Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) and Subnets
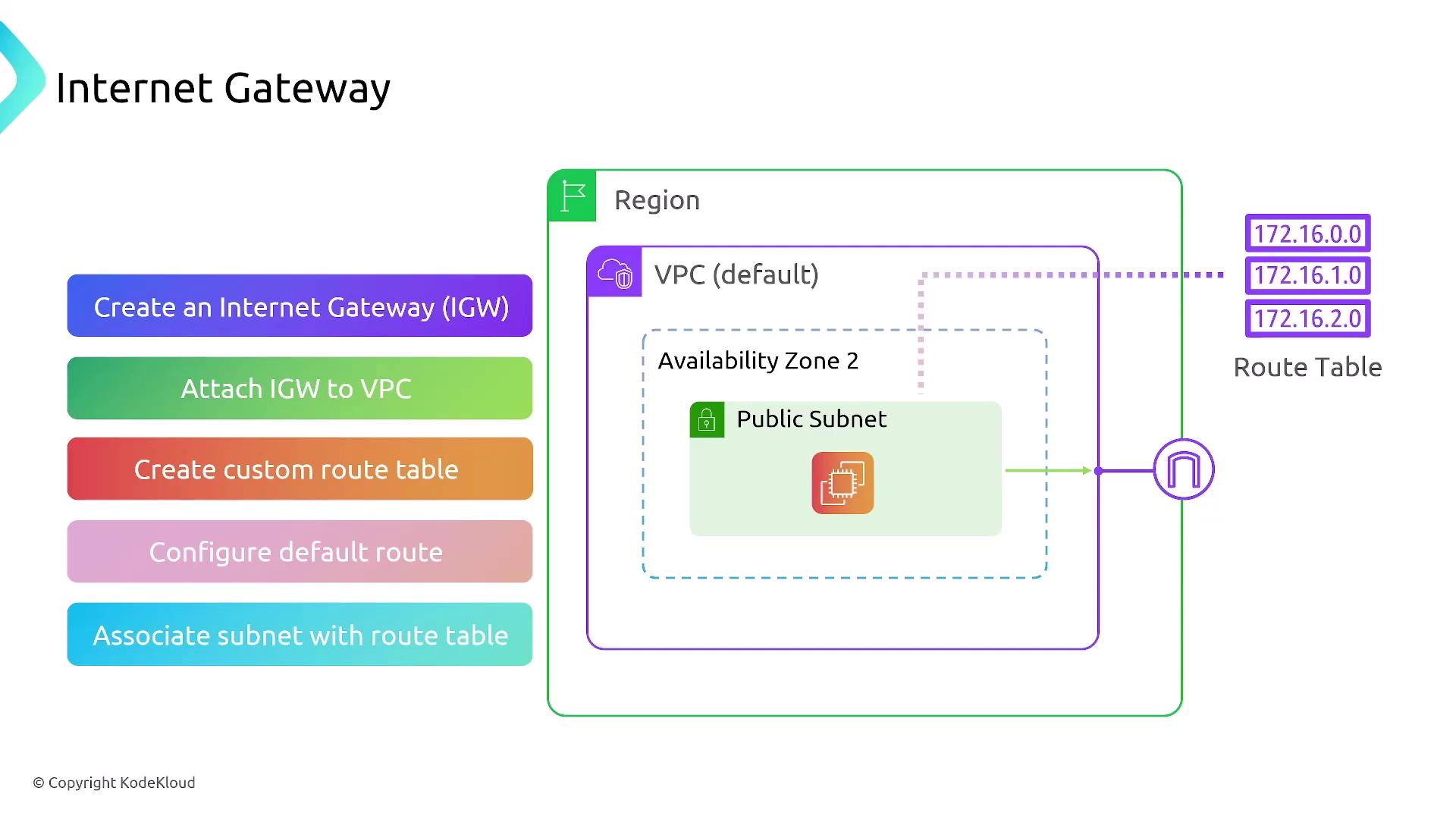
At the heart of your network infrastructure is the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). A VPC creates an isolated region in which you can define and manage your subnets, typically separated into private and public segments across multiple availability zones. The key elements include:- Internet Gateway (IGW): Attach an IGW to your VPC to secure internet connectivity.
- Route Tables: Associate route tables with subnets to dictate traffic flow.
