Reliability in Cloud Operations
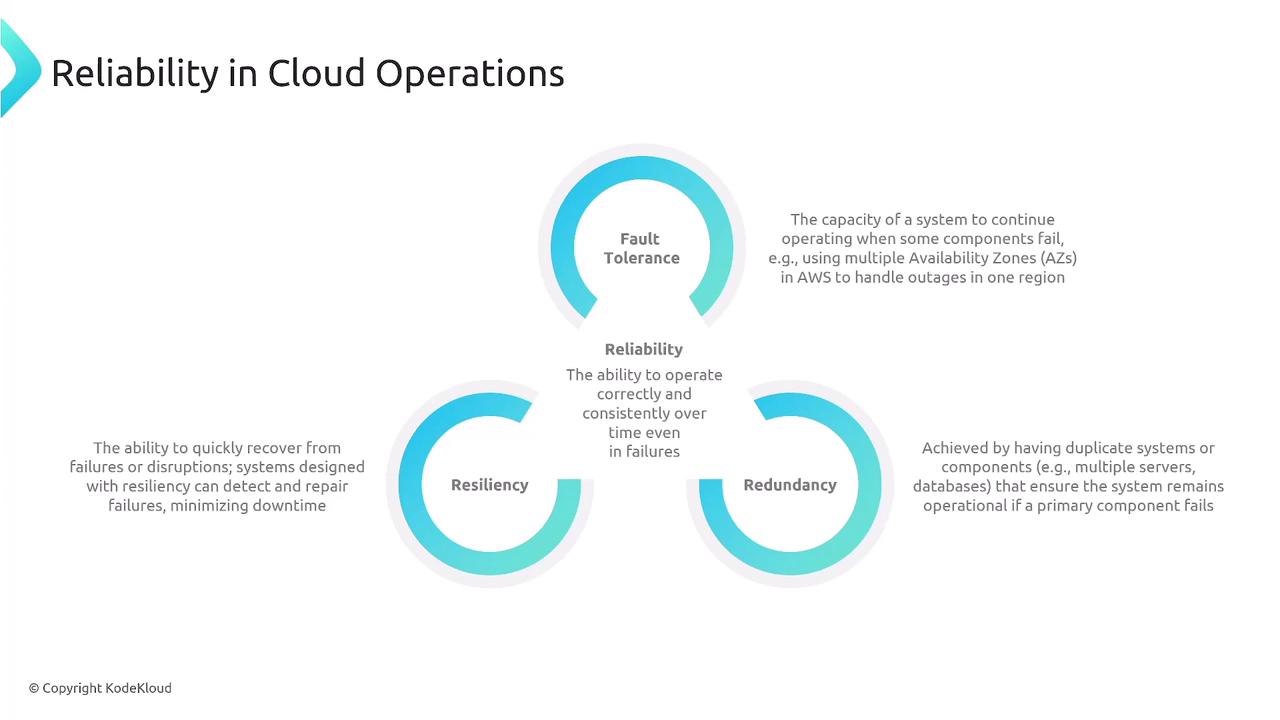
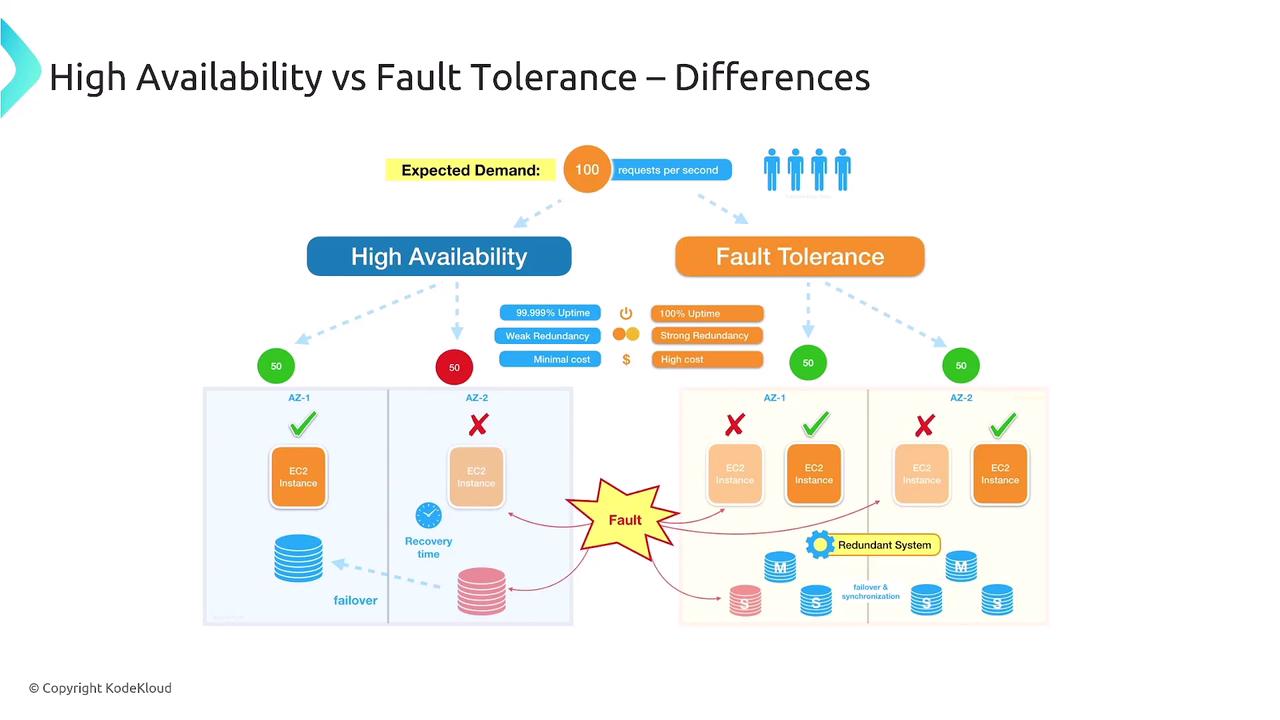
Reliability is the system’s ability to operate consistently and correctly over time, even when components fail. In Domain 2, the following topics were covered:- Fault Tolerance: The capacity of a system to continue operating when some components fail (for example, by leveraging multiple Availability Zones).
- Resiliency: The ability of a system to detect, recover from, and resist failures.
- Redundancy: The practice of duplicating systems or components so that if a primary component fails, the overall system remains operational.
