Cloud Financial Management
Design principles such as cloud financial management are critical. Instead of using a capacity-based model, adopt a consumption-based model to pay only for the resources you consume. For example, AWS Lambda charges only when your function executes, while EC2 instances incur costs continuously. Similarly, container services like ECS and EC2-based Kubernetes differ from Fargate, which offers a more consumption-based pricing model. This approach allows you to focus spending on core competencies while leveraging AWS for resource management.Right-Sizing Resources
Right-sizing is crucial for cost efficiency. Tools like AWS Compute Optimizer help evaluate whether your EC2 instances, EBS volumes, ECS on Fargate tasks, or Lambda functions are running efficiently. Additionally, implementing cost allocation tags offers clear cost attribution by labeling AWS resources.
- Identify needs
- Define and publish
- Collaborate with stakeholders
- Implement and enforce
- Measure and iterate
Evaluating Resource Utilization
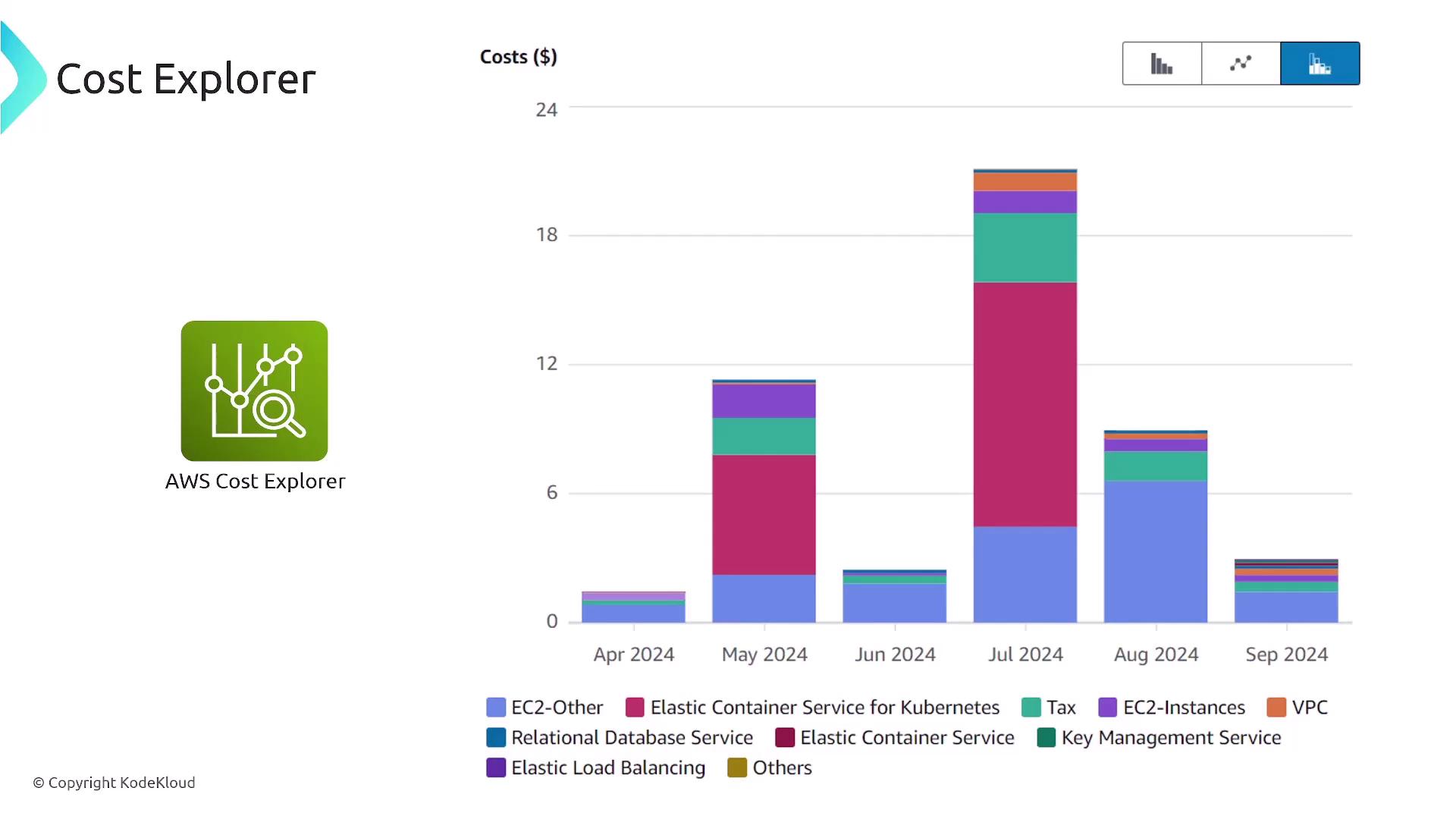
AWS Compute Optimizer evaluates resource utilization across services such as EC2, EBS, ECS on Fargate, and Lambda. Budget filters and alarms further help