AWS Security Lake stores logs in an Amazon S3 bucket, leveraging S3’s robust lifecycle policies, built-in encryption, and cost-effective storage solutions. After storage, logs are normalized—optimizing them for efficient querying with tools such as Amazon Athena using standard SQL.
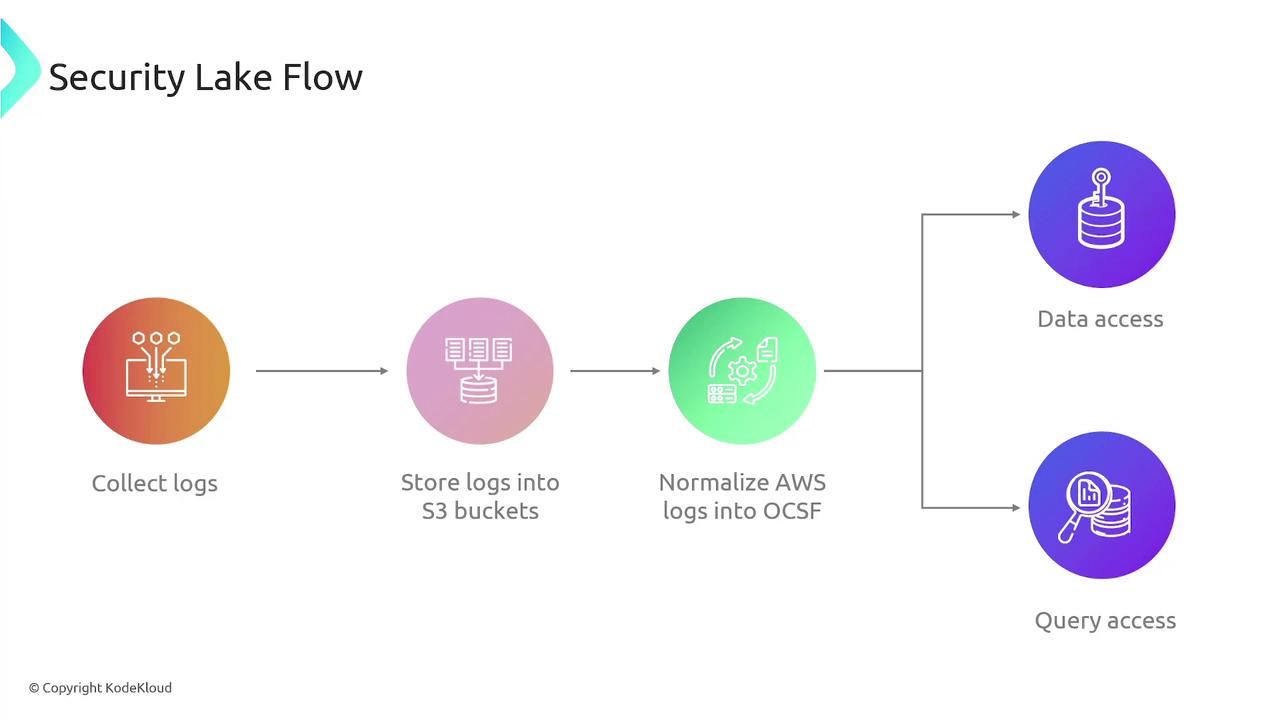
How AWS Security Lake Works
The workflow of AWS Security Lake consists of the following steps:- Log Collection: Gather logs from a variety of sources, including VPC flow logs, Route 53 logs, and CloudTrail logs that record user actions.
- Log Storage: Securely store the collected logs in an Amazon S3 bucket.
- Log Normalization: Convert logs into an optimized format, such as Parquet, and standardize them using the Open Cybersecurity Schema Framework (OCSF), making them easier to query.
- Data Querying: Utilize AWS tools like Amazon Athena to run ad hoc queries, enabling precise data extraction for investigations and analysis.
