In this guide, we’ll transform the existing Solar System Pipeline Jenkinsfile from using agent any to leveraging a Kubernetes agent. By externalizing Pod definitions into a YAML manifest and targeting specific Node.js containers for build stages, we achieve more consistent, scalable CI/CD workflows.
Original Jenkinsfile Overview The current pipeline uses a generic agent and defines global tools, environment variables, and stages:
pipeline { agent any environment { MONGO_URI = "mongodb+srv://supercluster.d83jj.mongodb.net/superData" MONGO_DB_CREDS = credentials( 'mongo-db-credentials' ) MONGO_USERNAME = credentials( 'mongo-db-username' ) MONGO_PASSWORD = credentials( 'mongo-db-password' ) SONAR_SCANNER_HOME = tool 'sonarqube-scanner-610' GITEA_TOKEN = credentials( 'gitea-api-token' ) } options { // Shared pipeline options } stages { stage( 'Installing Dependencies' ) { options { timestamps() } steps { // npm install, etc. } } // Additional stages... } }
Feature Description agent any Runs on any available Jenkins node environment variables Database URIs, credentials, and SonarQube scanner path stages Dependency install, tests, Docker build, security scans
Defining the Kubernetes Pod Manifest Create a k8s-agent.yaml at your repo root to specify two Node.js containers:
apiVersion : v1 kind : Pod spec : containers : - name : node-18 image : node:18-alpine command : [ "cat" ] tty : true - name : node-19 image : node:19-alpine command : [ "cat" ] tty : true
This manifest defines the node-18 and node-19 containers that Jenkins will schedule within a single Pod.
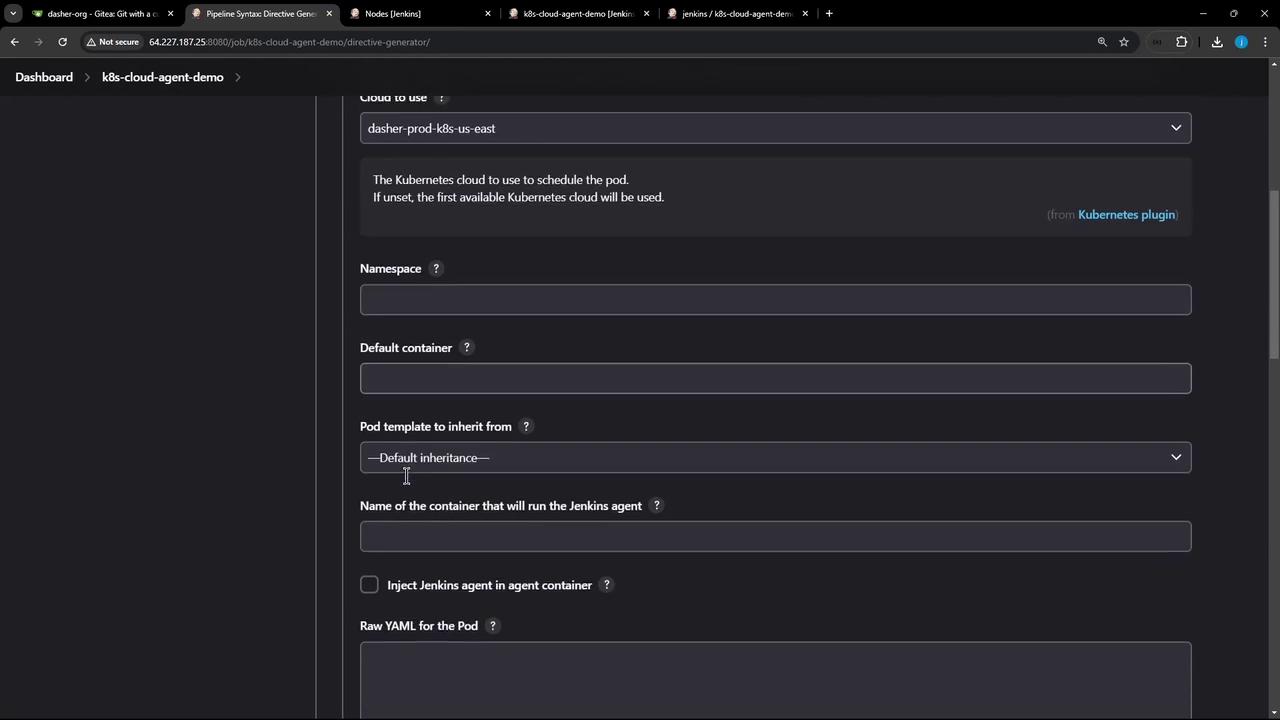
Ensure the Kubernetes plugin is installed in Jenkins and your Kubernetes cloud configuration (dasher-prod-k8s-us-east) is active before running the refactored pipeline.