- NAT Gateways and Egress-Only Gateways: These gateways enable secure traffic routing from private subnets to the internet.
Traffic Management and Network Interfaces
Effective management of network traffic is paramount. This section highlights strategies to ensure that data does not unnecessarily traverse the public internet:- VPC Gateway and Interface Endpoints: Utilize these endpoints to secure and streamline traffic.
- Elastic Network Interfaces (ENIs) and Elastic Fabric Adapters (EFAs): In addition to standard ENIs, high-speed networking options such as ENAs and EFAs are available for enhanced performance.
VPC Connectivity Methods
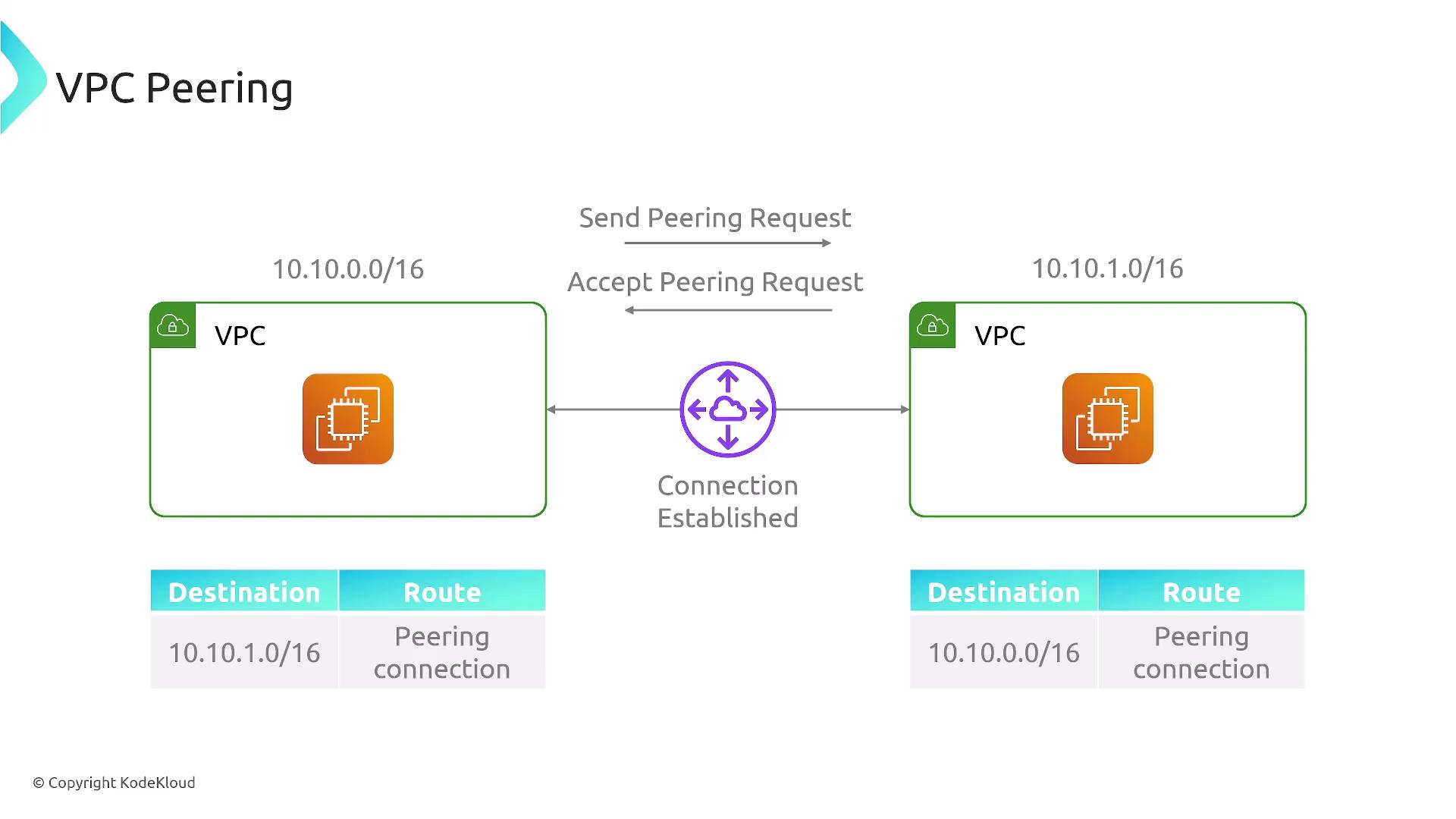
Connecting multiple VPCs can be achieved via two primary methods:- VPC Peering
VPC peering involves sending and accepting peering requests along with configuring necessary routes. This method is effective for global connectivity but may not be as scalable for larger environments.
