catchError, and publish an HTML coverage report. You’ll update your Jenkinsfile, use the Credentials Binding and HTML Publisher plugins, and ensure downstream stages always run.
Pipeline Stages Overview
| Stage Name | Purpose | Command |
|---|---|---|
| Installing Dependencies | Install application dependencies | npm install |
| Dependency Scanning | Run security and vulnerability scans | npm audit |
| Unit Testing | Execute unit tests | npm test |
| Code Coverage | Generate coverage metrics | npm run coverage |
1. Add the Code Coverage Stage
Open yourJenkinsfile and duplicate the Unit Testing stage for coverage:
2. Observe the Coverage Failure
If coverage falls below your global threshold (e.g., 90%), the pipeline will fail: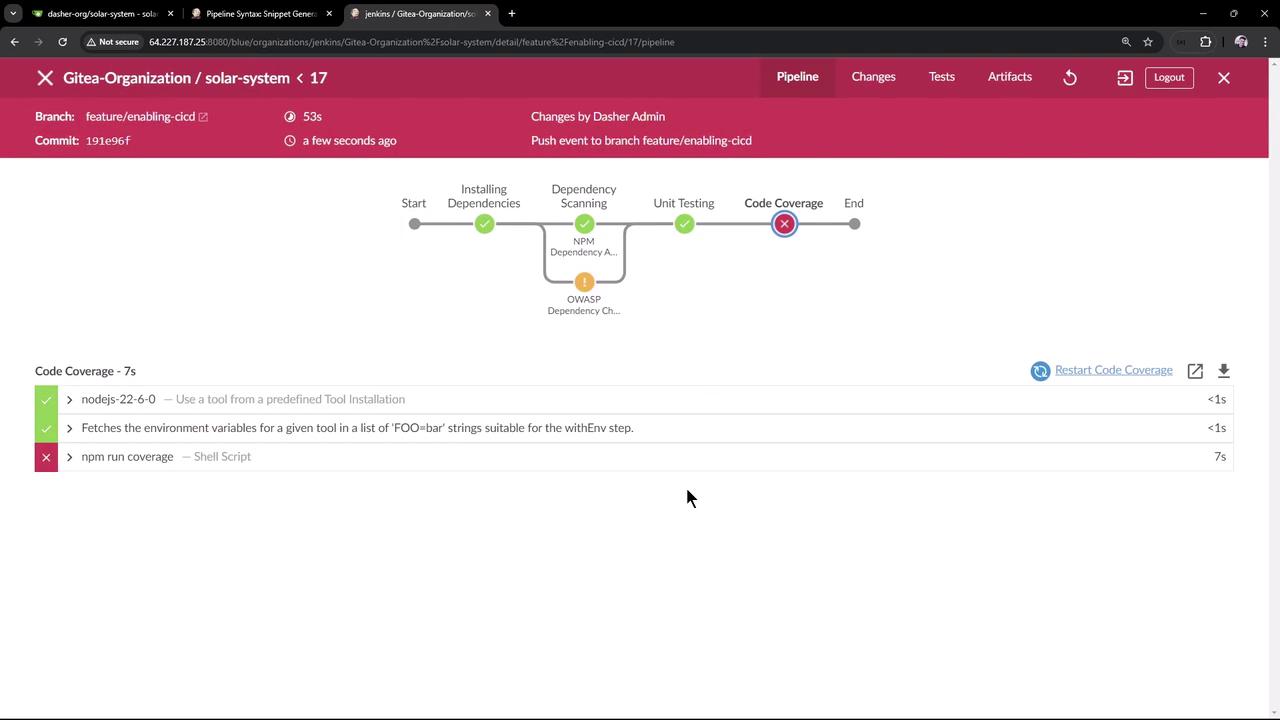
3. Introduce catchError
Wrap the coverage command incatchError so the stage becomes UNSTABLE instead of FAILED, allowing later stages to run.
