Provisioning Tools and Configuration Management
Provisioning tools enable you to manage infrastructure at scale. Key components include:- Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
- Configuration Management tools (e.g., AWS Systems Manager)
- CI/CD platforms
Automation in Cloud Environments
Automation in cloud environments covers a wide range of activities such as:- Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
- Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD)
- Image building processes
- Operational management and fleet maintenance
- Security and compliance monitoring
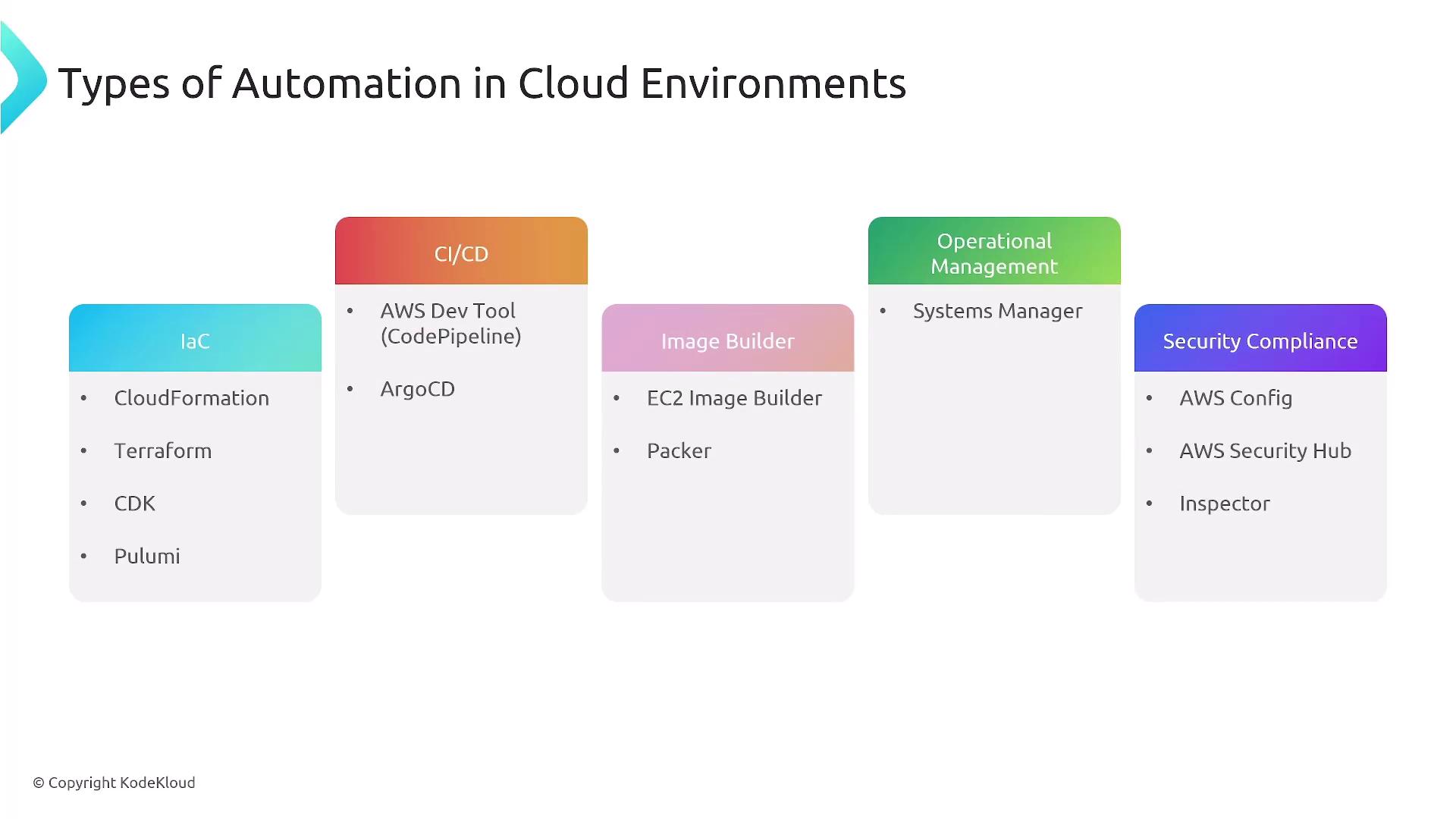
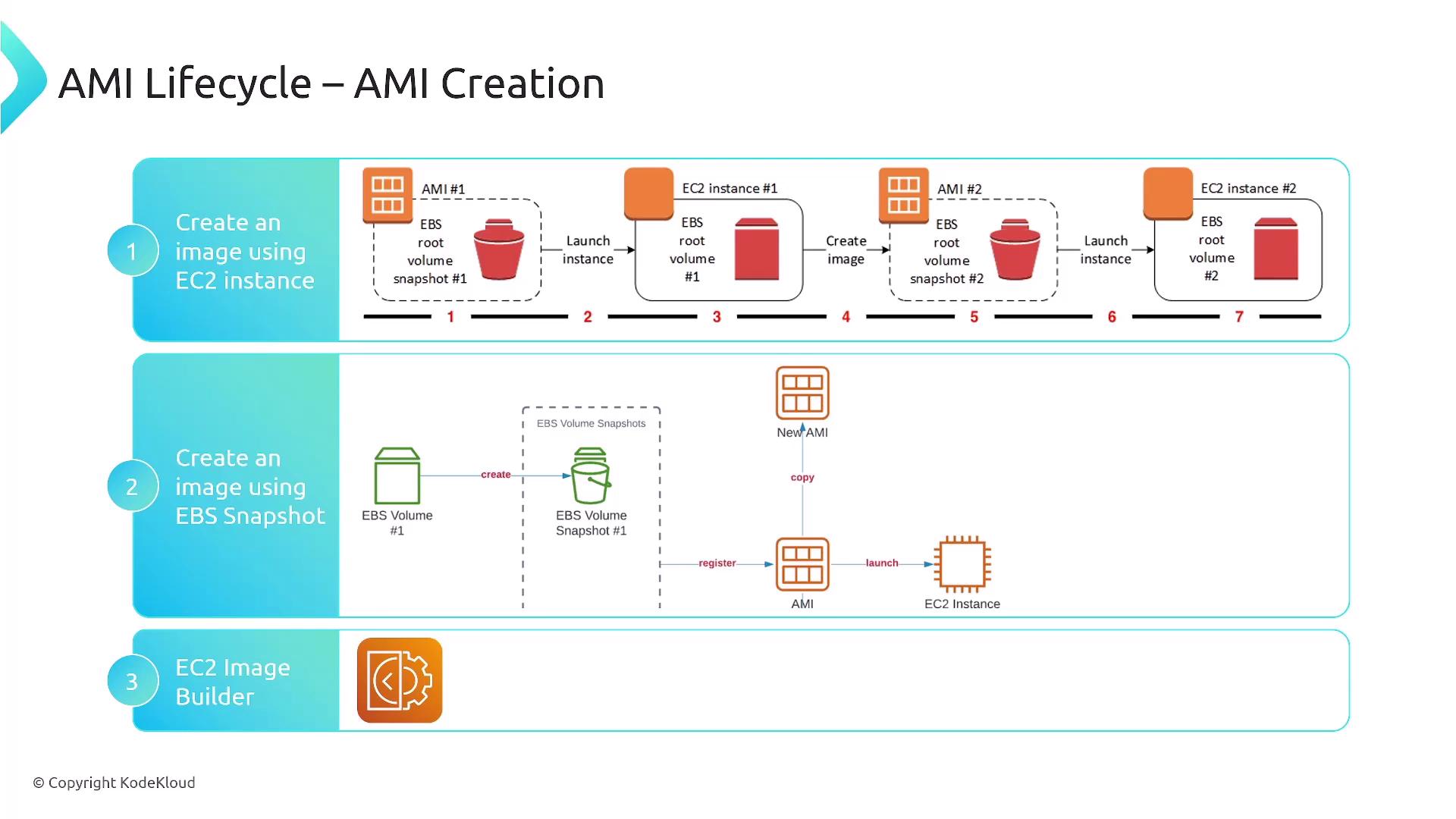
Image Creation (AMIs)
Creating Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) is