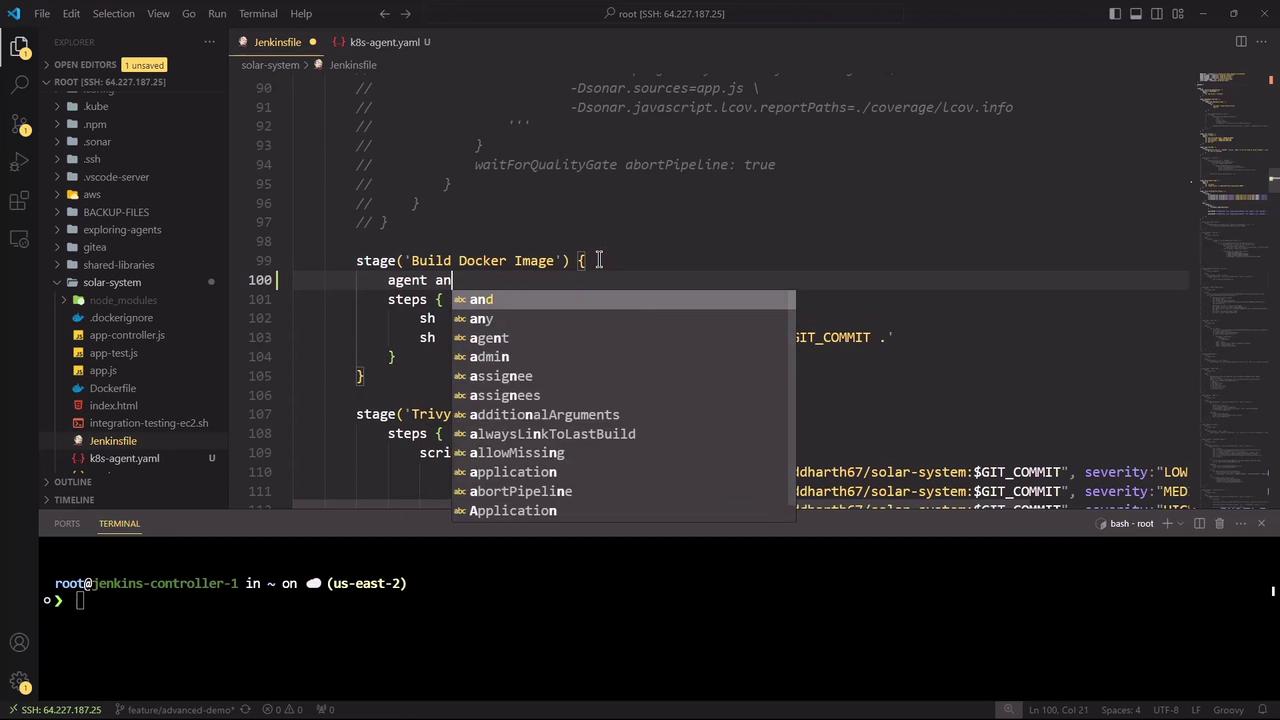
Refactoring Jenkinsfile to Use Kubernetes Agent Replace the top-level agent any with the kubernetes agent block, referencing the YAML manifest and defaulting to node-18:
pipeline { agent { kubernetes { cloud 'dasher-prod-k8s-us-east' yamlFile 'k8s-agent.yaml' defaultContainer 'node-18' } } tools { // Tool declarations here } environment { MONGO_URI = "mongodb+srv://supercluster.d83jj.mongodb.net/superData" MONGO_DB_CREDS = credentials( 'mongo-db-credentials' ) MONGO_USERNAME = credentials( 'mongo-db-username' ) MONGO_PASSWORD = credentials( 'mongo-db-password' ) SONAR_SCANNER_HOME = tool 'sonarqube-scanner-610' GITEA_TOKEN = credentials( 'gitea-api-token' ) } options { // Pipeline-level options } stages { // Updated stages below } }
Stage-Level Container Configuration We’ll run Node.js–specific stages in node-18, while Docker build and security scans fall back to agent any. Here’s the updated stage block:
stages { stage( 'Installing Dependencies' ) { options { timestamps() } steps { container( 'node-18' ) { sh 'node -v' sh 'npm install --no-audit' } } } stage( 'Dependency Scanning' ) { parallel { stage( 'NPM Dependency Audit' ) { steps { container( 'node-18' ) { sh ''' node -v npm audit --audit-level=critical echo $? ''' } } } } } stage( 'Unit Testing' ) { options { retry( 2 ) } steps { container( 'node-18' ) { sh 'npm test' } } } stage( 'Code Coverage' ) { steps { container( 'node-18' ) { catchError( buildResult : 'SUCCESS' , message : 'Coverage step failed, will fix later' , stageResult : currentBuild . currentResult) { sh 'node -v' sh 'npm run coverage' } } } } stage( 'Build Docker Image' ) { agent any steps { sh 'printenv' sh 'docker build -t siddharth67/solar-system:$GIT_COMMIT .' } } stage( 'Trivy Vulnerability Scanner' ) { agent any steps { script { trivyScanScript . vulnerability( imageName : "siddharth67/solar-system: $GIT_COMMIT " , severity : "LOW" ) trivyScanScript . vulnerability( imageName : "siddharth67/solar-system: $GIT_COMMIT " , severity : "MEDIUM" ) trivyScanScript . vulnerability( imageName : "siddharth67/solar-system: $GIT_COMMIT " , severity : "HIGH" ) } } } }