Resiliency Mechanisms and Auto Scaling
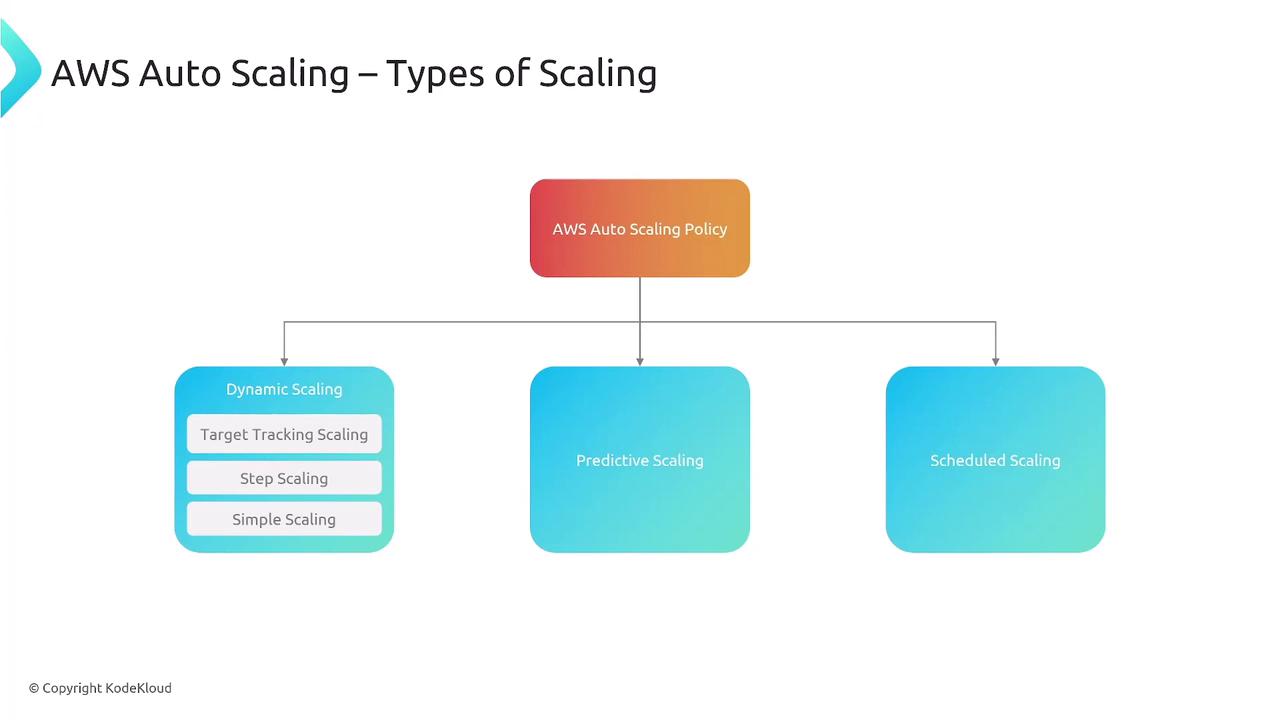
Enhancing resiliency leads to improved performance. AWS offers multiple auto scaling policies:- Dynamic Scaling: Implements policies such as target tracking, simple scaling, and step scaling.
- Predictive Scaling: Uses historical data to forecast traffic and adjust capacity accordingly.
- Scheduled Scaling: Adjusts resources based on pre-defined times, like scaling out during peak weekend usage.

The Importance of Caching
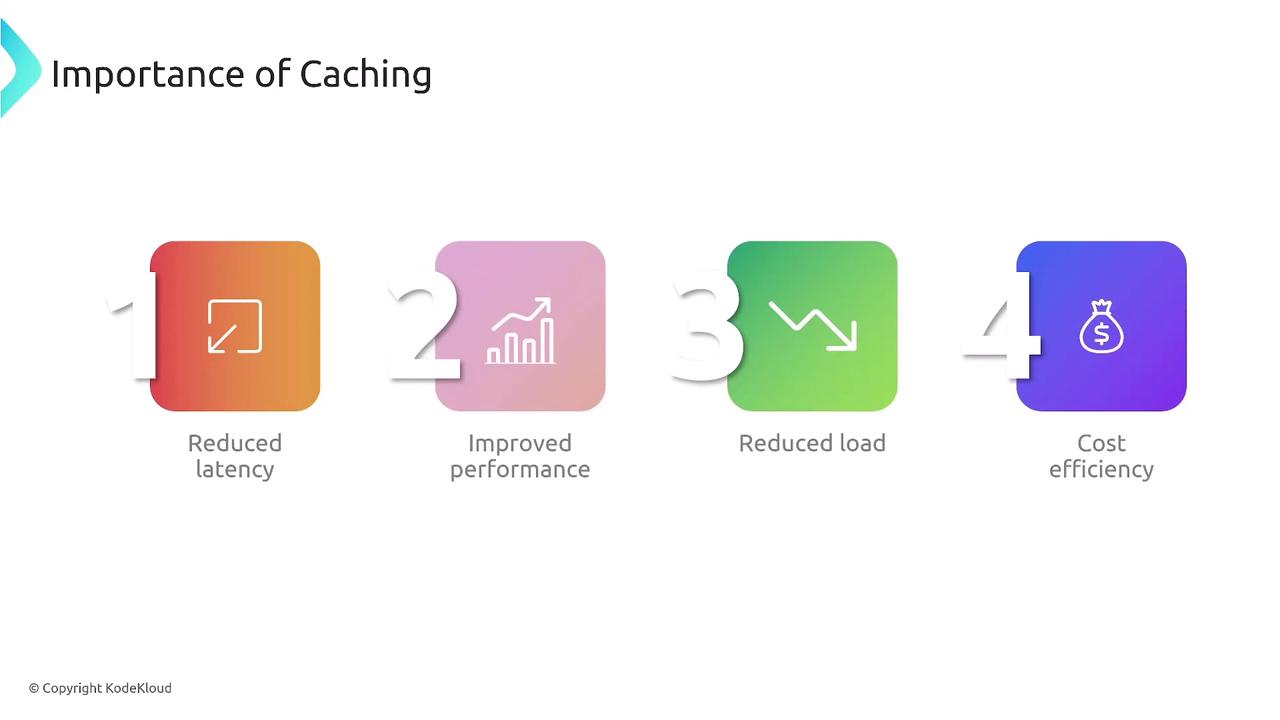
Caching improves performance by reducing latency and offloading server traffic while boosting resiliency. The benefits include:- Reduced latency and improved response times
- Lower server load
- Increased cost efficiency
- ElastiCache: Available in two forms:
- Redis: Supports multi-AZ deployments, complex data structures, and list sorting.
- Memcached: Offers a lightweight and simple caching solution.