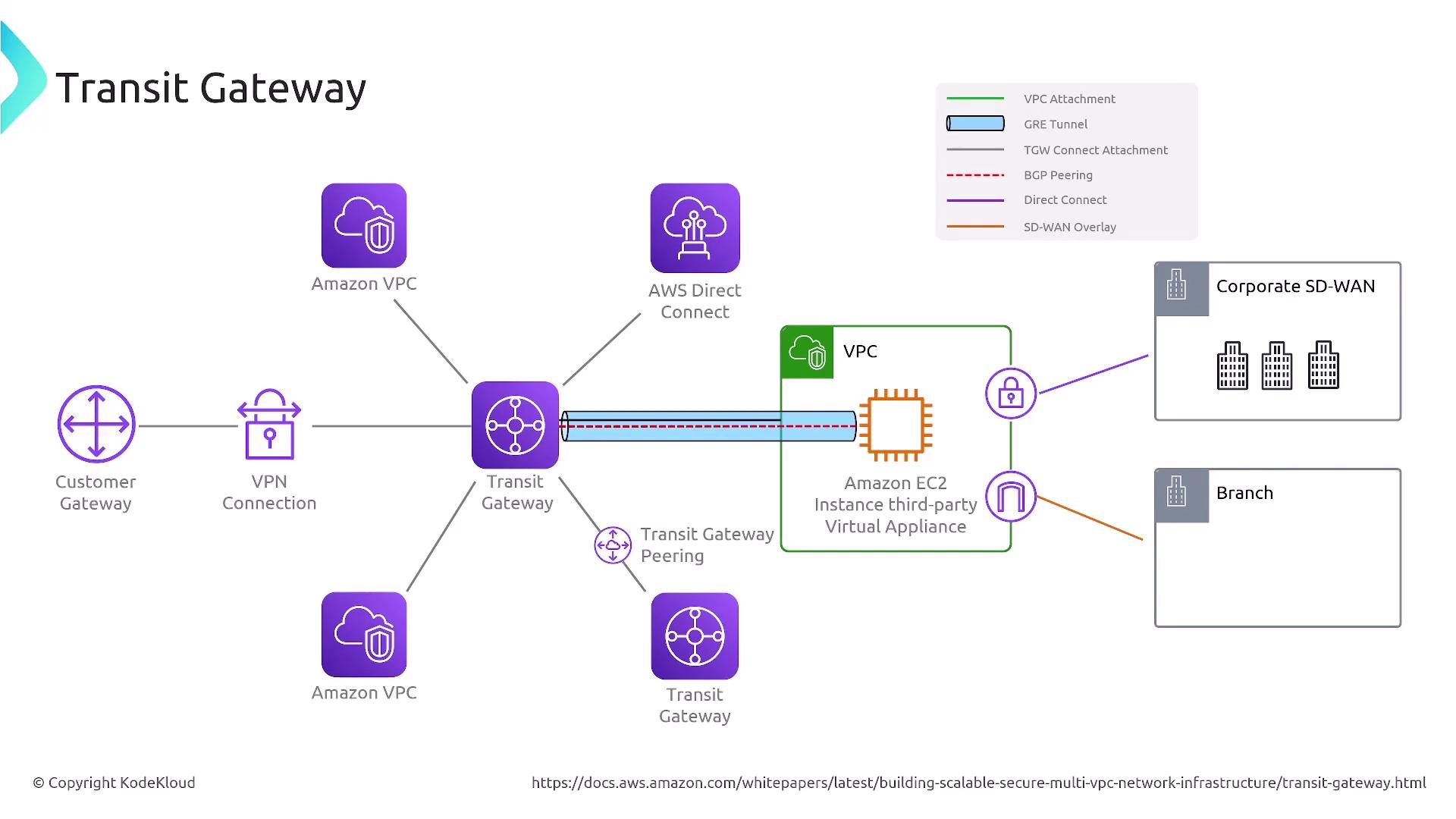
- Transit Gateway
The transit gateway is designed for complex networking scenarios, supporting connections across multiple VPCs, customer gateways, VPNs, and corporate SD-WANs.
