AWS Versioning in S3
When versioning is enabled on an S3 bucket, every time you upload a new or updated file, AWS saves it as a unique version while keeping previous versions intact. For instance, if a file is updated, the new version becomes the current one, yet the earlier version is preserved. As additional versions are added—such as a third version marked in orange—the most recent upload remains active while all prior versions are retained.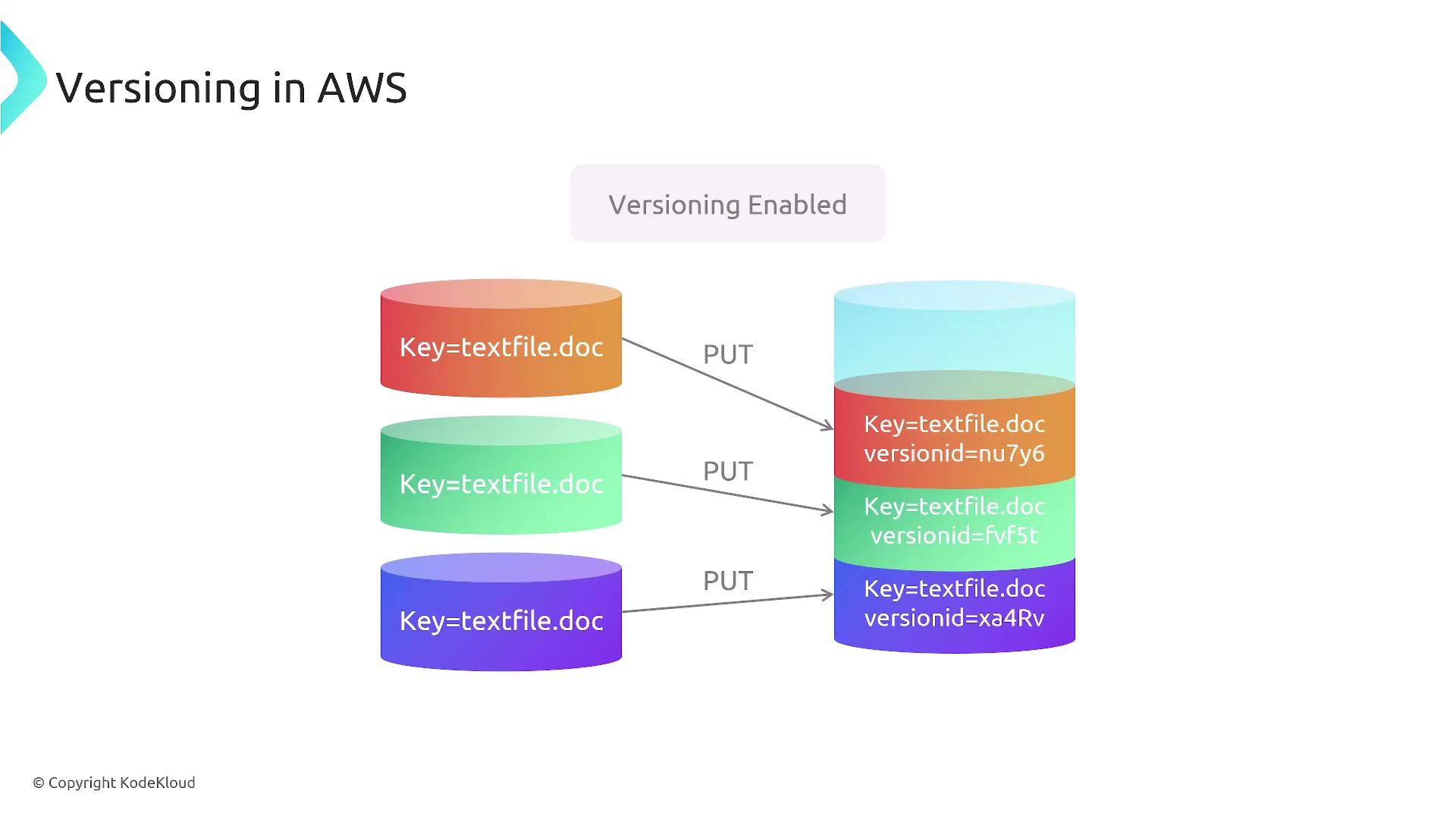
Enabling versioning in S3 offers significant benefits including straightforward data recovery and protection against inadvertent overwrites, while also maintaining an audit trail for every modification.