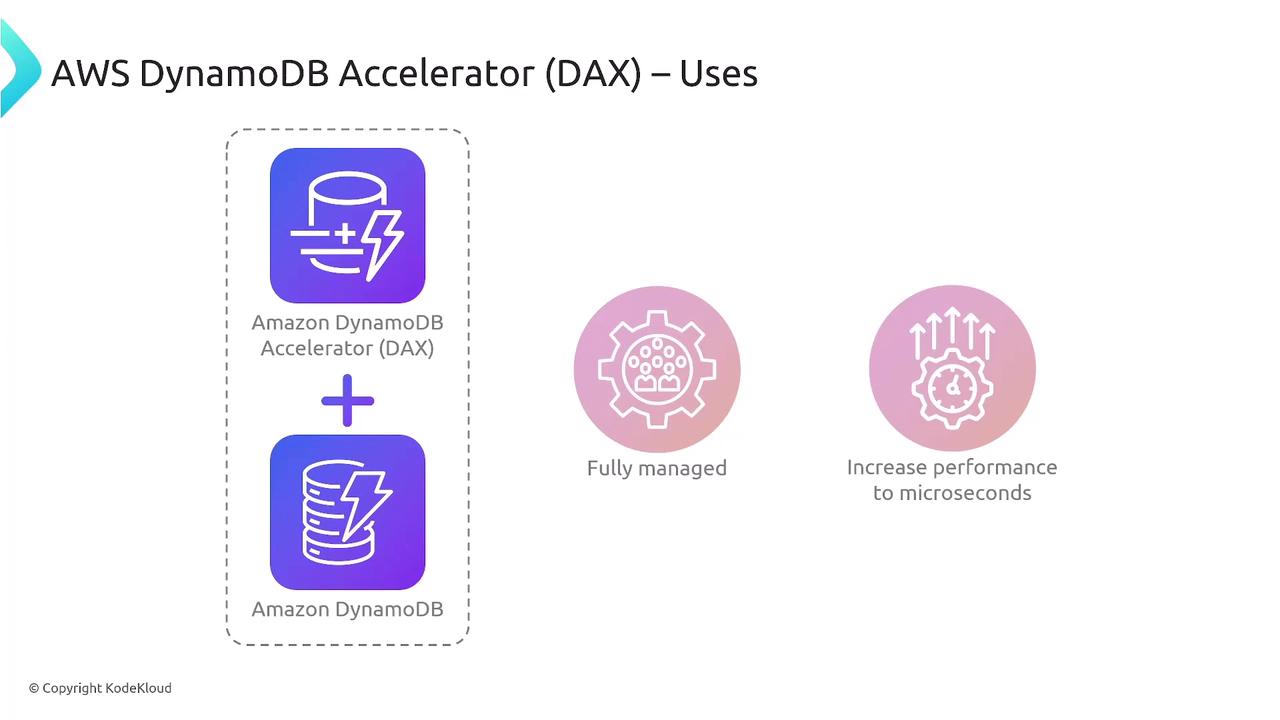
- DAX (DynamoDB Accelerator): A fully managed cache for DynamoDB, reducing read latencies to microseconds even under high load.
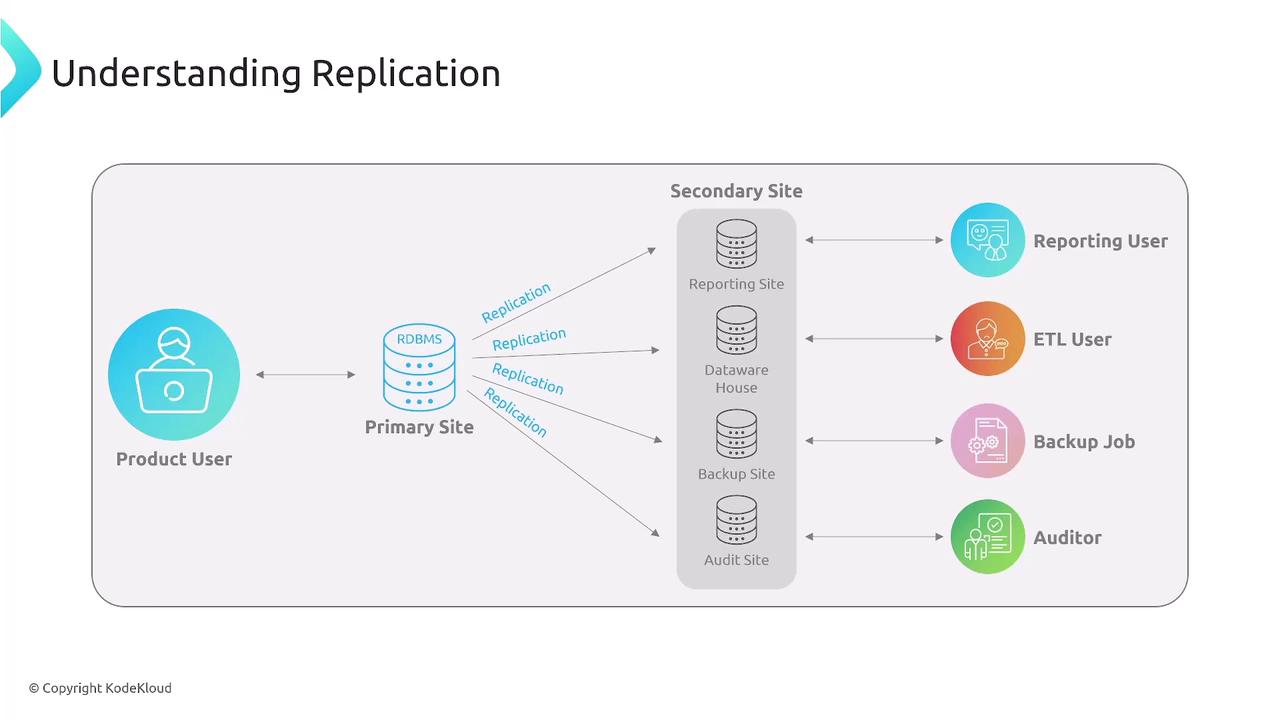
Data Replication and Resiliency
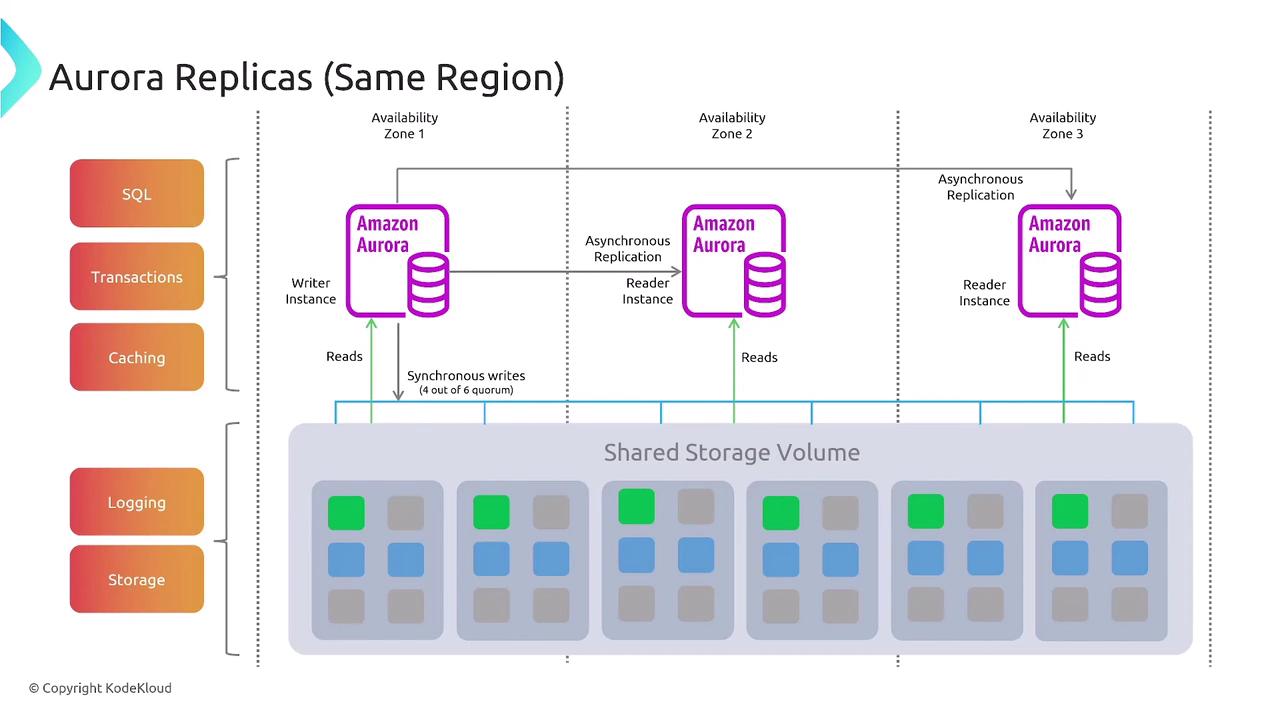
Replication plays a vital role in maintaining system resiliency, especially for stateful applications. It helps offload reporting tasks, populates data warehouses, performs backups, and supports auditing. Replication methods include:- Within a Region: Local replication for short distances and low latencies.
