Creating a New State Machine
Begin by searching for “Step Functions” in the AWS Console. This will take you to the page where you can create your first state machine. Click on Create state machine. A state machine is the location where you build your workflow logic by combining individual steps that process your tasks.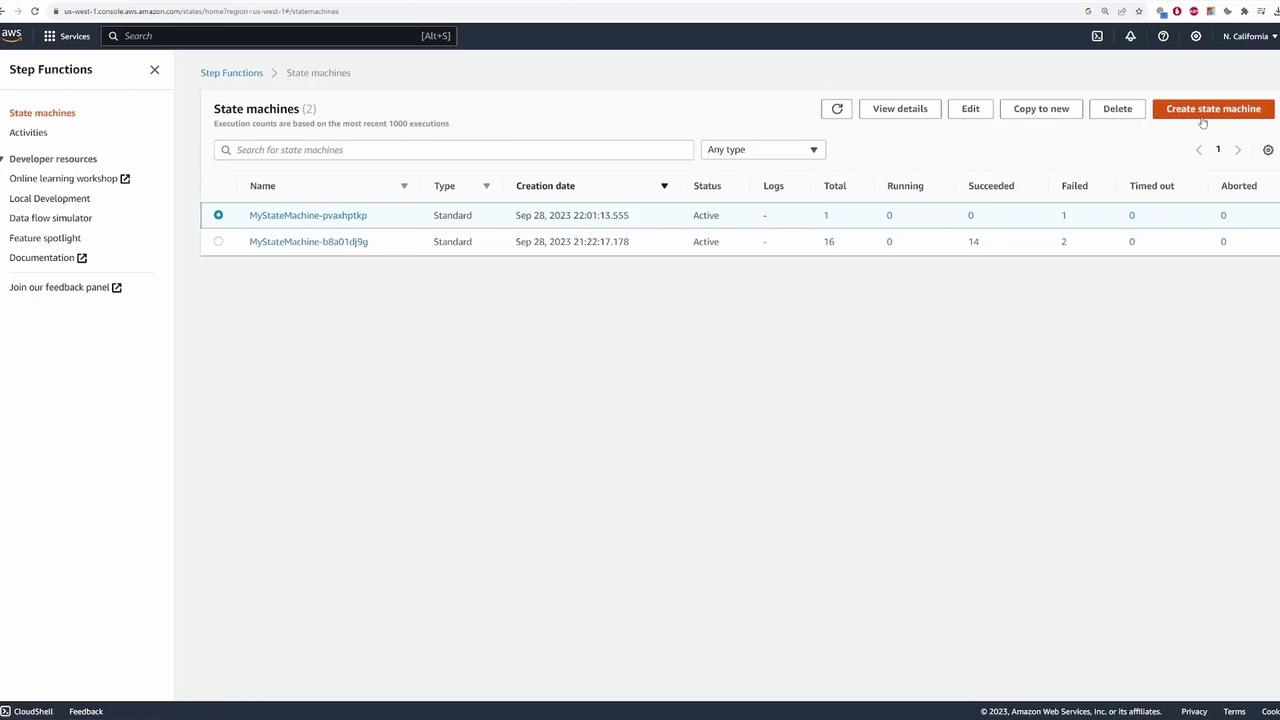
Overview of the State Machine Authoring Window
At the core of the authoring window, you will see the graphical depiction of your state machine