a critical step in deploying EC2 instances. There are several methods:- Using an existing EC2 instance to build and operationalize an image.
- Creating an image from an EBS snapshot.
- Utilizing EC2 Image Builder, which streamlines the creation of both AMIs and container images based on your specific requirements.
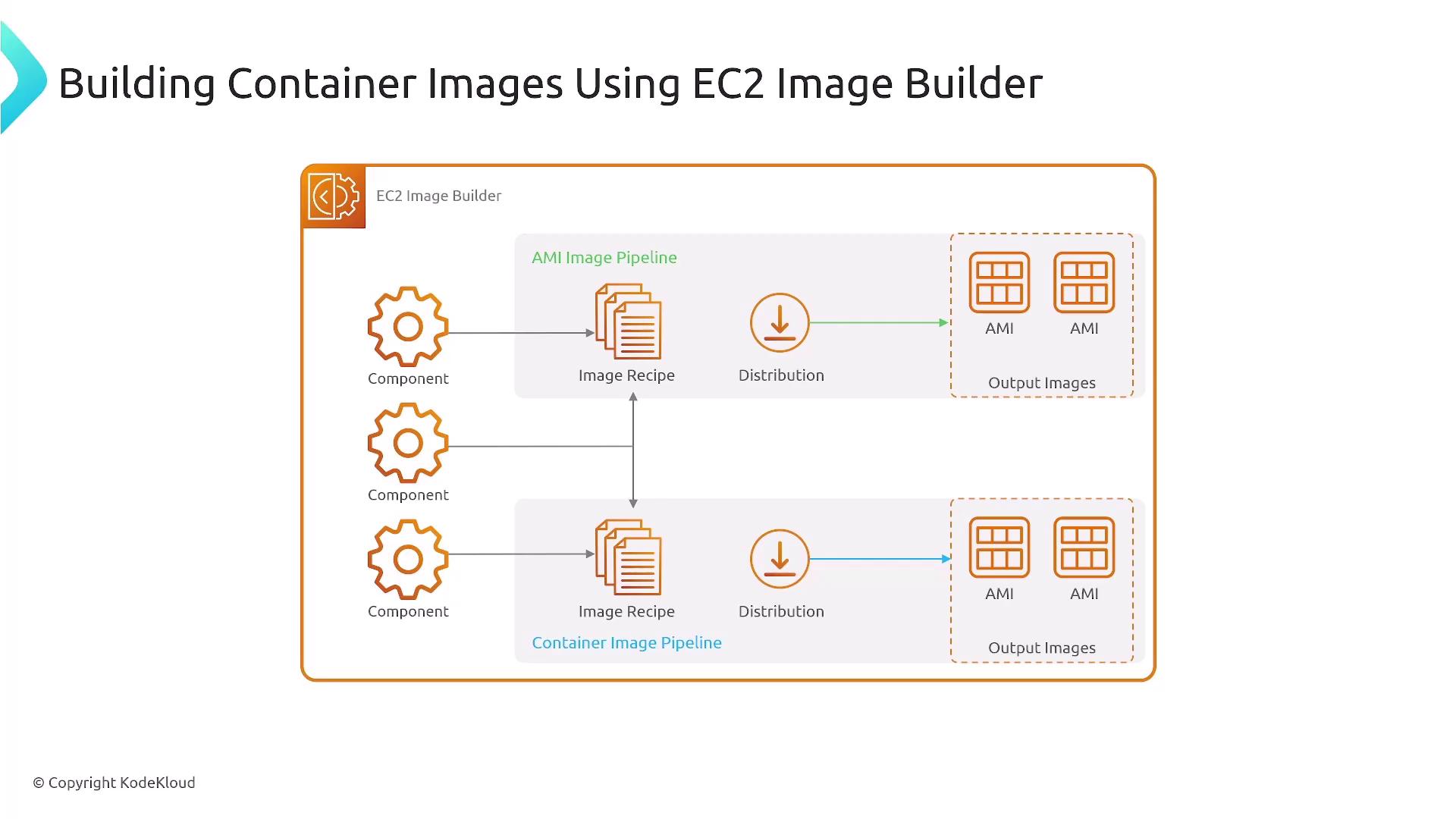
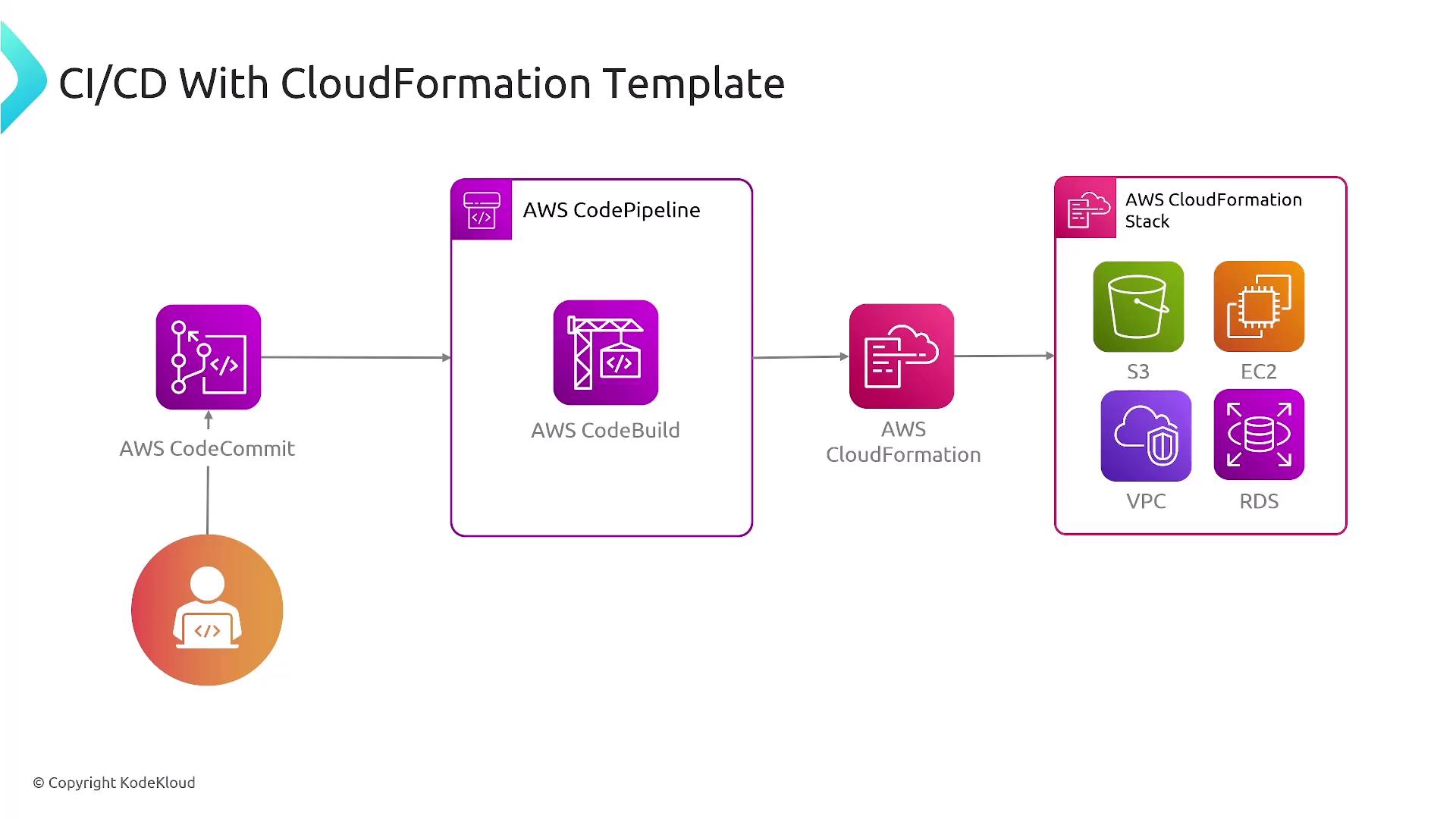
