E-commerce Workflow Example
Consider a typical e-commerce workflow that includes navigation from the shopping cart to payment processing, invoice generation, inventory updates, labeling, dispatch, and finally tracking the dispatch. In a sequential, tightly coupled system, a failure in one service—such as the payment service—halts subsequent processes like invoice creation, inventory updates, and shipment tracking.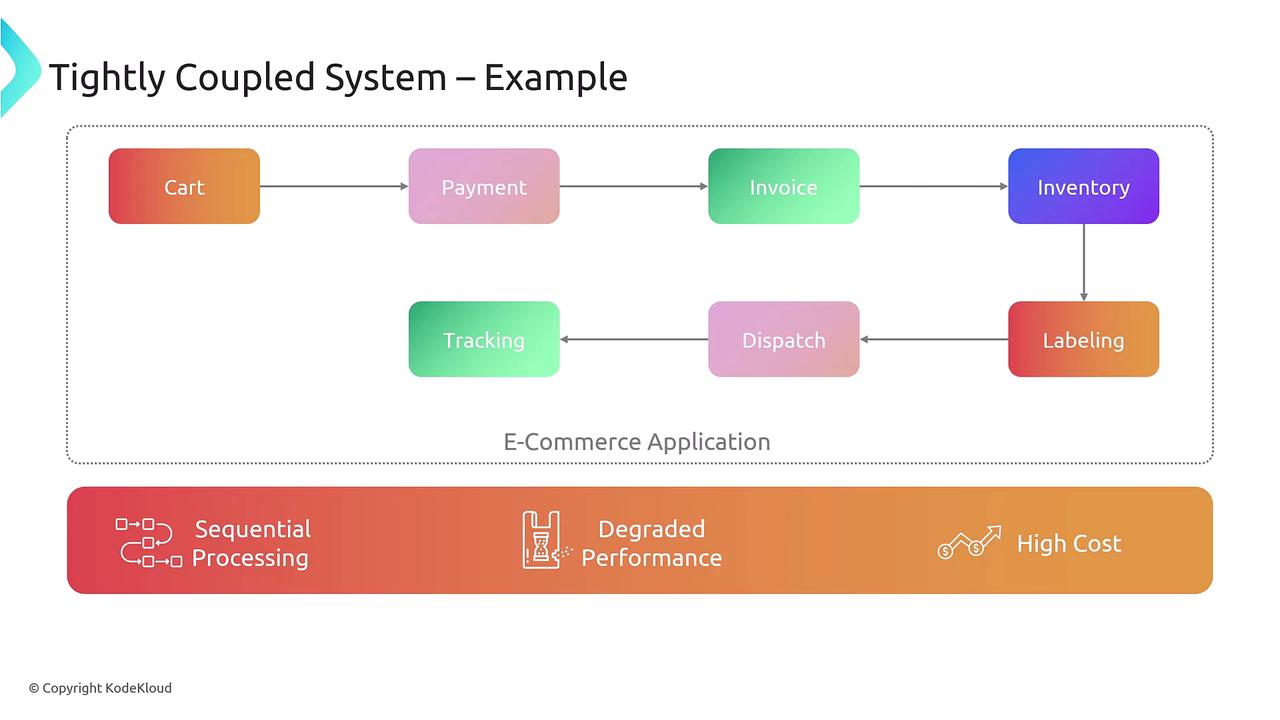
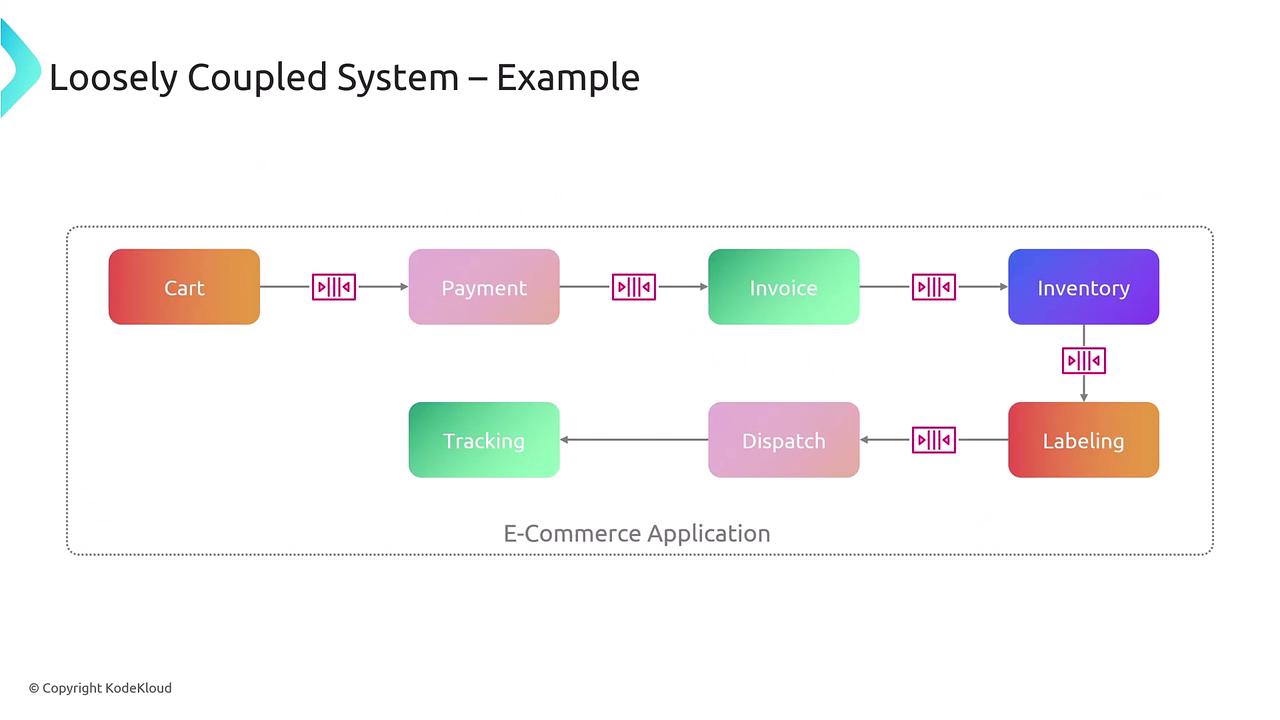
