Hosted Zones
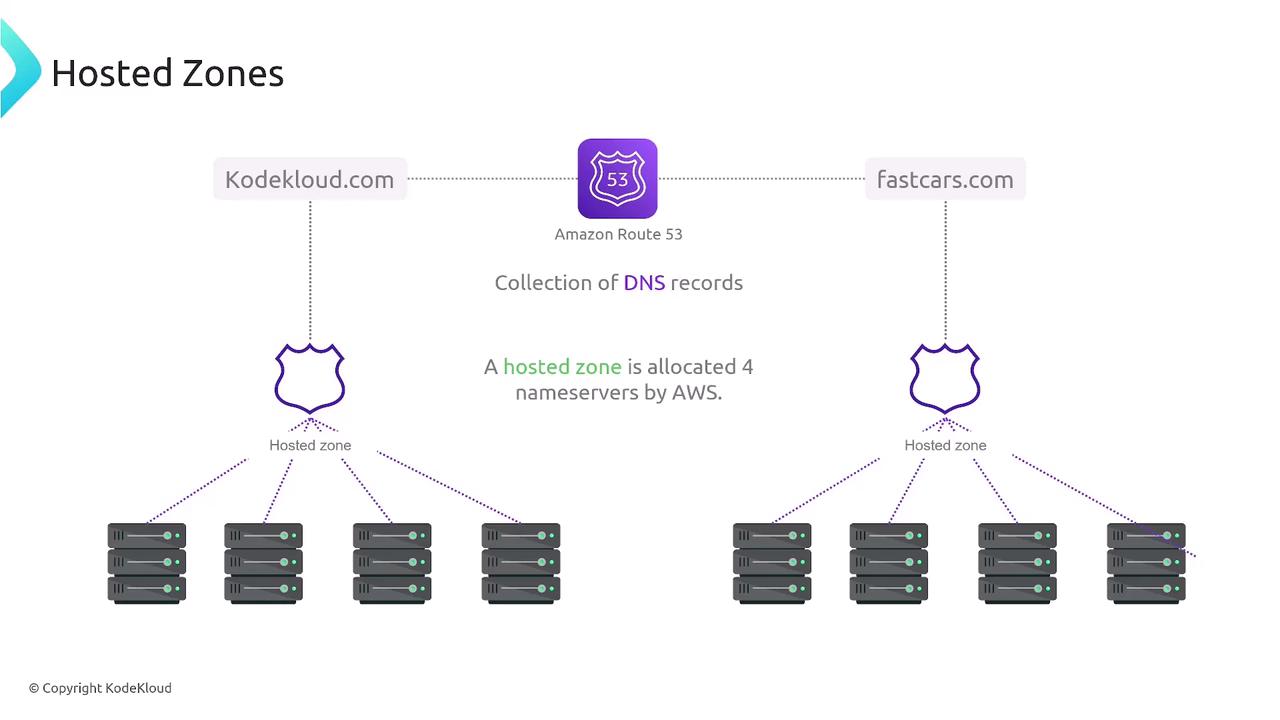
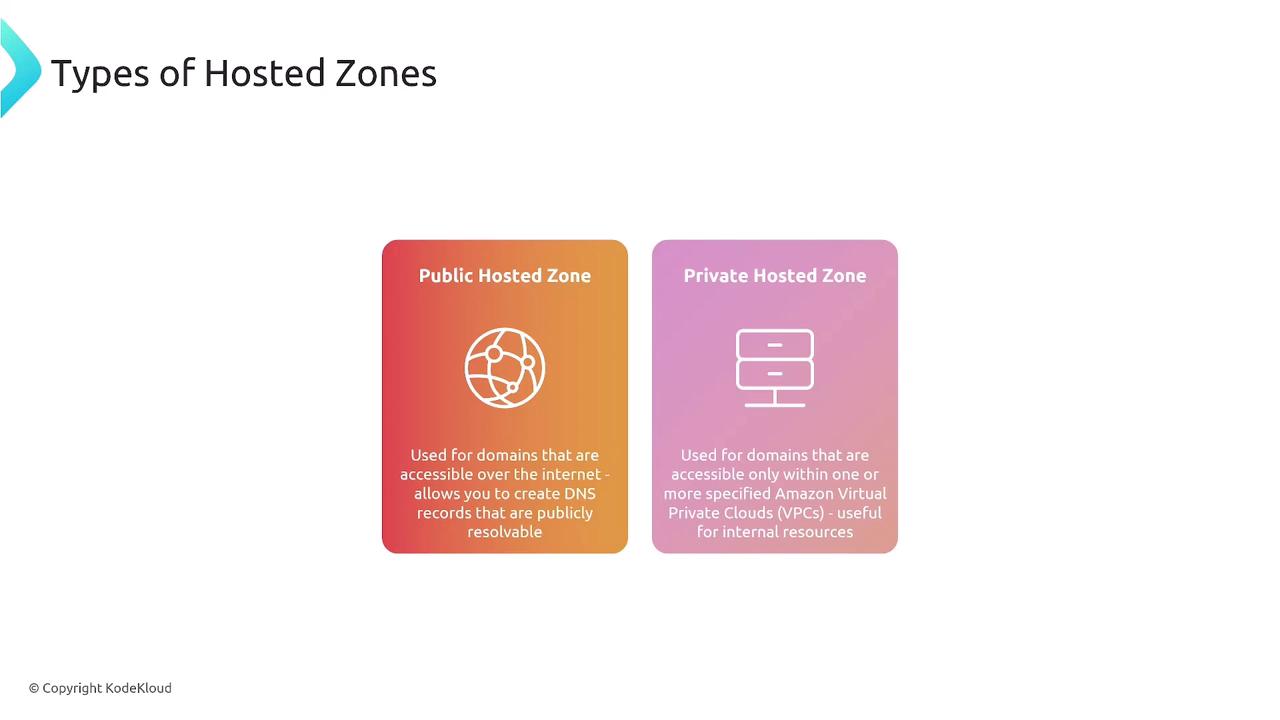
A hosted zone in Route 53 is a container that stores the DNS records for a specific domain and all its subdomains. It acts as a management boundary for routing the traffic for a domain. Hosted zones come in two flavors:- Public Hosted Zones: Designed for domains with internet-accessible records.
- Private Hosted Zones: Configured for use within specific Amazon VPCs or corporate networks, ideal for internal name resolution.
Types of Hosted Zones
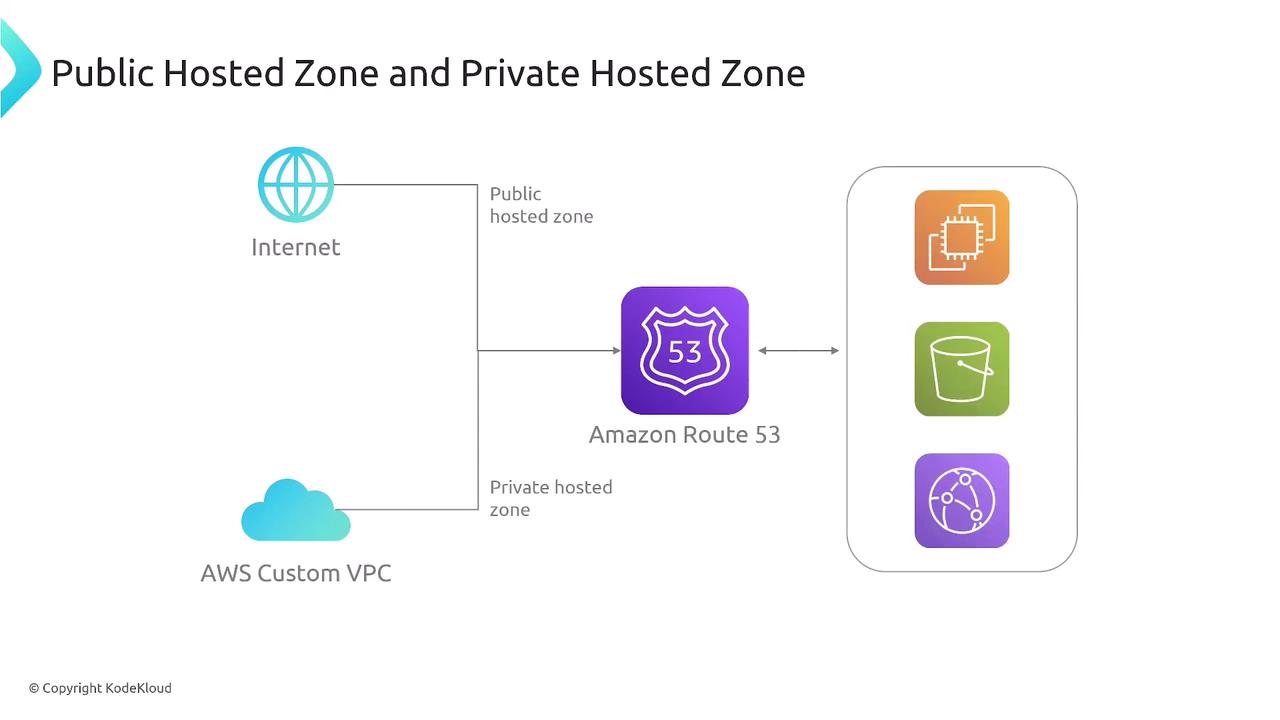
- Public Hosted Zone: Suitable for websites and applications intended for public access.