- Cross-Region: For long-distance replication using asynchronous techniques.

Loose Coupling and Abstraction
Design architectures with loose coupling to further enhance resiliency. Using microservices, message-driven, or event-driven approaches allows each component to operate independently, resulting in higher fault tolerance and easier scalability.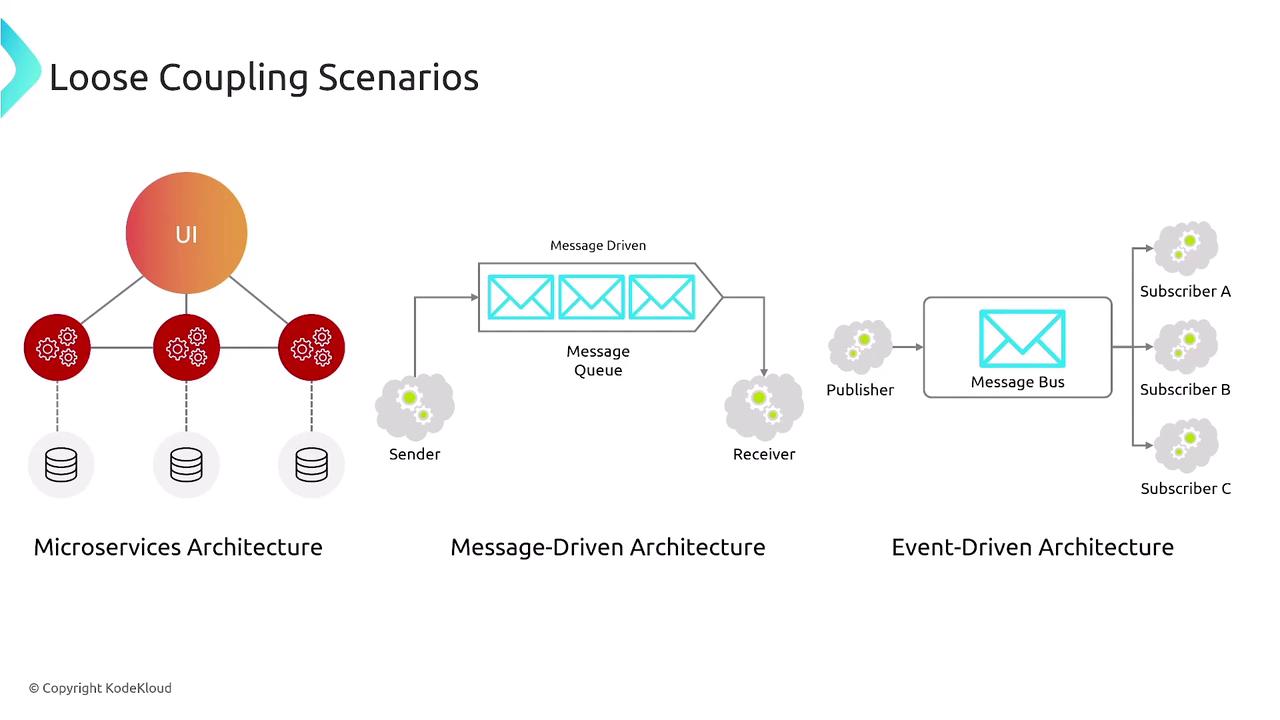
- Latency-based routing
- Geolocation routing
- Geoproximity routing
- Failover routing
- IP-based routing
- Multivalue answer routing
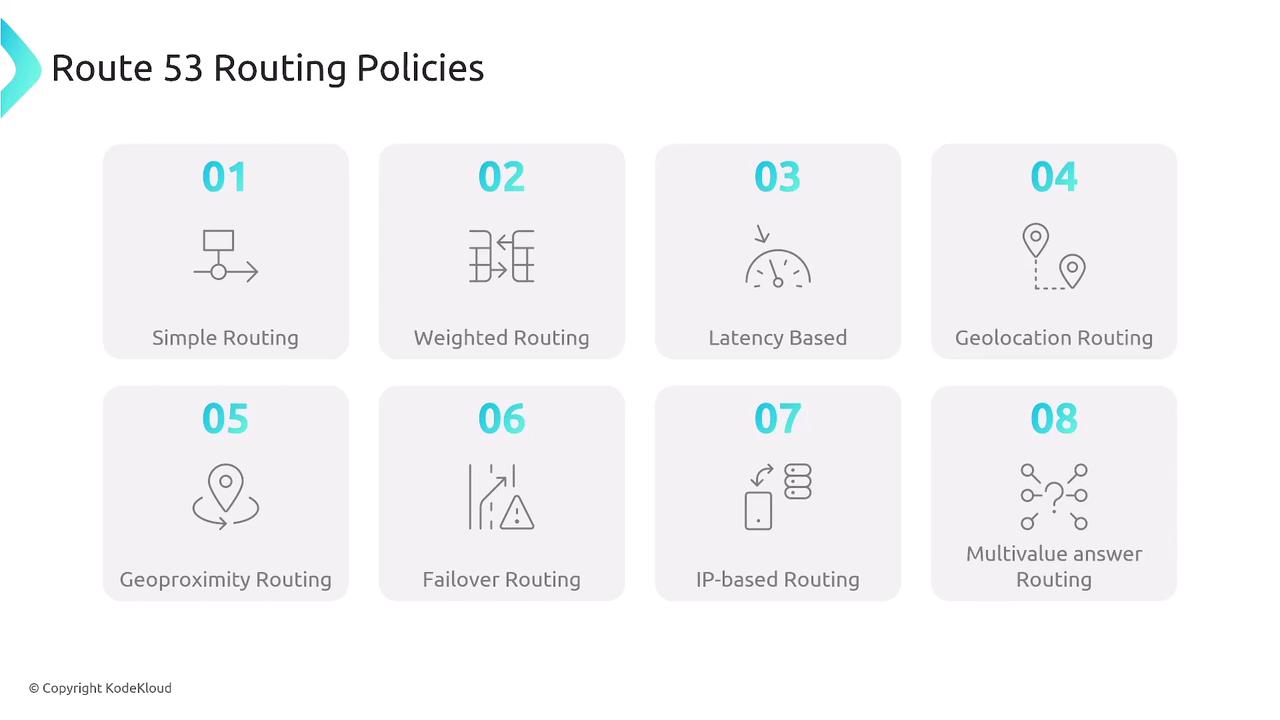

VPC Architecture and Availability Zones
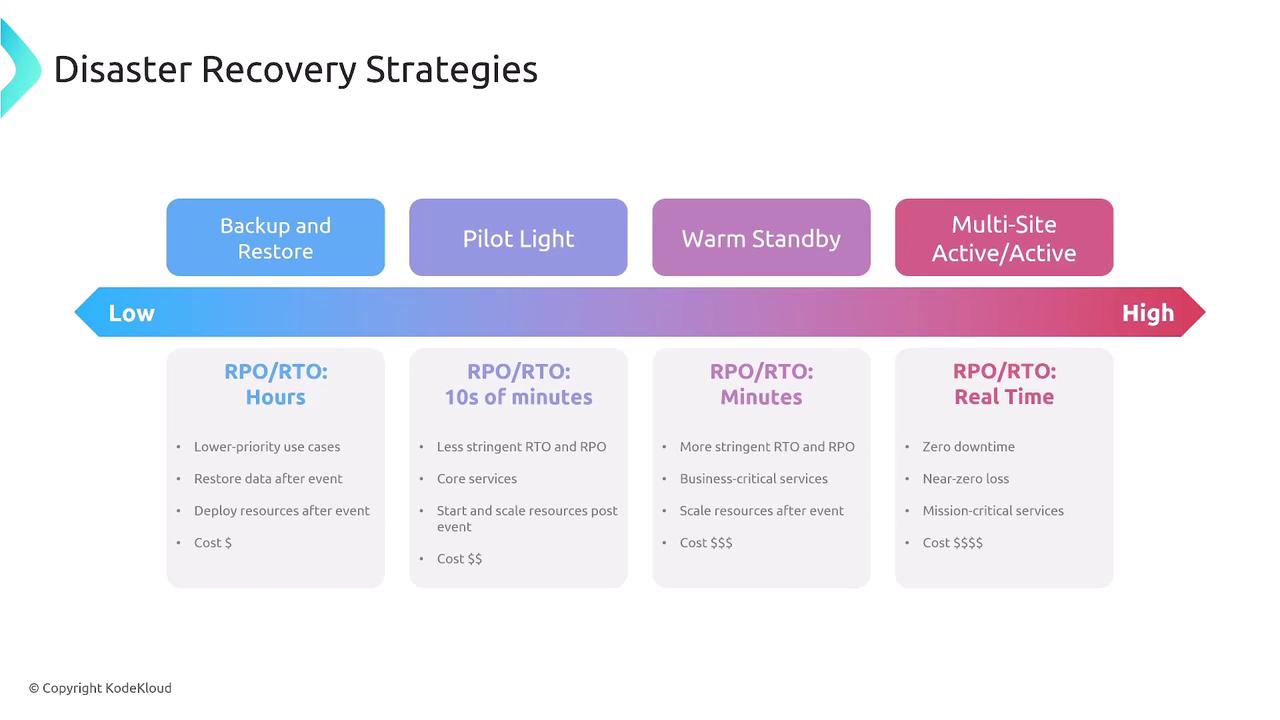