workflow. The flow begins from the Start node and progresses to the End node as all steps are executed.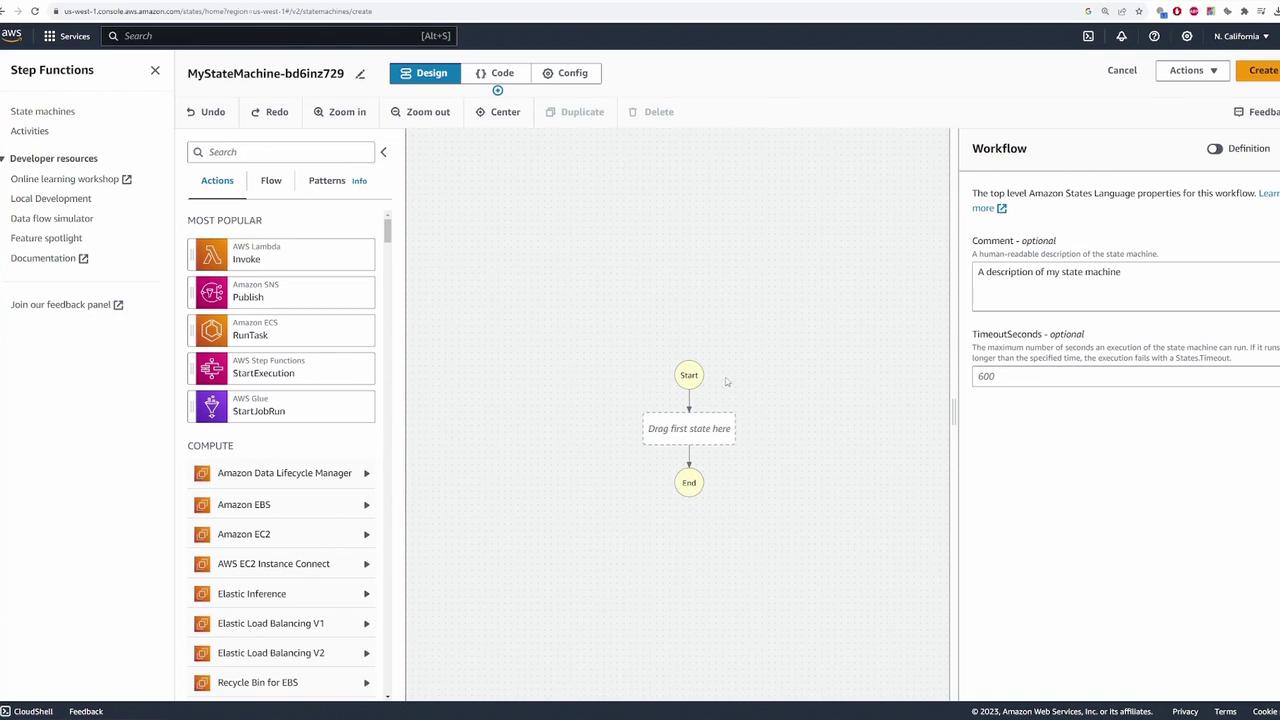
Demo Application Scenario
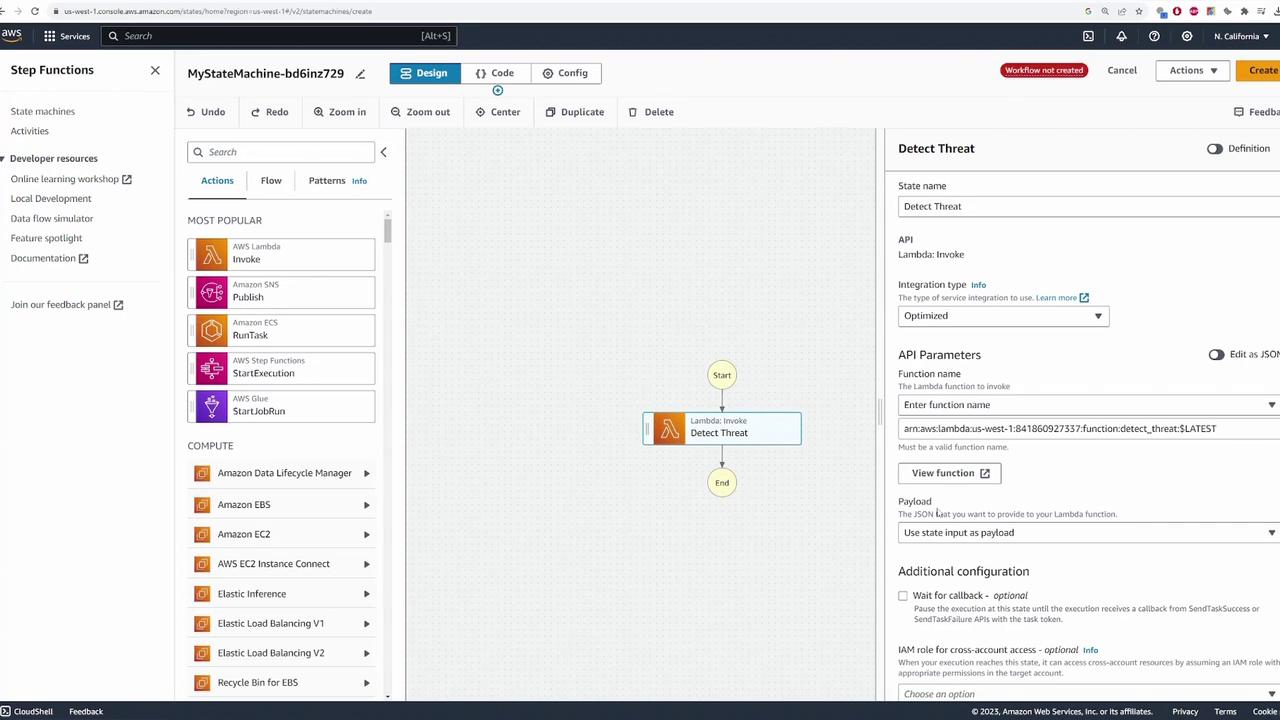
In our demo scenario, a camera records an event and sends the data (such as an image or video clip) to the state machine. The first step in the workflow is to invoke a Lambda function named detect_threat, which analyzes the input to determine if the event represents a threat.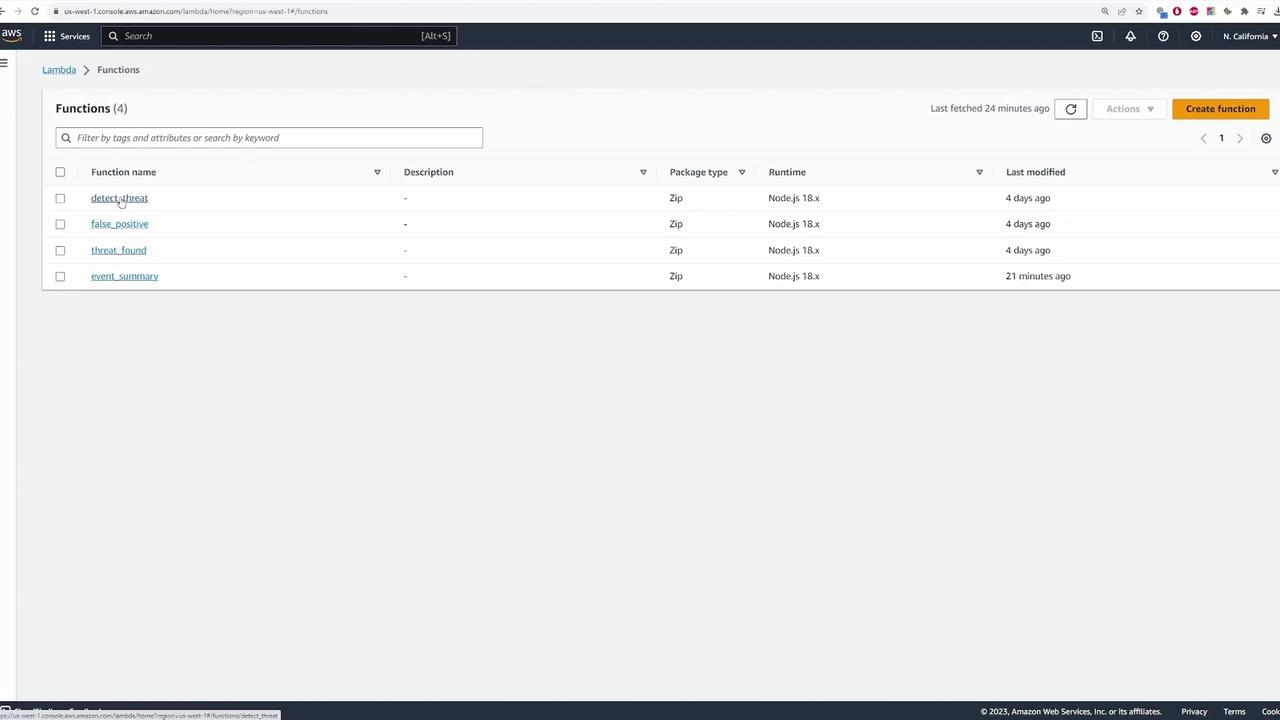