- Private Hosted Zone: Ideal for internal networks, allowing you to segregate internal traffic from public DNS queries.
You can configure separate public and private hosted zones for the same domain, enabling different IP resolutions based on whether the query originates from within your network or from the public internet.
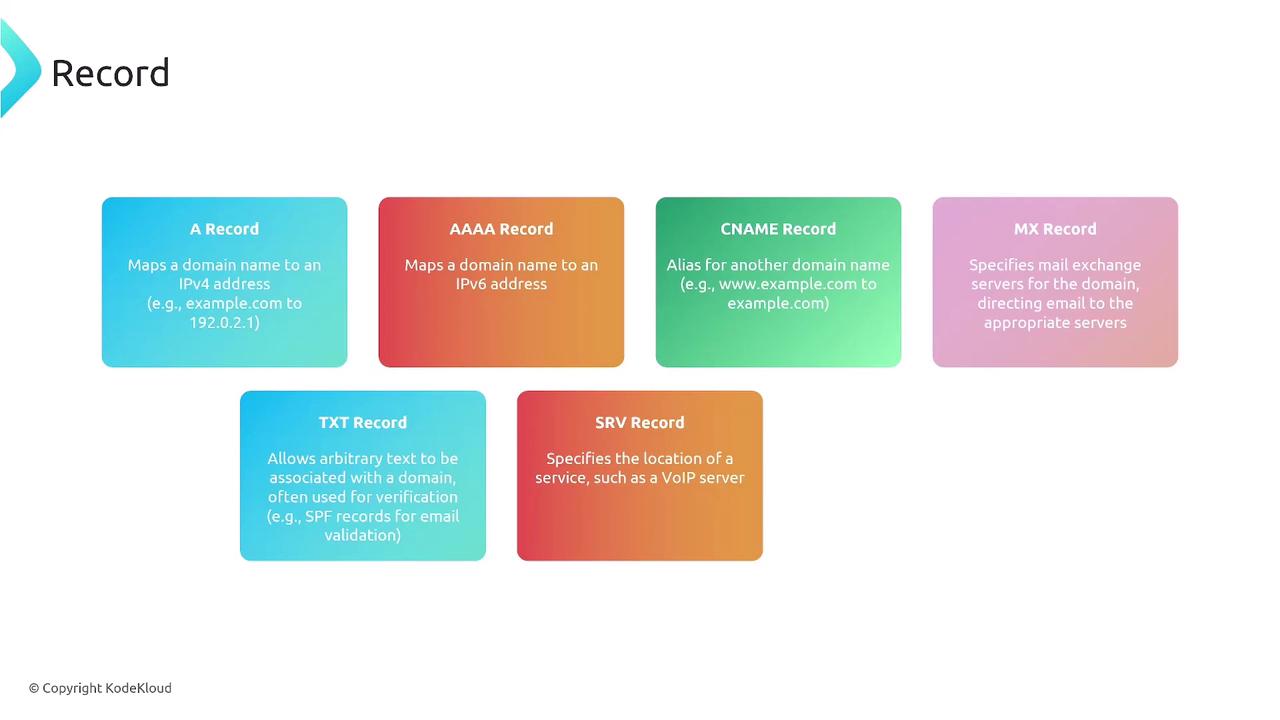
DNS Record Types
Once you have a hosted zone, you can define how your domain resolves by setting up various DNS record types. Here is an overview of the common records used in Route 53:- A Record: Maps a domain or subdomain (e.g., example.com or sub.example.com) to an IPv4 address.
- AAAA Record: Maps a domain or subdomain to an IPv6 address.
- CNAME Record: Creates an alias from one domain name to another, useful for domain redirection.
- MX Record: Identifies the mail servers responsible for handling email for the domain.
- TXT Record: Used for domain verification and authentication purposes (commonly required by services like Google Workspace or Office 365).
- SRV Record: Indicates the locations of specific services, such as VoIP or messaging servers.
- PTR Record: Facilitates reverse DNS lookups, mapping an IP address back to a domain name.

The DNS resolution process is universal, serving as the backbone for how domains are linked to their resources across the internet—not just within AWS.