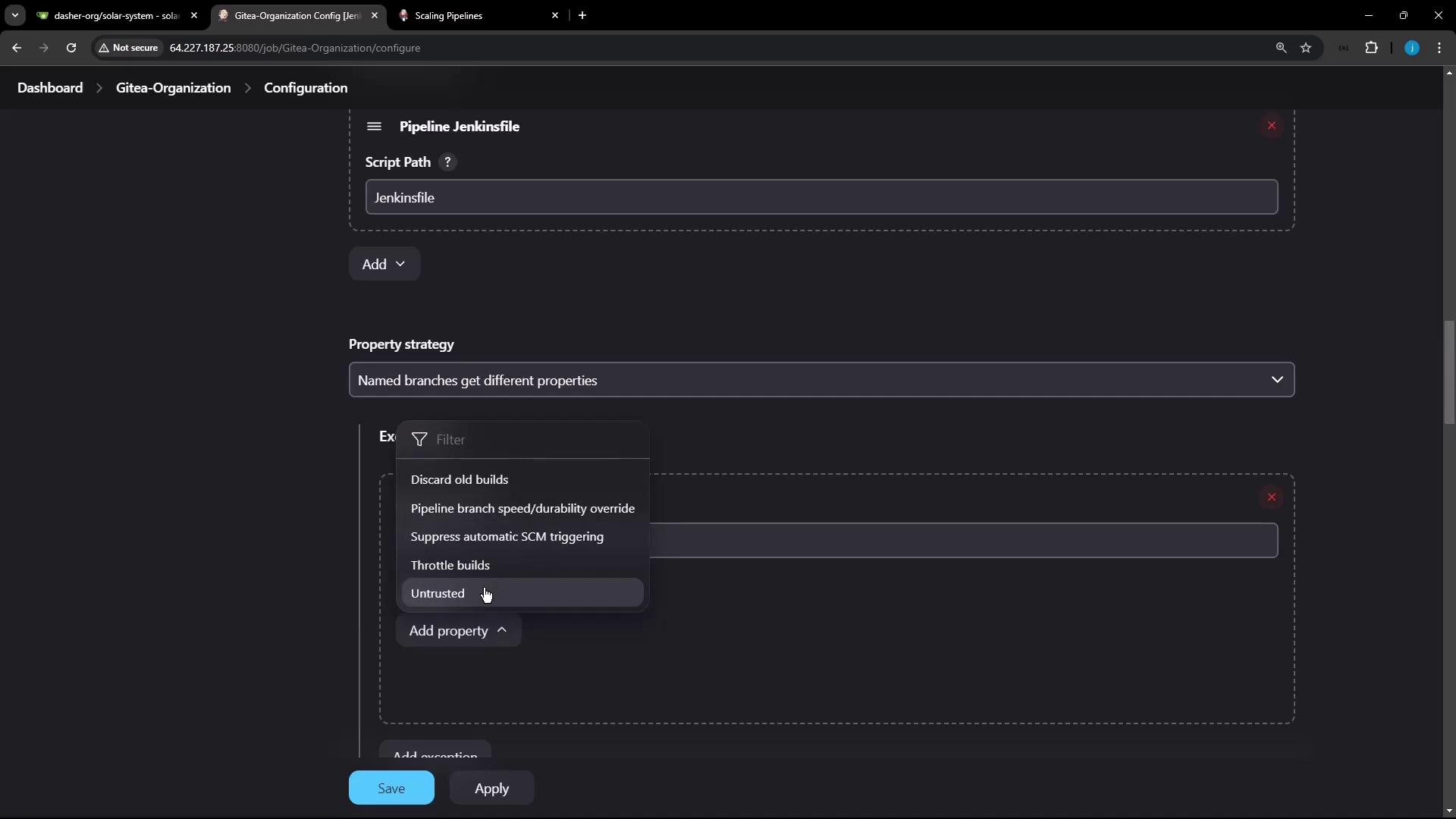
For multibranch pipelines, you can assign durability per branch:- Go to your project’s Configure page.
- Under Repository Sources → Property strategy, choose Named branches.
- Add a property for
main(ormaster) with MAX_SURVIVABILITY. - Set PERFORMANCE_OPTIMIZED (or another level) for all other branches.
3. Per-Pipeline Job
To set durability for a single pipeline job:- Open the job and click Configure.
- Scroll to Pipeline Speed and Durability.
- Select the desired durability level from the dropdown.

Live Demo
Demo 1: MAX_SURVIVABILITY
This demo writes numbers to a file once per second. With MAX_SURVIVABILITY, the build will resume after a Jenkins restart.- Save and start the build.
- On the controller host, kill Jenkins:
- After Jenkins restarts, the console shows:
Demo 2: PERFORMANCE_OPTIMIZED
Switch the same job to PERFORMANCE_OPTIMIZED, rerun, and repeat the kill/restart:Under PERFORMANCE_OPTIMIZED, incomplete builds cannot resume after an unclean shutdown. Plan accordingly if you require resumability.
Conclusion
- MAX_SURVIVABILITY: Best for mission-critical pipelines that must survive crashes.
- PERFORMANCE_OPTIMIZED: Ideal when speed is paramount and resumability is not required.
- SURVIVABLE_NON_ATOMIC: Use as a balanced choice between safety and performance.