Autoscaling in AWS
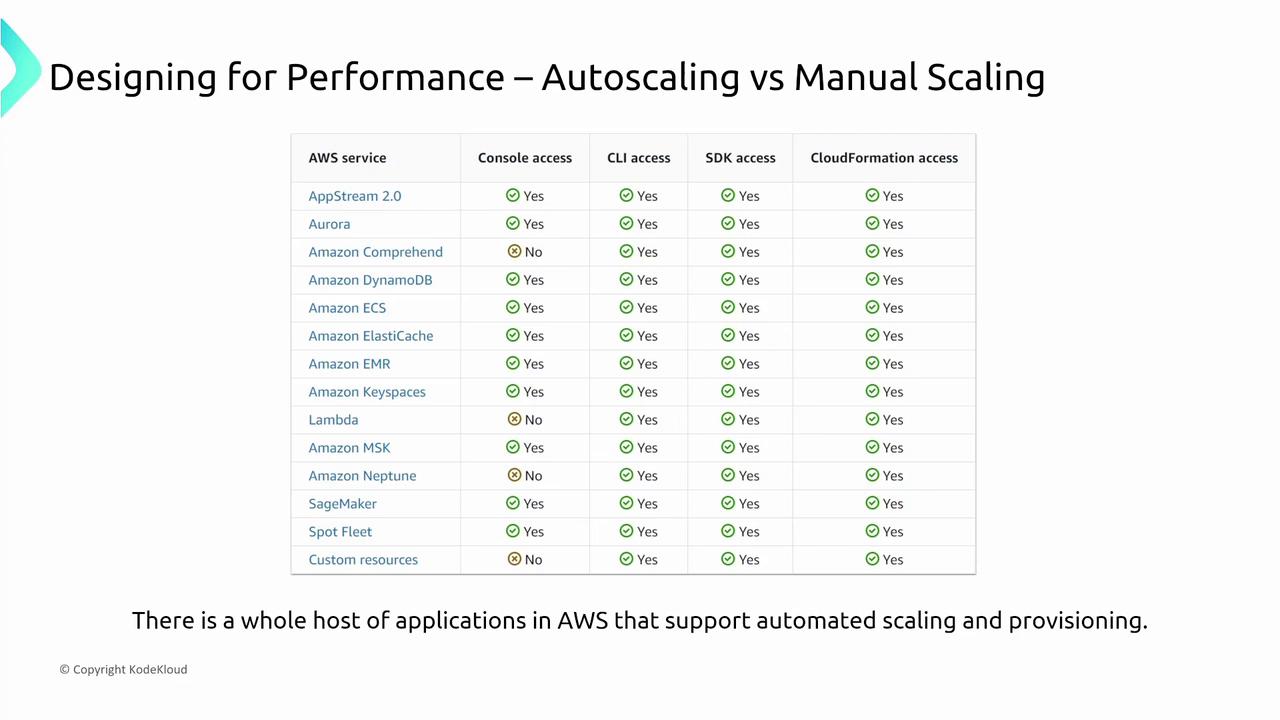
Autoscaling automatically adjusts resource capacity based on demand. While it is commonly associated with EC2—using scaling groups to add or remove servers based on load—AWS extends this capability to many other services. For example, DynamoDB adjusts capacity behind the scenes, with changes reflected in performance metrics rather than visible infrastructure modifications.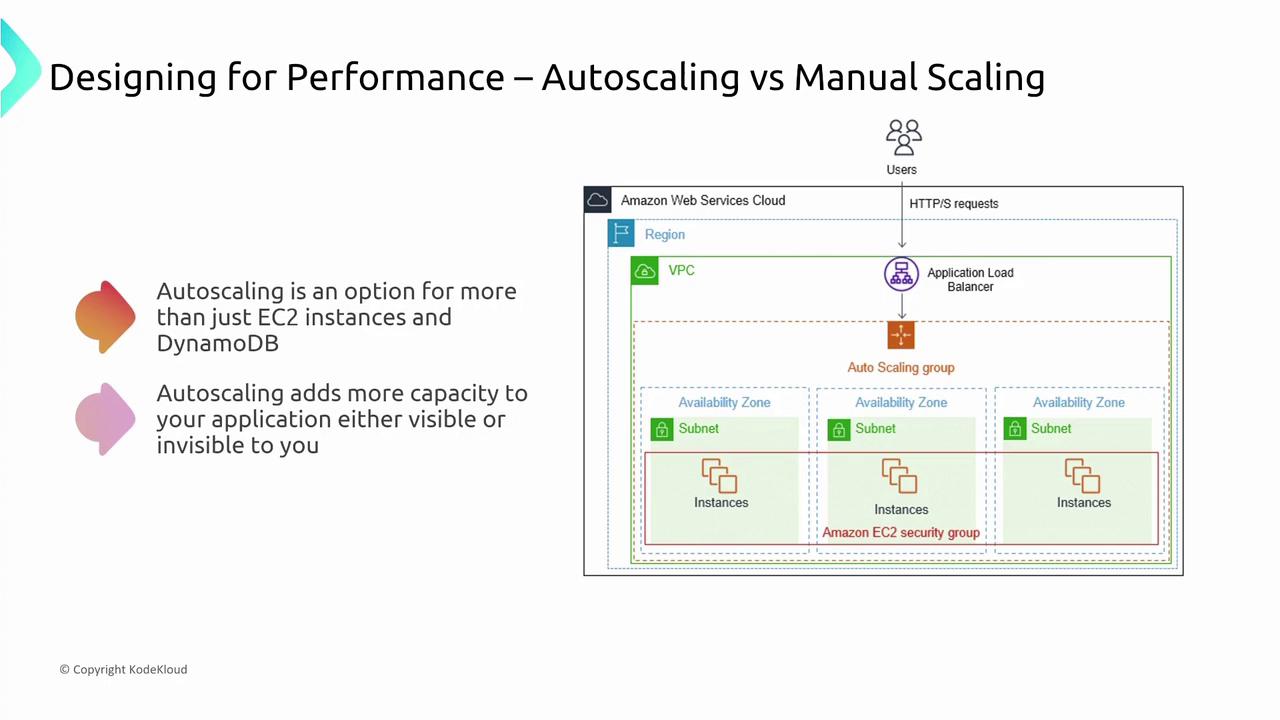