AWS CloudFormation
AWS CloudFormation allows you to define and provision AWS infrastructure using JSON or YAML templates. It supports nested stacks, which help manage complex deployments by breaking them into modular components. Below is an example CloudFormation template that demonstrates defining an EC2 instance: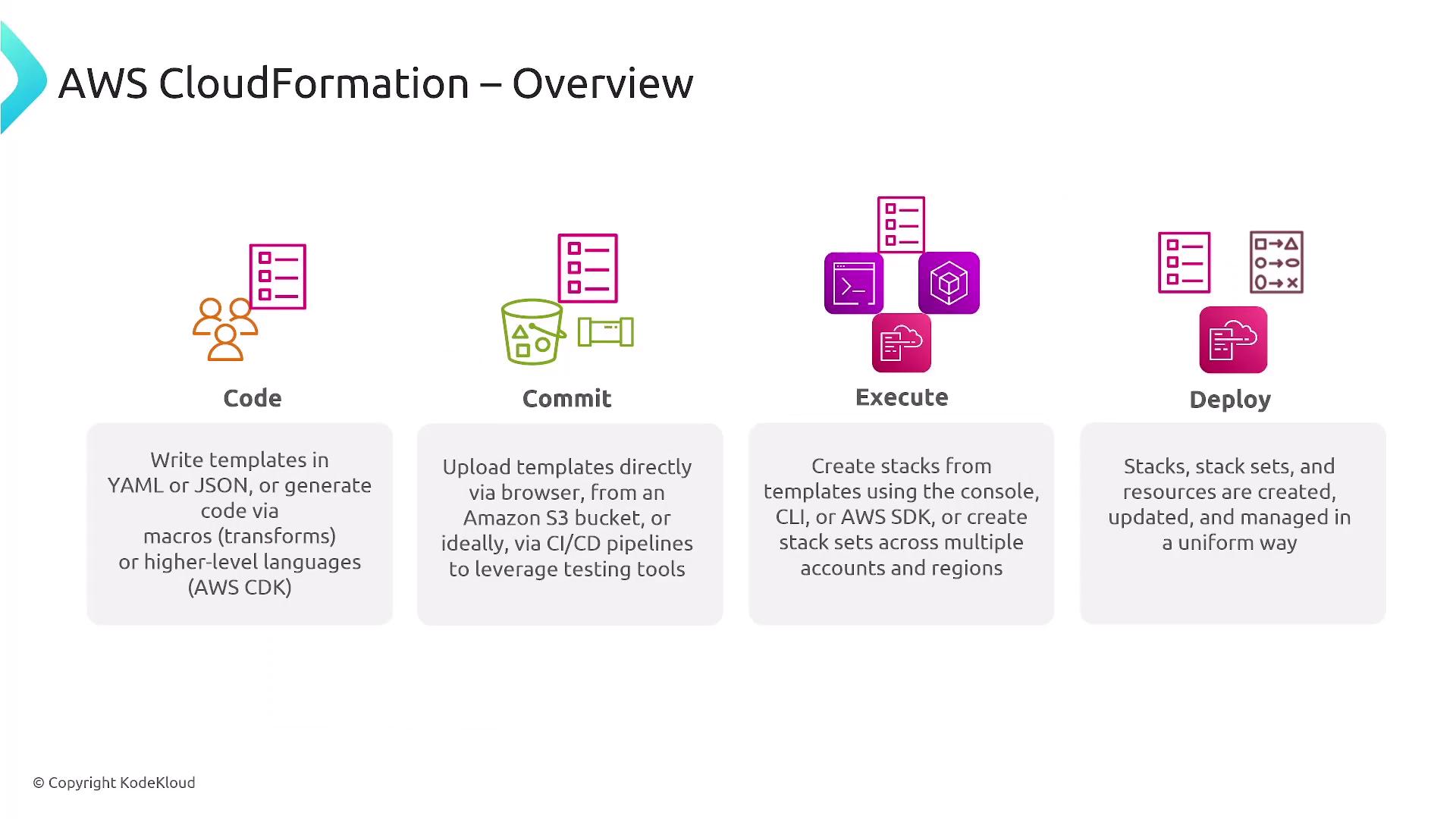
