Networking Load Balancers
Consider a scenario where a gaming company deploys a real-time multiplayer game on AWS. The backend is hosted on EC2 instances within a VPC, and it is crucial that only legitimate gaming traffic on a specific UDP port reaches the servers, with traffic distributed evenly across instances. Since UDP demands low latency and high throughput, a Network Load Balancer (NLB) is an excellent choice. In previous implementations, security groups were not supported on load balancers; only Network ACLs (attached to subnets) were available. In this scenario, the recommended approach is to assign a security group to the NLB that permits traffic solely through the specified UDP port, while configuring a network ACL to allow all inbound and outbound traffic. Although reverse configurations or sole reliance on network ACLs are possible, security groups offer greater control and flexibility.
Gateway Load Balancers
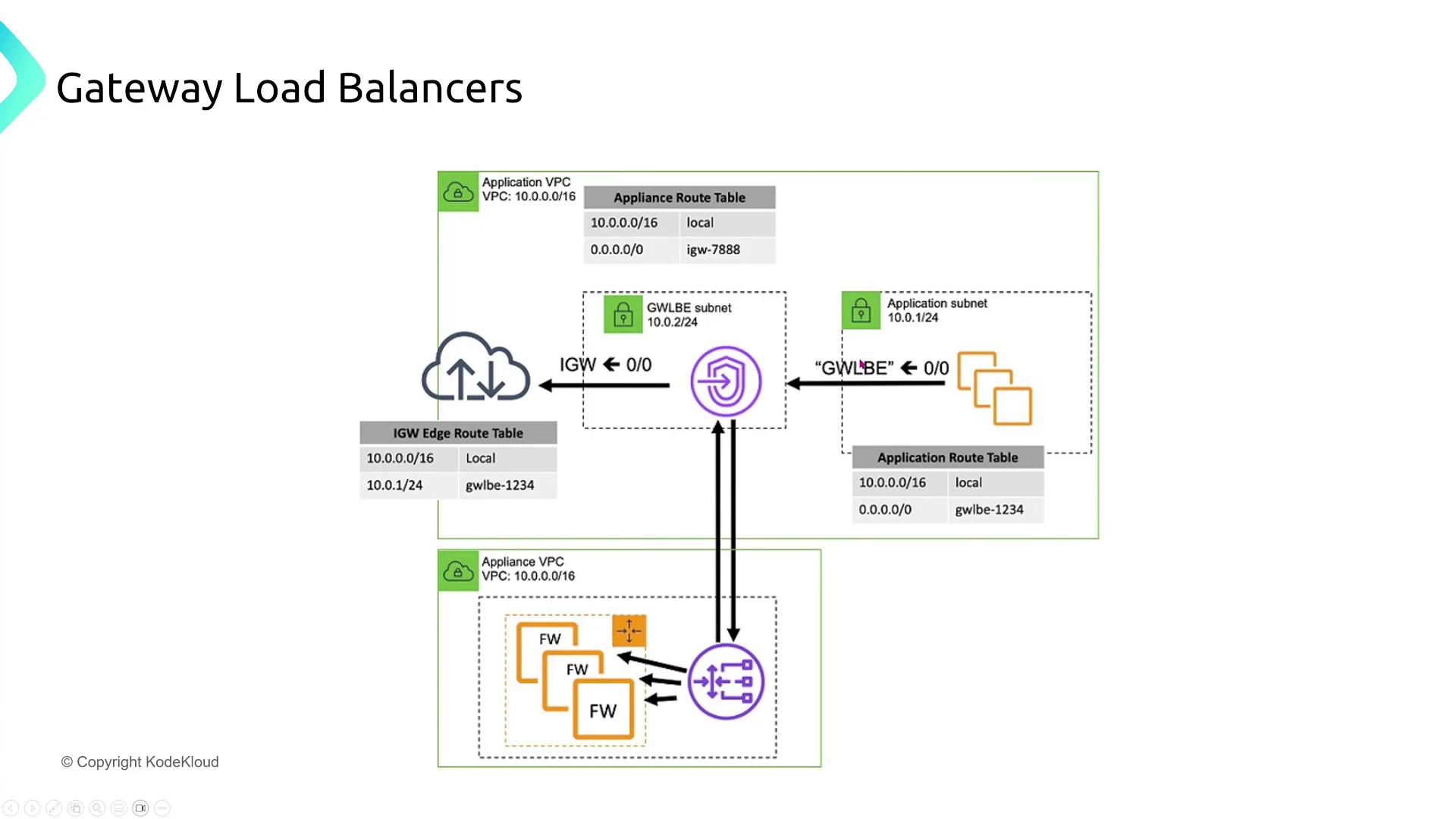
Gateway load balancers are built to filter and inspect traffic when managing virtual appliances—such as firewalls—used for in-depth security inspections. For example, a global e-commerce company might deploy several virtual appliances in its VPC to inspect and filter traffic. By using an AWS Gateway Load Balancer, the company can scale the deployment uniformly while satisfying the security team’s requirements. When implementing a gateway load balancer, ensure that routing and target groups are configured correctly to map application components and dependencies. The load balancer distributes incoming traffic across firewall appliances, which then perform deep packet inspection and enforce security policies.
