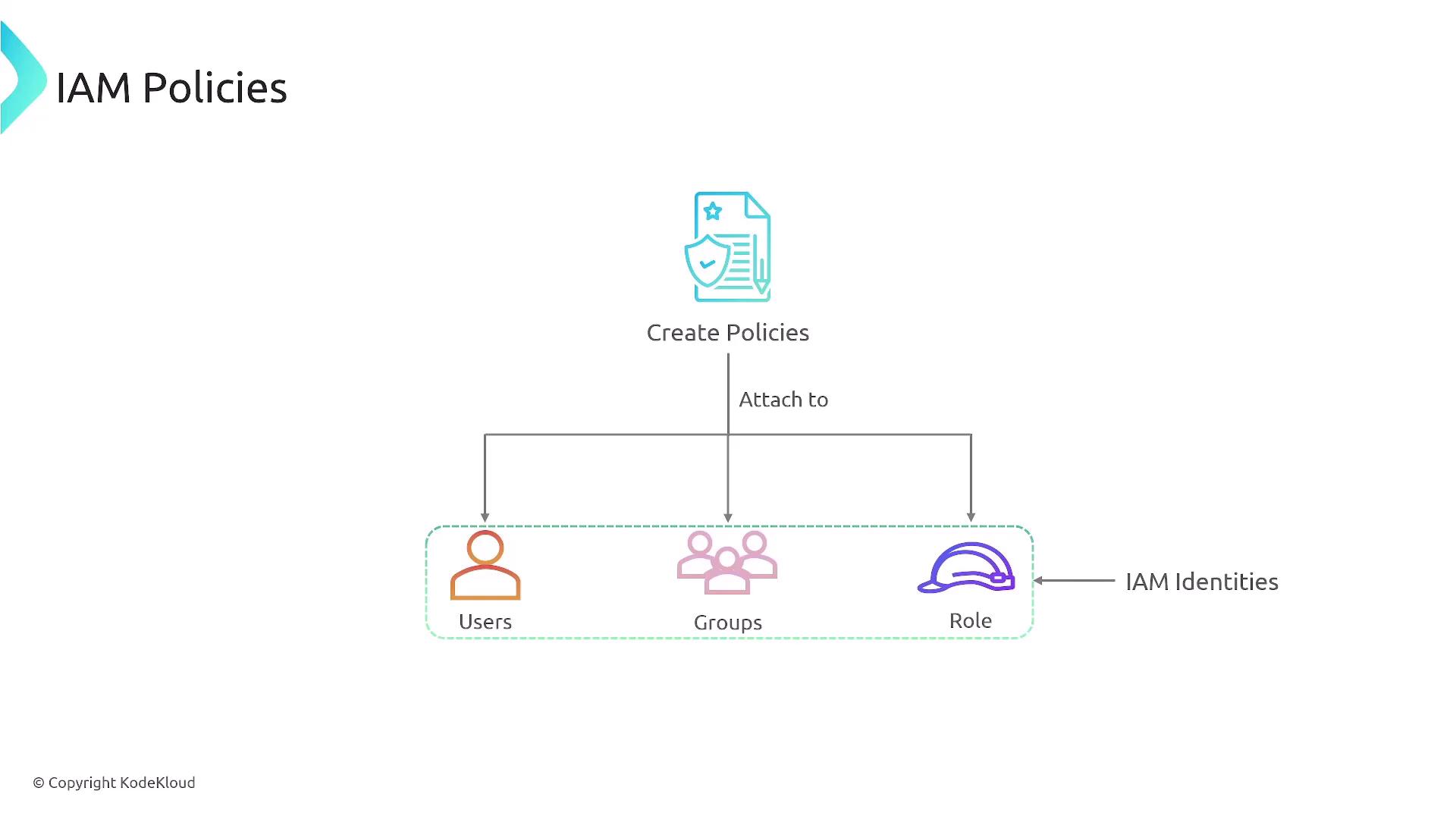
Identity-Based Policies
IAM policies are typically identity-based and are attached to a user, group, or role. In contrast, resource-based policies are directly attached to AWS resources, such as S3 buckets or SQS queues. It is recommended to attach policies to groups and roles, allowing users to inherit the appropriate permissions.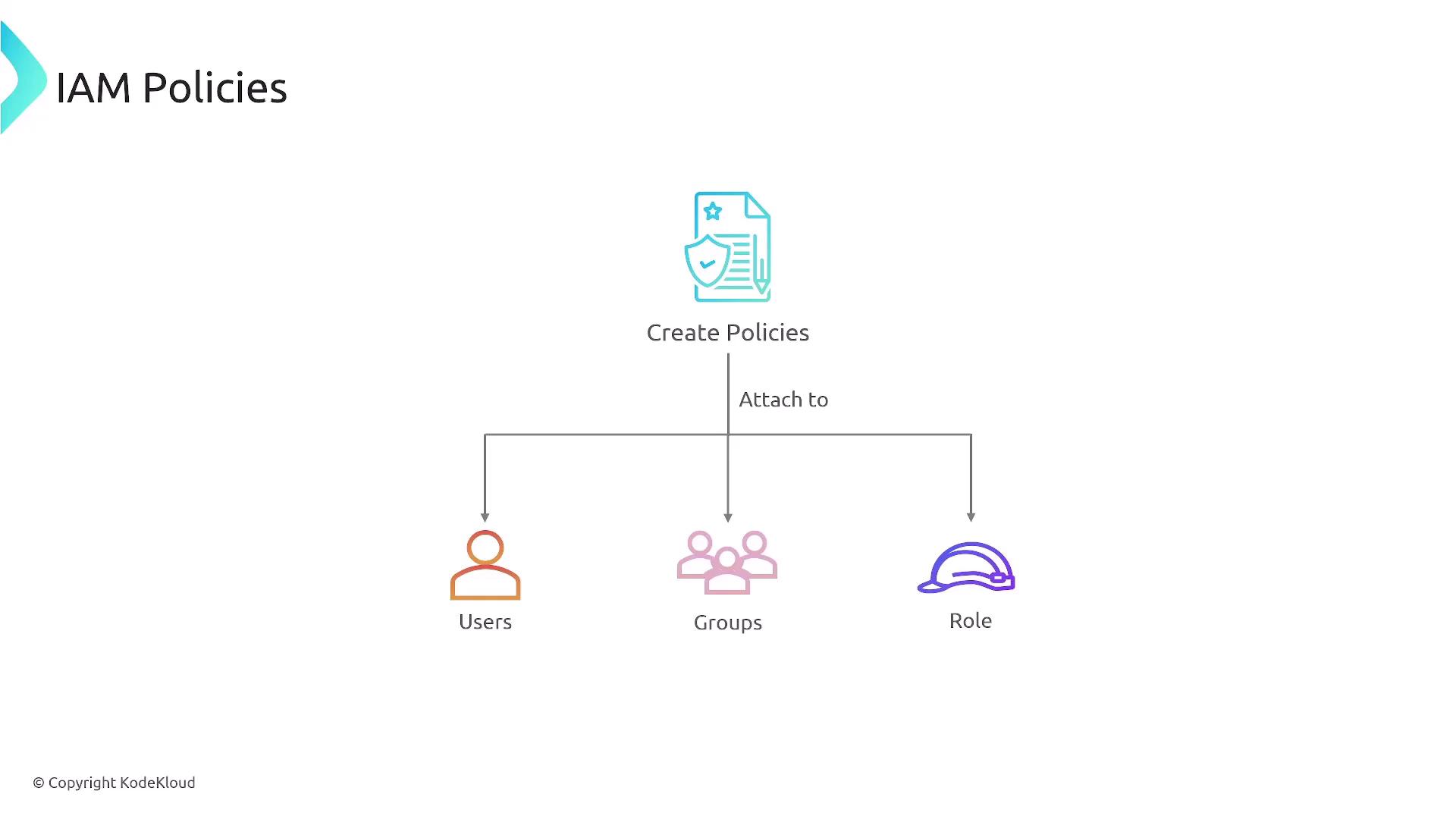
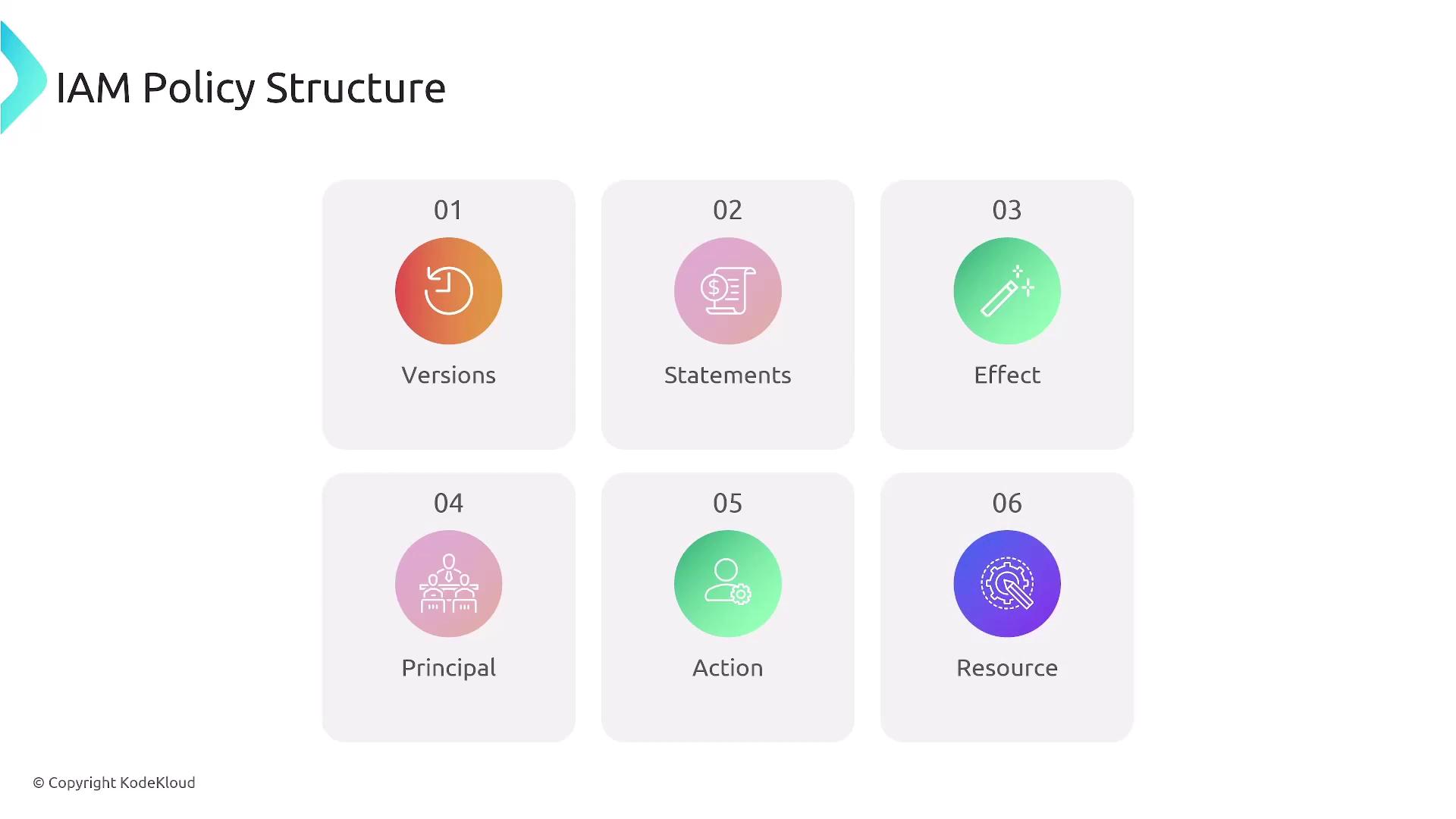
JSON Document Structure
IAM policies are defined as JSON documents. Consider a policy that permits a user to upload objects to a specific S3 bucket using conditions such as restricting access by days or specific IP ranges.- Version: The version of the policy language.
- Statement Block: One or more statements that detail:
- Effect: Whether the statement allows or denies access.
- Action: The actions enabled or restricted.
- Resource: The AWS resources (identified by ARNs) to which the statement applies.
- Conditions (Optional): Additional restrictions, such as specific times, IP addresses, or security constraints (SSL/TLS).
Be sure to specify both the bucket (“arn:aws:s3:::KodeKloud-bucket”) and its objects (“arn:aws:s3:::KodeKloud-bucket/*”) to correctly define the scope of permissions.
IAM Policy Components
When creating IAM policies, keep the following components in mind:- Version: Usually “2012-10-17”.
- Statement: Consists of one or more statements that define:
- Effect: “Allow” or “Deny” specific actions.
- Action: The AWS service actions like “s3:ListBucket” or “s3:GetObject”.
- Resource: Specifies the AWS resources (using ARNs).
- Condition (Optional): Enforces additional checks, such as IP address or time-based restrictions.