Regional Deployment and StackSets
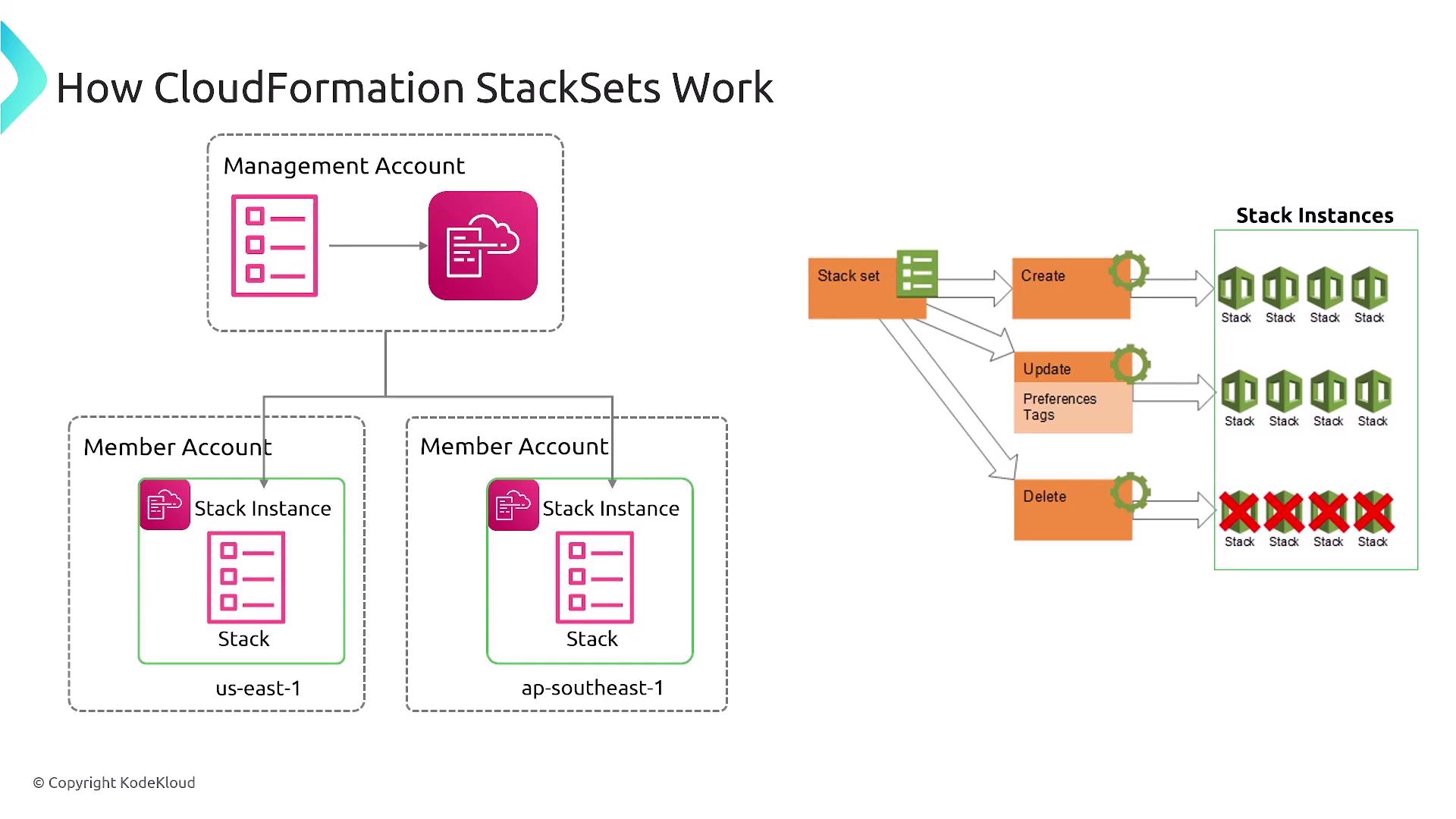
For organizations operating in multiple geographic regions, designing templates that support regional deployment is crucial. AWS CloudFormation StackSets enable you to deploy approved stacks across various accounts and regions efficiently.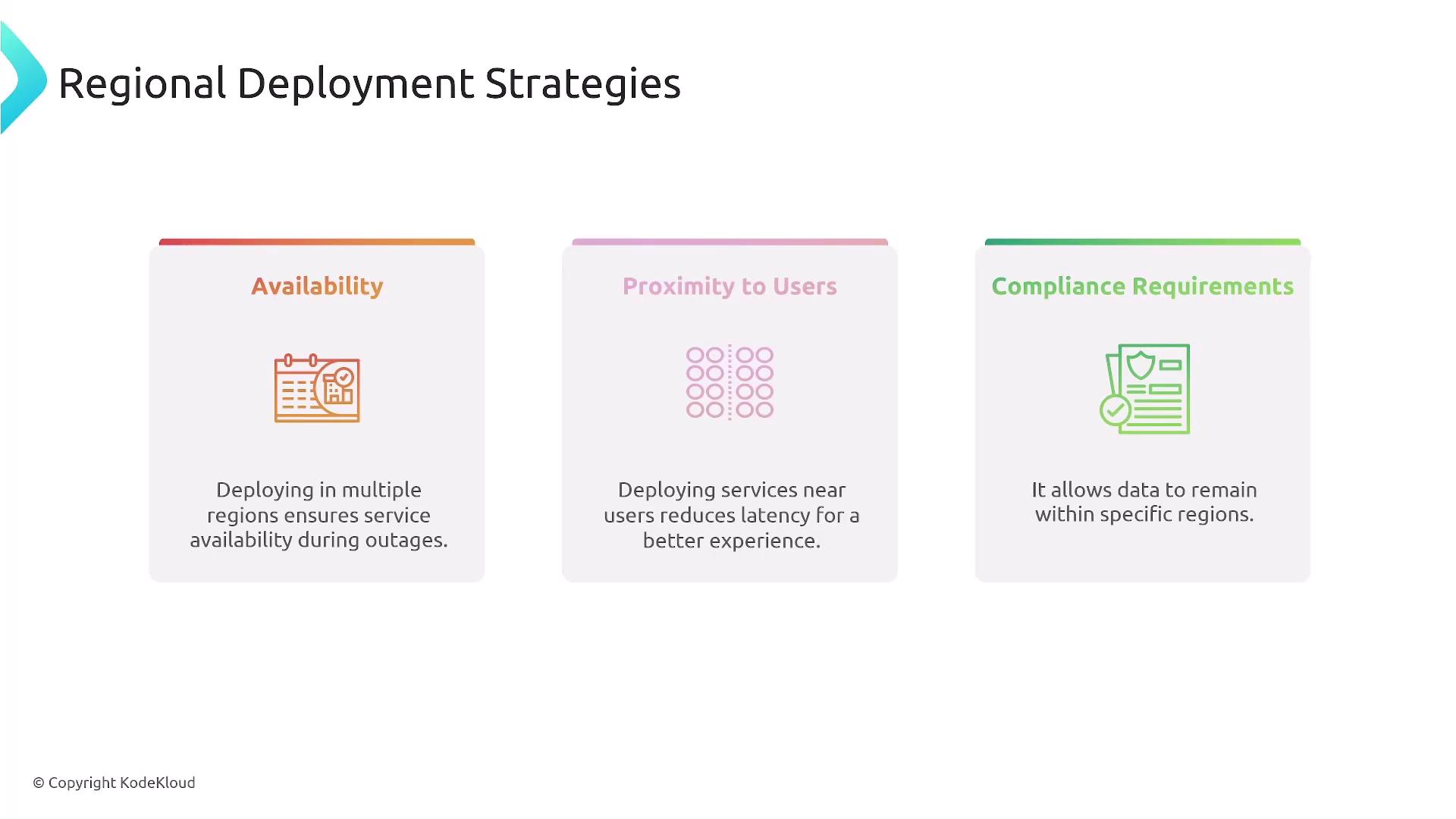
AWS Resource Access Manager (RAM)
