package-lock.json changes. Leveraging the Job Cache Plugin’s cacheValidityDecidingFile option ensures that any update to your dependencies triggers a fresh cache, keeping your builds both fast and reliable.
Prerequisites
- A Jenkins instance with the Job Cache Plugin installed
- A Git repository named
solar-systemchecked out on your Jenkins agent - Node.js and npm configured on the build agent
1. Install a New Dependency
First, switch to thesolar-system repository on your local machine or CI checkout:
localtunnel package:
package.json and package-lock.json:
Changing or adding a dependency always modifies
package-lock.json. We’ll use this file’s hash to decide cache validity.2. Observe Cache Invalidation in Jenkins
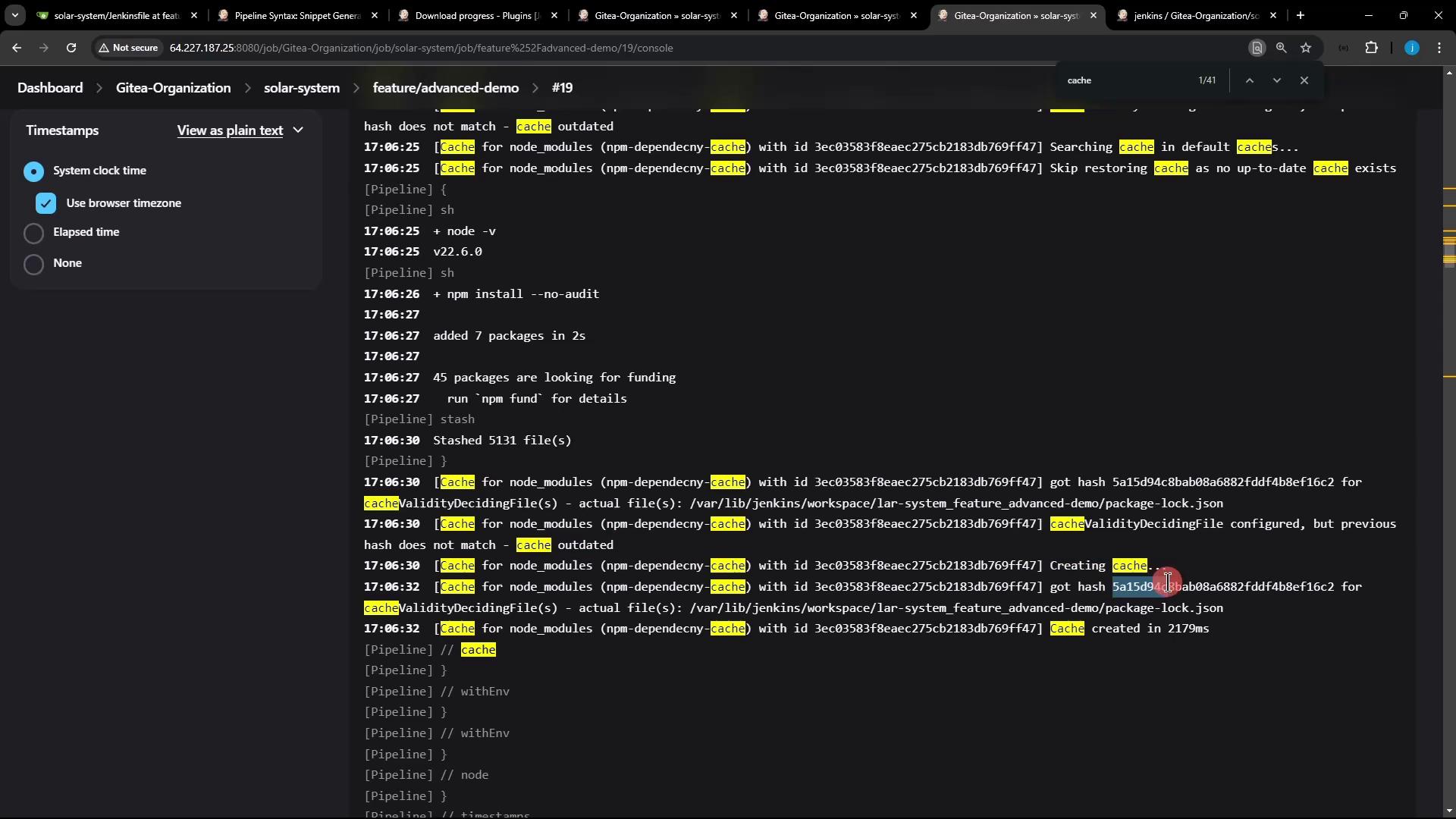
Navigate to your Jenkins job’s Installing Dependencies stage for build #19, and search the logs for “cache”:
Build #19 Logs (Cache Miss)
package-lock.json changed, the Job Cache Plugin calculates a new hash, decides the existing cache is outdated, skips the restore, and then stashes all files to create a fresh cache.
Prior Build (Cache Hit)
Cache Invalidation Details
3. Cache Behavior Comparison
| Scenario | Cache Restored | Action Taken |
|---|---|---|
package-lock.json unchanged | Yes (cache hit) | Skip install, restore cache |
package-lock.json modified | No (cache miss) | Reinstall & stash new cache |
Conclusion
By configuring the Job Cache Plugin’scacheValidityDecidingFile to point at package-lock.json, Jenkins automatically invalidates the cache whenever your dependencies change. This ensures that you always rebuild on the latest set of packages, while still benefiting from caching on subsequent runs.