Configuration Drift
Configuration drift occurs when the deployed system configuration deviates from the originally specified state. This misalignment can cause unanticipated issues if not detected early. Many cloud management platforms offer drift detection features—for instance, you might find a “detect stack drift” option in the upper right-hand corner of the interface. This tool helps you pinpoint differences between the intended configuration and the actual deployment state.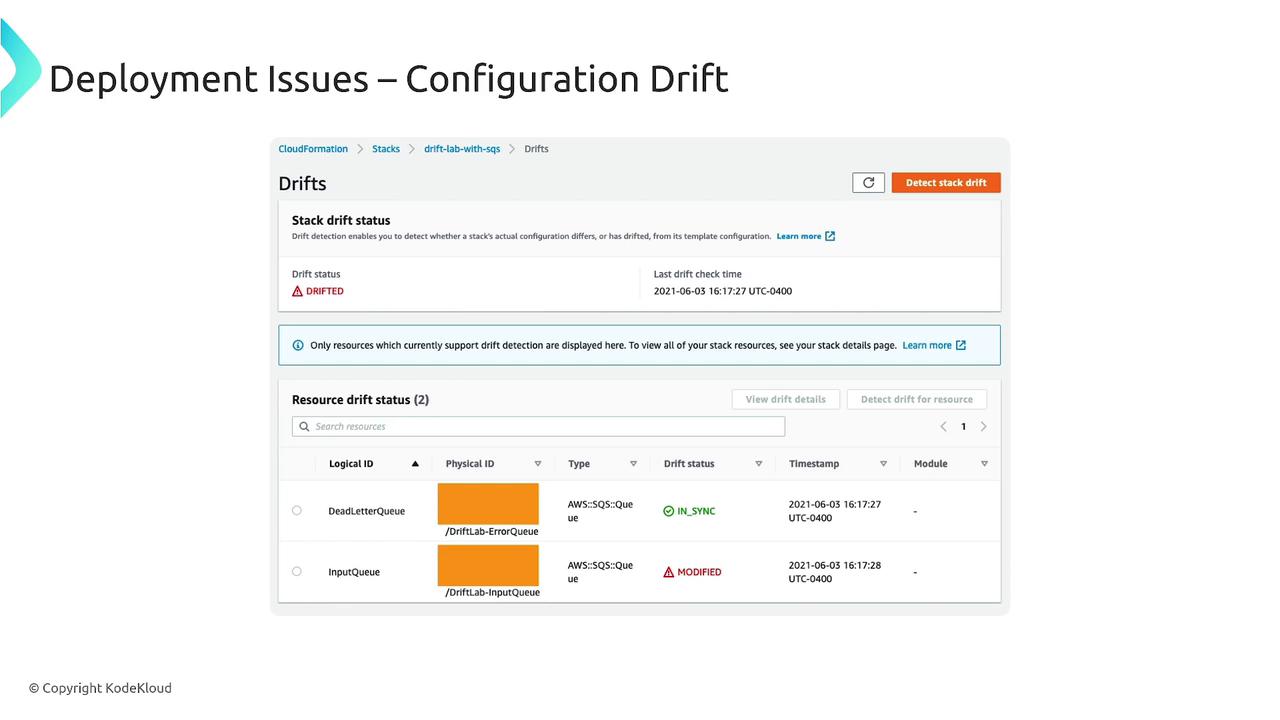
Monitoring configuration drift is crucial to ensure that your deployments remain consistent with the defined infrastructure-as-code.
Dependency Management
Modern applications heavily rely on third-party libraries and various internal services. Managing these dependencies effectively is essential both for application code and infrastructure setups. For code dependencies, package management services like CodeArtifact can be used to host and manage packages (e.g., npm packages). However, dependency conflicts can arise. For instance, the error below demonstrates a dependency resolution issue with npm:Consider using dependency management frameworks and orchestration tools to handle service start-up order and avoid conflicts.