Offloading and Load Distribution
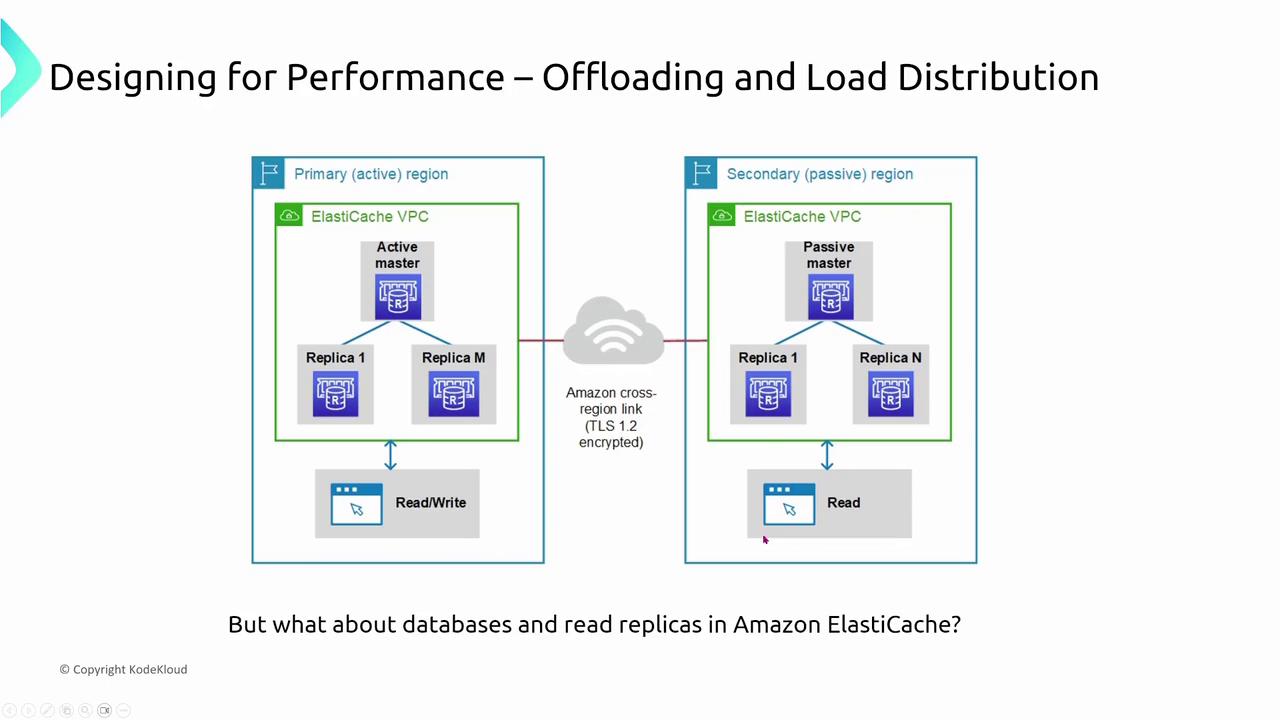
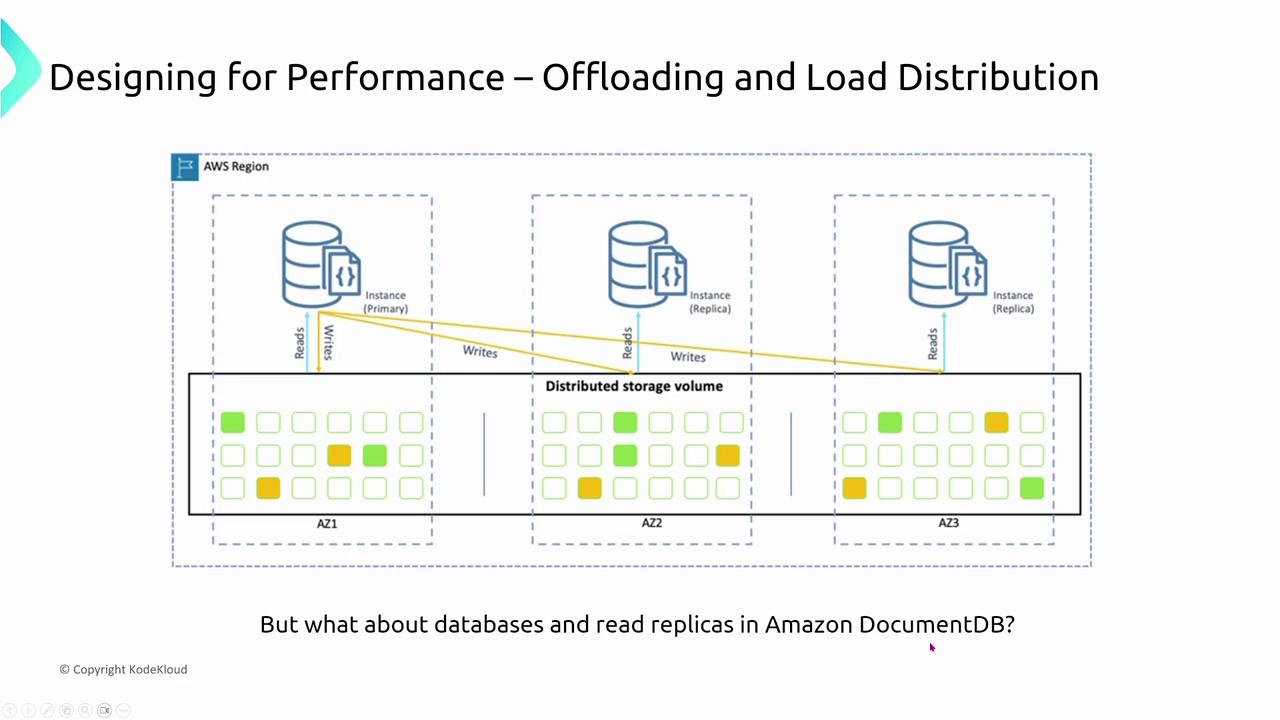
Offloading shifts tasks to auxiliary systems, reducing the processing load on a primary server. A common approach pairs offloading with load balancers. Instead of routing all traffic to a single web server, Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) distributes incoming