Loosely coupled systems typically offer increased scalability, enhanced resilience, easier maintenance, and simpler troubleshooting.

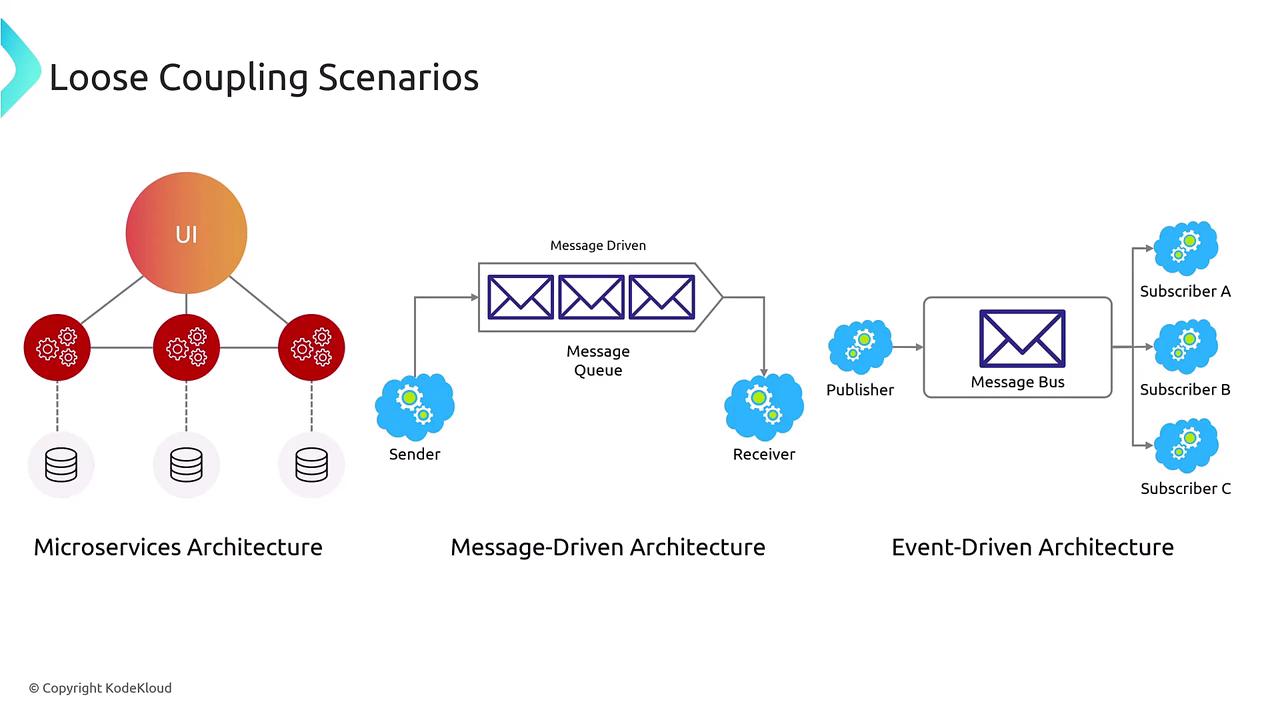
Scenarios for Implementing Loose Coupling
Loose coupling can be applied across multiple architectural scenarios:-
Microservices Architecture:
In a microservices environment, if one user interface or service instance goes down, the remaining instances continue to serve the load without disruption. -