Transit Networking
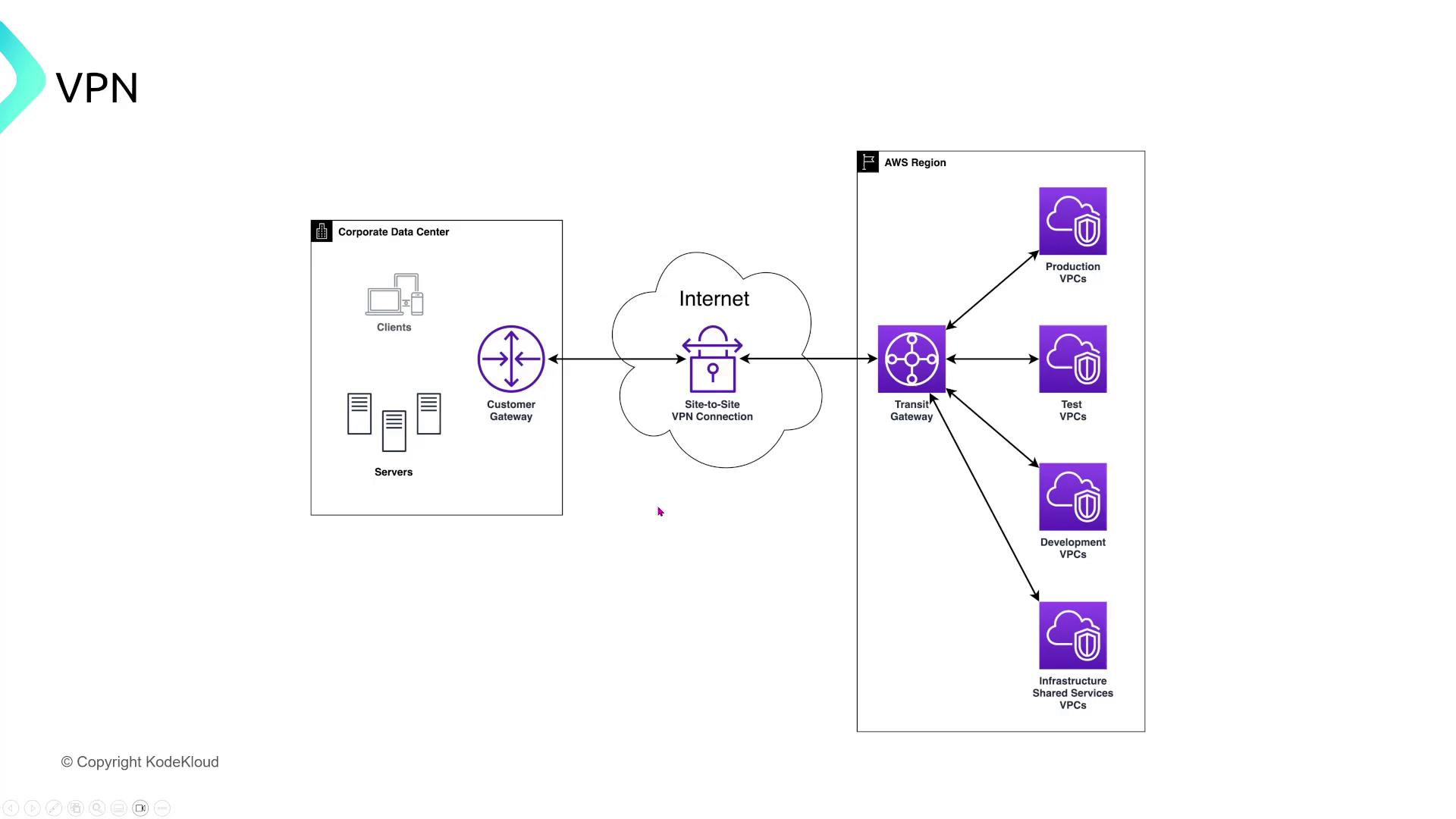
Transit networking ensures secure data transfers between on-premises data centers and AWS environments. Below are several key strategies:VPN for Secure Data Transfer
A healthcare organization uses AWS to host its patient management application while storing sensitive patient data on-premises. To securely transfer data for processing in the cloud, the organization plans to use an AWS site-to-site VPN with dynamic routing via BGP and encryption enabled. Although VPN connections occur over the internet, they provide encryption by default.
