CPU Utilization
Monitoring CPU utilization is critical. A consistently high CPU usage may indicate that your database instance is under heavy load. Depending on your configuration, you can:- Reboot or vertically scale a standard RDS instance.
- Add read replicas for Aurora or read-heavy workloads to distribute the load more effectively.
Regularly review CPU metrics to proactively address performance bottlenecks before they impact your application’s availability.
Database Connections
Keeping track of the number of open database connections via Amazon CloudWatch helps you detect potential issues such as connection leaks or too many simultaneous connection attempts. One effective way to address this is by using RDS Proxy, which establishes a fixed number of connections to your RDS database and efficiently handles new connection requests.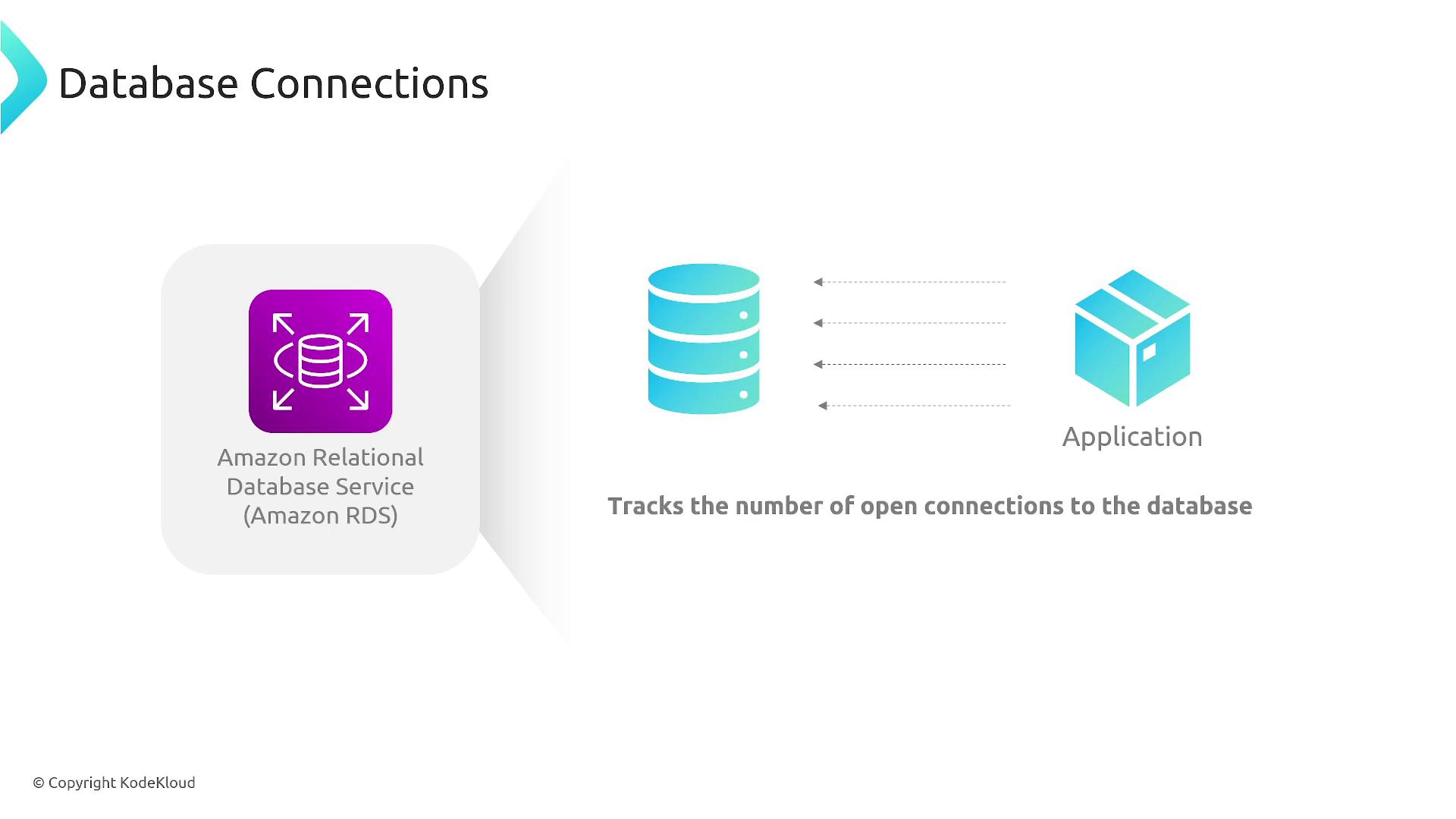
Implement RDS Proxy to prevent connection overload and ensure smoother application performance.