requests. In some setups, an NGINX proxy layer routes traffic before it reaches the servers, and services like S3 handle static content so that web servers can focus on dynamic content.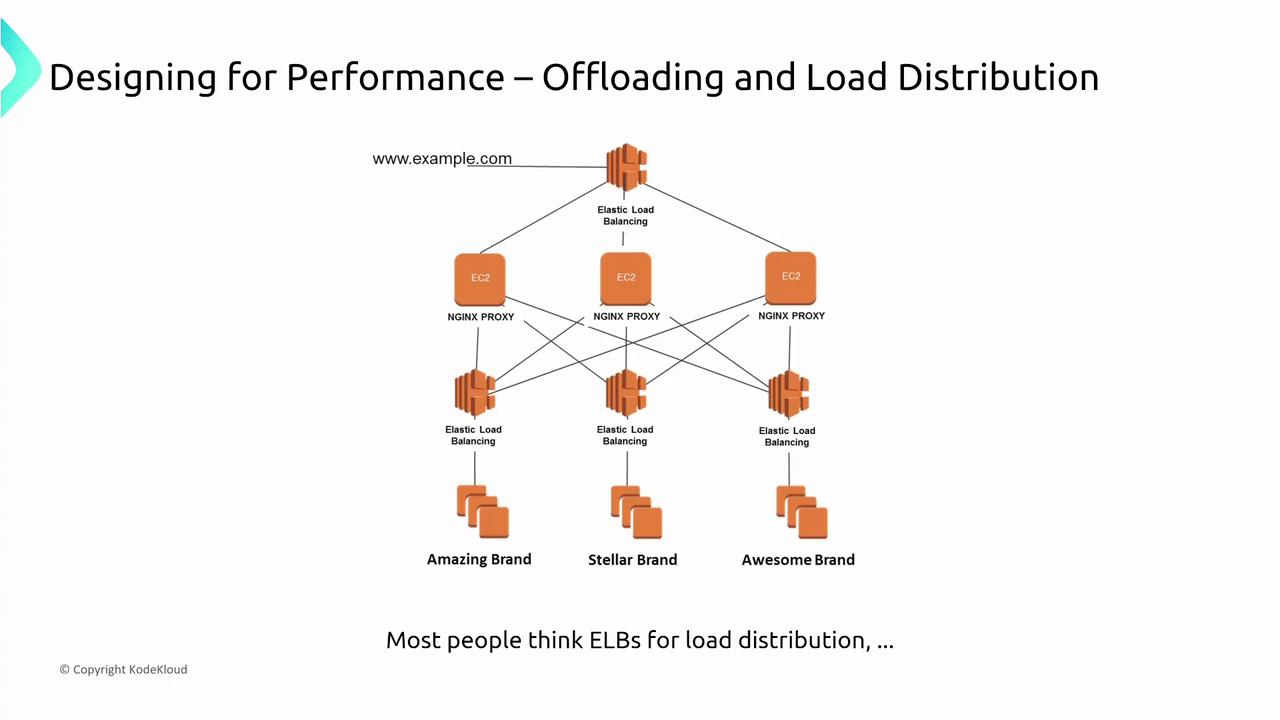
- API Gateway: Offers caching to improve response times for read-only endpoints.
- CloudFront: Distributes static content across hundreds of edge locations worldwide, decreasing the load on the origin servers.