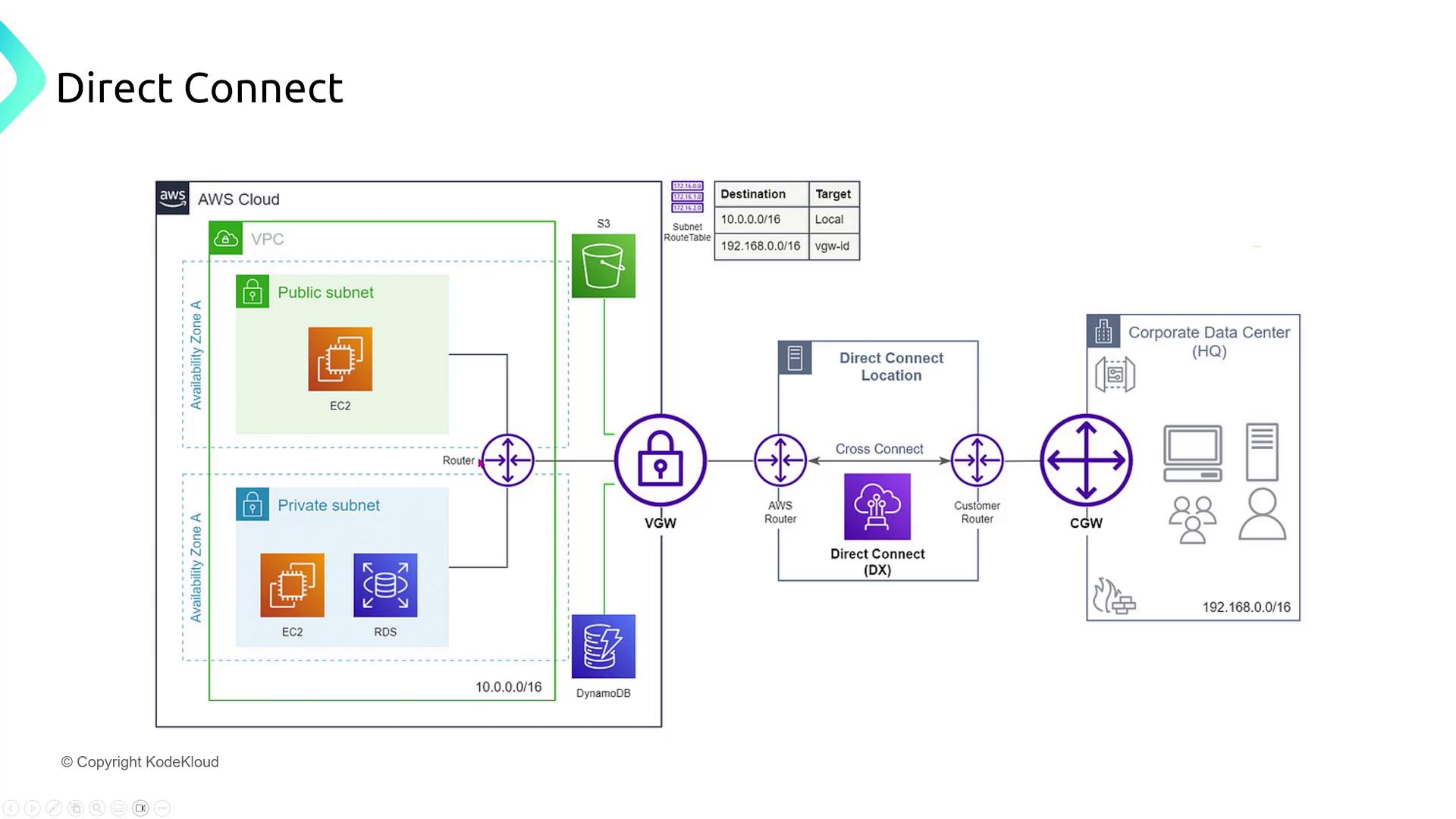
Direct Connect and Enhanced Security
For a multinational corporation transferring large amounts of data between on-premises data centers and AWS, AWS Direct Connect offers a dedicated connection without relying on the public internet. For even greater security, a VPN can be established over the Direct Connect connection, or MACsec can be used to encrypt data in transit.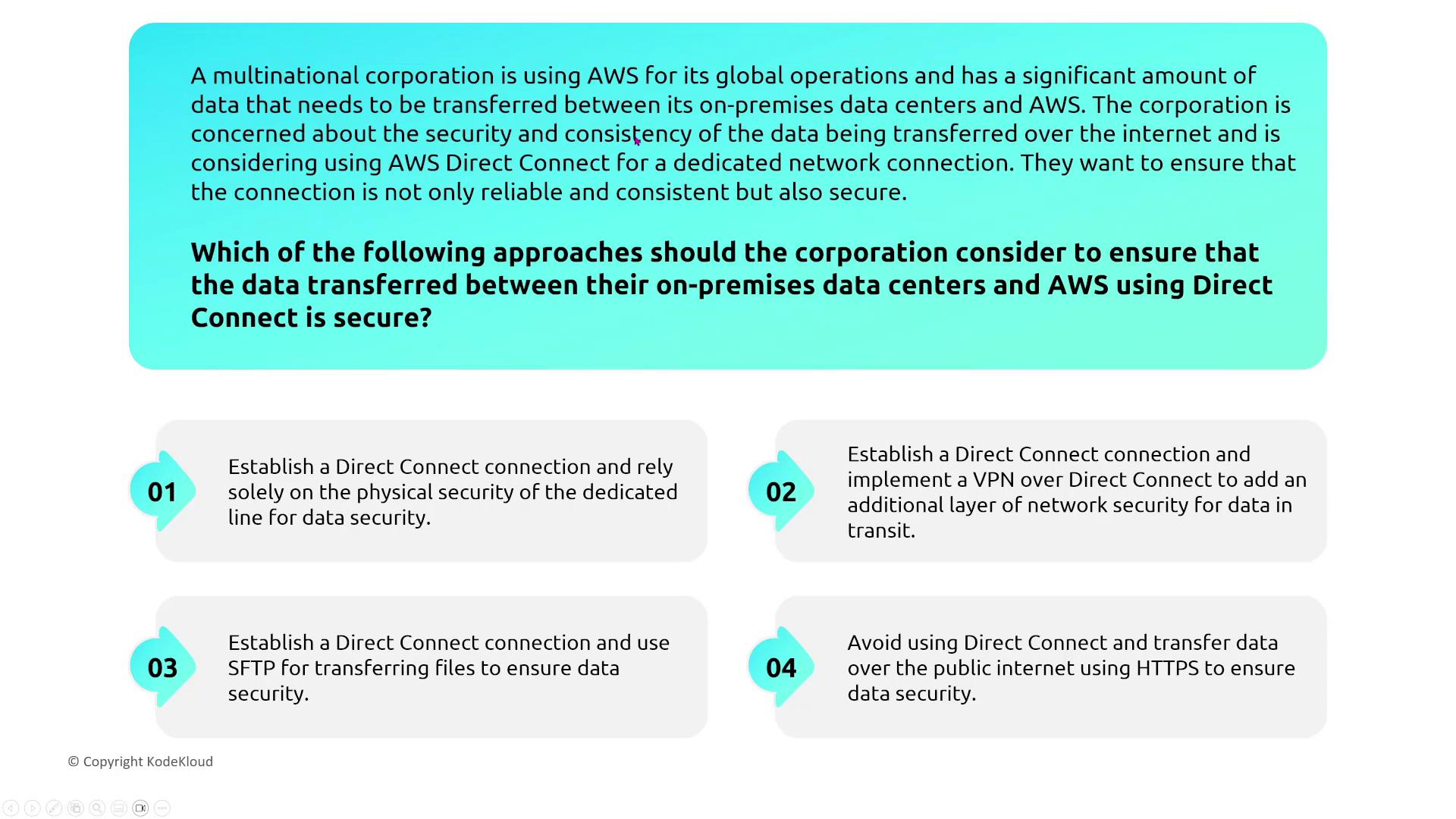
VPC Peering and Transit Gateway
A large company manages three VPCs (Dev, UAT, and Prod) in separate AWS accounts with non-overlapping CIDR blocks. Although UAT is peered with both Prod and Dev, transitive routing is not allowed. Therefore, a direct VPC peering connection between Prod and Dev is necessary for effective communication. Note that VPC peering only supports direct point-to-point