AWS best practices recommend deploying resources across multiple Availability Zones to enhance resiliency. Typically, private subnets house most resources while load balancers reside in public subnets. This design supports auto scaling groups and ensures that the failure of one zone does not impact the overall system.Disaster Recovery Strategies
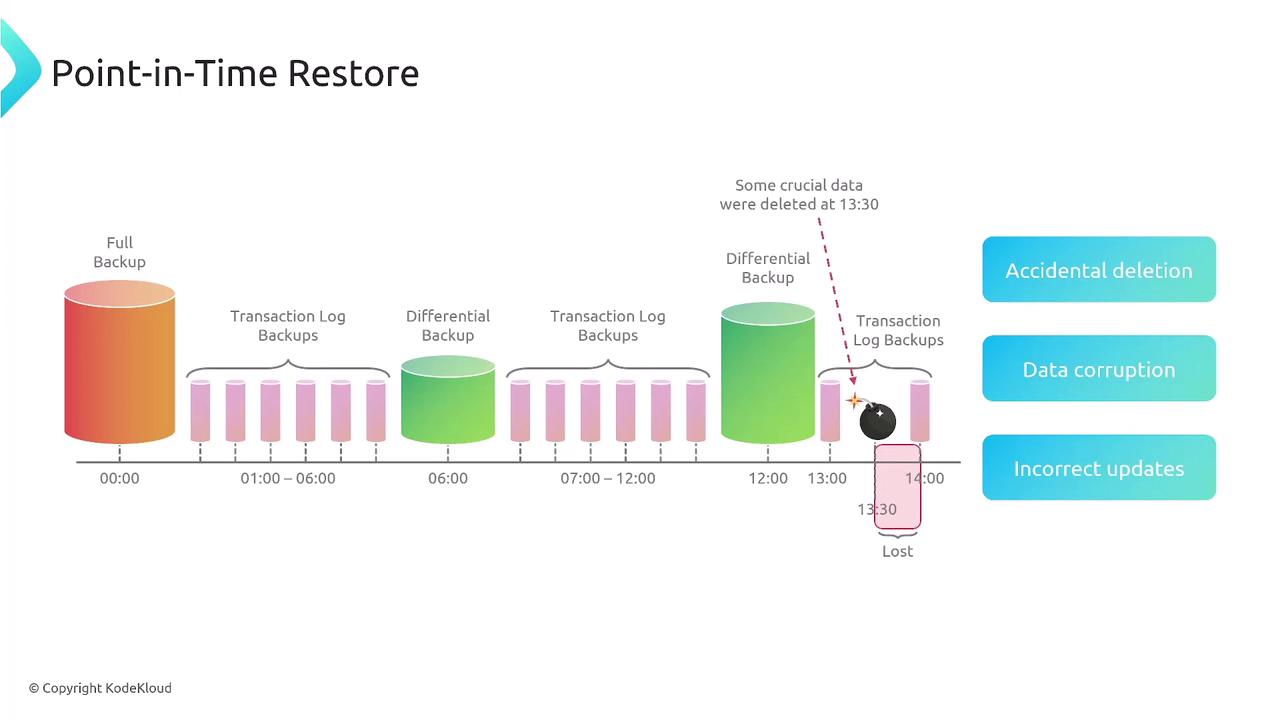
Disaster recovery (DR) strategies are essential for maintaining business continuity. Key concepts include:- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): The maximum acceptable downtime.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO): The maximum tolerable period in which data might be lost.