Adding Decision Logic with a Choice State
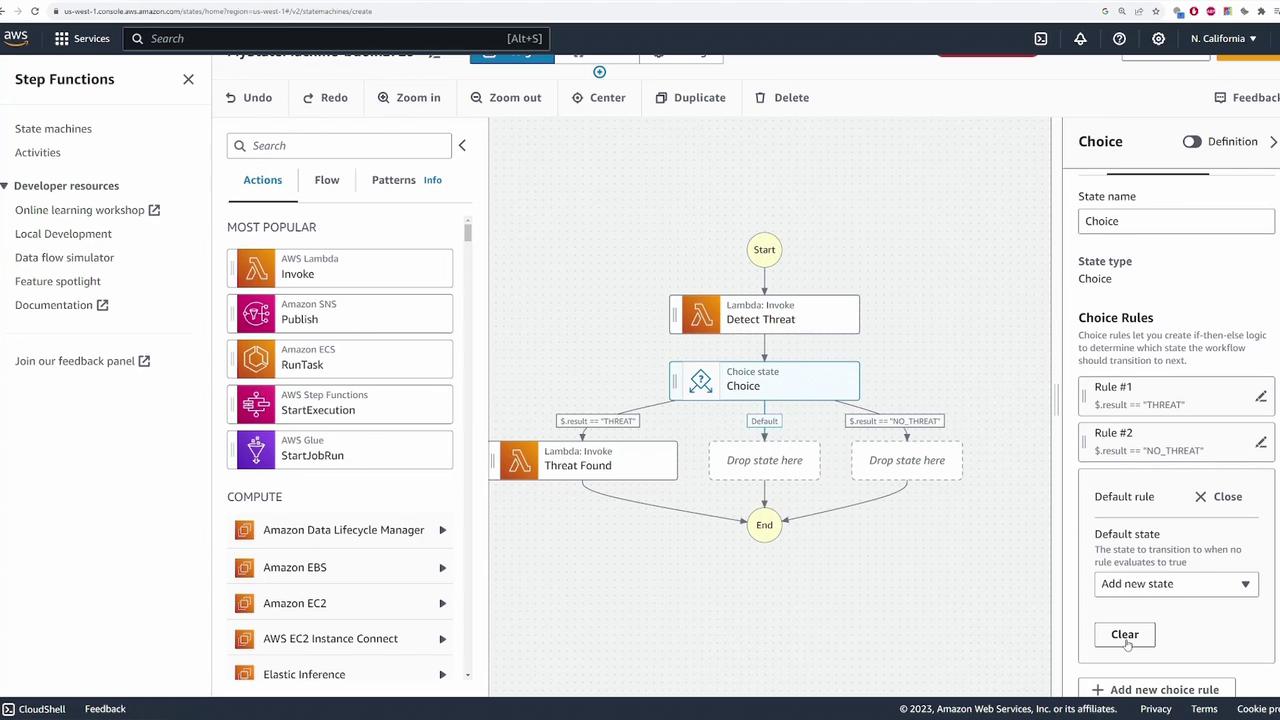
Based on the output from detect_threat, the state machine must decide which branch to follow. This is accomplished by adding a choice state to the workflow. Configure the choice state with two conditions:-
If Result Equals “THREAT”:
- Set the condition by specifying the variable
$.result, choosing “is equal to” as the comparator, and enteringTHREATas the string value. - Drag a new Lambda state into the workflow and name it Threat Found.
- Select the corresponding Lambda function (e.g., threatfound) from the dropdown.
- Configure the branch to end the workflow after execution.
- Set the condition by specifying the variable
-
If Result Equals “NO_THREAT”:
- Add another rule where the result is equal to
NO_THREAT. - Drag in the Lambda state for handling false positives, name it No Threat, and select its associated Lambda function (e.g., falsepositive).
- Set the transition for this branch to lead to the End state.