Principle of Least Privilege
A core security principle in AWS IAM is the principle of least privilege, which dictates that users should only have the permissions they require for their tasks. Fine-grained control through IAM policies simplifies enforcing this principle.
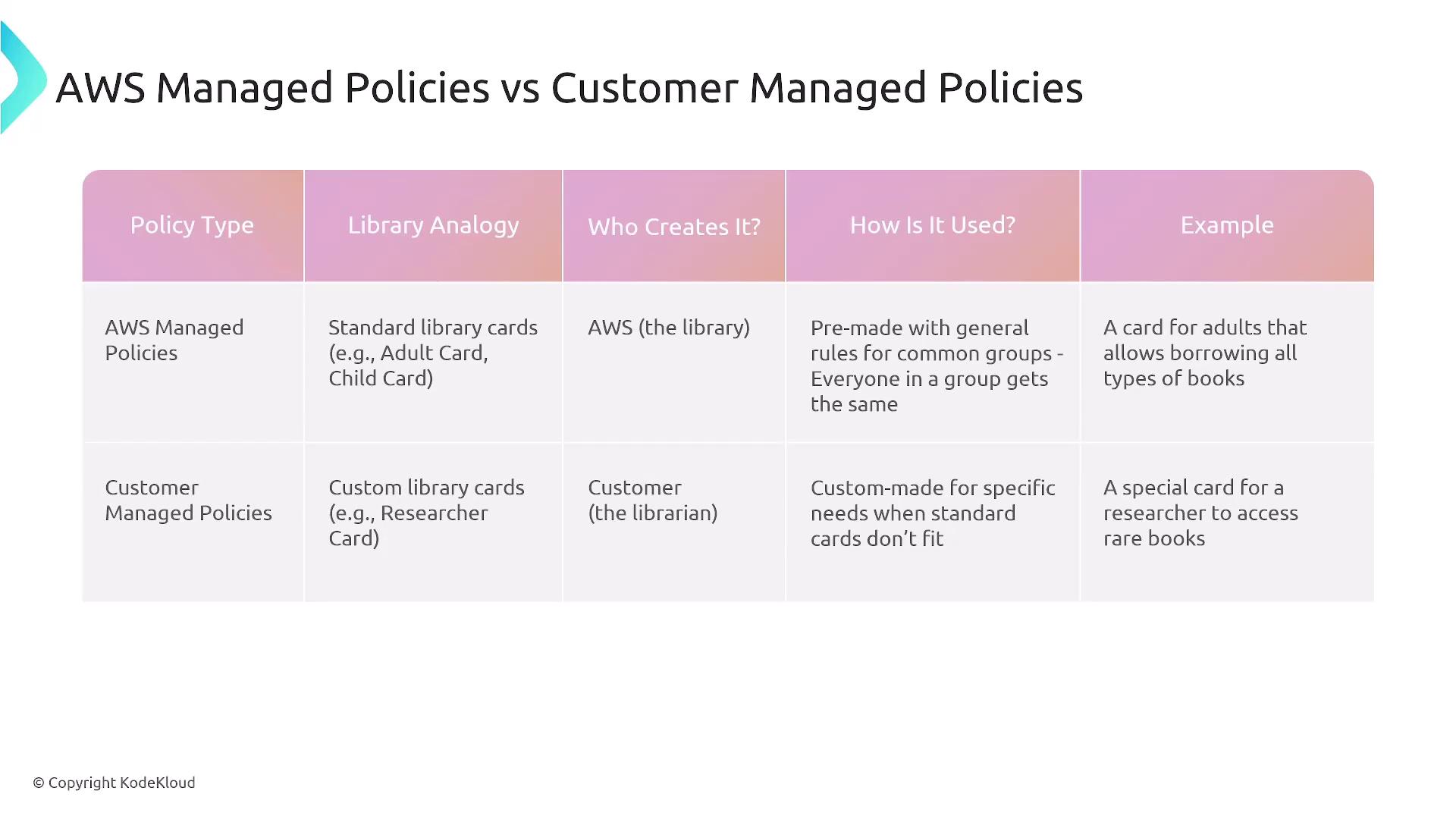
Managed Policies: AWS vs. Customer Managed
There are two main types of IAM policies:1. AWS Managed Policies