AWS Resource Access Manager (RAM) facilitates resource sharing across AWS accounts. It allows you to create resource shares, specify which resources are included, and manage access permissions. When sharing resources across accounts, ensure that recipients accept the invitation to gain access. The guide below provides a visual step-by-step process for using AWS RAM: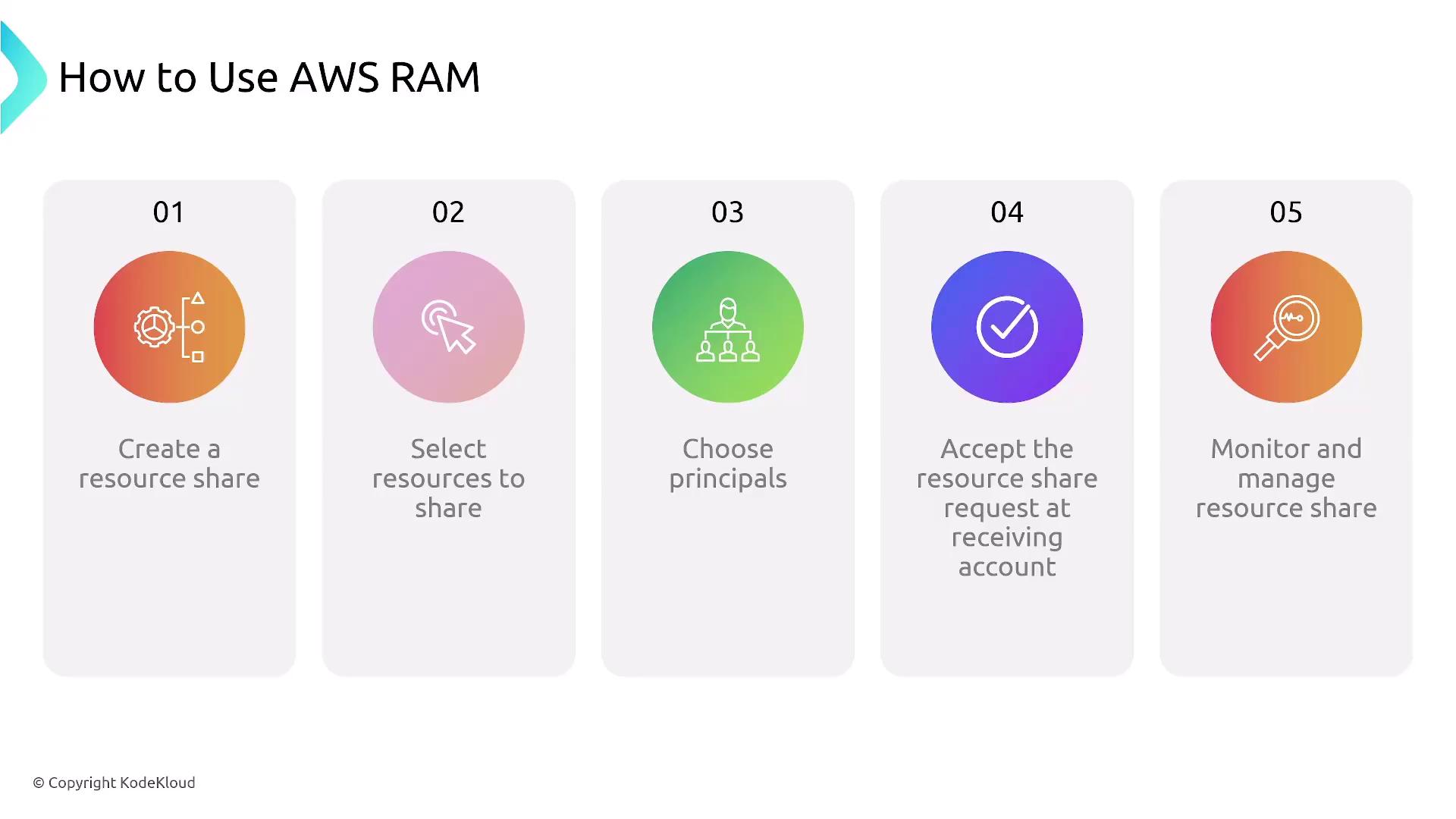