connections; transitive routing across peered VPCs is not supported by AWS. Each communication channel must be explicitly established. A transit gateway diagram illustrates how flexible routing and proper routing table permissions facilitate communication among multiple VPCs in a multi-VPC architecture while supporting disaster recovery.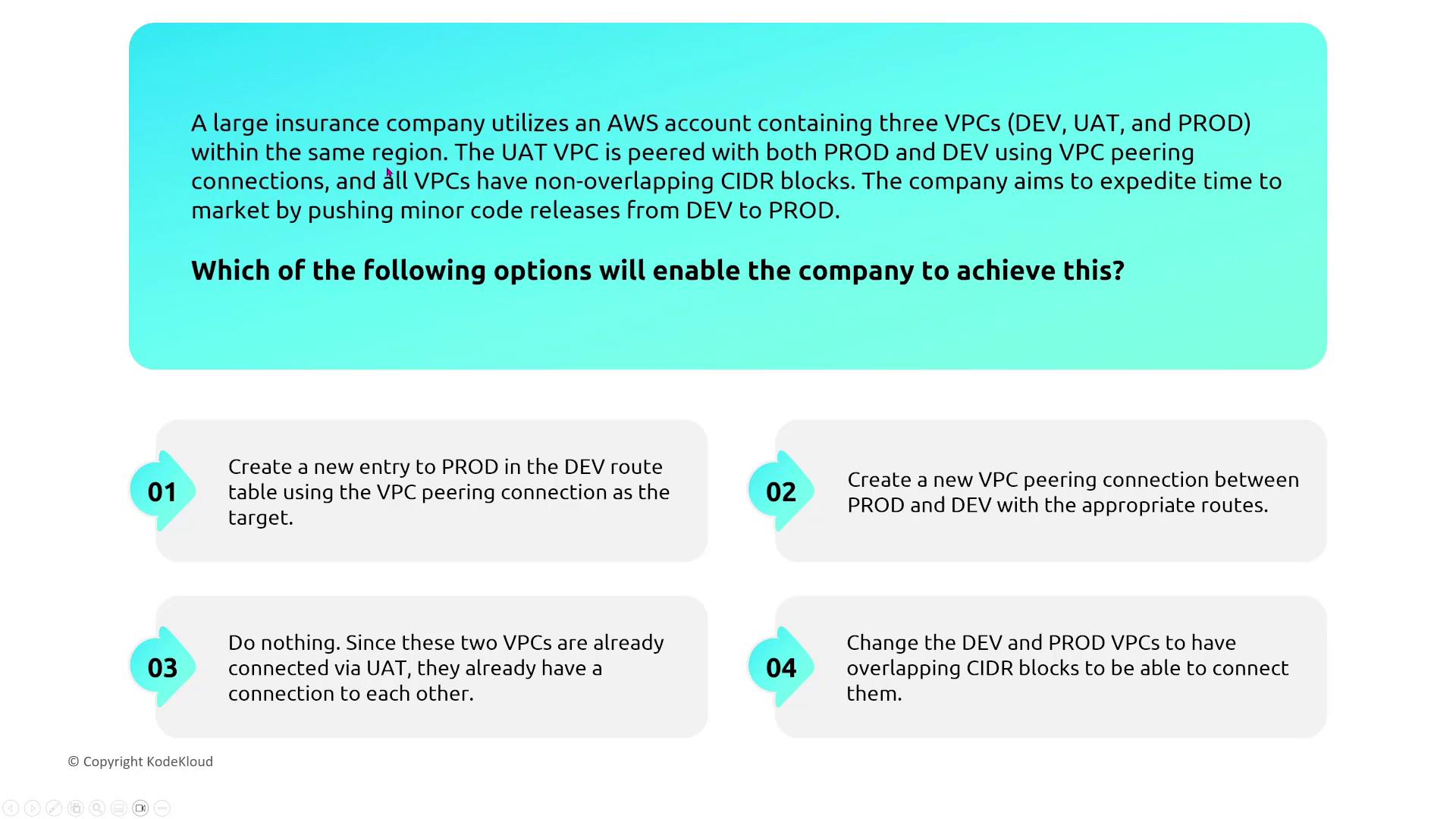
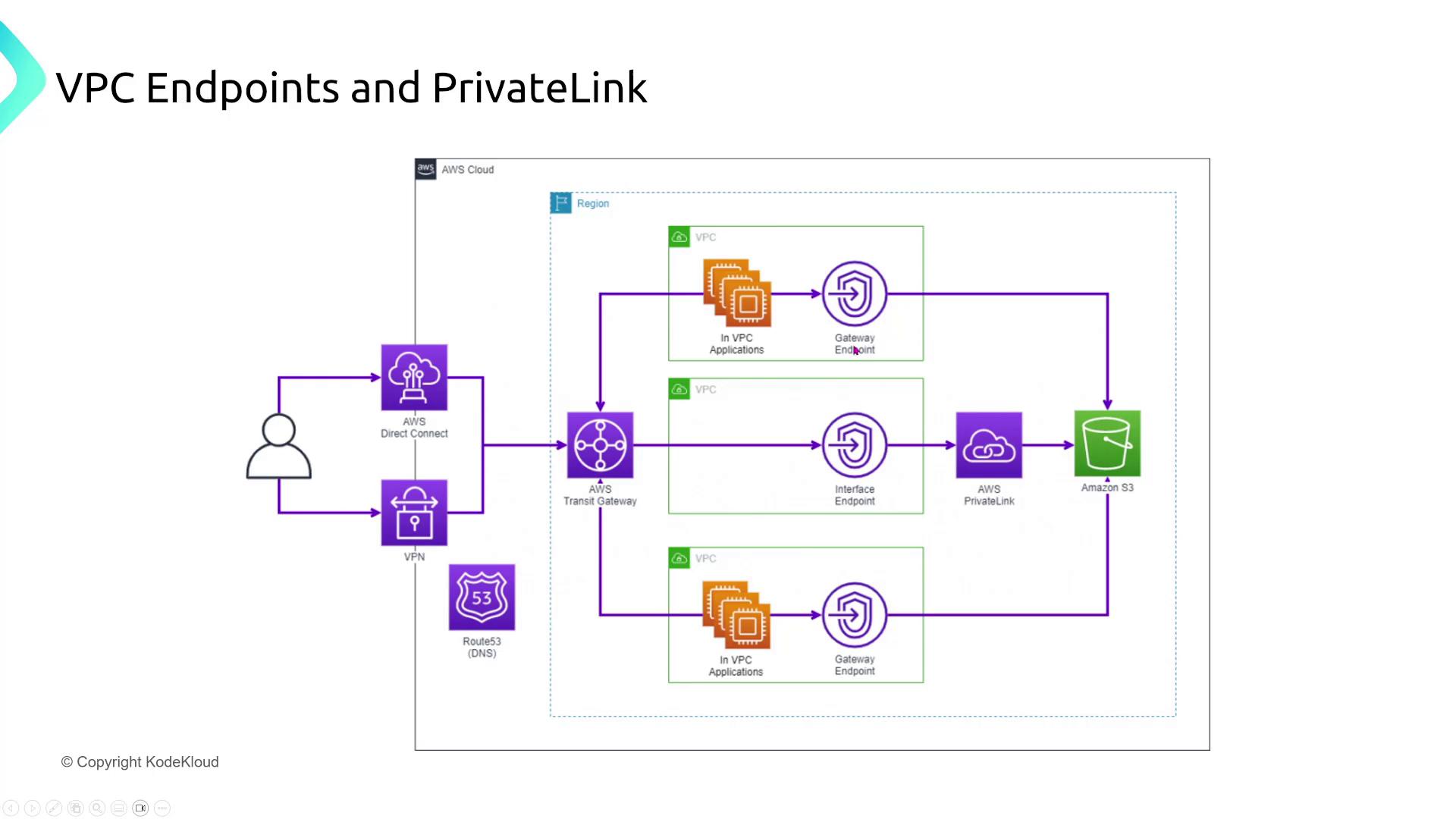
Endpoints and PrivateLink
Secure Access to External APIs
For a healthcare application that requires secure communication between microservices and an external API, utilizing a VPC endpoint through PrivateLink creates a secure route without exposing traffic on the public internet. When the external API is hosted within AWS (for example, by a partner), PrivateLink ensures that traffic remains private.
Accessing AWS Secrets Manager Securely
A fintech company developing a microservices-based application on AWS needs one of its services to securely retrieve configuration data from AWS Secrets Manager without exposing it publicly. The solution is to create a VPC interface endpoint for Secrets Manager and associate it with a security group that restricts access to required IP addresses and ports. Remember that gateway endpoints are available only for S3 and DynamoDB.
Edge Networking with CloudFront
Field-Level Encryption
A media streaming company using Amazon CloudFront collects sensitive user information (such as credit card details) via web forms. They require encryption of specific fields as data travels from the user to the origin server. CloudFront’s field-level encryption feature, combined with a customer-managed KMS key, addresses this need by protecting sensitive data while in transit.