AWS Managed Policies are predefined by AWS and cannot be edited. They offer various access levels, such as full access, power user, read-only, and job function-specific policies, each with a unique ARN.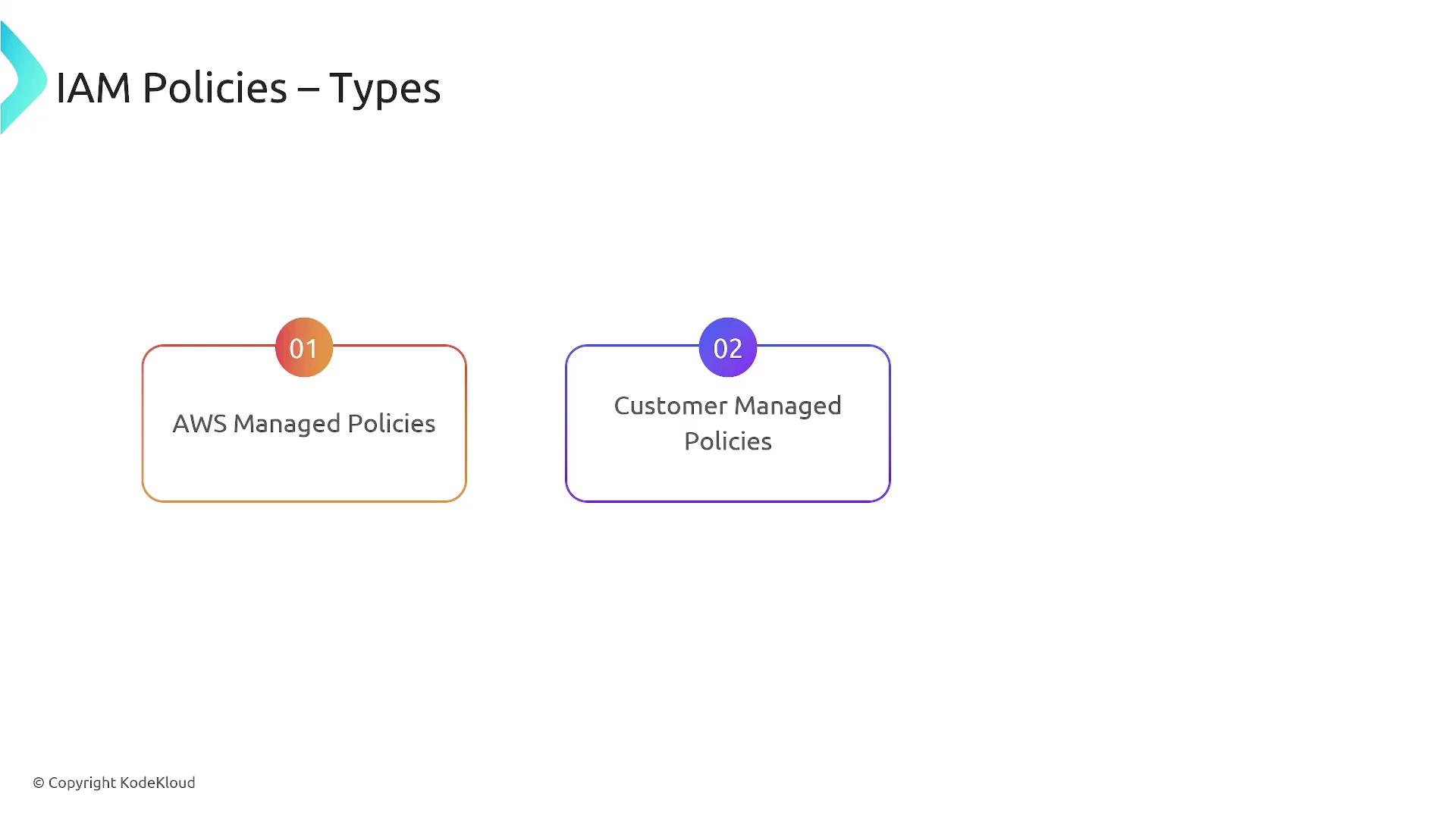
2. Customer Managed Policies
Customer Managed Policies are custom policies that you create and manage. They allow for tailor-made permission sets that can be attached to multiple users, groups, or roles and can be updated as requirements change.


