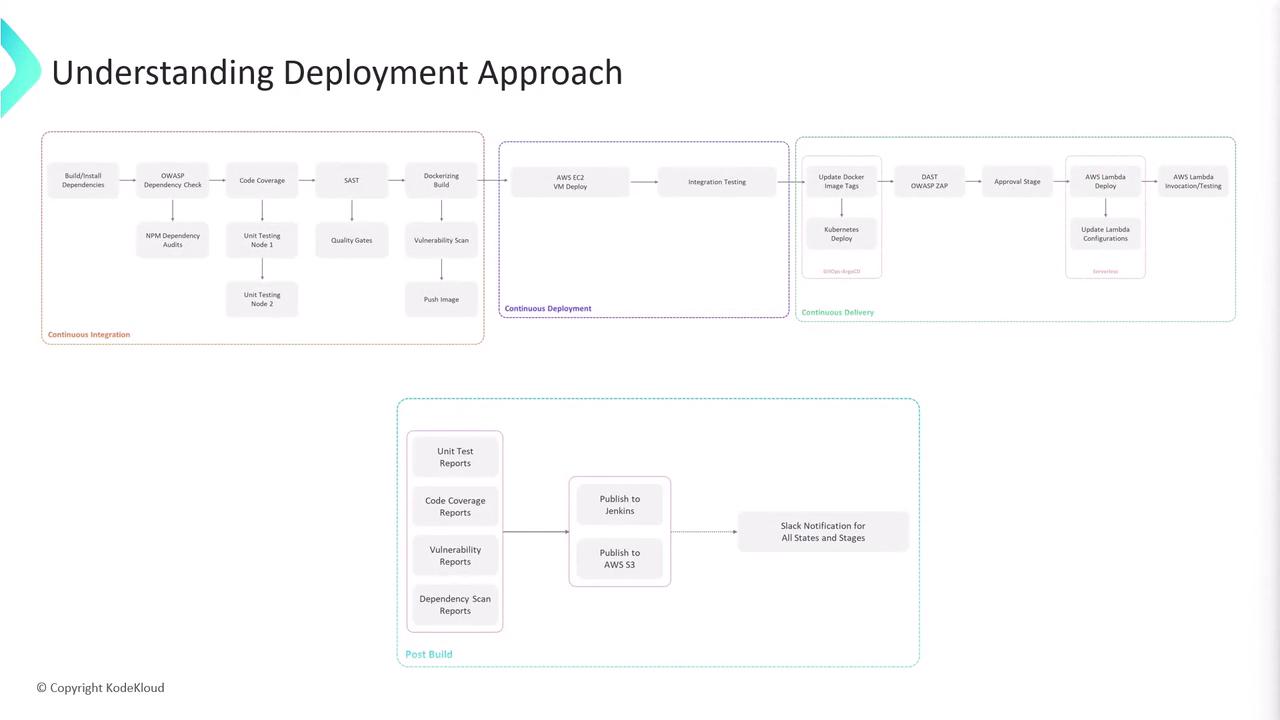
1. Feature Branch Deployment to AWS EC2
When a new commit is pushed to any feature branch, the CI pipeline automatically:- Executes build, unit tests, and lint checks.
- Builds a Docker image and pushes it to a container registry.
- Connects to a designated AWS EC2 instance via SSH.
- Pulls and deploys the updated Docker image.
- Runs integration tests against the EC2-hosted service.
Ensure your AWS credentials and SSH keys are securely stored in your CI/CD environment variables.
2. Pull Request Validation with Kubernetes & DAST
On opening a pull request, we spin up an ephemeral preview environment:- Argo CD syncs the Docker image to a Kubernetes namespace.
- Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) is performed using OWASP ZAP against the running application.
DAST scans can produce false positives—review findings carefully and tune your OWASP ZAP policies.
main.
3. Main Branch Deployment to AWS Lambda
Once pull requests are merged intomain, the pipeline proceeds to production:
- Packages the application as an AWS Lambda deployment package.
- Updates Lambda configuration (environment variables, memory allocation, timeouts).
- Deploys via the AWS CLI or Infrastructure as Code tool.
- Invokes the function to confirm successful deployment and correct behavior.
Workflow Summary
| Stage | Trigger | Environment | Deployment Target | Tests |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feature Branch Deployment | Push to feature/* | AWS EC2 | Docker container on EC2 | Integration tests |
| Pull Request Validation | Open PR against main | Kubernetes (Argo CD) | Synced pods/services | OWASP ZAP DAST scans |
| Main Branch Production Deploy | Merge into main | AWS Lambda | Serverless function | Post-deployment invocation check |