1. Understanding the Groovy Sandbox
Jenkins executes user-provided Groovy scripts inside a restricted environment known as the Groovy Sandbox. This sandbox limits available APIs and prevents potentially harmful operations without administrator approval.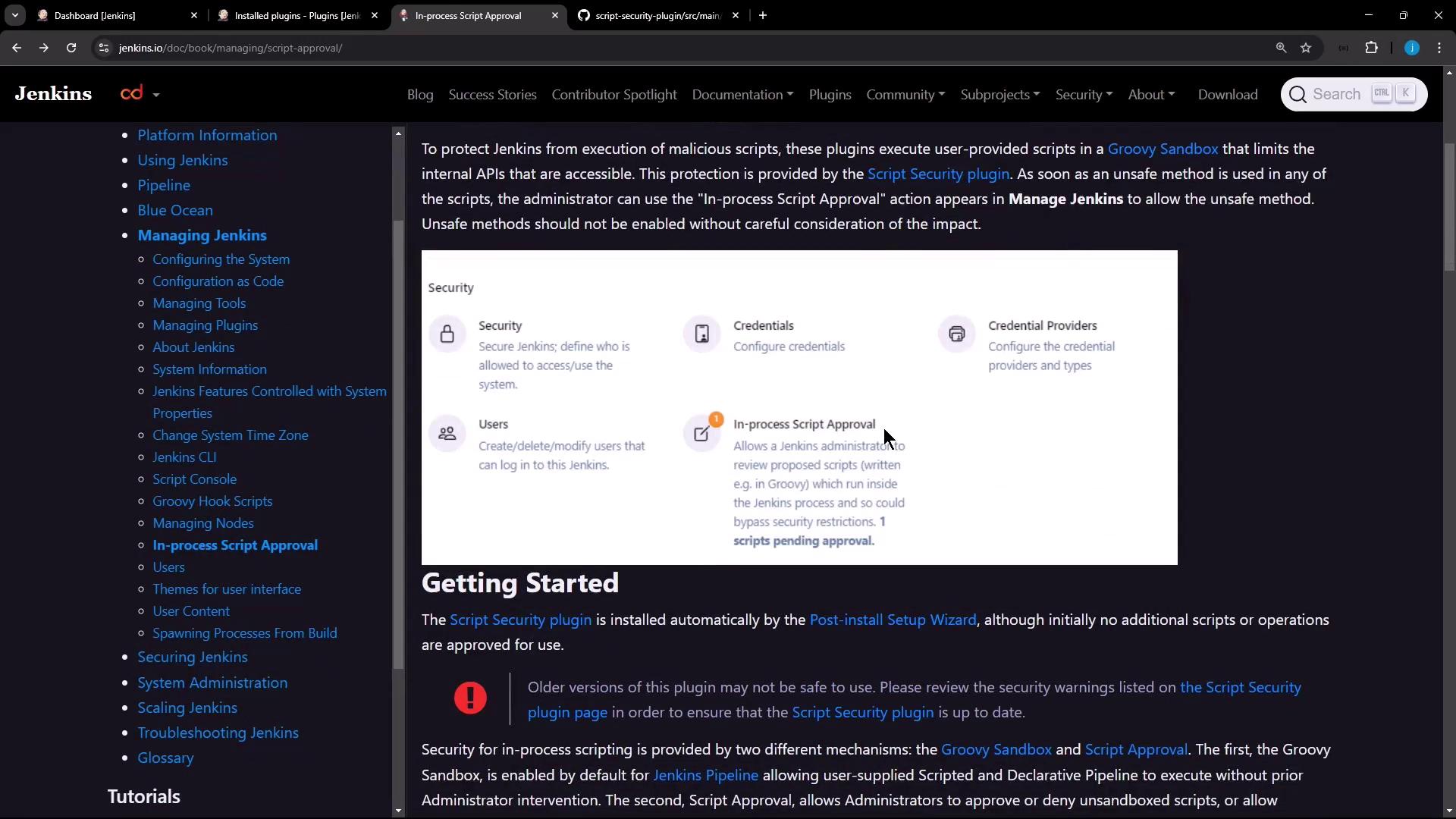
- Groovy Sandbox
Runs scripted and declarative pipelines by default, restricting unapproved methods and classes. - In-Process Script Approval
Queues any script usage that requires extra permissions. Administrators can review and approve or deny these requests.
2. Verifying the Script Security Plugin
Ensure the Script Security plugin is installed and up to date:- Navigate to Manage Jenkins → Manage Plugins.
- Select the Installed tab.
- Look for Script Security in the list.