Access Advisor
Access Advisor is a helpful tool in the IAM framework that audits user activity by showing which services a user has accessed and when. This information is invaluable for ensuring adherence to the principle of least privilege. For example, if a user rarely accesses certain services like Auto Scaling or CloudWatch, it may be beneficial to remove those permissions after confirming with the user.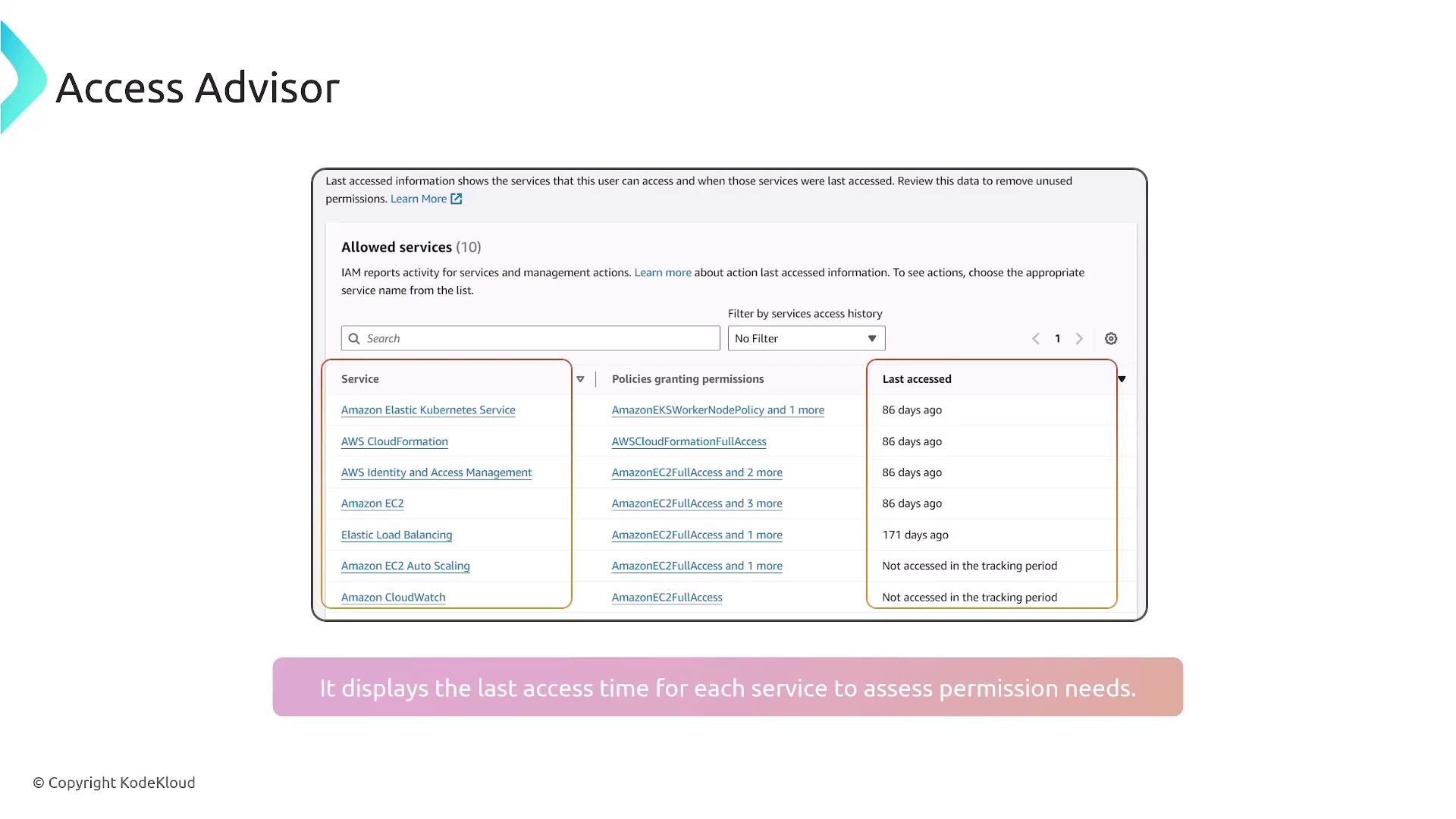
Summary
IAM policies, defined as JSON documents, offer fine-grained control over AWS access by specifying permissions for users, groups, roles, and resources. They help enforce the principle of least privilege and are available in two forms:- AWS Managed Policies: Predefined and unmodifiable policies suitable for standard access patterns.
- Customer Managed Policies: Customizable policies that allow for granular permissions and can be updated as needed.
By default, AWS entities have no access. You must explicitly grant permissions through these policies. Use conditions and tools like Access Advisor to align permissions with actual user activity and adhere to security best practices.