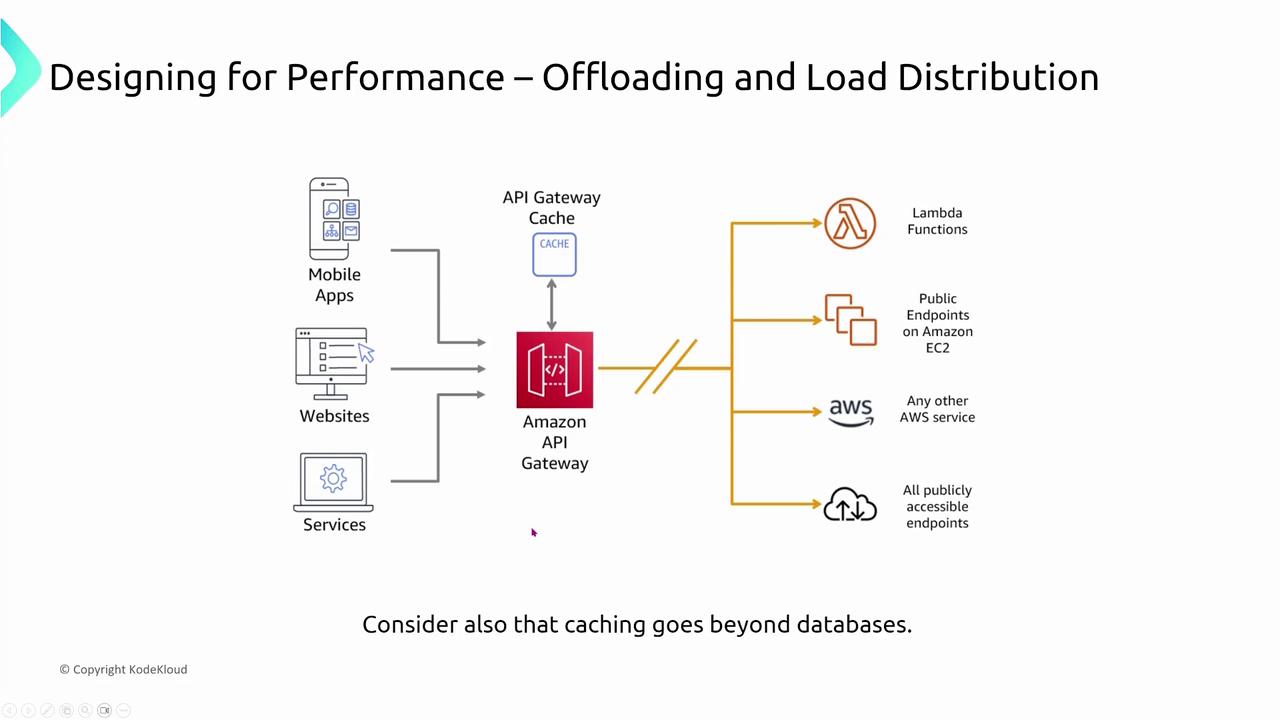
Offloading improves performance by distributing workloads efficiently across various systems, ensuring that primary servers remain unburdened.
Embracing Serverless Architectures
Transitioning from a server-based model to a serverless architecture can dramatically enhance performance by automating scaling at granular levels. AWS serverless services—such as Lambda, Fargate, serverless Aurora, serverless