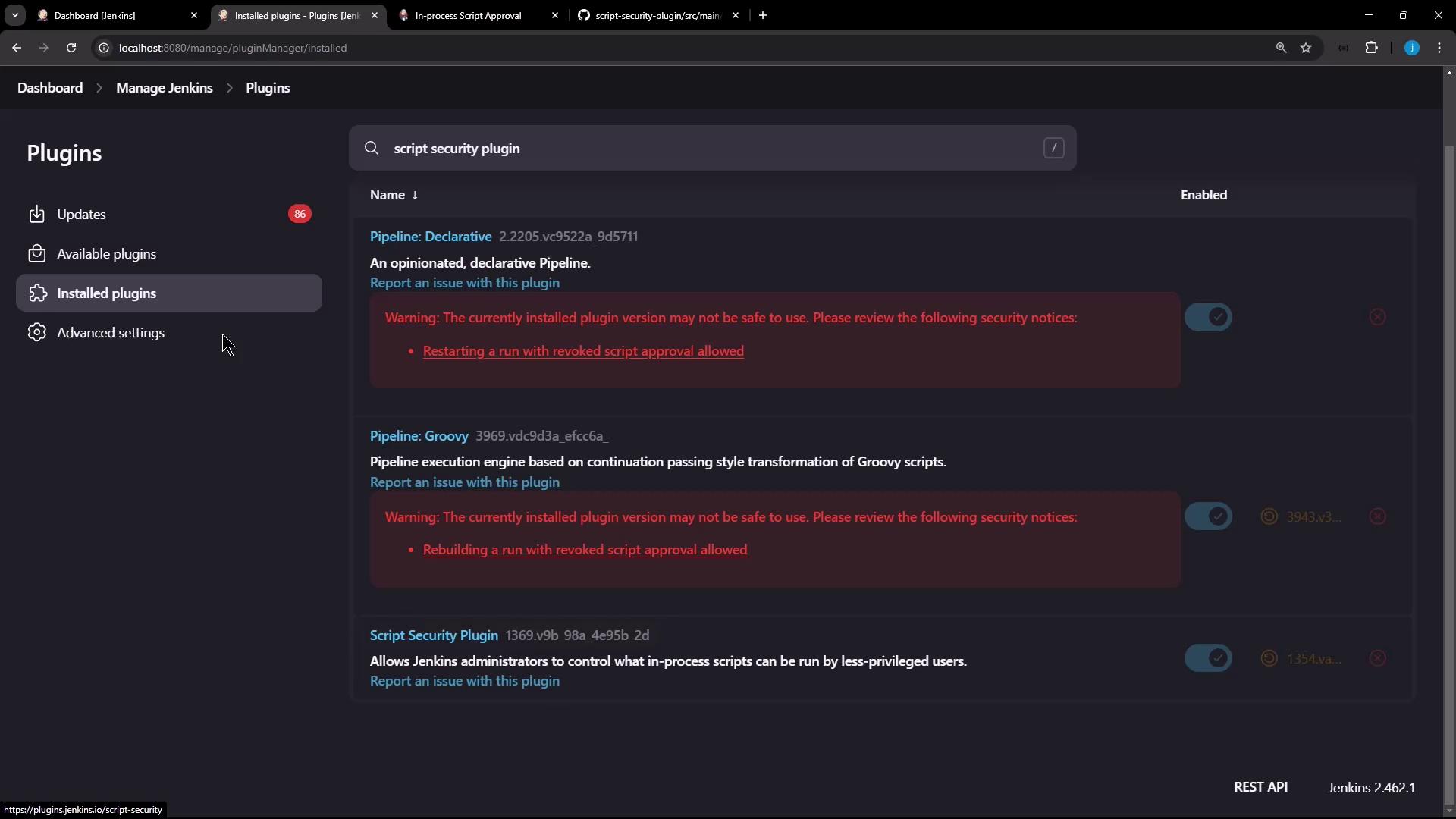
Keeping the Script Security plugin updated reduces your exposure to known vulnerabilities.
3. Creating a Declarative Pipeline (Sandbox Enabled)
Let’s create a new pipeline job with sandboxing:- Go to New Item, enter a name (e.g., Groovy Sandbox Test), and select Pipeline.
- In the Pipeline section, paste the following script. The Use Groovy Sandbox checkbox is enabled by default.