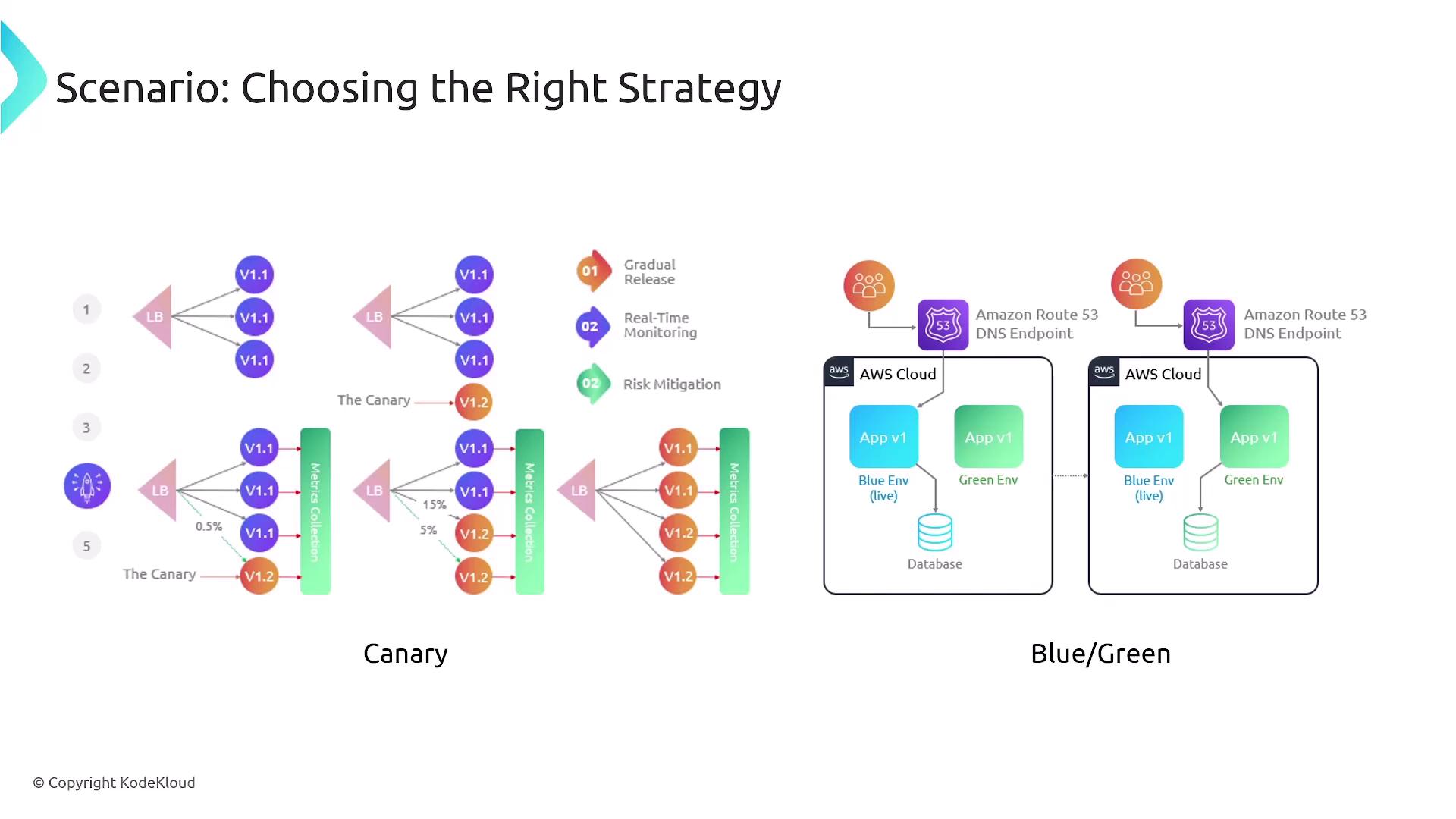
Deployment Strategies
Implementing effective deployment strategies is vital for minimizing risk during application updates. The two primary strategies highlighted include:- Canary Deployment: Initially route a small percentage of traffic to the new deployment. Traffic is gradually increased as confidence in the release builds.