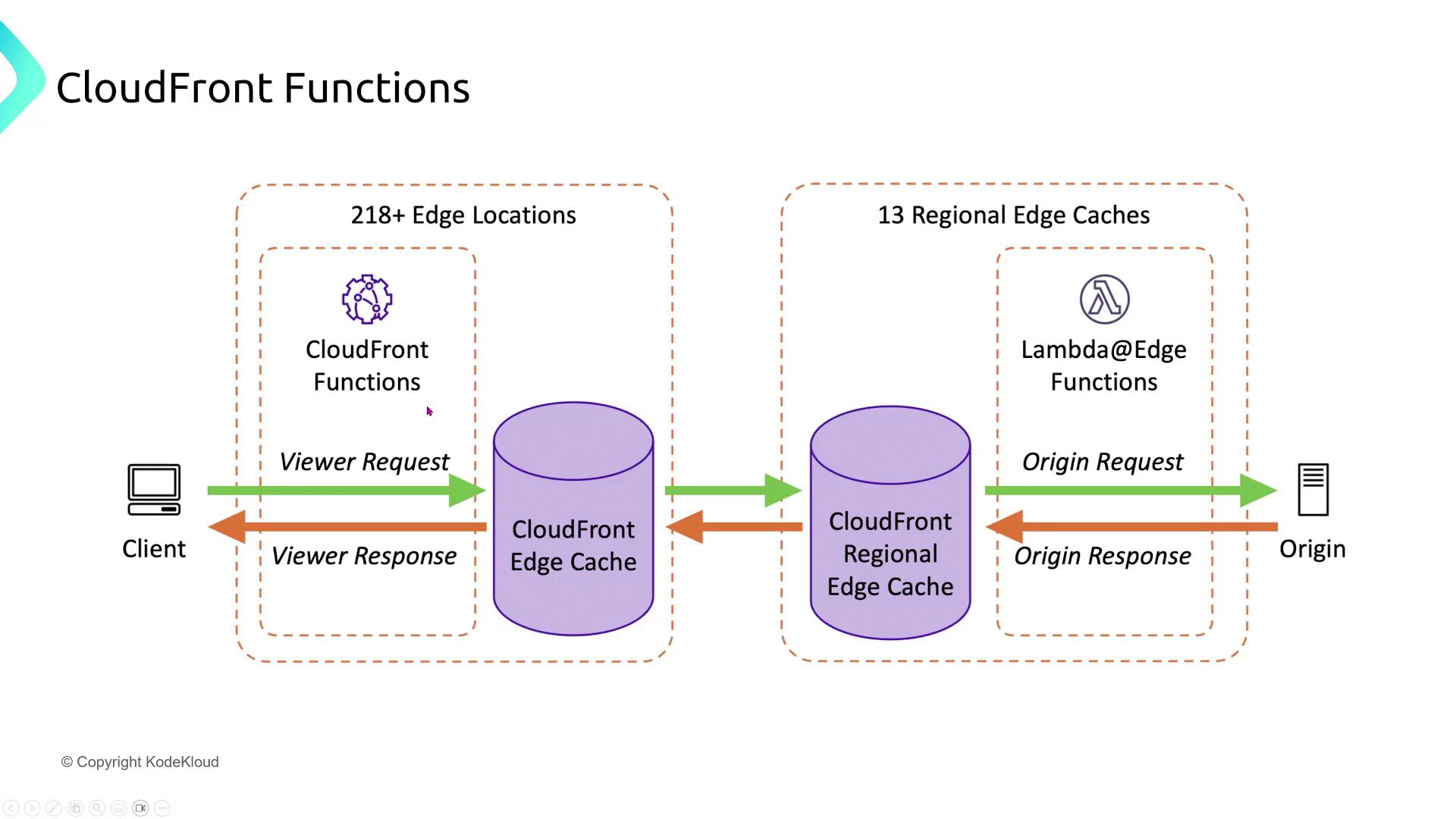
CloudFront Functions and Lambda@Edge
For a global e-commerce platform, deploying lightweight serverless functions at the edge can enhance both security and user experience by modifying HTTP requests or responses. When using CloudFront Functions, ensure that the functions run with the least privileges necessary to limit risk. Likewise, Lambda@Edge functions allow companies to deliver customized content directly from CloudFront without having to manage servers. It is crucial to assign only the minimal set of permissions necessary to perform their designated tasks.
DNS Security with Route 53
Amazon Route 53 provides global DNS routing for critical applications. For a multinational corporation, protecting DNS configurations against threats—like distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks—is paramount. Implement strict access controls and routing policies using Route 53 features. Recommended practices include restricting write access and validating DNS responses through well-crafted policies.