4. Disabling the Sandbox and Handling Approval Errors
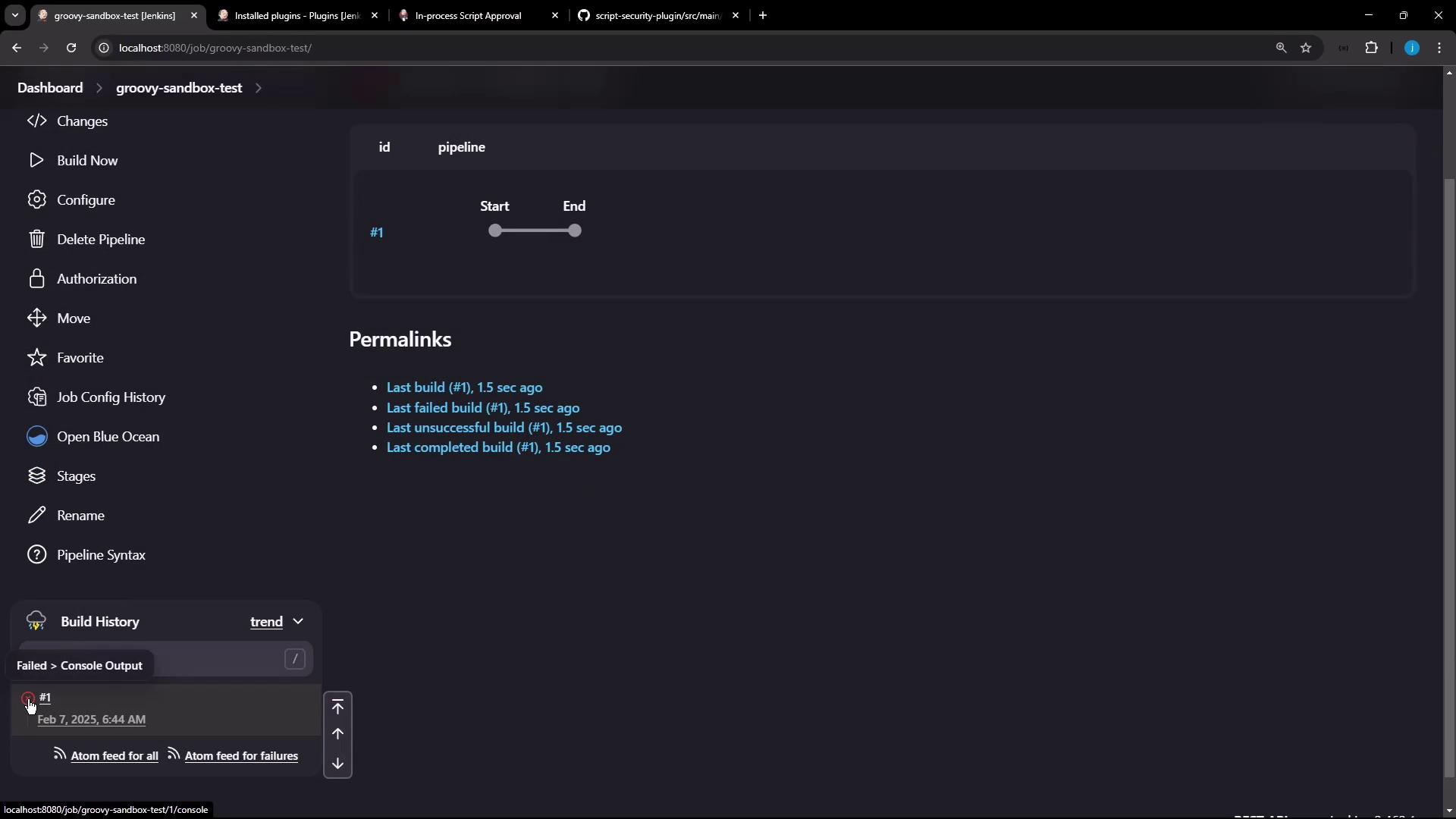
When you disable the sandbox, Jenkins will block any unapproved methods:- Edit the pipeline job, uncheck Use Groovy Sandbox, and save.
- Run the build again.
Disabling the sandbox without prior approvals will cause builds to fail. Only trusted pipelines should run outside the sandbox.
5. Approving Scripts In-Process
To authorize the pending script:- Go to Manage Jenkins → In-Process Script Approval.
- Review the pending signature(s), submitter, and the job name.
- Click Approve for each entry.
6. Verifying a Successful Build
After approval, the pipeline runs without sandbox restrictions:7. Updating Scripts and Re-Approval
Any change that introduces new method calls or signatures requires re-approval:- Edit the script and save.
- Approve the new signature under In-Process Script Approval.
- Rebuild the job to confirm success.
8. Summary and Best Practices
- Always run user-provided scripts within the Groovy Sandbox unless absolutely necessary.
- Use In-Process Script Approval to review new or unsafe method calls.
- Enforce sandboxing globally via script-security configuration to prevent unauthorized toggling.