Message-Driven Architecture:
In this design, messages are written to a queue by the sender and processed by the receiver at its own pace. Additional receivers can be added to handle increased loads, ensuring the sender is never blocked by processing delays. -
Event-Driven Architecture:
Using a publish/subscribe model, the publisher broadcasts events while multiple subscribers process these events concurrently or in quick succession. This minimizes the need for direct, continuous interaction between services.
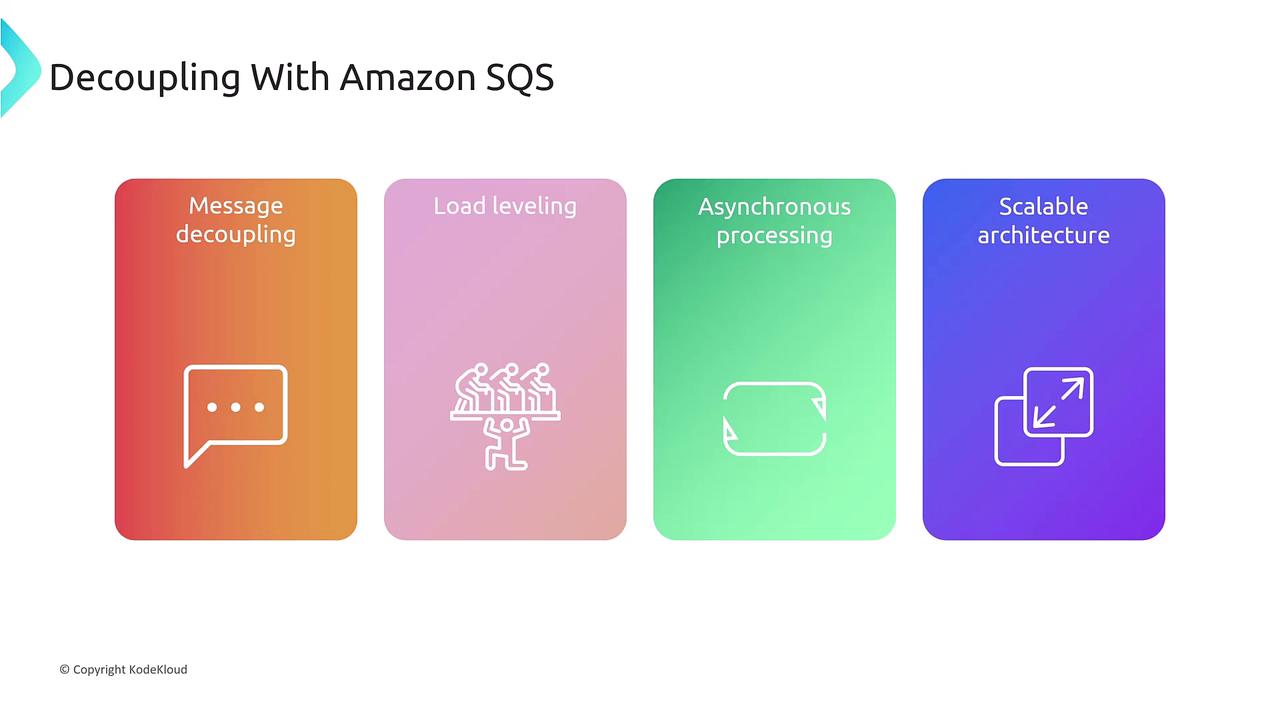
Amazon SQS Overview
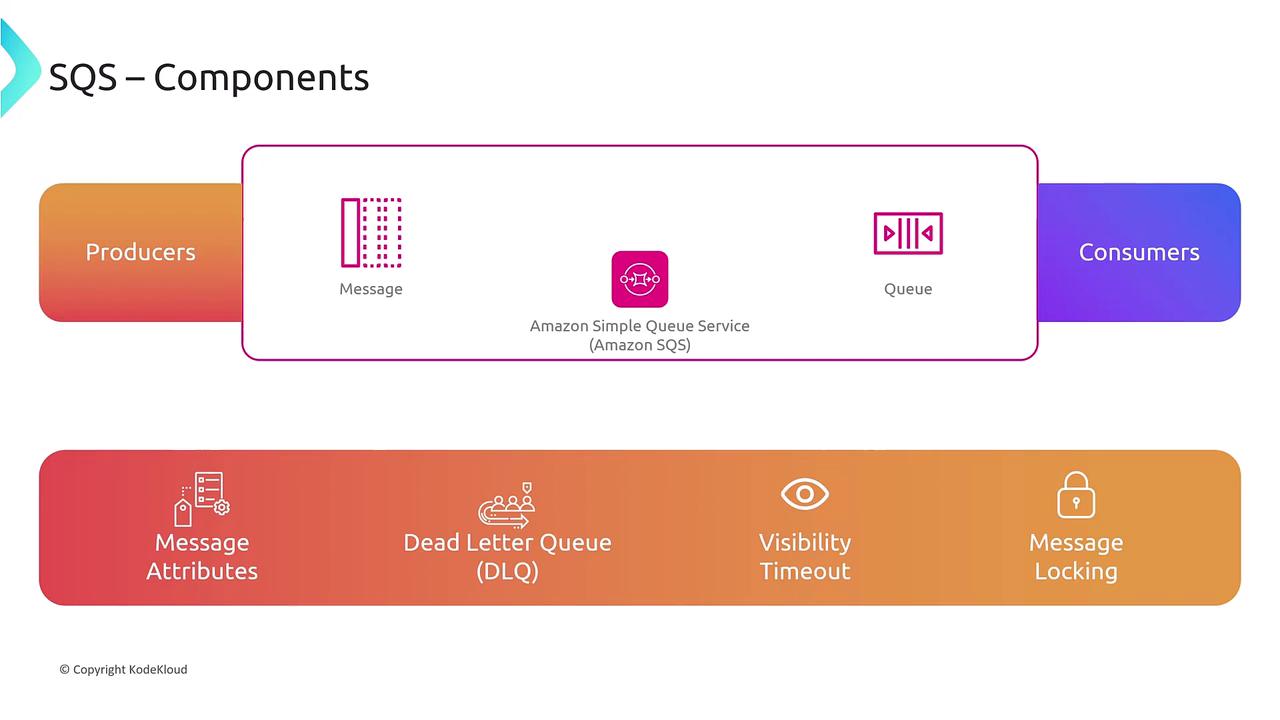
Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS) is a powerful tool for decoupling components within distributed systems. Key benefits of SQS include:- Load leveling through asynchronous message processing.
- Automatic scalability via the addition of consumers.
- A proven producer/consumer model ensuring at least once processing.
