- Design Principles and Foundation
- Categories for Performance in AWS
- Specific Performance Choices for AWS Services

Section 1: Design Principles and Performance Optimization
When optimizing performance, it is essential to ask the right questions and scrutinize key design choices. Consider whether you can leverage managed services, simplify technology, and foster a culture of experimentation and innovation. These focal points are core to the design principles we explore in this section.
Remember, the right design strategy is the backbone of enhanced performance. Analyzing your architectural decisions early can streamline your subsequent optimizations.
Section 2: Categories for Performance Improvement
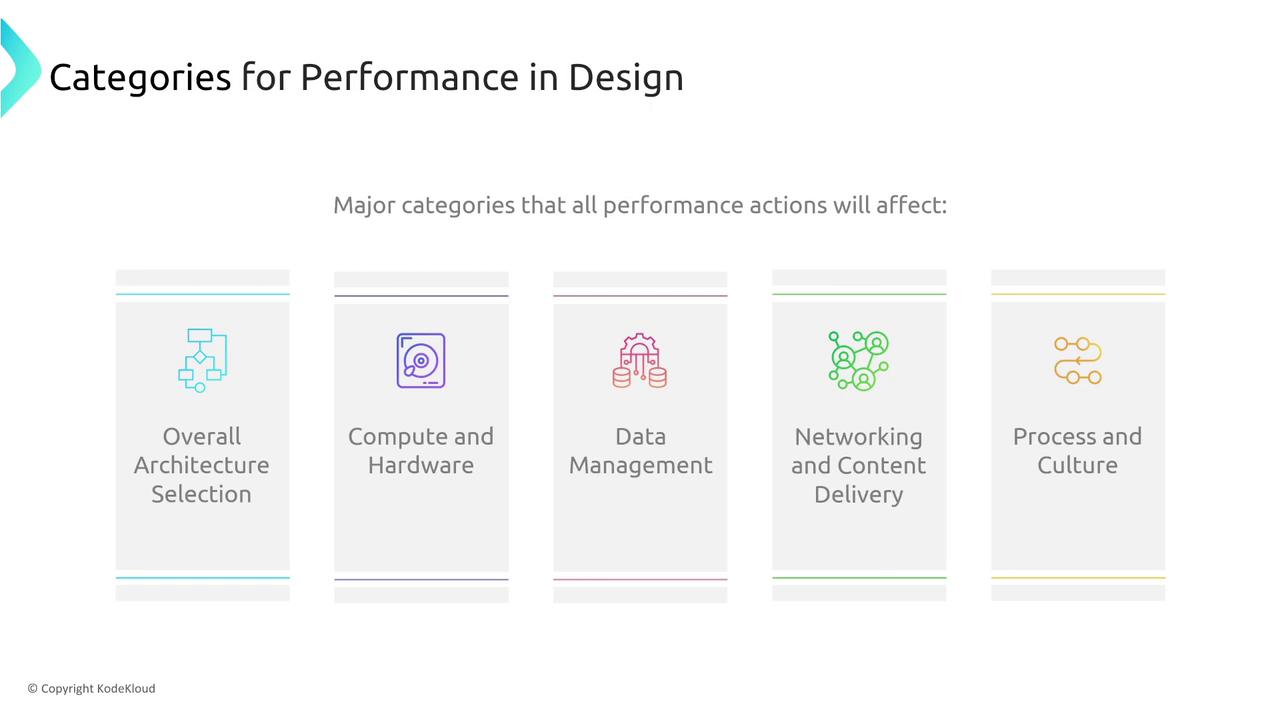
Next, we review the major categories where performance improvements can be applied. Each category focuses on a different aspect of system design:-
Overall Architectural Selection
Evaluate how your application’s architecture influences its performance profile. The choice of architecture significantly affects the efficiency and scalability of your services. -
Compute and Hardware
Consider memory optimization, CPU sizing, and the selection of efficient compute services to ensure you are achieving optimal performance. -
Data Management (Storage)
Managed databases and storage services play a pivotal role in performance by handling data efficiently. Optimizing your data management strategy is therefore crucial. -
Networking and Content Delivery
Fine-tuning networking performance involves selecting the right virtual machine sizes and leveraging edge locations—using technologies like CloudFront Functions or AWS Lambda@Edge—to reduce latency. -
Process and Culture
Adopting automated processes such as infrastructure as code and promoting a culture of continual improvement can lead to significant performance gains.
| Category | Focus Area | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Overall Architectural Selection | Application design and structure | Scalability, fault tolerance, and modularity |
| Compute and Hardware | Service performance and resource allocation | Memory management, CPU optimization, and compute service efficiency |
| Data Management (Storage) | Efficient and scalable data handling | Managed services, data accessibility, and storage performance |
| Networking and Content Delivery | Data transmission and edge optimizations | VM sizing, latency reduction, and edge computing |
| Process and Culture | Operational efficiency and continuous improvement | Infrastructure as code (IaC) and performance monitoring |
Section 3: Specific Performance Scenarios for AWS Services
This section addresses performance scenarios and concerns unique to AWS services. The discussion covers:- Auto scaling versus manual scaling
- Load offloading and distribution techniques
- Differentiating between serverless and server-based architectures
- Compute at the edge might be best served by AWS Lambda.
- Flexible object storage is synonymous with Amazon S3.
- A simple, scalable key-value data store aligns with Amazon DynamoDB.
- Application user management can be facilitated by Amazon Cognito.
Summary
Designing for performance is a cornerstone of robust AWS architectures. In this article, we covered the following key points:- Fundamental design principles for performance optimization
- Major categories impacting performance, including architectural design, compute, data management, networking, and process/culture
- Detailed performance scenarios specific to AWS services such as auto scaling, load offloading, and service differentiation
- A hands-on interactive challenge to reinforce your learning
