Understanding AWS Read Replicas
Consider an RDS database instance configured with asynchronous replication to a read replica. In configurations without multi-AZ support—such as single-instance deployments—the system employs asynchronous replication. Although this may introduce replication lag, the primary database always maintains read/write capability, while the read replica remains read-only. The primary benefit of this setup is that you can interrupt asynchronous replication to promote the read replica, turning it into a standalone database with full read/write functionality. This process is ideal for offloading read operations, scaling capacity, and ensuring data redundancy through controlled replication.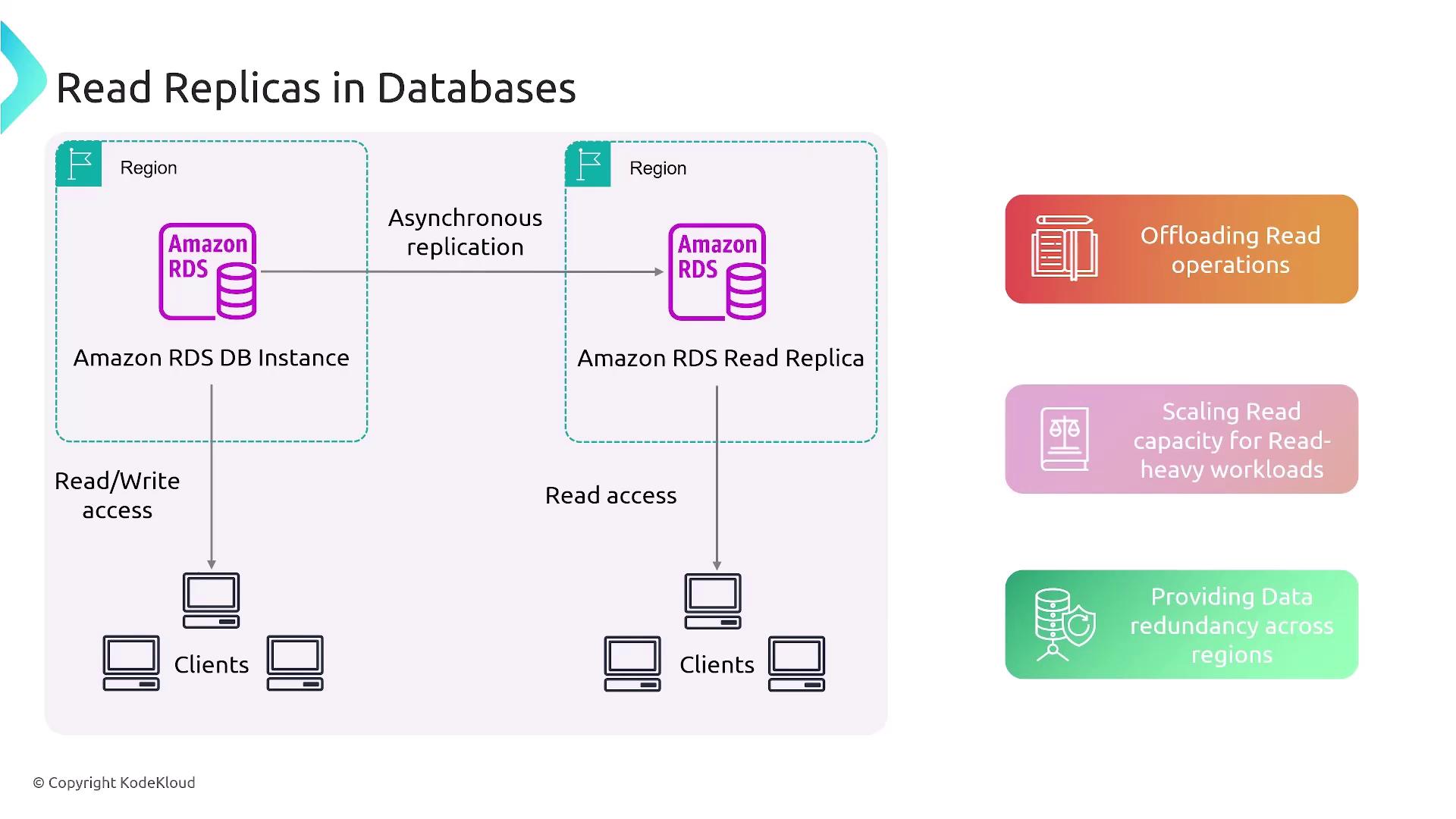
Differences in Multi-AZ Deployments
In multi-AZ configurations, the setup behaves differently. For multi-AZ cluster deployments:- Secondary instances are available for read operations.
- There is a dedicated mechanism to promote a secondary as the primary in the event of a failure.
In single-instance deployments that use multi-AZ, the secondary instance is inaccessible for direct reads because there is no dedicated URL provided.
Considerations for Standalone Read Replica Setups
For configurations utilizing pure read replicas (i.e., those not part of a multi-AZ deployment), it remains essential to maintain a robust backup strategy. Read replicas are not substitutes for backups; they do not capture point-in-time snapshots. Backups are indispensable for recovering from data corruption or unexpected failures. Before promoting a read replica, follow these precautions:- Pause write transactions on the primary database to minimize data inconsistencies.
- Set the read-only parameter to zero in the database parameter group for the replica.
This adjustment allows you to perform modifications—such as creating indexes or executing DDL operations—on the replica prior to its promotion.

Steps to Promote a Read Replica
Follow these steps to successfully promote a read replica:- Verify that the replication state is current.
- Identify the appropriate read replica.
- Initiate the promotion process (commonly via a right-click action) to break the replication link.
- Provide any additional parameters needed, such as backup settings or adjustments to the parameter group.
- Monitor the process to ensure that replication has ceased and that the new primary database is functioning correctly.