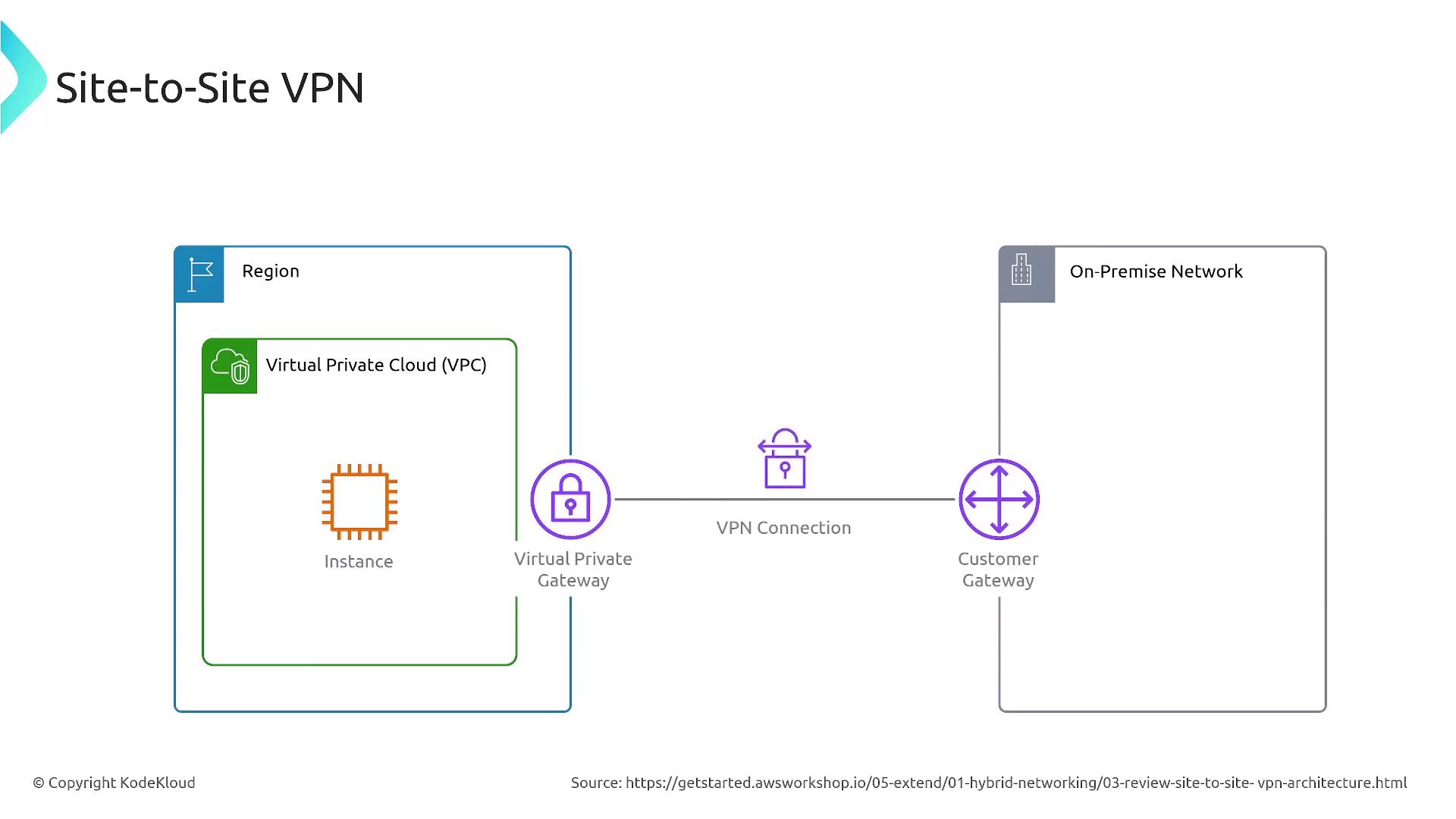
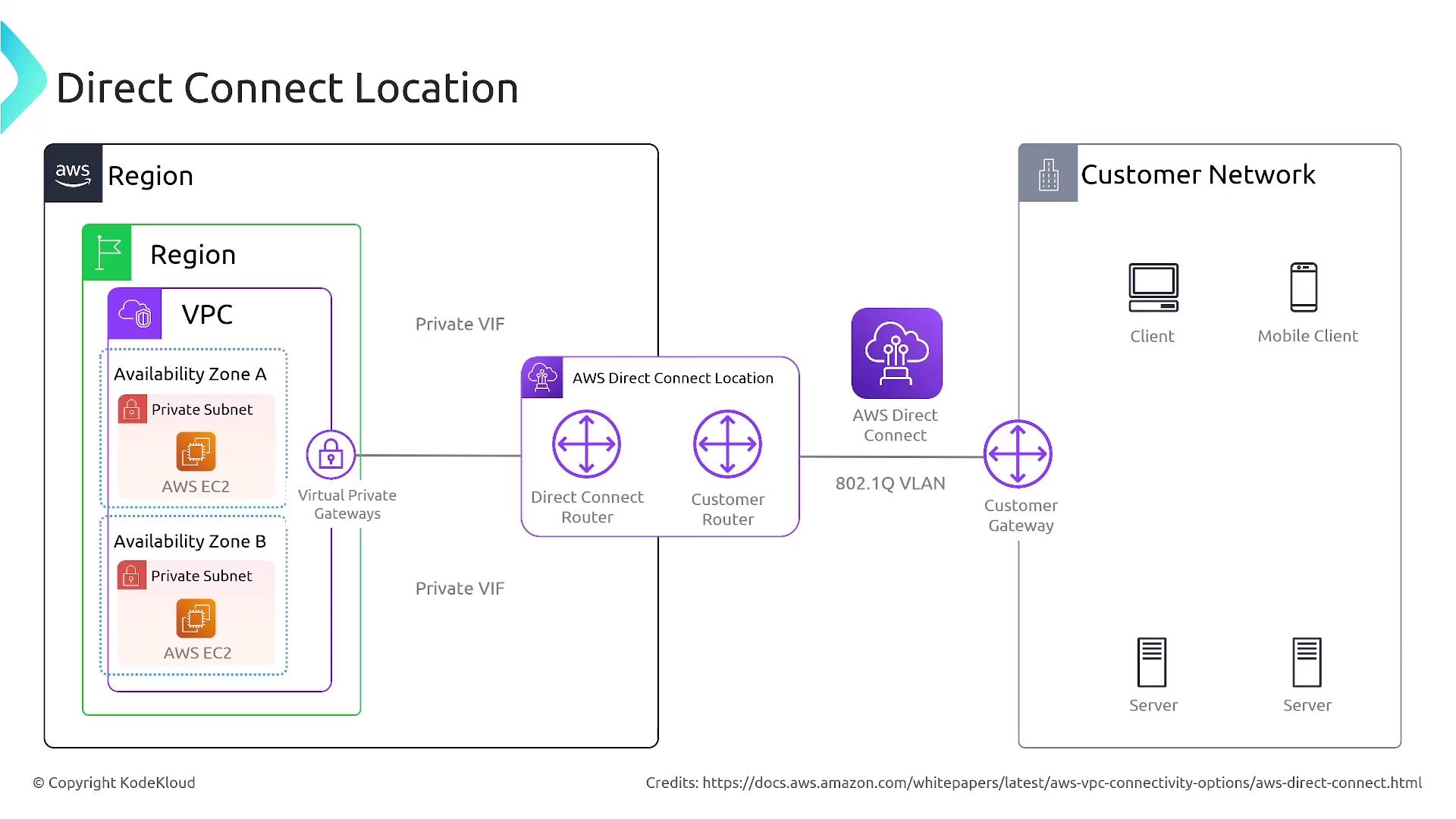
Client VPN was also briefly addressed as an extension of networking capabilities, further enhancing secure access across diverse network setups.
Domain Name System (DNS)
A robust Domain Name System (DNS) setup is essential for directing traffic efficiently. Key topics in this area include:- Public vs. Private Hosted Zones: Differentiating between zones to manage where and how website requests are served.
- Routing Policies: Explore various routing policies such as latency-based, geolocation, and weighted routing, among others, to optimize traffic direction.