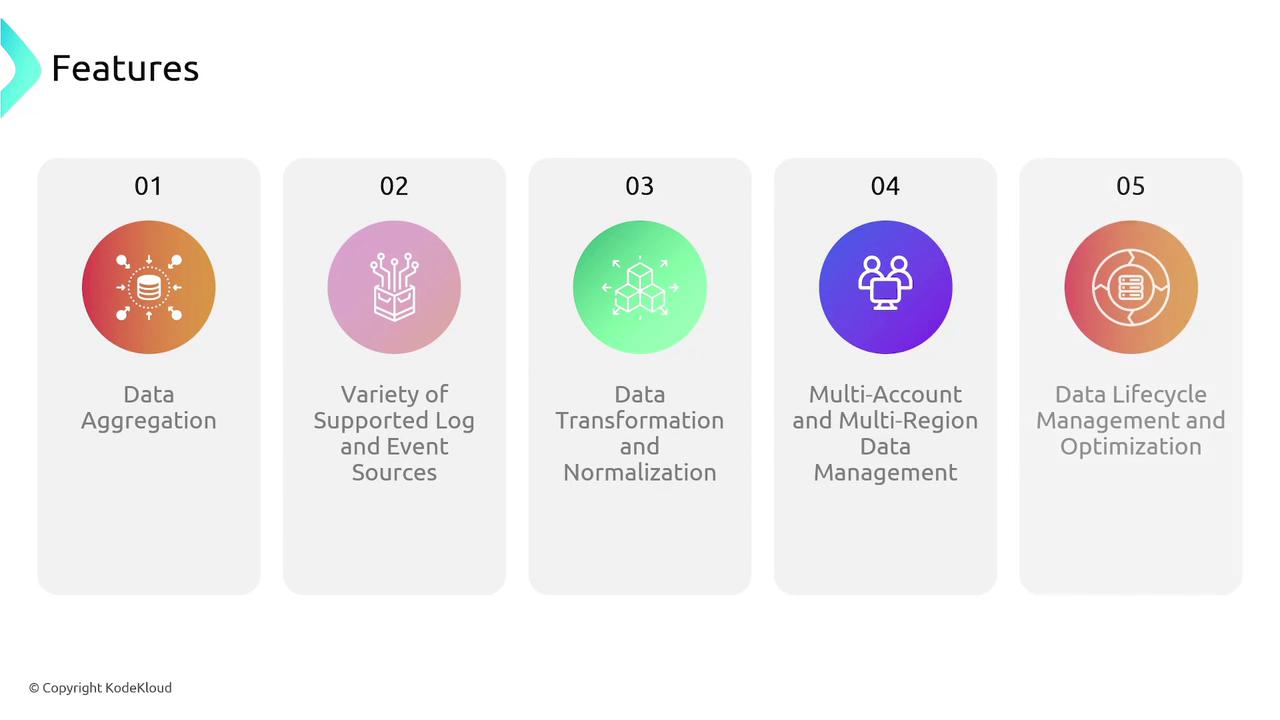
Key Features of AWS Security Lake
AWS Security Lake offers numerous features designed to simplify multi-environment log management:- Data Aggregation: Consolidate data from various environments, supporting a wide range of events and third-party integrations.
- Data Transformation and Normalization: Automatically partition and convert incoming data into efficient formats, ensuring consistency with standards like the OCSF.
- Multi-Account and Multi-Region Support: Seamlessly operate across multiple AWS accounts and regions.
- Data Lifecycle Management: Manage retention policies and storage costs using automated tiering within S3.
Benefits of Centralized Log Management
Centralizing log collection and management through AWS Security Lake provides several advantages:- Operational Efficiency: Eliminate the complexities of handling logs from disparate systems by maintaining a single source of truth.
- Enhanced Security: Streamline security monitoring and compliance audits with comprehensive data visibility.
- Cost Optimization: Leverage cost-effective storage solutions and automated lifecycle management to reduce expenses.
- Simplified Investigation: Use robust querying capabilities, such as identifying logs for a specific subnet at a particular time, to quickly trace events and mitigate issues.