Redshift, and serverless EMR—reduce the overhead associated with server provisioning and autoscaling. Typically, serverless options offer superior cost efficiency, enhanced performance, and reduced operational complexity compared to traditional server-based setups.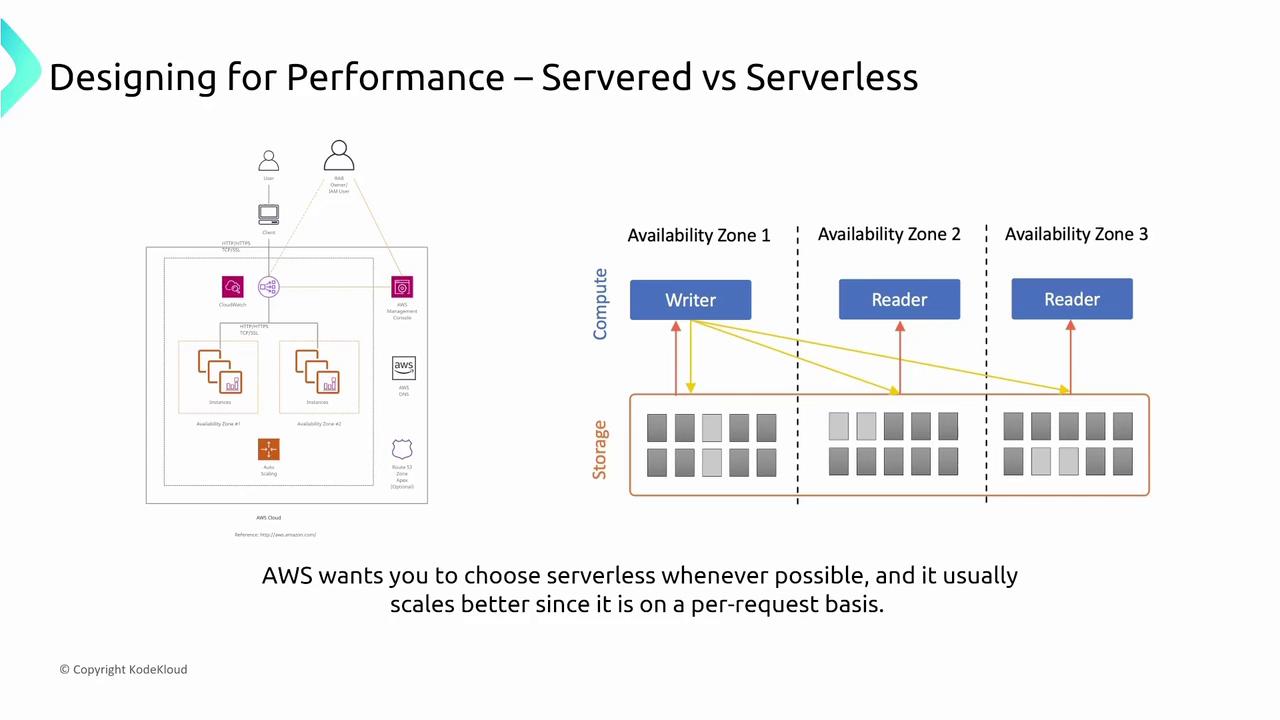
Serverless architectures deliver benefits including automatic scaling, minimized management effort, and improved resource utilization.