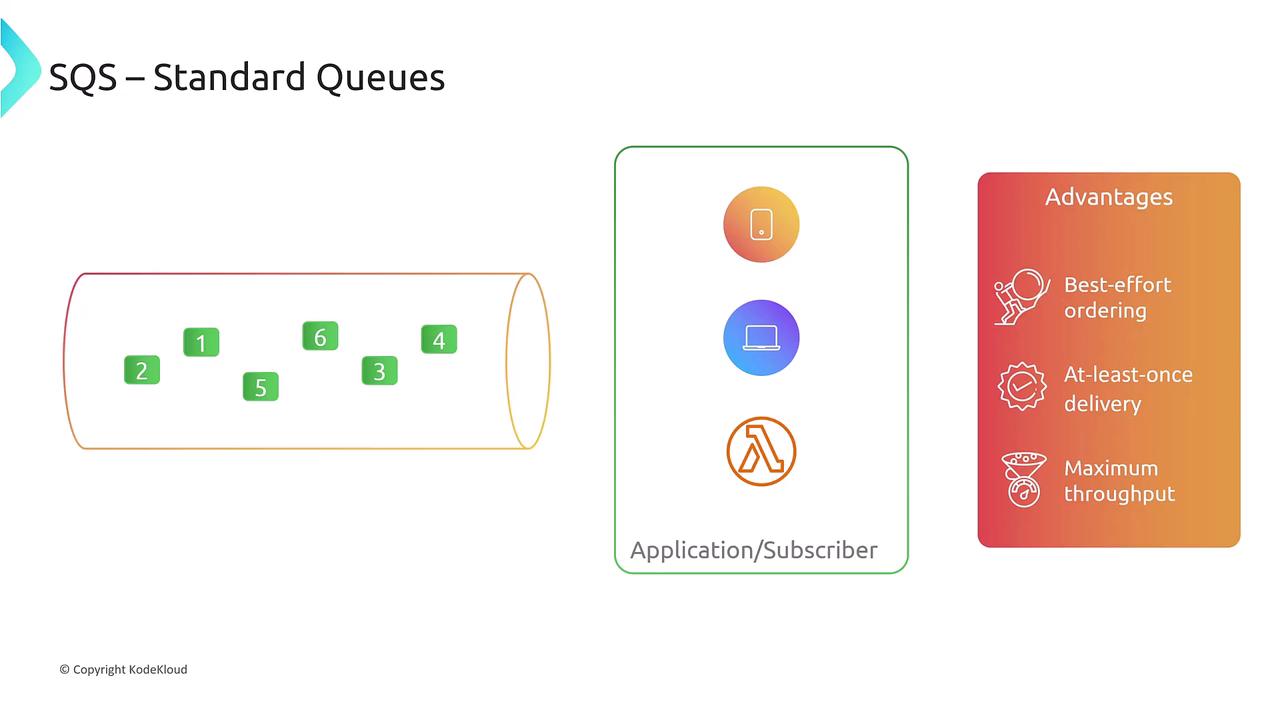
Standard vs. FIFO Queues
Amazon SQS provides two types of queues to meet different needs:- Standard Queue:
These queues offer high throughput and can handle hundreds of thousands of messages per second. However, message ordering is best-effort, meaning sequential delivery is not guaranteed, though at-least-once delivery is ensured.