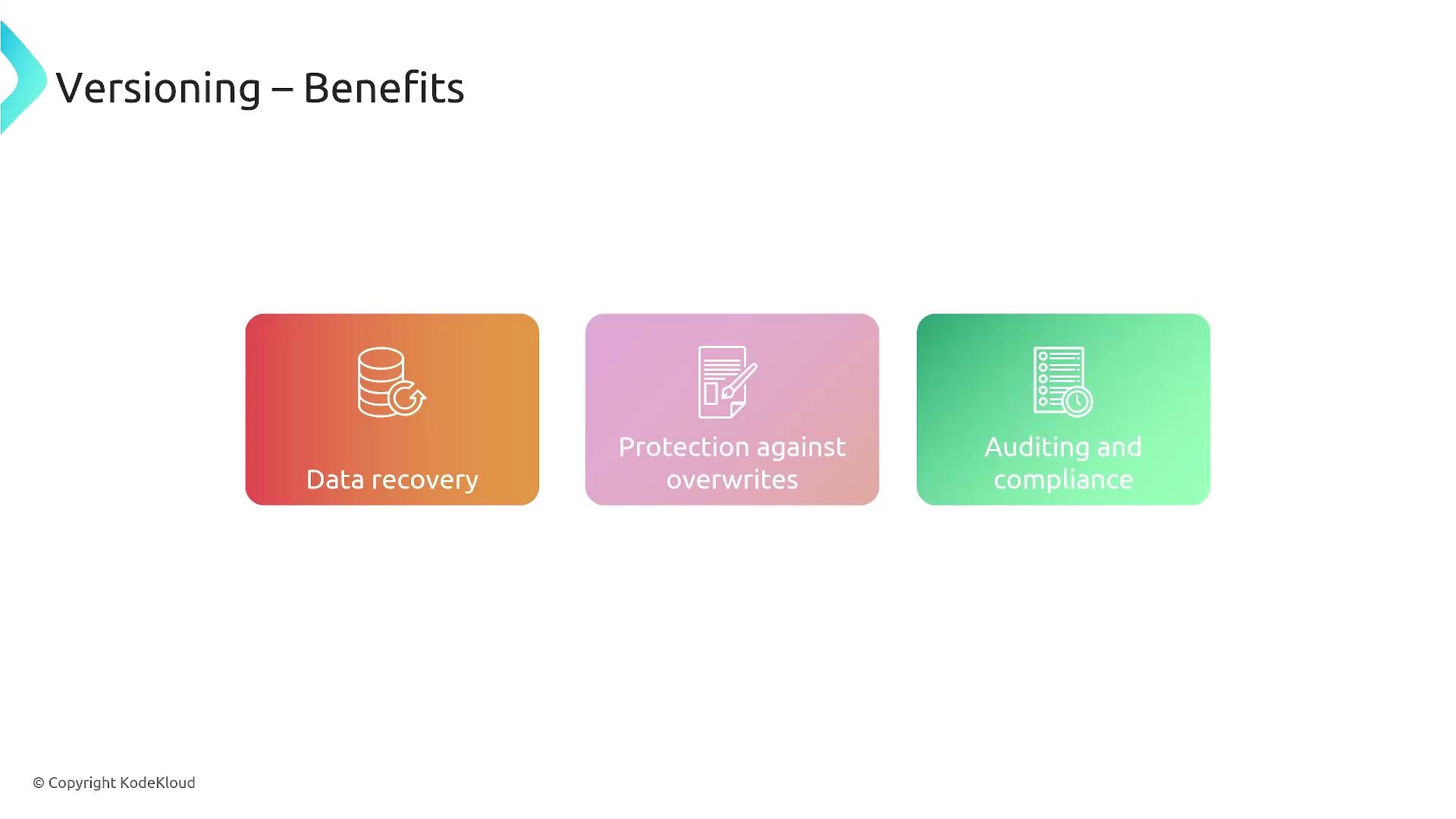
Benefits of Versioning
Versioning delivers multiple advantages:- Easy recovery of previous file versions.
- Prevention of accidental or intentional overwrites.
- Comprehensive audit trails that support compliance, especially useful when object locks are not in place.