Summary
This lesson covered three essential AWS performance improvement concepts:- Autoscaling: AWS services such as EC2, DynamoDB, Aurora, DocumentDB, Managed Kafka, and Lambda offer robust autoscaling, which is crucial for maintaining optimal performance.
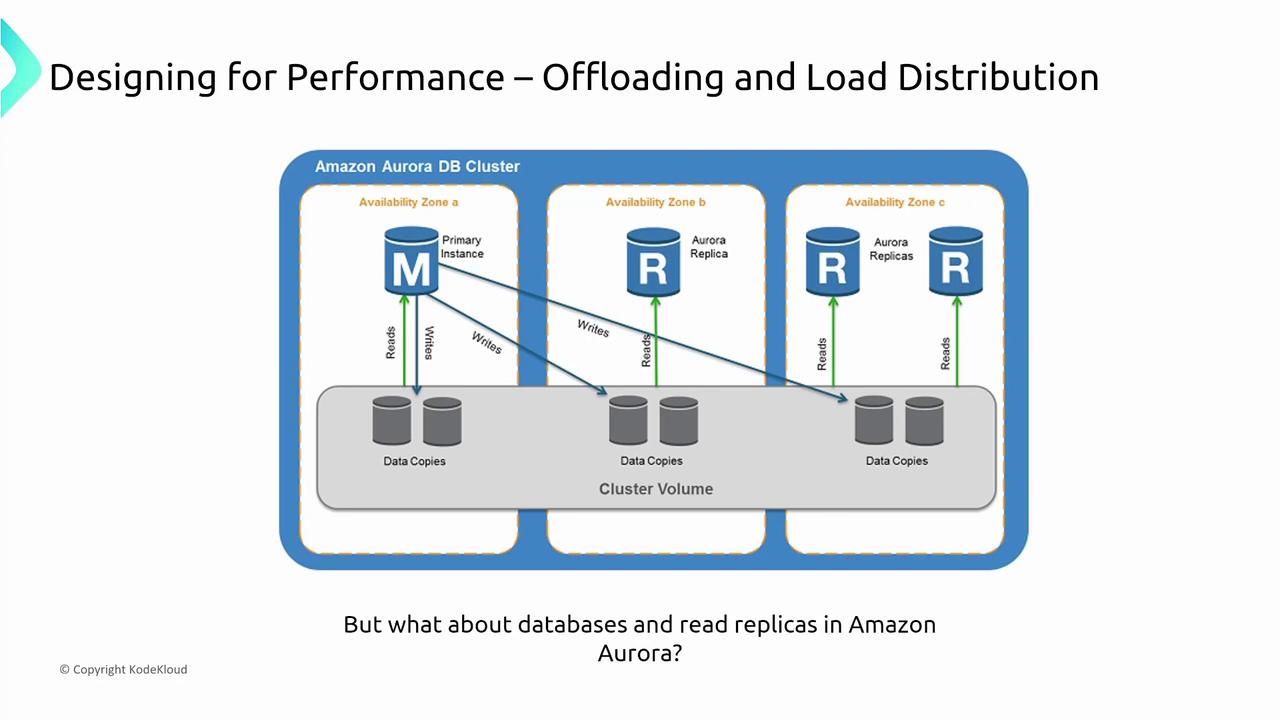
- Offloading and Load Distribution: By delegating tasks like read operations to replicas and caches, offloading reduces the load on primary systems across both application and database layers.
- Serverless Architectures: Employing serverless solutions like AWS Lambda and serverless database services minimizes operational overhead while enhancing scalability and performance.