Stage Container Agent Installing Dependencies node-18 kubernetes Dependency Scanning node-18 kubernetes Unit Testing node-18 kubernetes Code Coverage node-18 kubernetes Build Docker Image default host any Trivy Vulnerability default host any
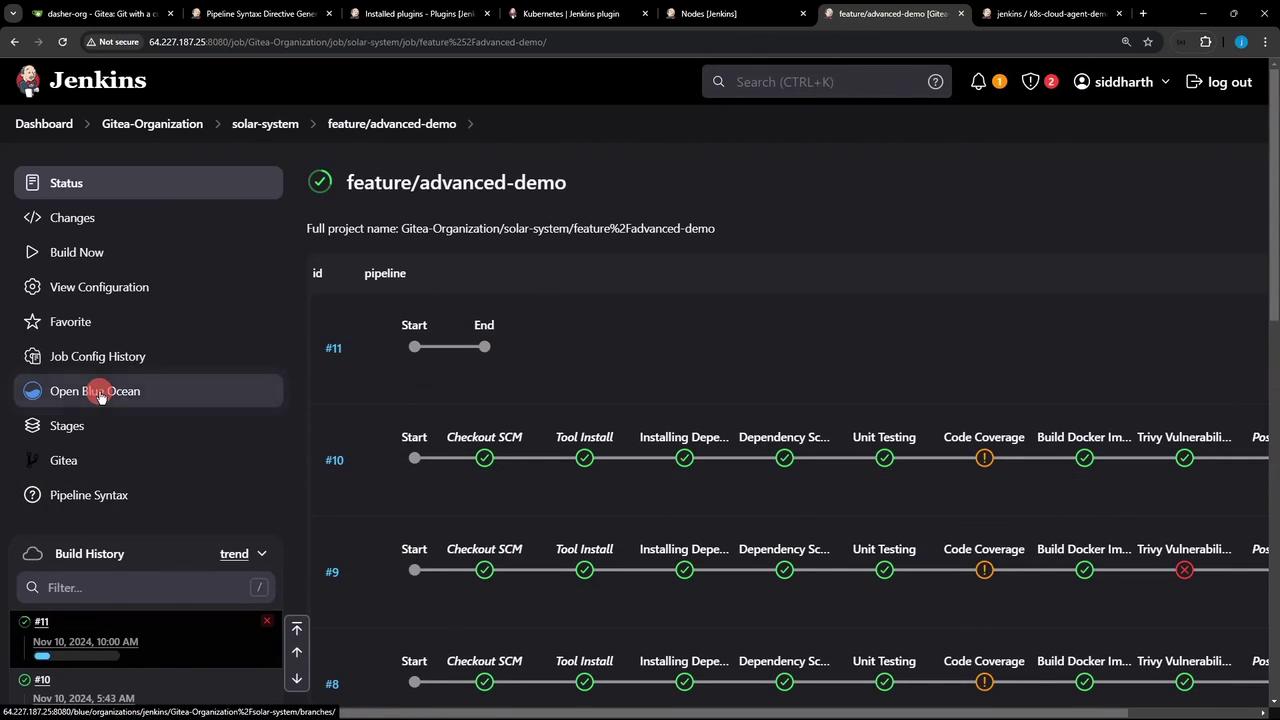
Running and Monitoring the Refactored Pipeline Commit your changes and push to trigger the pipeline. You can monitor status and logs in Blue Ocean:
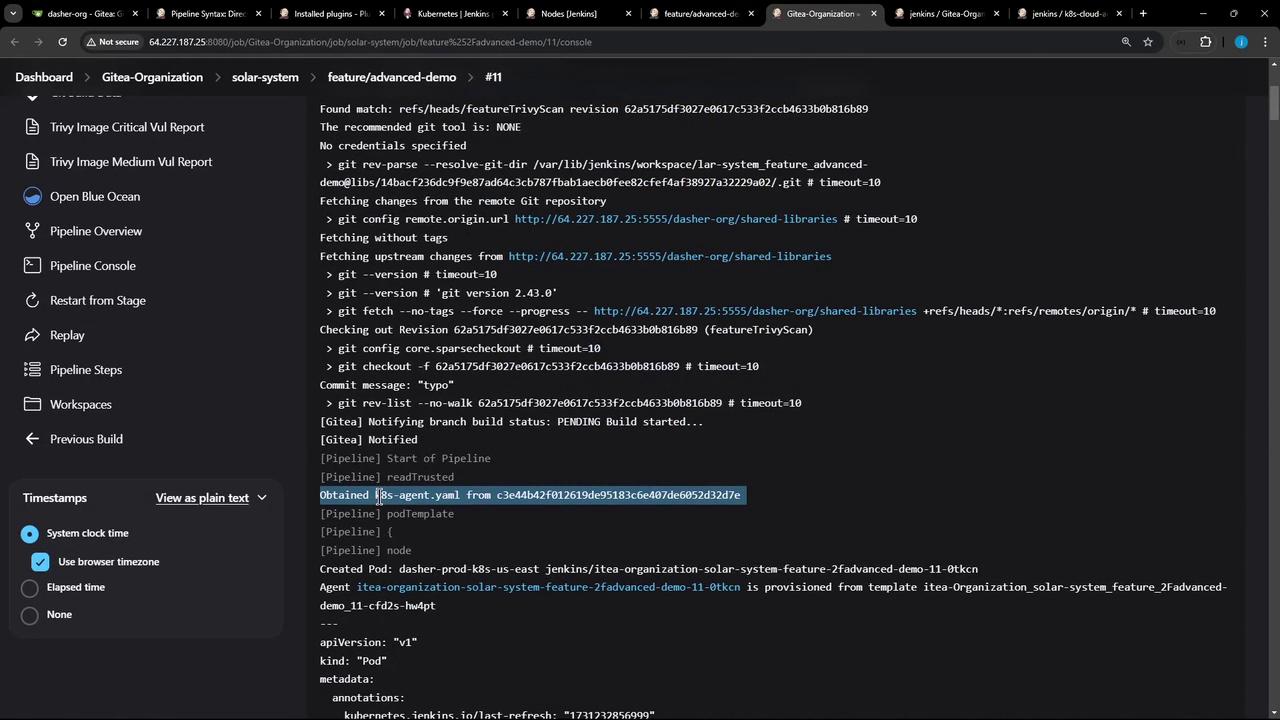
The console output confirms that the Pod definition was fetched and containers spun up:
15:31:10 + node -v 15:31:10 v18.20.4 15:31:11 + npm install --no-audit 15:31:16 added 358 packages in 4s ... 15:31:30 + npm test ... 15:32:02 + npm run coverage ...
All Node.js stages share an emptyDir volume by default, so dependencies installed in one stage persist for subsequent stages within the same Pod.
Links and References