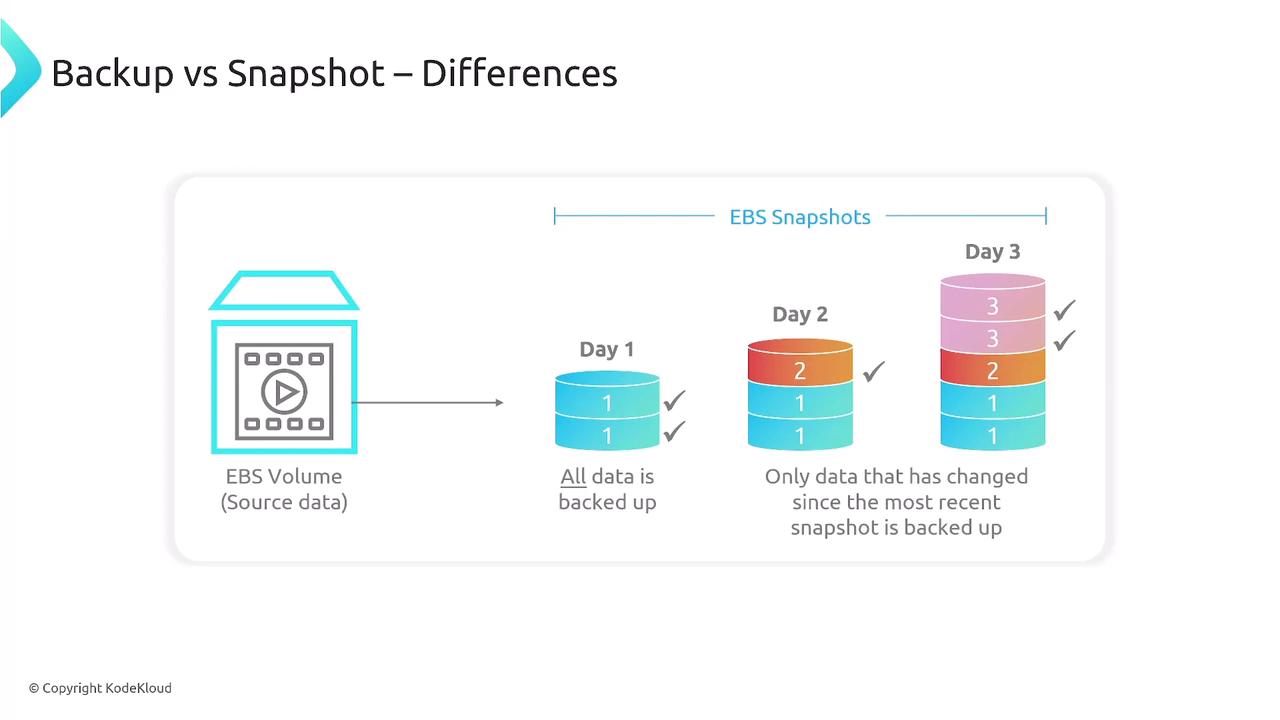
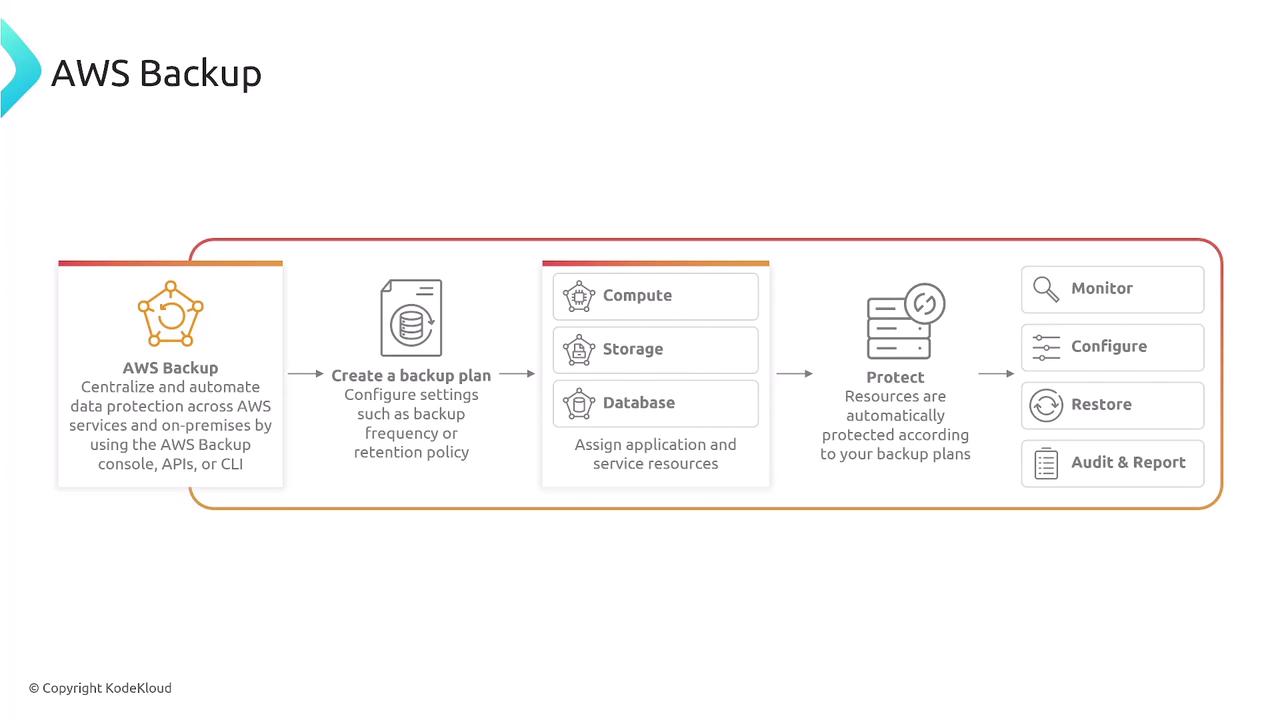
Backup and Restore Processes
An effective backup plan should include:- Creating backup vaults and plans.