The
catchError step lets you control both the stage and build result. For full syntax, see the Jenkins Pipeline Syntax reference.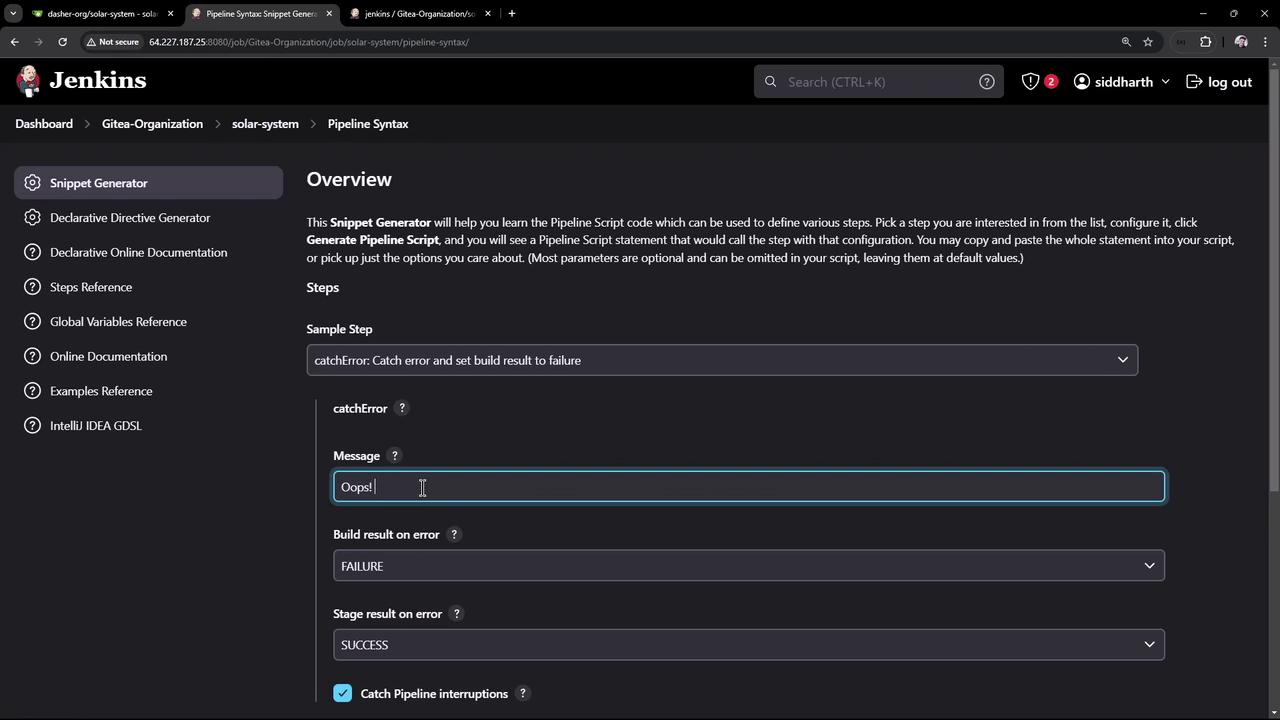
4. Update the Jenkinsfile
CombinecatchError with the HTML Publisher plugin to publish coverage reports:
5. Verify the Results