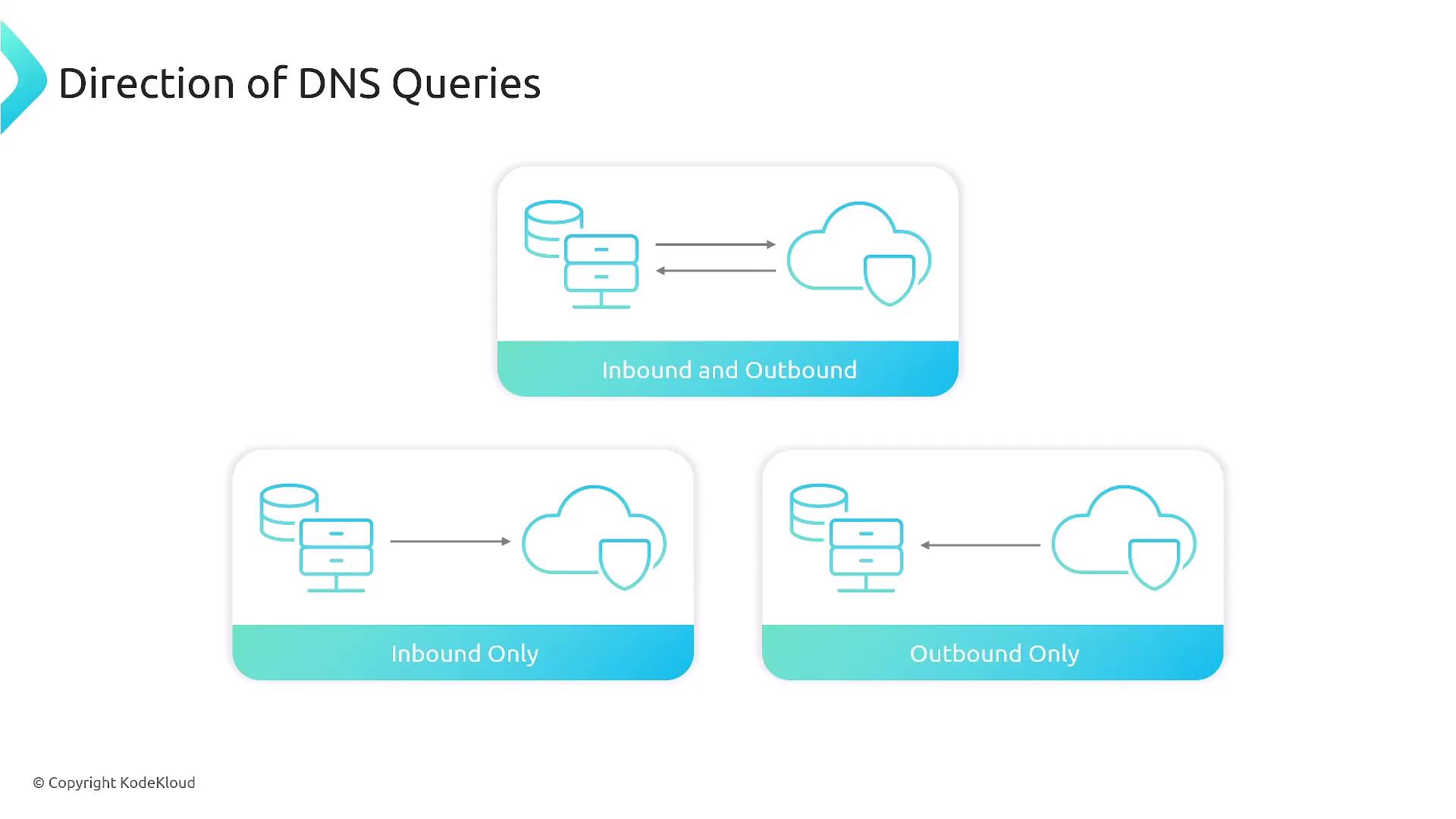
- Route 53 Resolver: This service handles both inbound and outbound DNS queries, facilitating smooth resolution within your VPC.