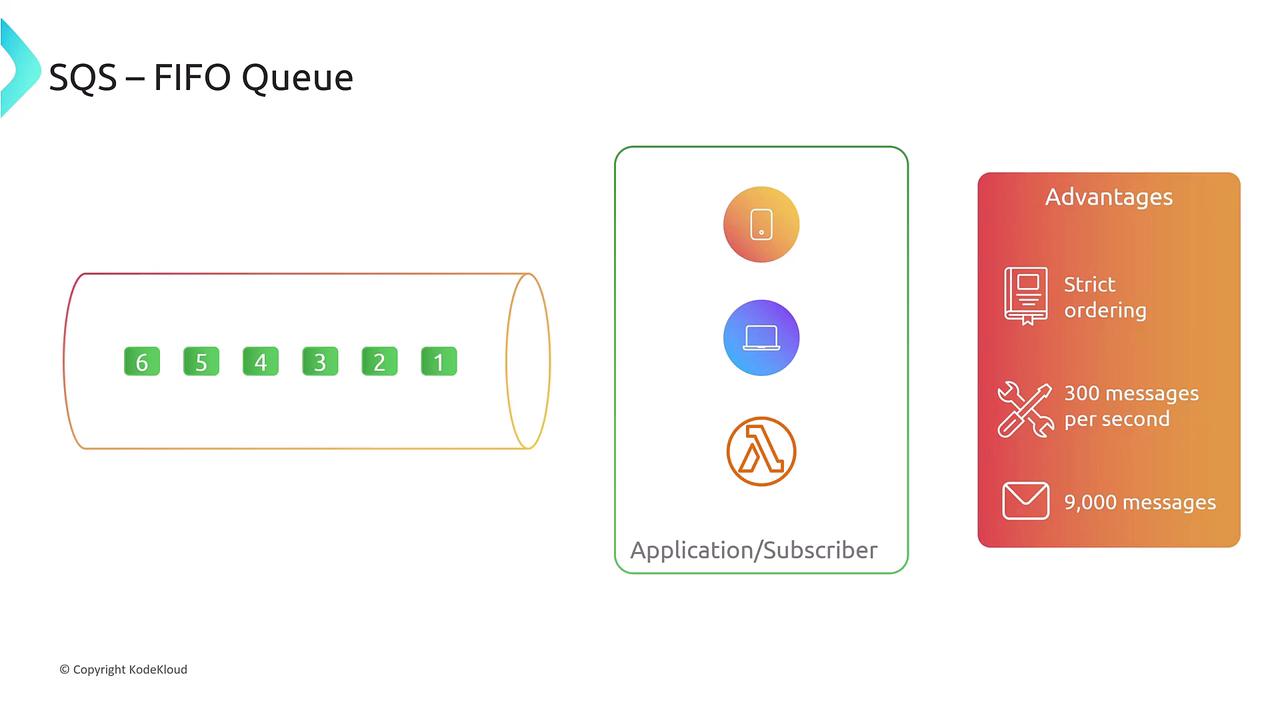
- FIFO Queue:
FIFO queues guarantee strict ordering with exactly-once processing. They have a throughput limit of approximately 300 messages per second (which can be increased to about 9,000 messages per second using batching). Although FIFO queues are slightly more expensive, they are essential when maintaining message order is critical.
- Batching of messages.
- Configurable message retention (up to 14 days).
- Message prioritization through attributes.
- Handling failed processing using a dead letter queue.
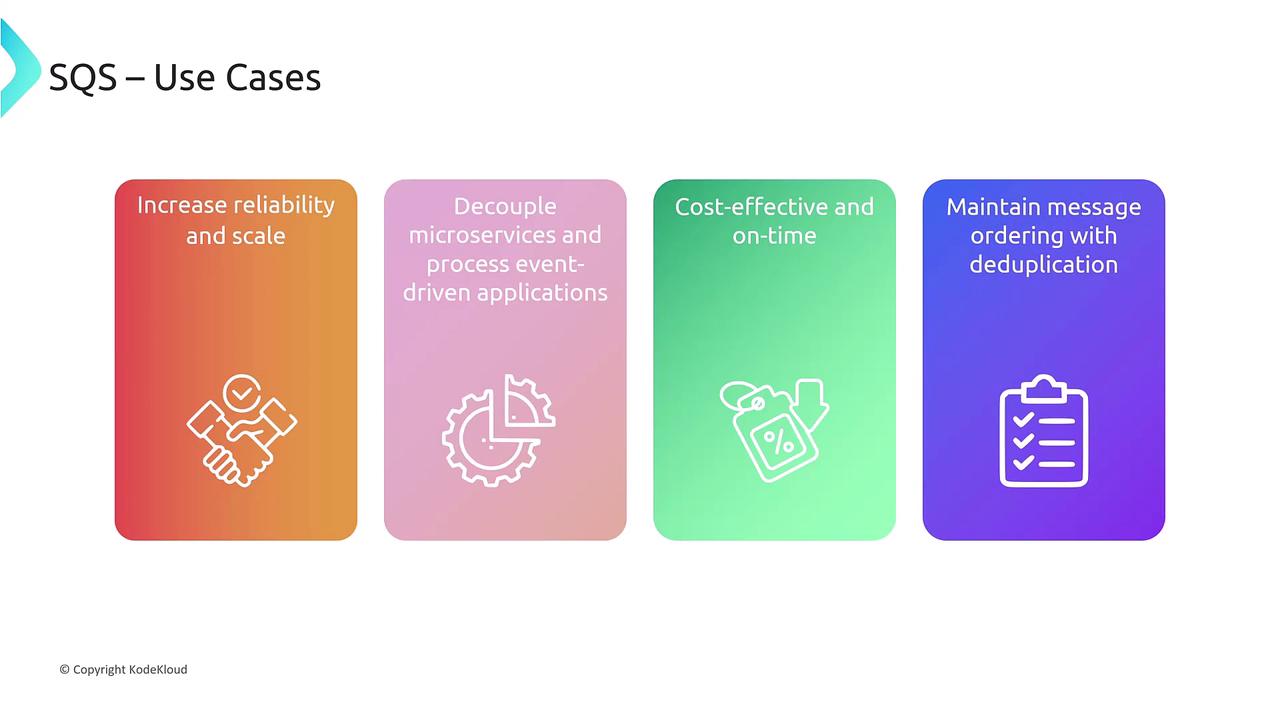