- Add another rule where the result is equal to
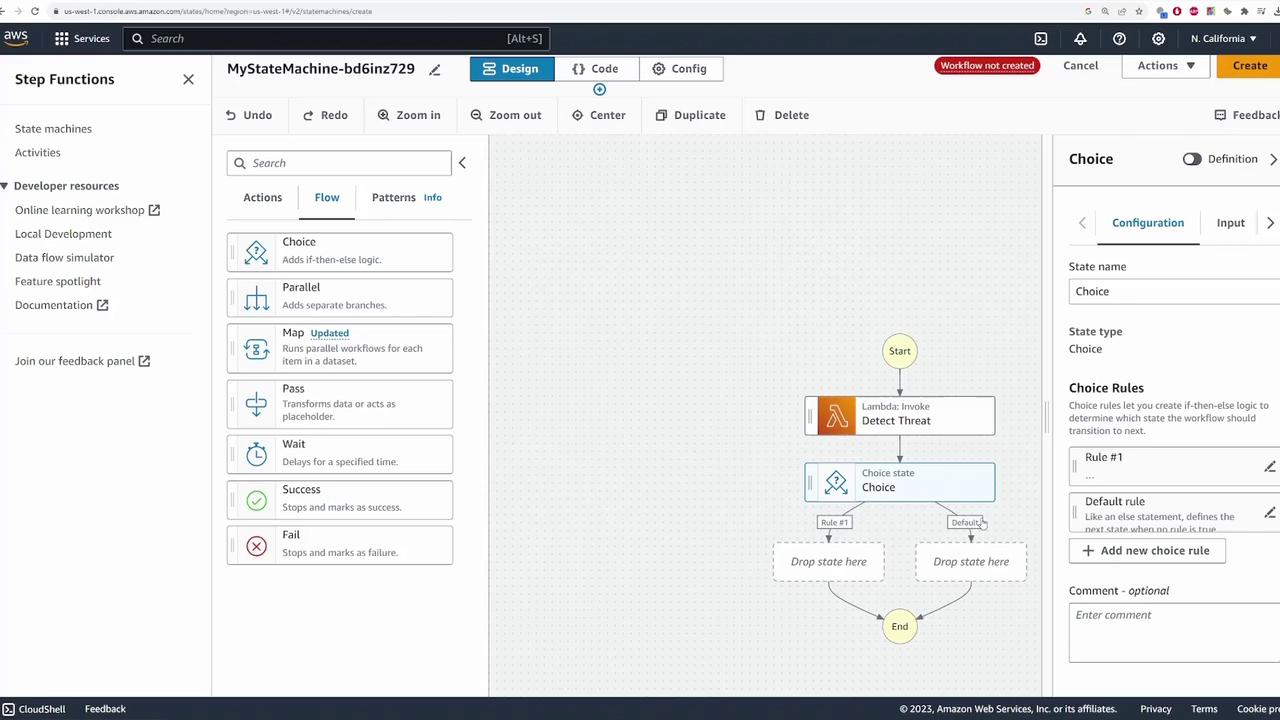
THREAT and another for NO_THREAT.
Lambda Function Logic for Post-Detection
After the detect_threat function returns its result, the state machine executes one of two Lambda functions:-
Threat Found Function:
This function runs when a threat is detected. It may handle actions such as sending alerts and notifications. -
False Positive Function:
This function addresses situations where the detected event is a false alarm. Here is a simple implementation:
For production environments, ensure that each Lambda function is thoroughly tested and secured according to AWS best practices.
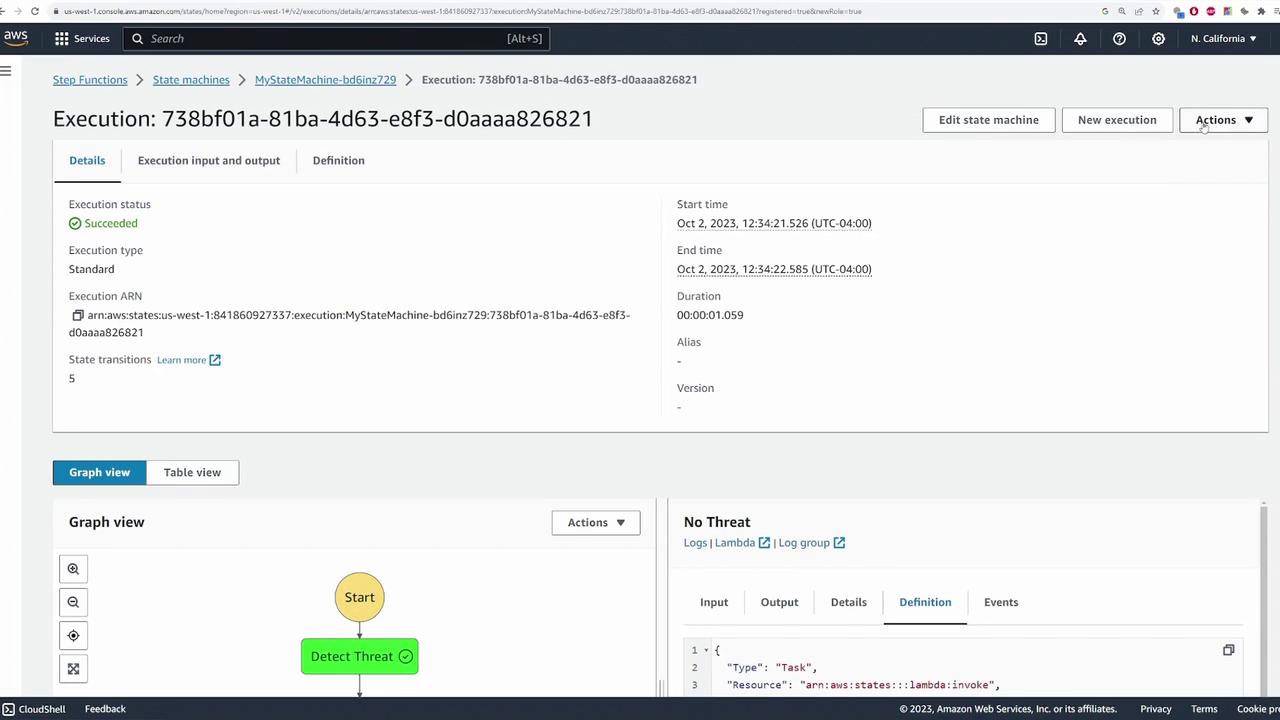
Testing the State Machine