Global Content Delivery and Caching
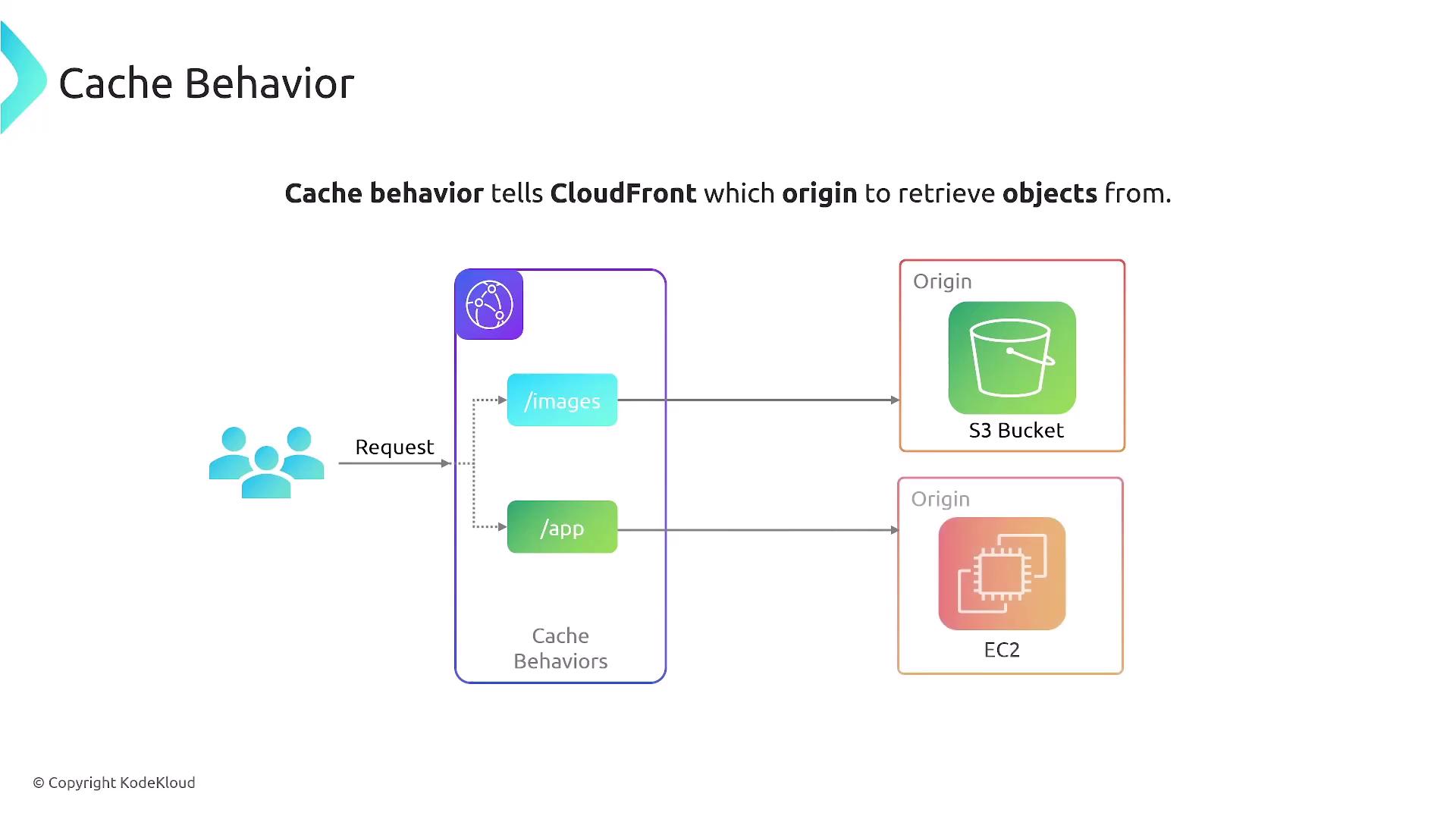
Optimizing content delivery on a global scale can significantly improve user experience. Important services in this area include:- CloudFront: Caches content closer to the end user, reducing latency and accelerating performance.
- Global Accelerator: Enhances traffic routing by optimizing the network paths, albeit mentioned briefly.
- Field-Level Encryption: CloudFront supports encryption of specific data fields to secure sensitive information.
- Hosting Static Sites on S3: A popular and cost-effective method for serving static websites.
Security and Data Capture
Security is a critical pillar in network design. Topics in this section include:- Potential risks from misconfigured firewalls and route tables.