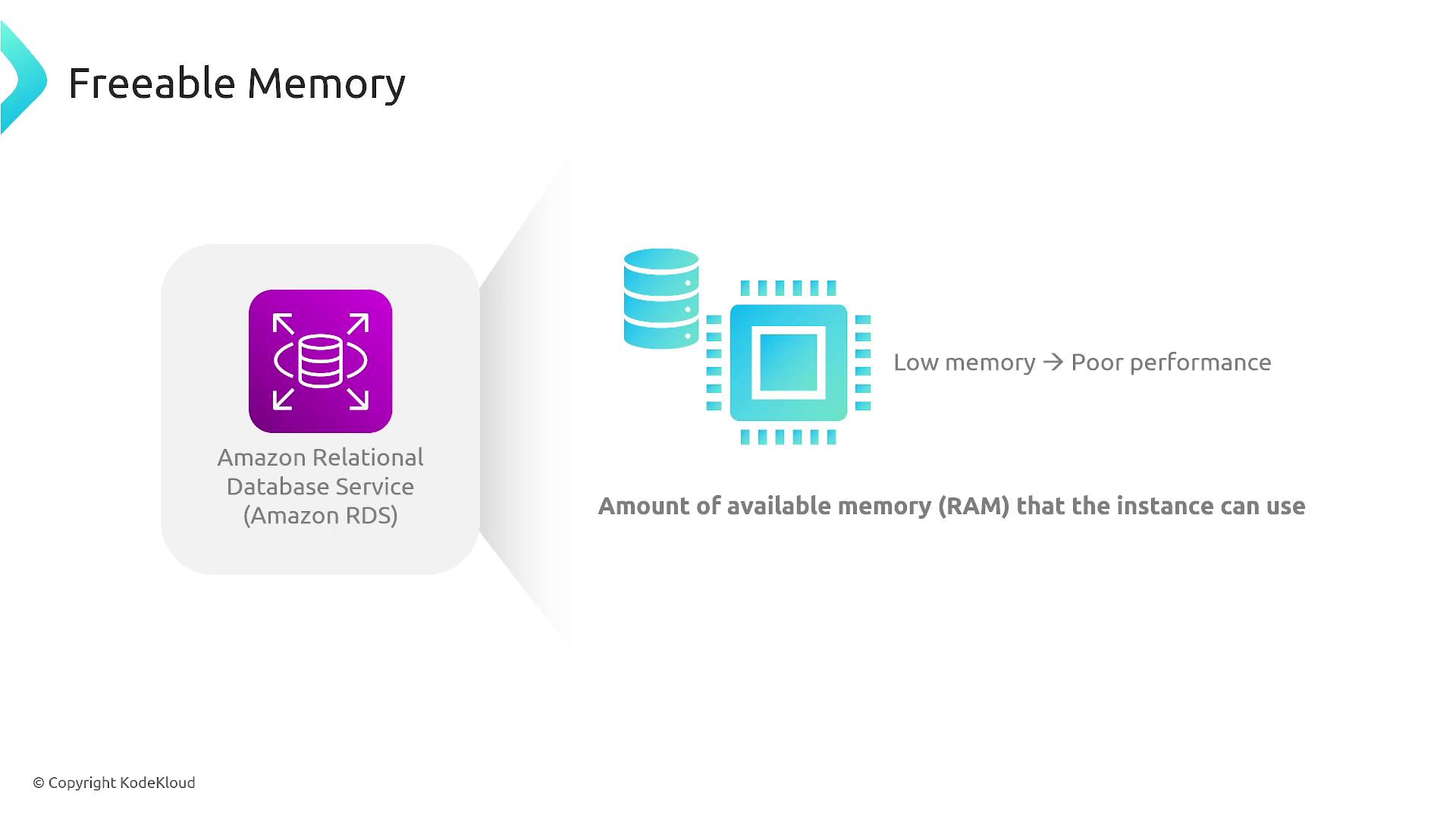
Freeable Memory
Freeable memory represents the available RAM on your database instance. Insufficient memory can lead to performance degradation. Consider the following strategies to manage freeable memory:- Upsize your instance if memory consumption is high due to write-heavy operations.