After configuring all states and decision logic, click Create. AWS automatically provisions the necessary IAM role with permissions that allow the state machine to invoke the configured Lambda functions and access other services like AWS X-Ray. If you encounter errors related to error handling (such as an extraneous error catcher on the Detect Threat state), simply remove or adjust the configuration. Once the state machine is created, test it by initiating an execution. Provide sample input data simulating a camera event. For example, you may supply a simple JSON payload like: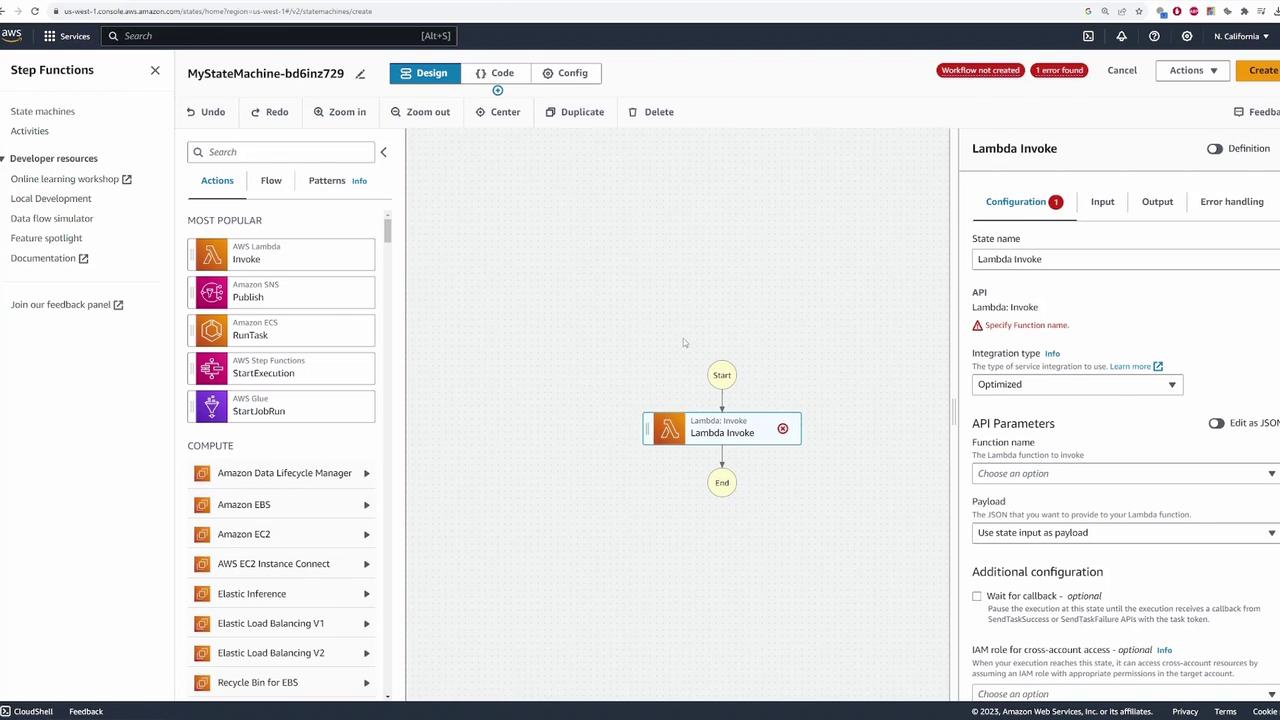
"NO_THREAT", triggering the false positive function. A different execution might reveal the threat branch being taken.