- Replicating backups across different regions.
- Automating data restoration as necessary.
- Ensuring data integrity to avoid corruption.
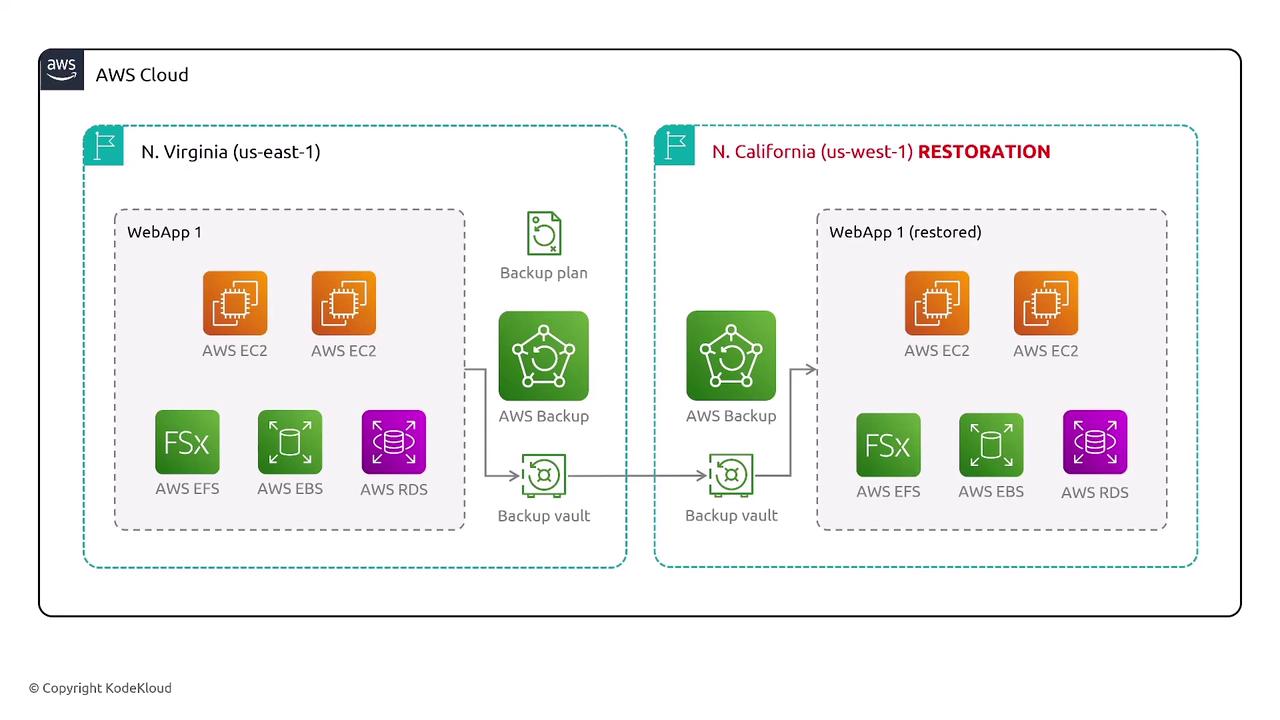

Amazon S3, Versioning, and Lifecycle Management
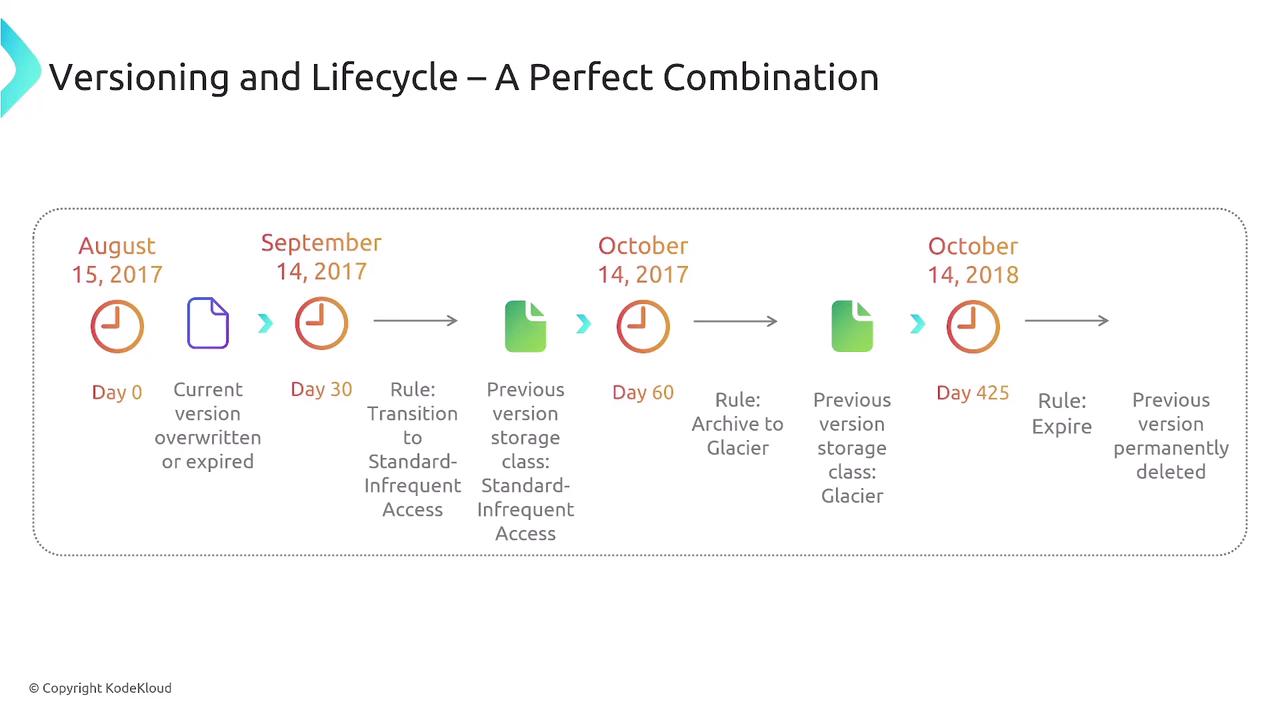
Amazon S3 contributes to resiliency through versioning, which keeps a history of every change to an object. Versioning is useful for delete protection and historical recovery. However, to manage potential storage cost increases, it is advisable to combine versioning with lifecycle rules. These rules transition older versions to colder storage classes like S3 Glacier, optimizing both performance and cost.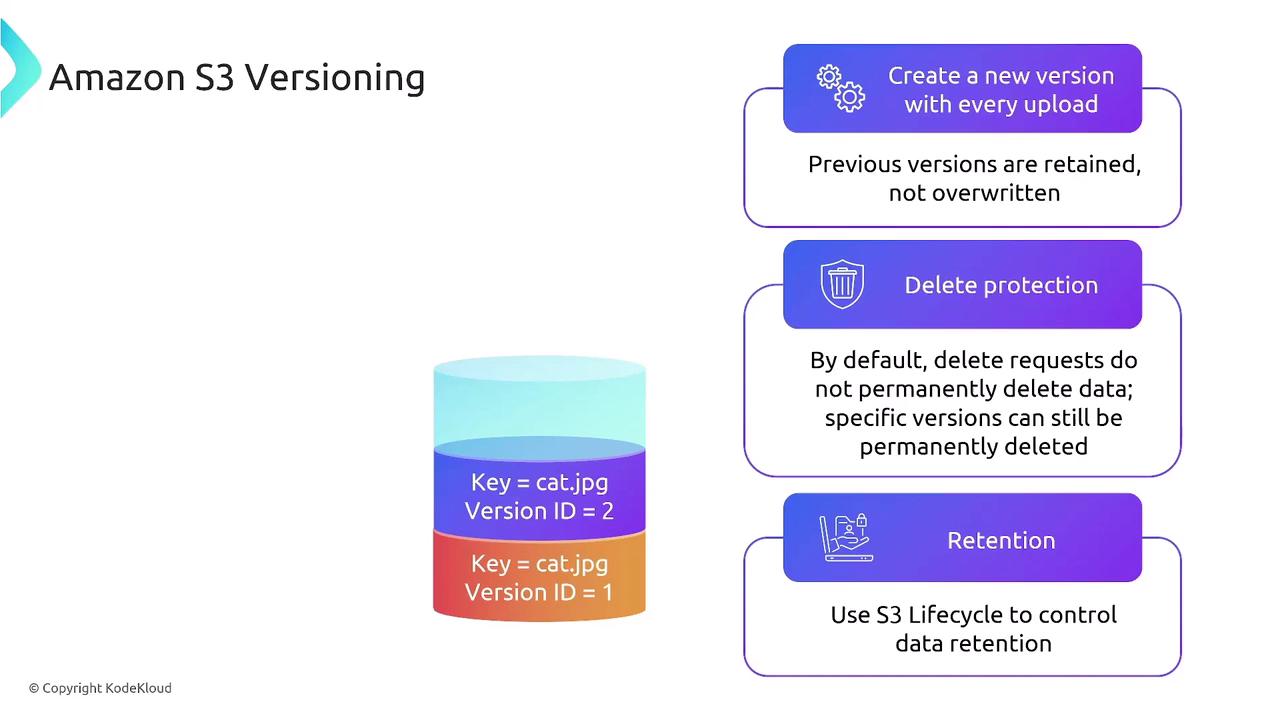
- S3 Standard
- S3 Standard Infrequent Access
- One Zone Infrequent Access
- Glacier Instant Retrieval
- Glacier Flexible Retrieval
- Glacier Deep Archive
- Intelligent Tiering
S3 Cross-Region Replication