monitor spending and trigger notifications when costs approach predefined thresholds. Remember, understanding the filters and notifications available is more valuable than memorizing each option.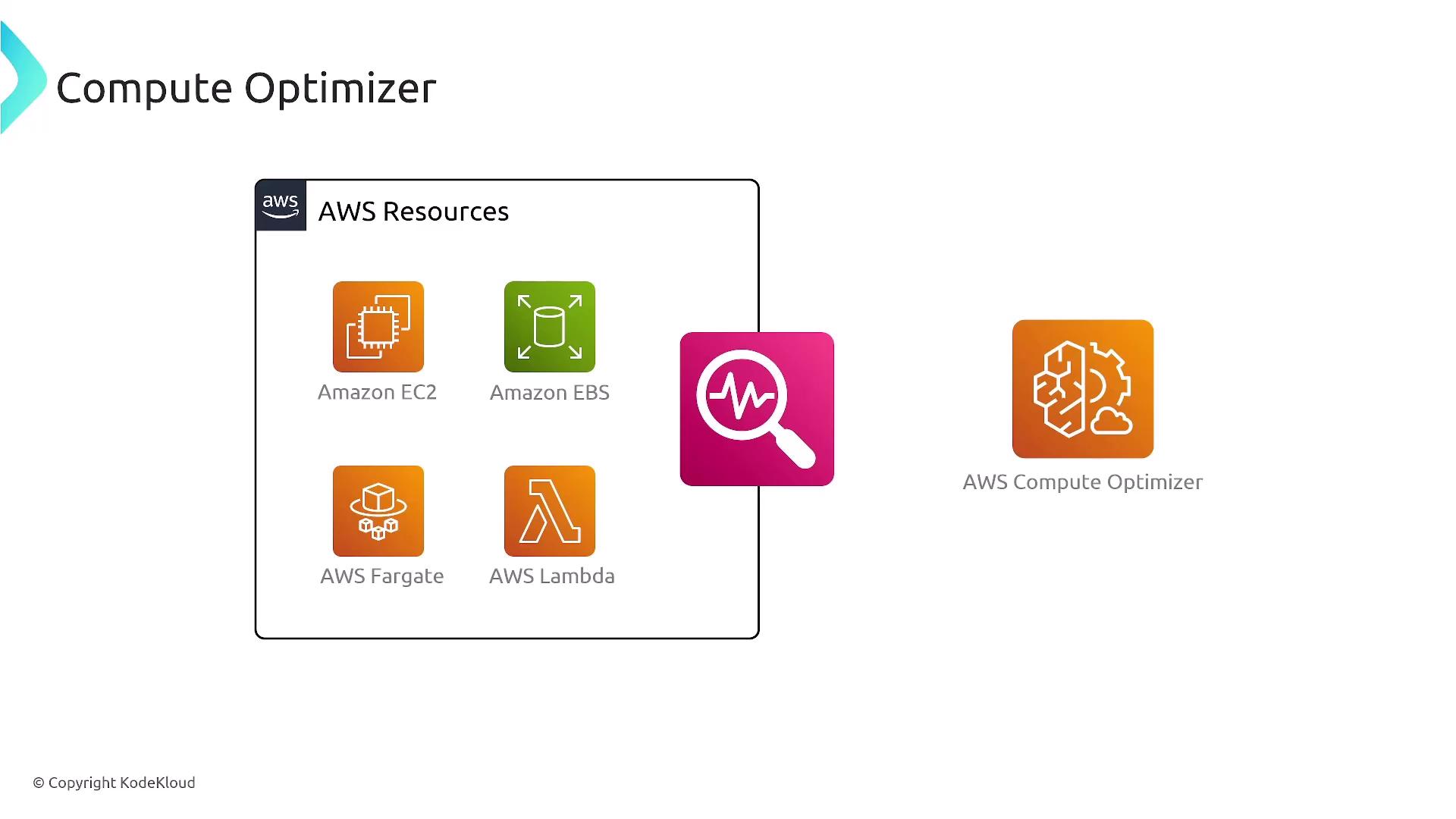

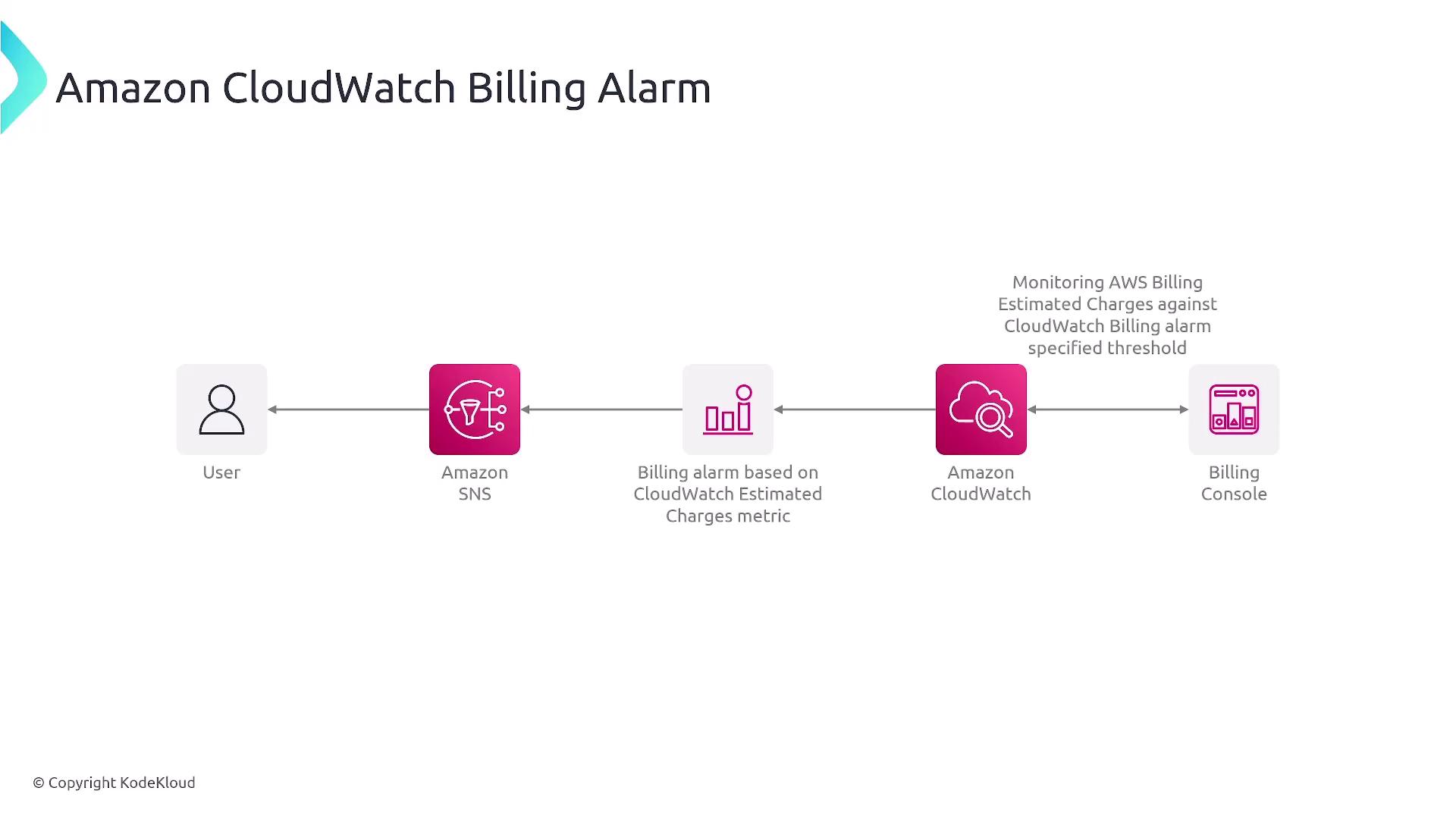
Configure CloudWatch billing alarms via AWS Budgets or CloudWatch to get notified when your estimated charges reach critical thresholds, thereby mitigating unexpected costs.
EC2 Purchasing Options
A comprehensive understanding of EC2 purchasing options is essential. These options include:- Spot Instances: Least expensive but can be interrupted.