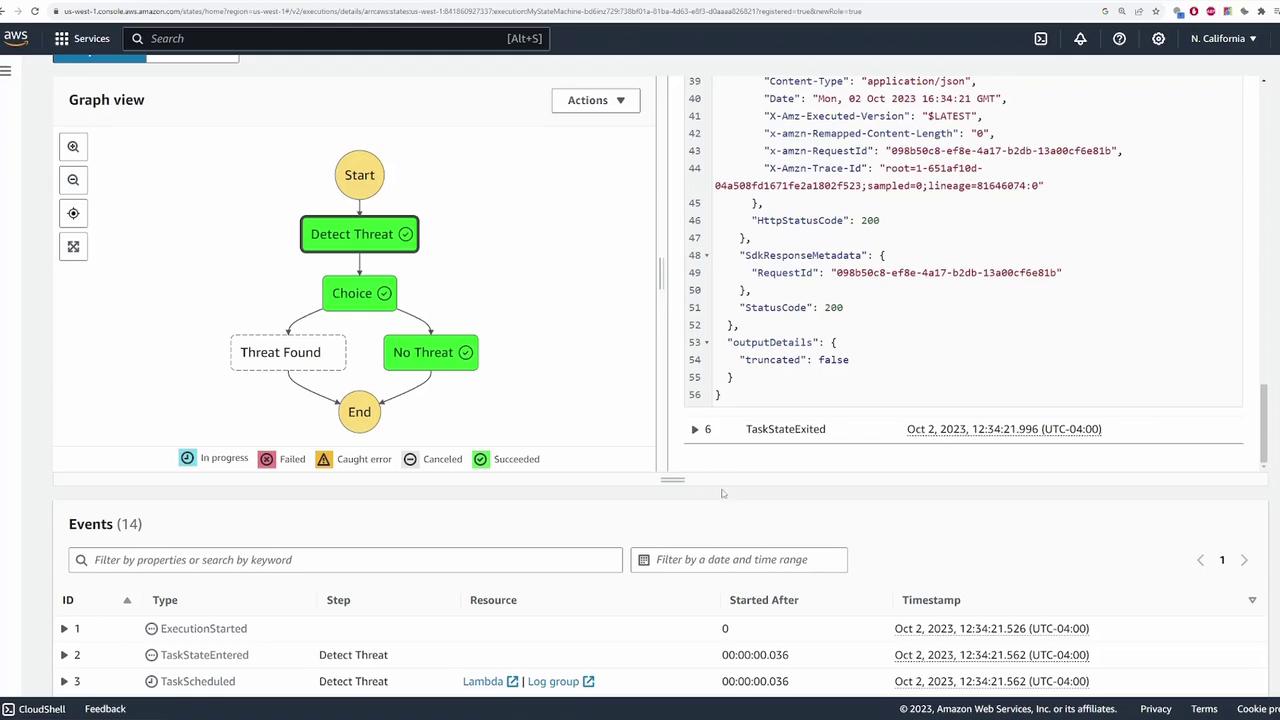
Conclusion
This demo has guided you through building a simple AWS Step Functions state machine that processes an event from a simulated camera service. We implemented conditional logic based on Lambda function outputs to handle distinct branches for threat and false positive scenarios. This example serves as a foundation for developing more complex workflows by integrating multiple AWS services and advanced custom logic.Consider expanding this demo by integrating additional services like Amazon SES for notifications or more advanced error handling strategies. For more information, explore the AWS Step Functions Documentation.