- Offload specific indexes or operations to a read replica in environments with predominantly read-heavy workloads.
I/O Performance
Evaluating I/O performance is essential for maintaining a responsive database. Key I/O metrics include:- Number of read and write operations
- Write IOPS
- Read and write latency
- Upgrade your disk performance
- Provision additional IOPS
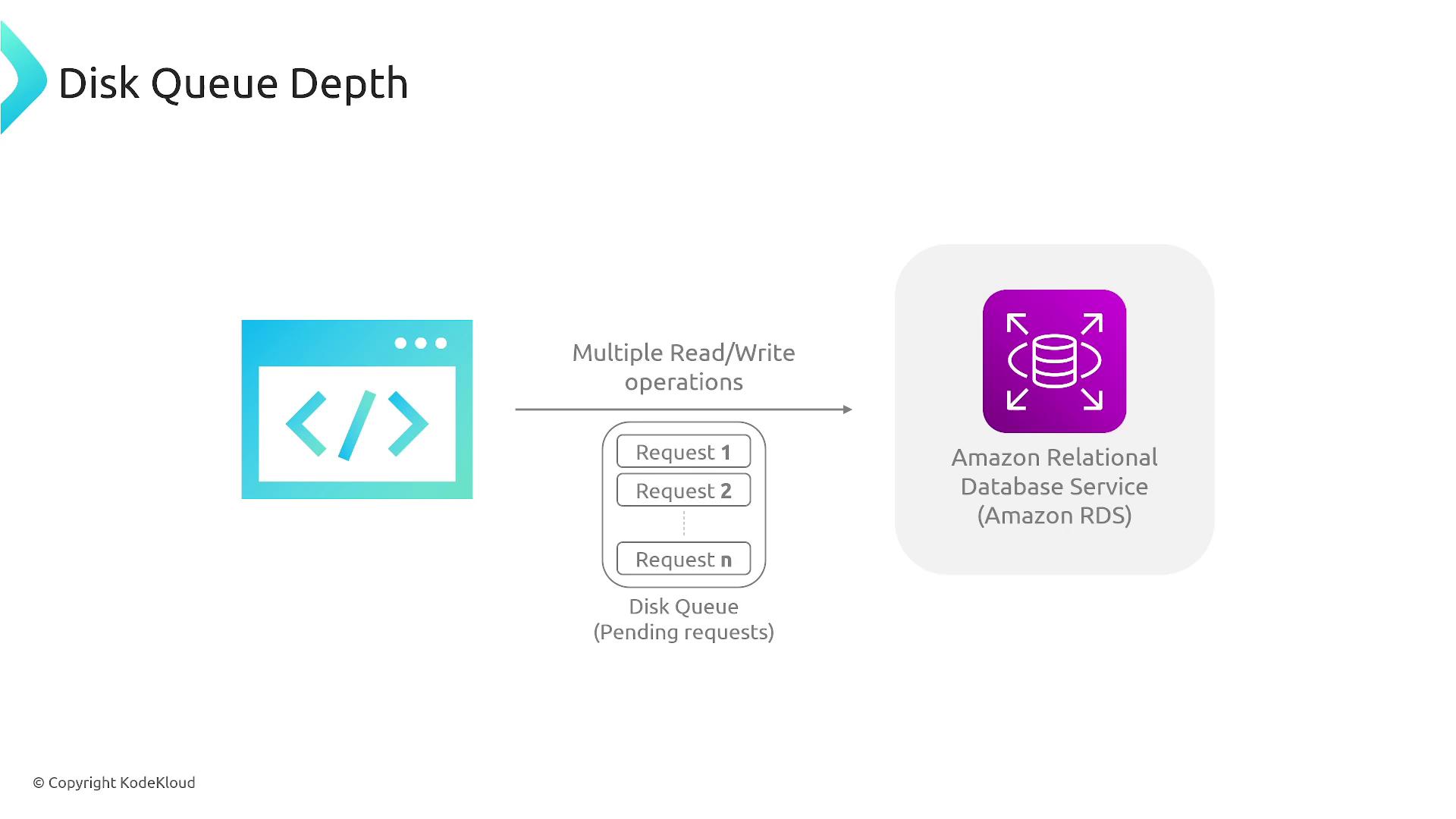
A consistently high disk queue depth can lead to severe performance bottlenecks. It’s important to address disk I/O limitations before they affect critical operations.