- On-Demand Instances
- Compute Savings Plans
- EC2 Savings Plans
- Reserved Instances (convertible, standard, and scheduled)
- Dedicated Hosts and Instances: The most expensive options.

Storage Optimization
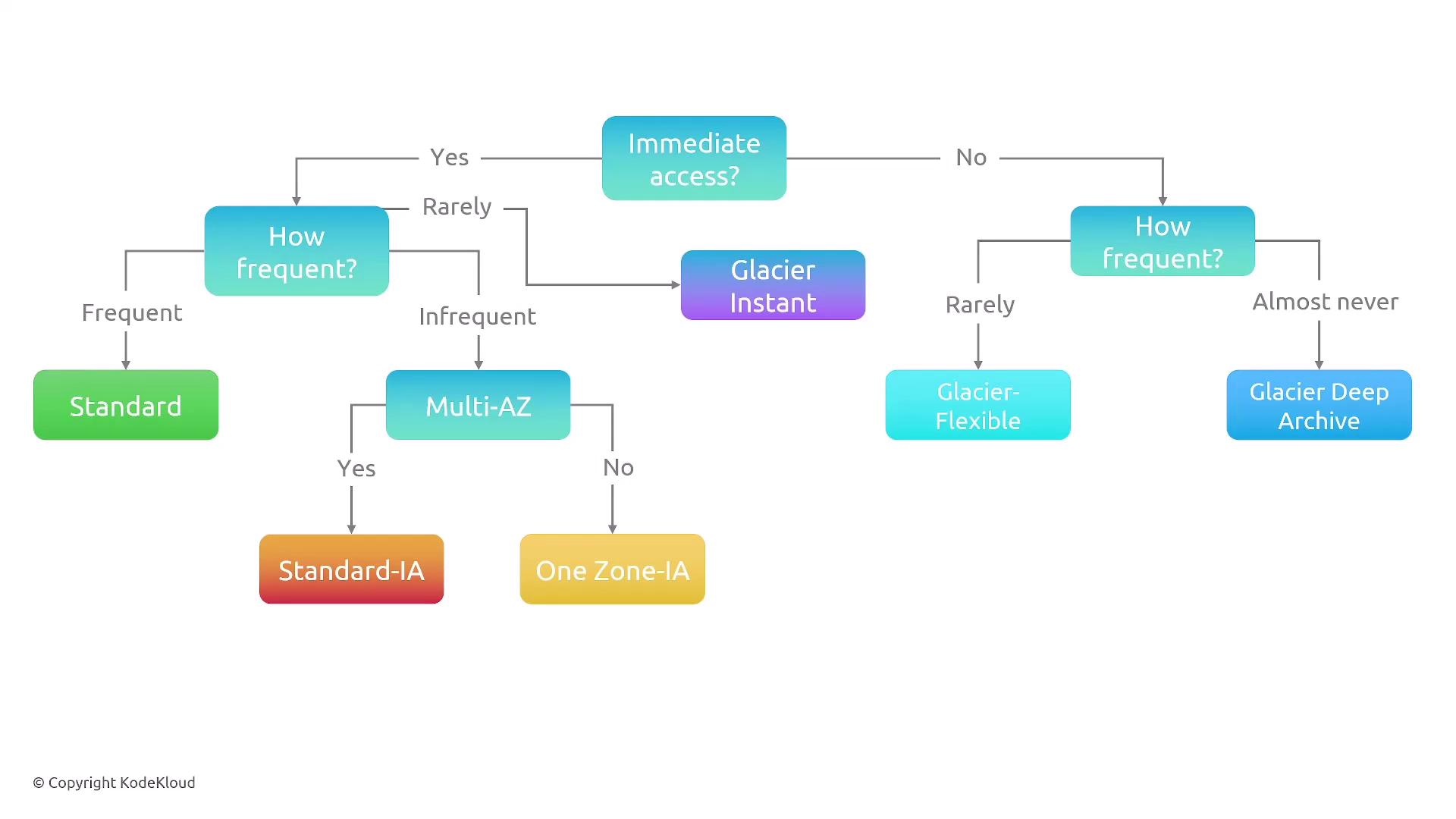
Storage optimization involves selecting the right managed or self-managed solutions. Self-managed services offer greater control but require additional operational overhead. Managed services, however, usually offer more cost-effective performance unless extensive customization is needed.
- For seldom-accessed data, colder storage options like Glacier Deep Archive are cost-effective.