Rerun the pipeline. The Code Coverage stage will be marked UNSTABLE and subsequent stages will still execute. View the build history and status in the Jenkins dashboard: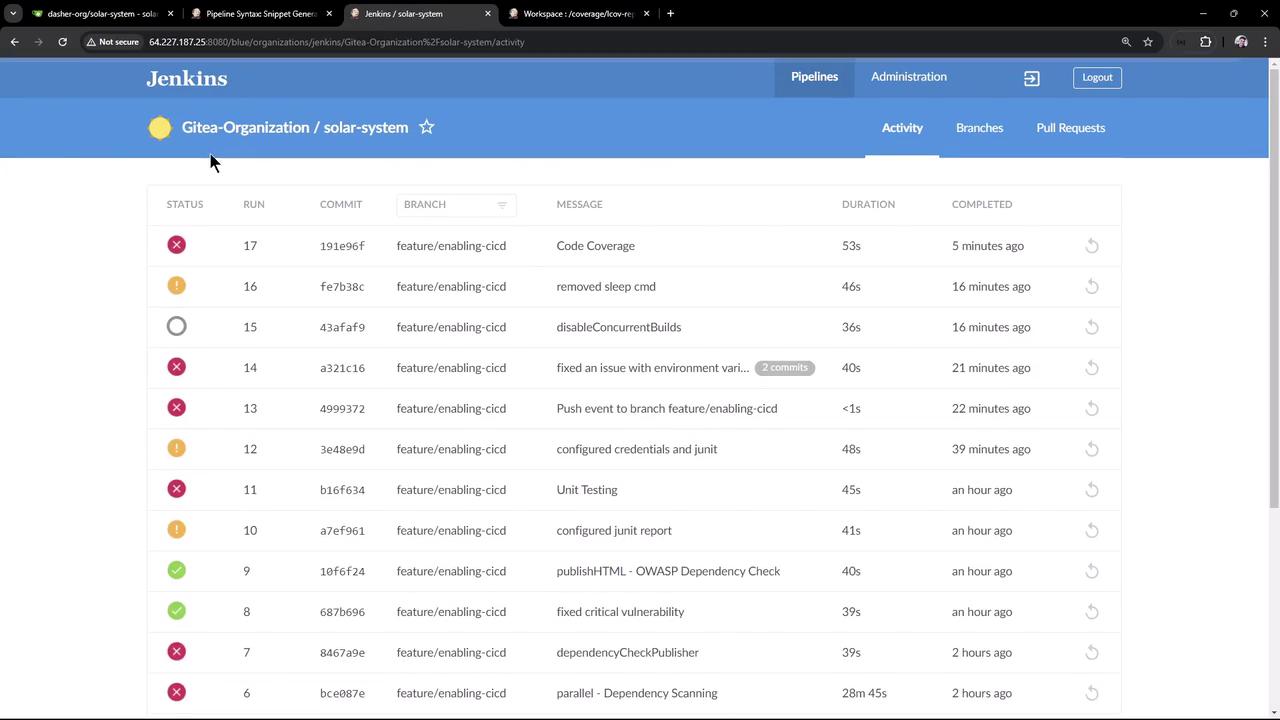
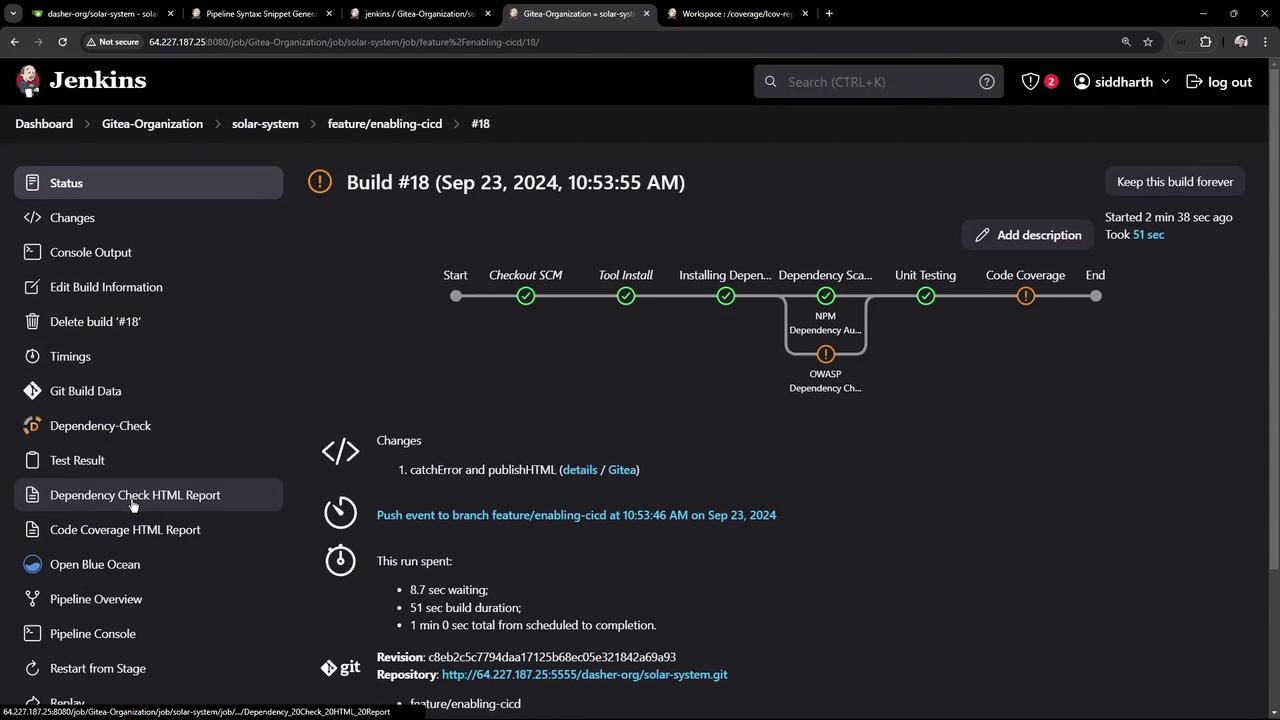
6. View the HTML Coverage Report