S3 Cross-Region Replication offers disaster recovery benefits, regulatory compliance, improved latency for global applications, and enhanced data protection. It allows data in one bucket to be replicated to another bucket in the same or a different region, with customizable options for ownership override and storage class adjustments.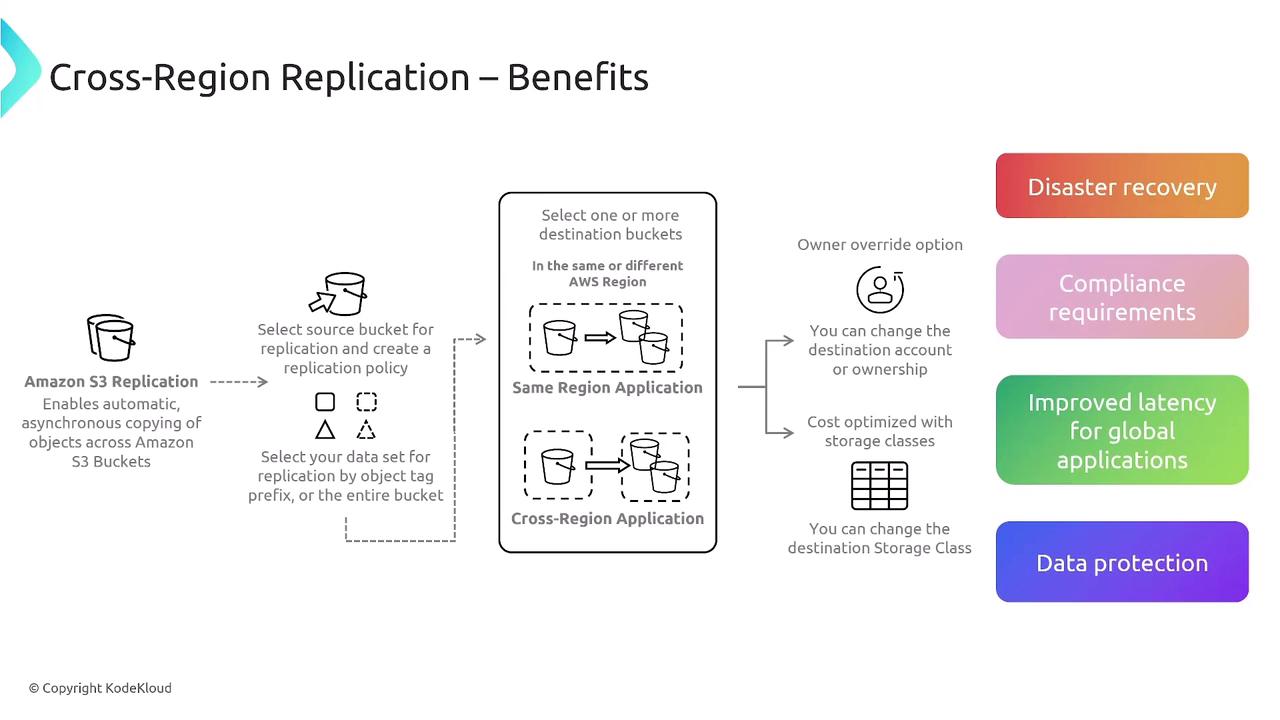
Conclusion
This lesson on Domain 2 has explored a broad spectrum of AWS resilience and business continuity topics—from fault tolerance and auto scaling to caching, replication, and disaster recovery strategies. By integrating strategies such as loose coupling, effective backup plans, and comprehensive data management solutions, you can design highly resilient cloud architectures.As you continue your studies, use this overview as a refresher and a reference point to reinforce your understanding of AWS resiliency and continuity strategies. For deeper insights, consider exploring the AWS Documentation.