- Blue-Green Deployment: Maintain two separate environments (blue for the current version and green for the new version), switching traffic only once the green environment is fully verified.
- All-at-Once: Replace the current version instantly.
- Linear: Deploy incrementally at fixed intervals (e.g., 10% every 10 minutes).
- Canary: Gradually increase the traffic based on stability confirmation.

Addressing Deployment Issues
A common challenge during deployments is configuration drift, where the deployed state deviates from the defined template. To mitigate this, employ monitoring and observability tools such as:- AWS CloudWatch
- Managed Prometheus
- Container Insights
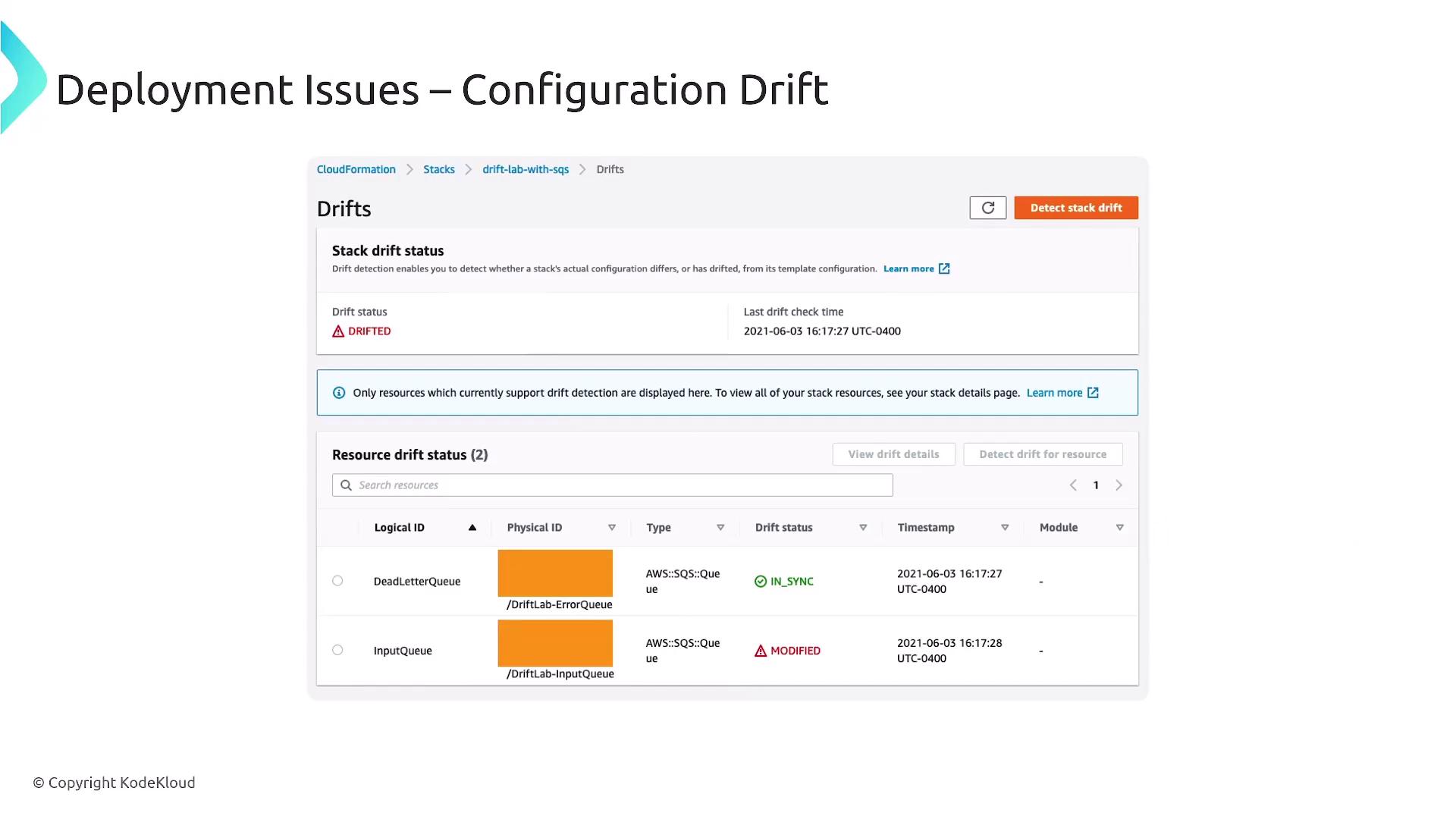
Regular monitoring is essential to detect configuration drift early and maintain service reliability.