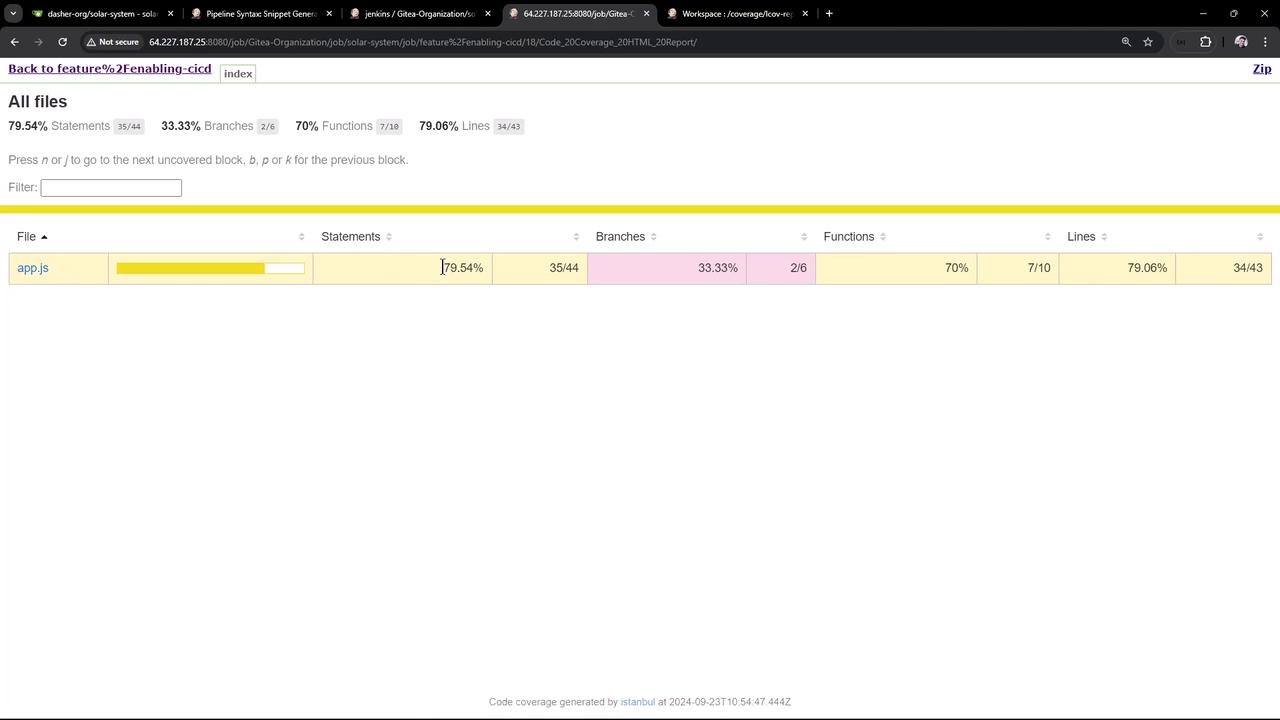
Click Code Coverage HTML Report in Jenkins to opencoverage/lcov-report/index.html. You’ll see detailed metrics for each file—e.g., for app.js:
- Statement coverage: 79.54%
- Branch coverage: 33.33%
- Function coverage: 70%
- Line coverage: 79.06%