Network and Compute Performance
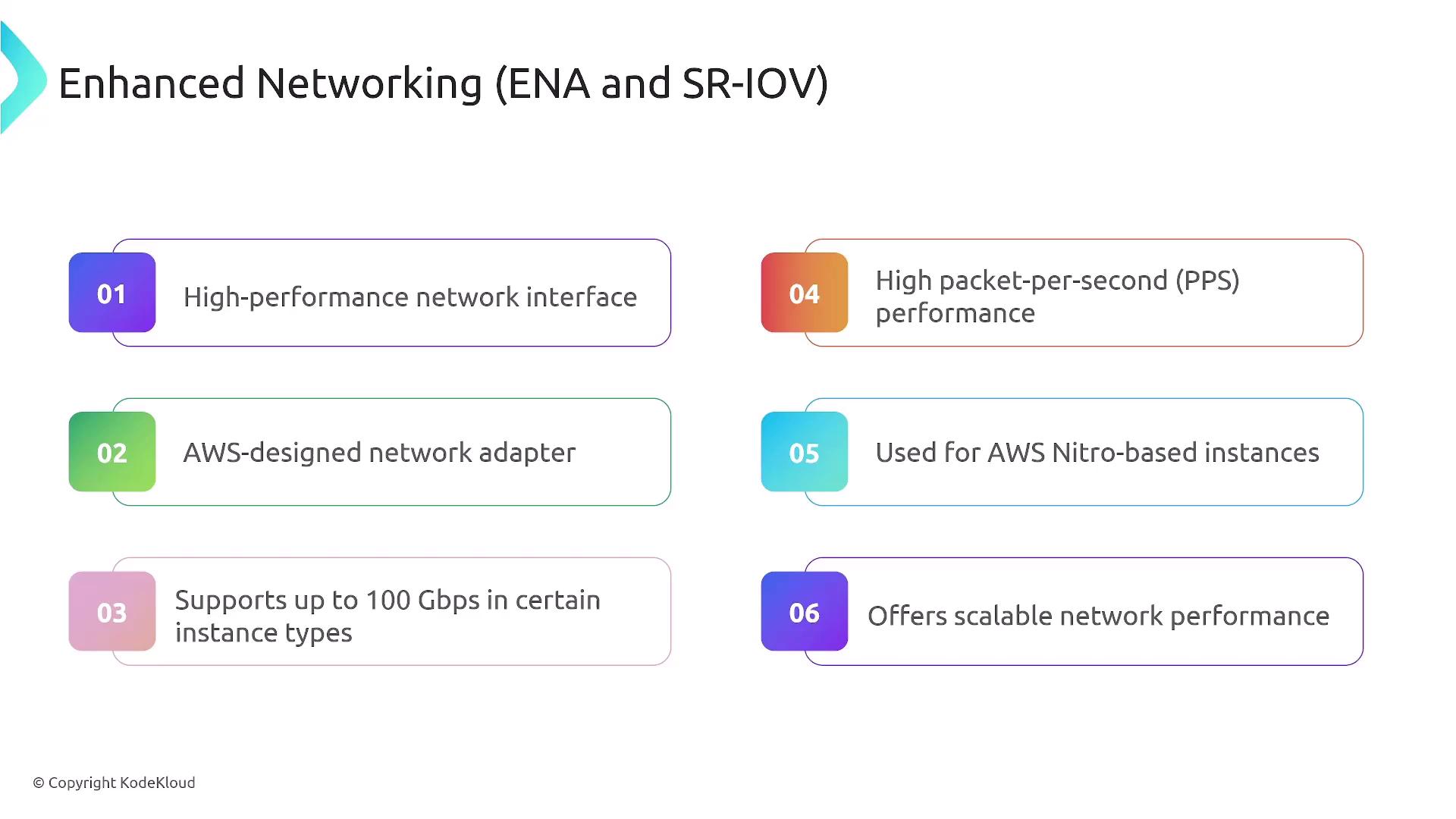
Enhancing network performance can be achieved using Elastic Network Interfaces (ENIs) and Elastic Fabric Adapters (EFAs). ENIs add bandwidth to an EC2 instance, while EFAs are designed for high-performance computing scenarios.