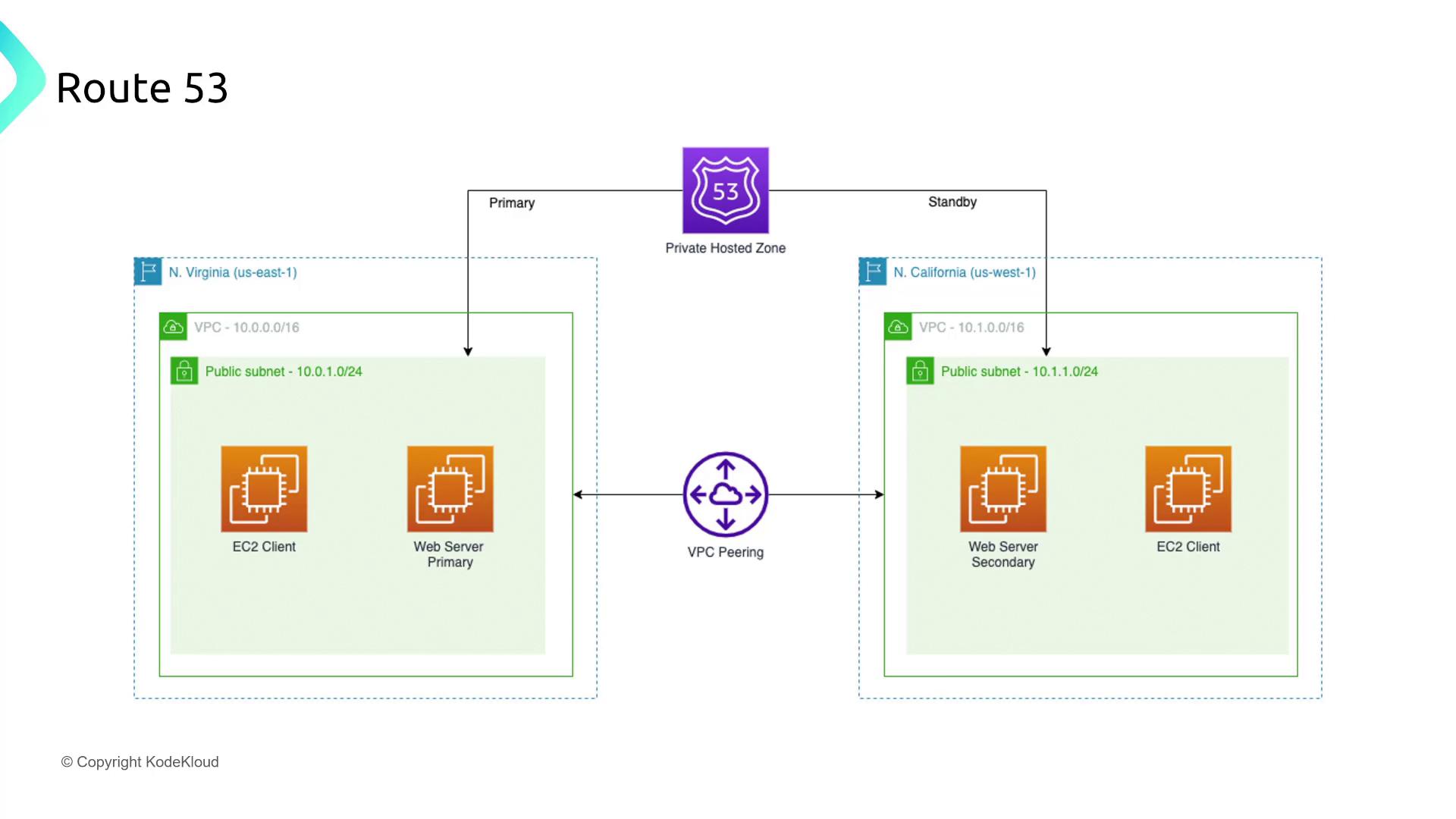
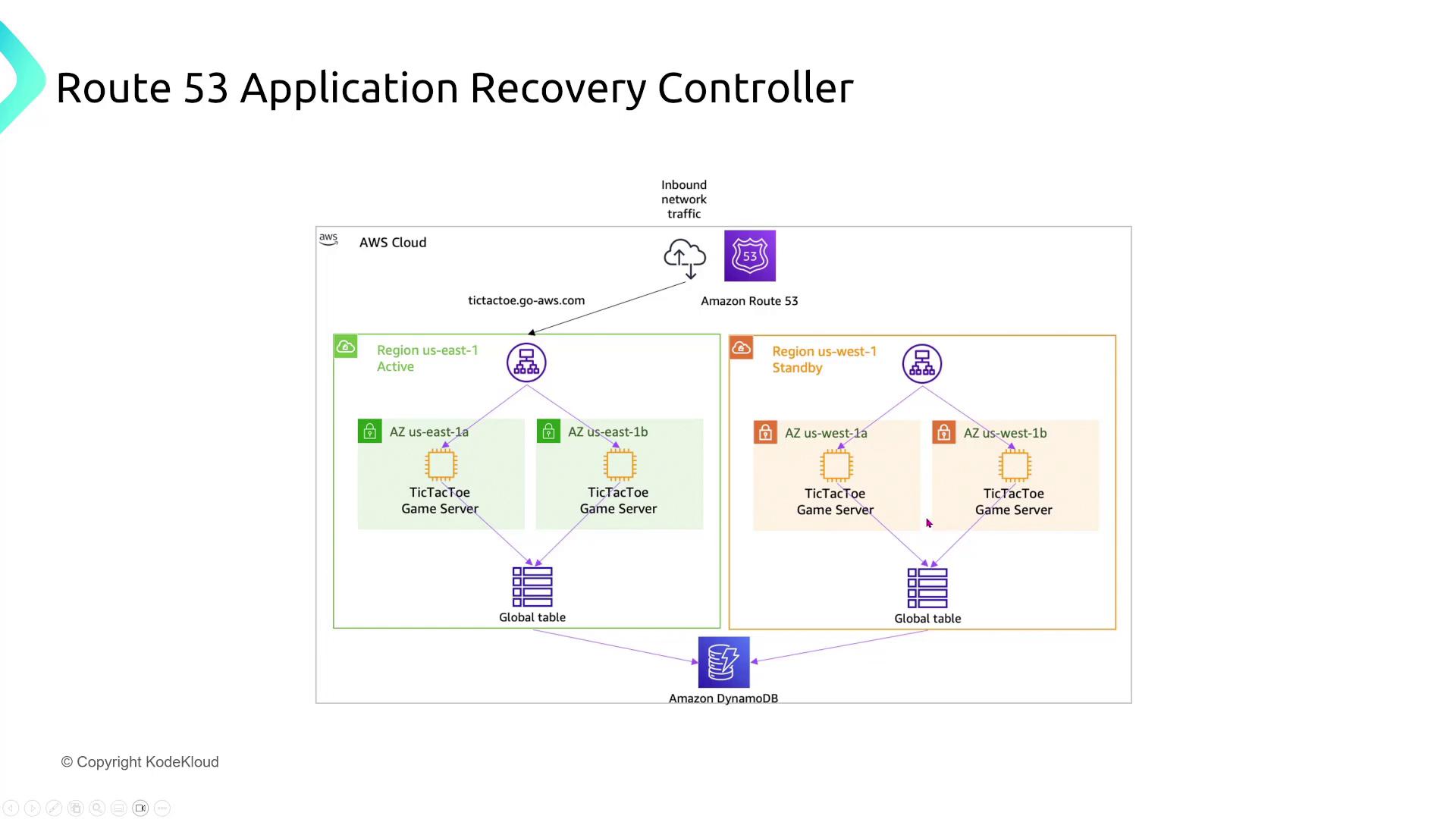
Route 53 Application Recovery Controller
For a financial technology company, the Route 53 Application Recovery Controller assists in rapid recovery from failures while ensuring robust security and resiliency. The recommended configuration includes establishing recovery readiness checks and grouping related application components. Correctly mapping dependencies and securing connections with strict IAM policies is essential.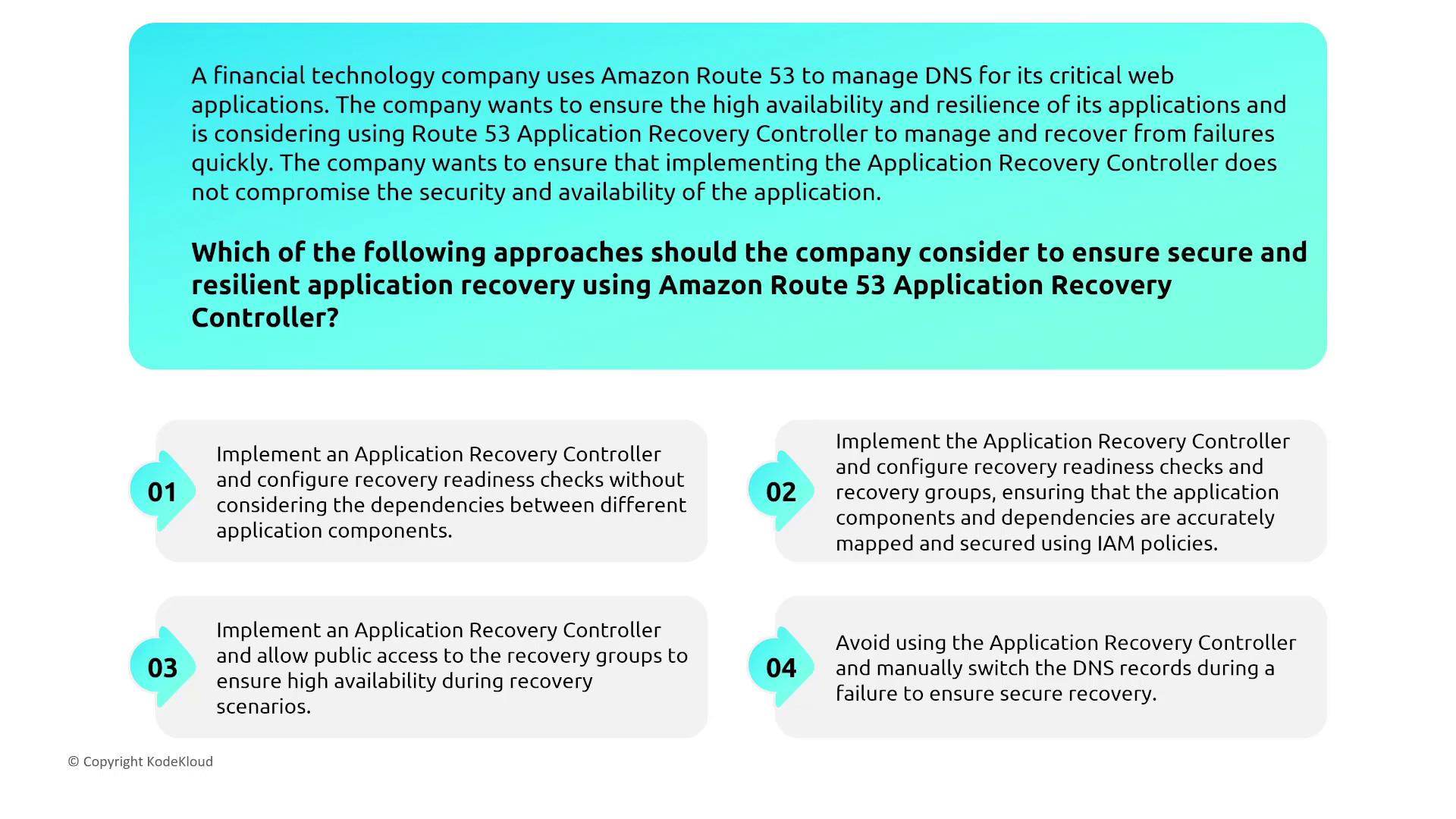
Conclusion
This lesson provided a comprehensive overview of security strategies for AWS network services—from load balancers and VPNs to Direct Connect, VPC endpoints, CloudFront, and Route 53. Each section emphasized best practices and proper configurations, ensuring robust security while maintaining optimal performance and high availability.For more insights into AWS network security best practices, be sure to visit the AWS Documentation and explore detailed case studies on secure cloud architectures.