Use Cases for Amazon SQS
SQS can be utilized in various ways to enhance system reliability and scalability:- Decoupling microservices for enhanced reliability.
- Cost-effective event-driven processing.
- Maintaining strict message ordering and deduplication when necessary.
Introducing AWS EventBridge
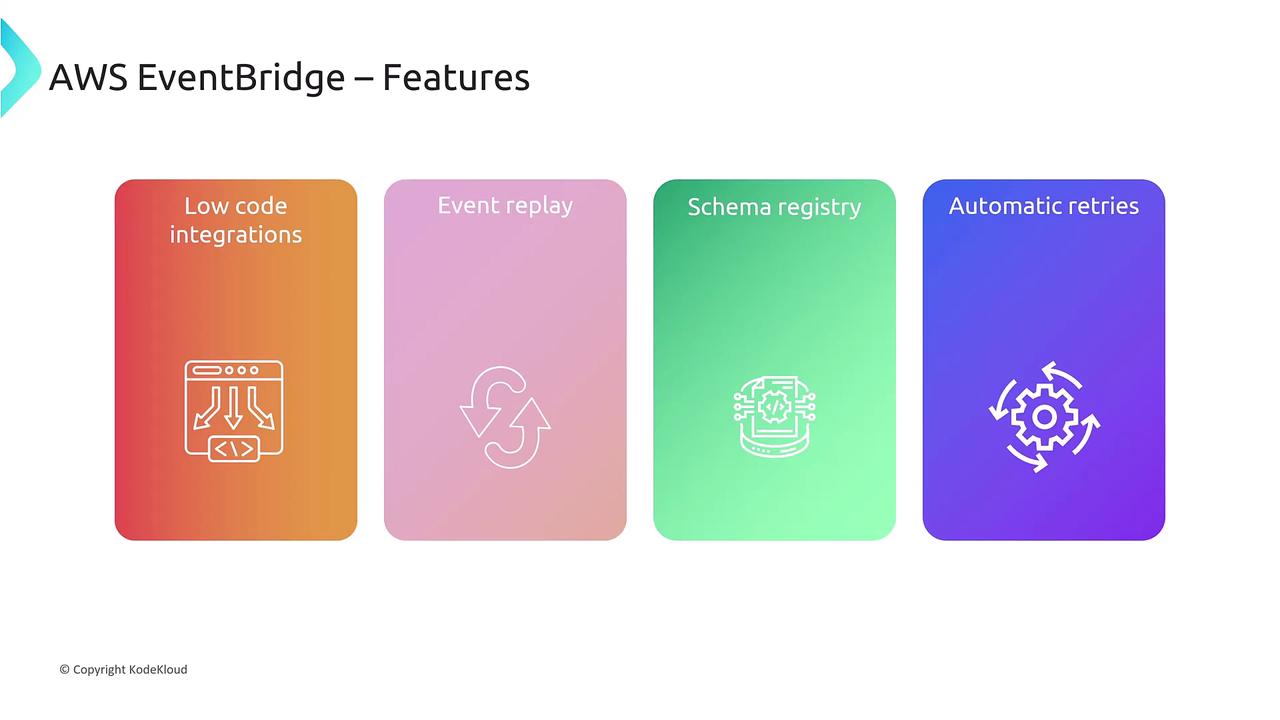
For scenarios involving larger event sizes or more complex event decoupling, AWS EventBridge provides a comprehensive solution. EventBridge is a fully managed, serverless event bus that:- Supports high-volume event ingestion.