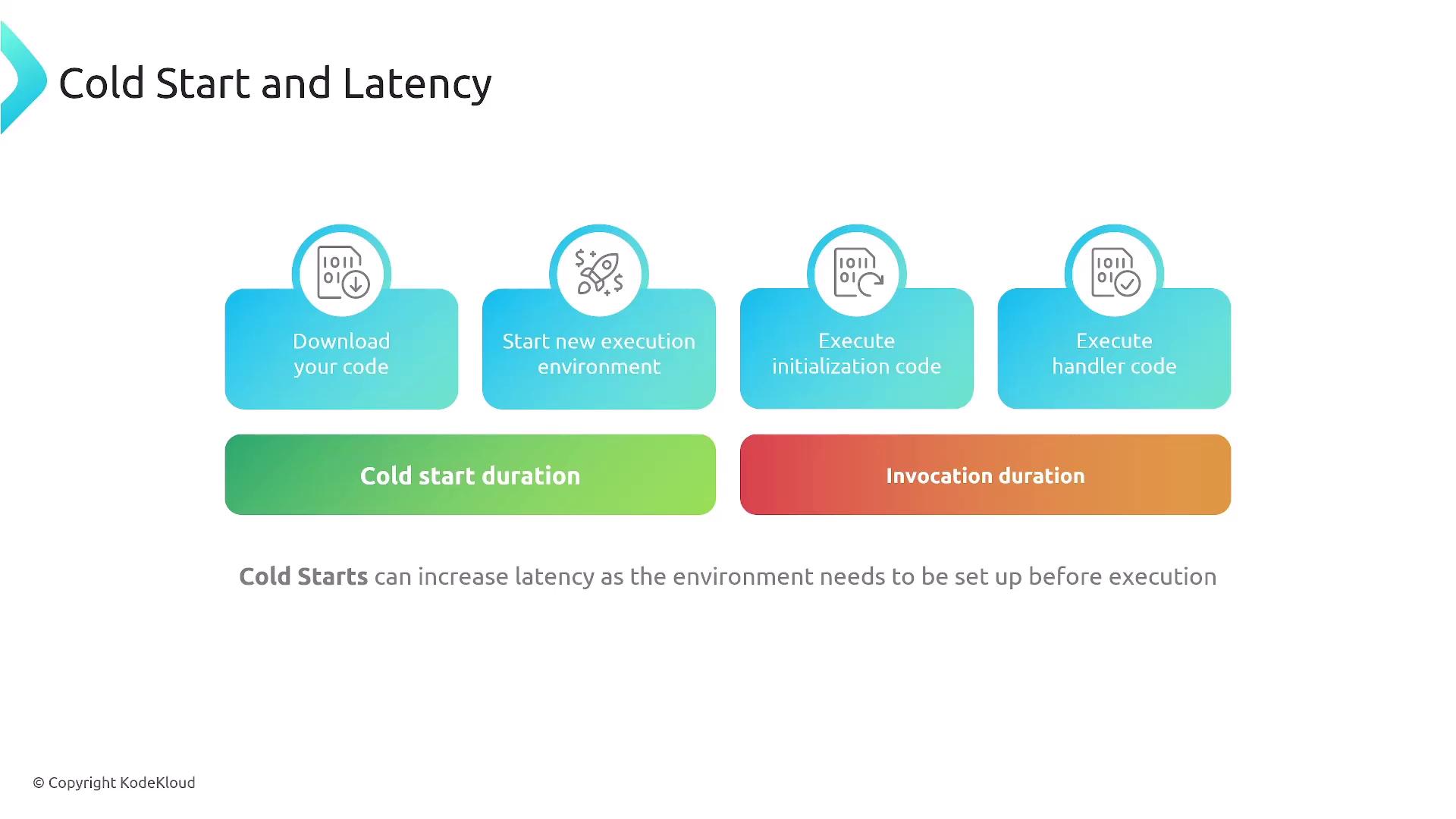
- Reducing code initialization time
- Using provisioned concurrency
- Periodically invoking your function to keep it warm

EC2 Instance Types and Use Cases
Understanding the different EC2 instance families is also important. There are five main instance types:- General Purpose
- Compute Optimized
- Memory Optimized
- Storage Optimized
- GPU Instances (categorized under accelerated computing)

Final Thoughts
This article has covered key topics in cost and performance optimization within Domain 6:- Cloud financial management and consumption-based pricing models
- Strategies for right-sizing resources with tagging and optimization tools
- A deep dive into EC2 purchasing options and storage optimization
- Best practices for improving compute, network, and database performance
Review these concepts carefully as you prepare to complete your SysOps course. Mastering these techniques will help you optimize costs and improve performance as you advance in your cloud journey.