- Network security best practices through AWS Direct Connect—while noting that additional MACsec encryption is recommended for enhanced security.
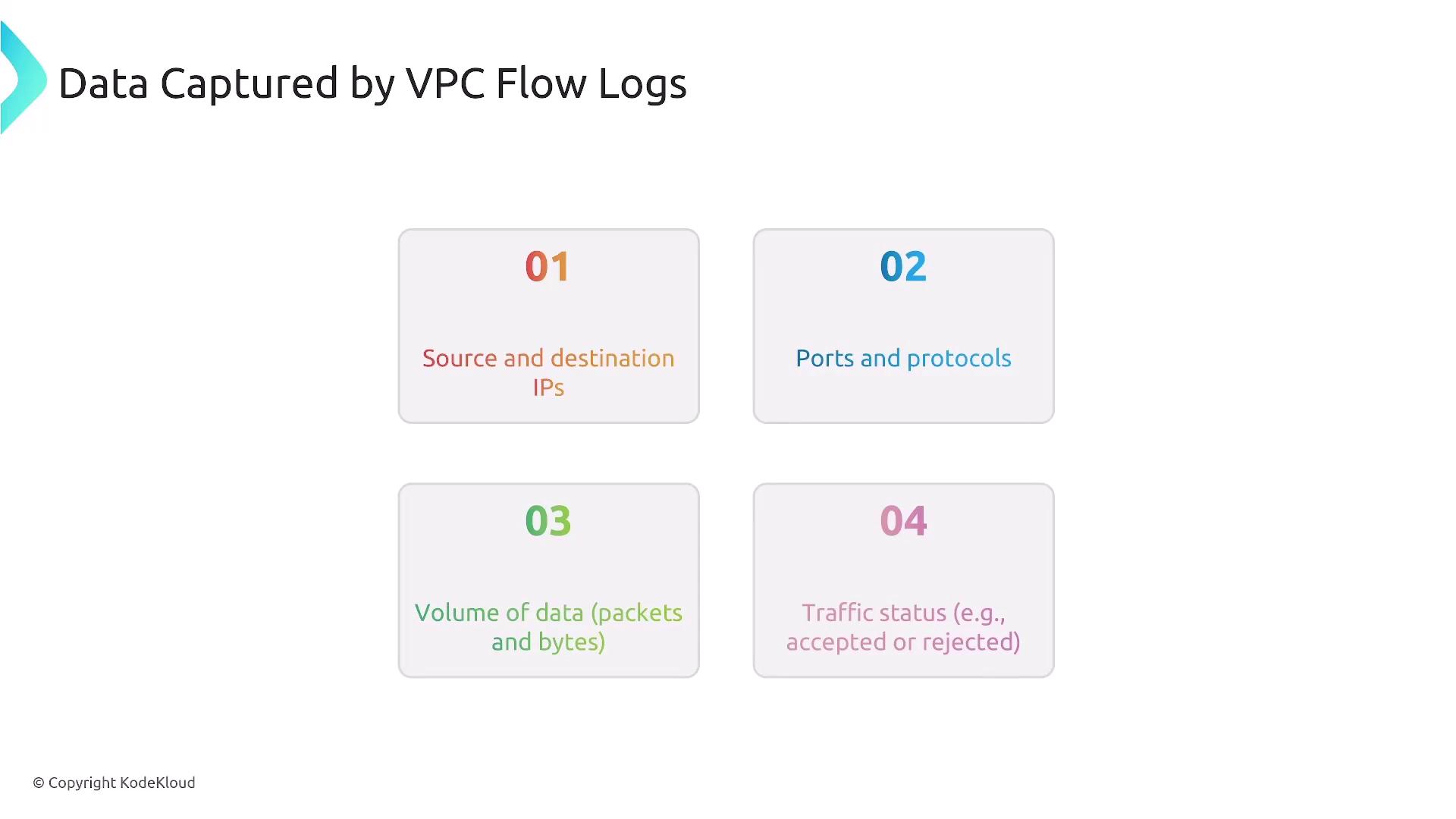
- VPC Flow Logs
- Transit Flow Logs
- Load Balancer Logs
- S3 Access Logs
Always ensure that firewalls, route tables, and encryption standards are correctly configured to protect your networks from vulnerabilities.