- Routes and filters events using predefined rules.
- Enables event replay for debugging and error recovery.
- Provides a schema registry to manage and share data schemas.
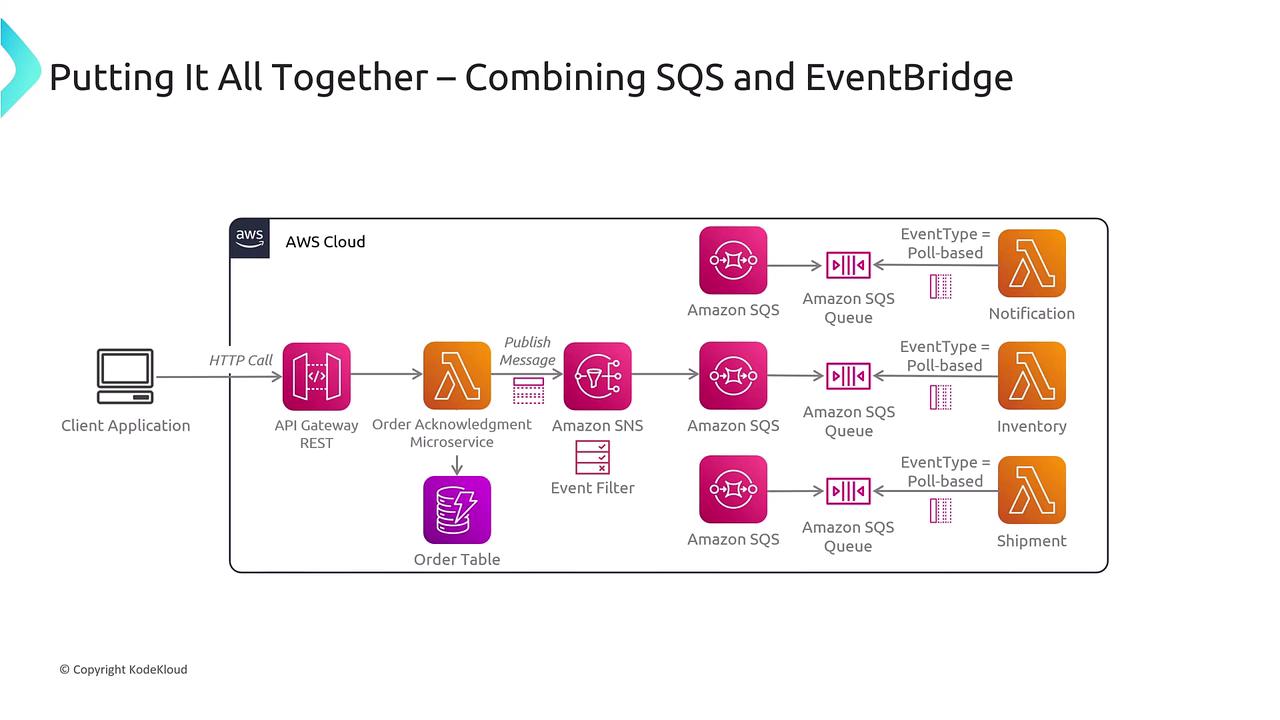
Integrating SQS and EventBridge
Combining SQS with EventBridge enables the design of sophisticated, decoupled architectures. Consider the following integration:- A client application sends requests to a RESTful API Gateway.
- A Lambda function processes the order acknowledgments and interacts with an order database.
- The Lambda function publishes messages to SNS. Using event filters, SNS forwards copies of those messages to multiple SQS queues.
- These SQS queues are polled by additional Lambda functions dedicated to notifications, inventory updates, and shipment processing.