Lifecycle Management in AWS
Lifecycle management complements versioning by helping you control storage costs and manage data efficiently. With lifecycle rules, you can transition objects from high-performance hot storage to more economical cold storage tiers. For example, a frequently accessed object in S3 (stored in standard hot storage) can be moved to Glacier for long-term archival after it reaches a set age. For context, the standard S3 hot tier costs approximately 1 per terabyte for Glacier. AWS provides seven different storage classes, allowing you to balance performance and cost according to your needs. Lifecycle rules also let you automate the expiration and deletion of objects, such as temporary files that only need to be retained for 30 or 60 days.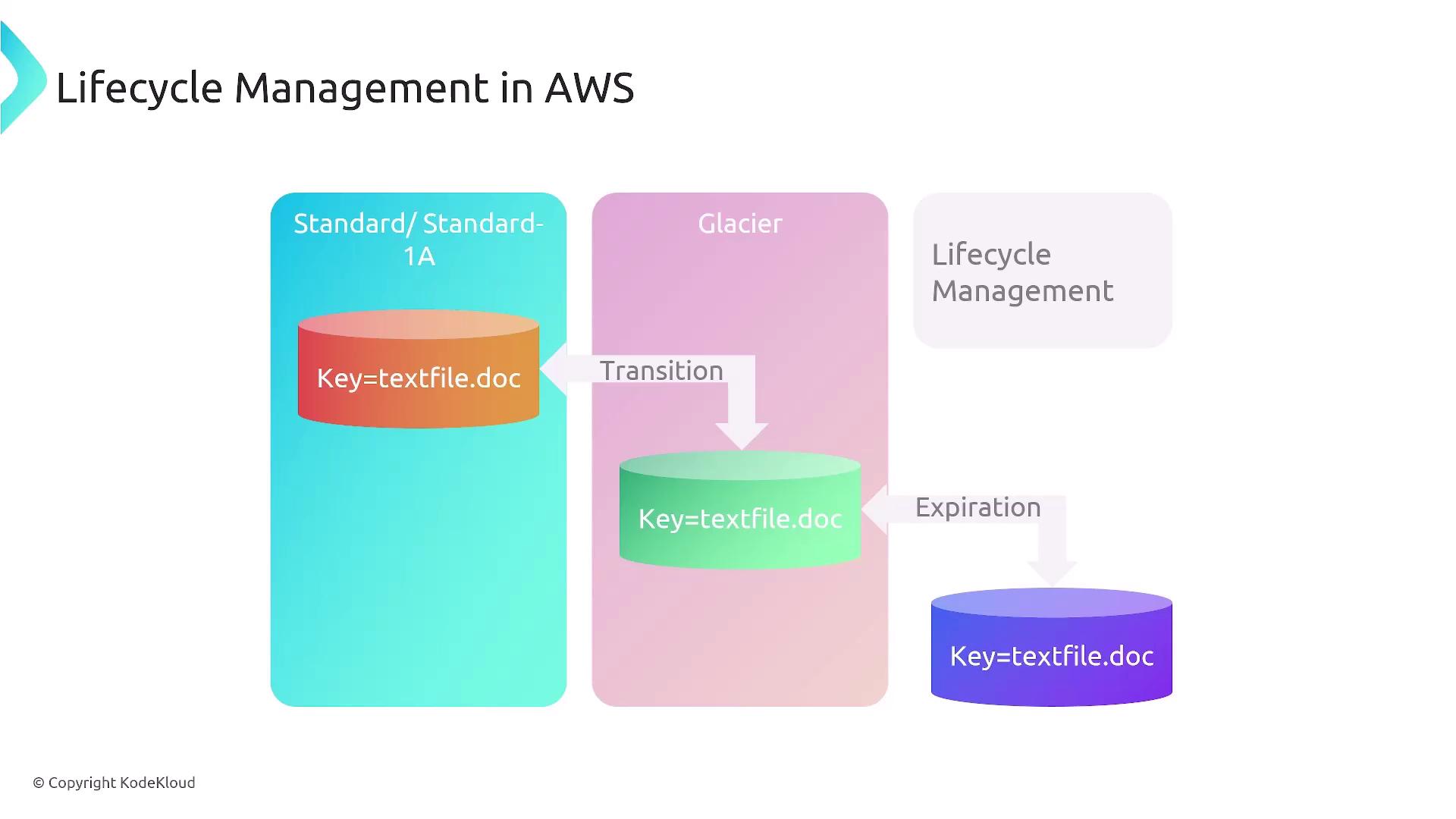
Implementing lifecycle management not only reduces storage costs by transitioning infrequently accessed data to cheaper tiers but also helps maintain compliance by automatically removing outdated or temporary resources.
Combining Versioning and Lifecycle Management
Utilizing both versioning and lifecycle management creates a robust file management strategy in AWS. This combination ensures that:- Every change is tracked and auditable.
- Files are automatically moved to cost-effective storage classes over time.
- Outdated versions can be automatically expired to maintain cost efficiency and compliance.
Always ensure that your lifecycle policies are tested and validated in a non-production environment to avoid unintended data loss.
Additional AWS Services and Lifecycle Considerations
It is important to note that similar lifecycle management rules extend to other AWS services. Other solutions, such as databases, EFS, and DynamoDB, have their respective retention and transition policies. For instance, DynamoDB provides infrequent access tables as a cost-effective alternative for data that doesn’t require constant access.Table of AWS Storage Options
| AWS Storage Service | Use Case | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Amazon S3 | File storage with versioning and lifecycle management | Easy recovery, cost optimization, and auditability |
| Amazon EBS | Block storage for EC2 instances | Reliable, low-latency performance |
| Amazon Glacier | Long-term archival storage | Significant cost savings for infrequently accessed data |