Traffic Spikes and Scaling Challenges
Handling unexpected traffic surges is another common deployment challenge. When demand increases, a resilient system must scale to accommodate the additional load. Auto Scaling combined with load balancers dynamically adjusts the number of instances to meet traffic demands.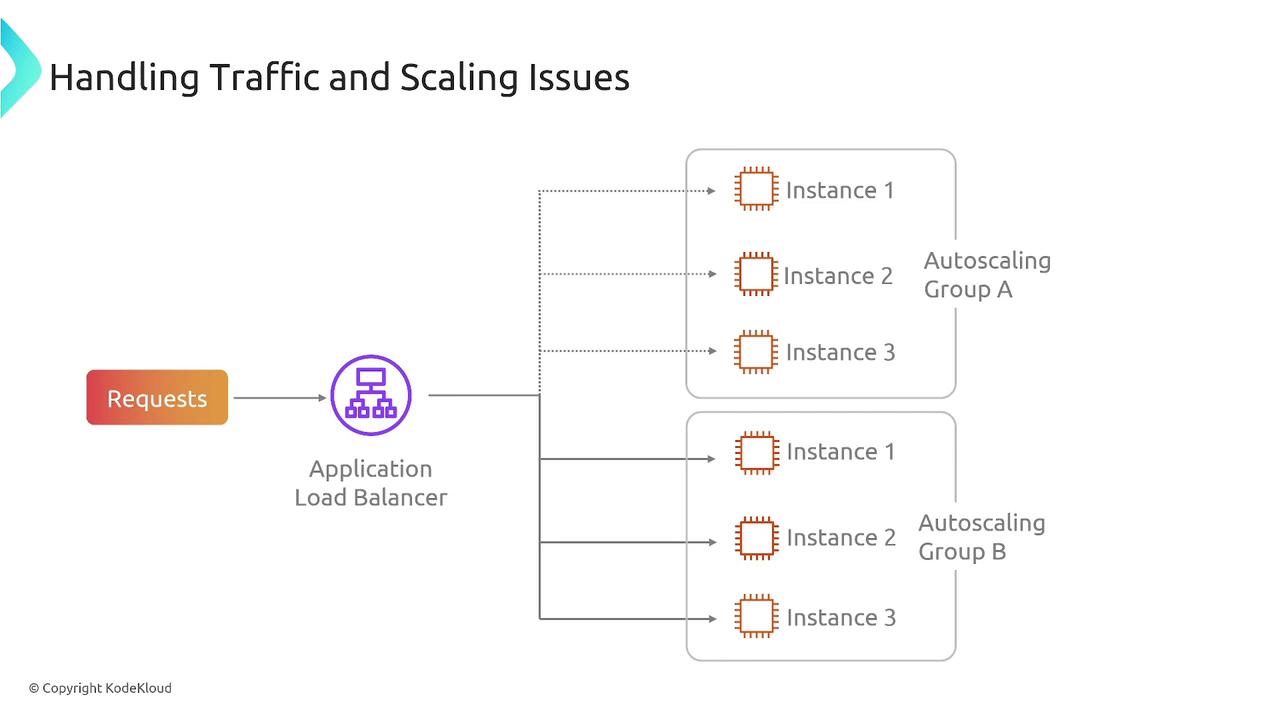
Deploy auto scaling policies that allow your system to adapt to varying traffic patterns automatically.
Rollback and Deployment Strategies
Managing rollbacks effectively is critical when deploying new software versions. Whether you’re using tools like CloudFormation or deploying serverless functions on AWS Lambda, having a clear rollback strategy ensures that you can quickly revert to a stable state if issues arise. For example, during a canary deployment, you might begin by directing only 10% of the traffic to the new version and gradually increase the exposure once confirmed stable. Decisions to either freeze the deployment or perform a rollback depend on real-time performance feedback.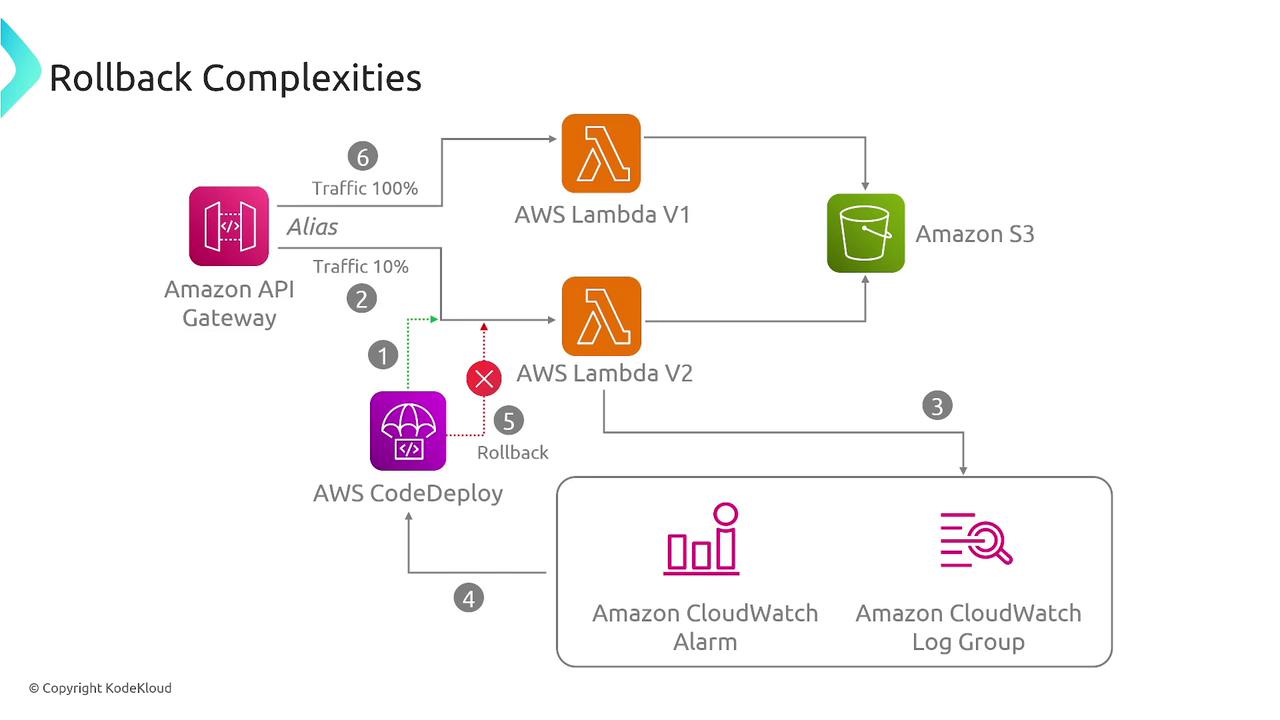
Always test your rollback procedures in a staging environment to ensure they work as expected during production failures.
Health Checks, Network, and Connectivity Issues
Maintaining overall system health extends beyond smooth deployment and scaling. Regular health checks are essential to ensure that microservices remain available and operate correctly. Network and connectivity problems—such as difficulties accessing message brokers or instances receiving imbalanced traffic—can severely hamper service quality.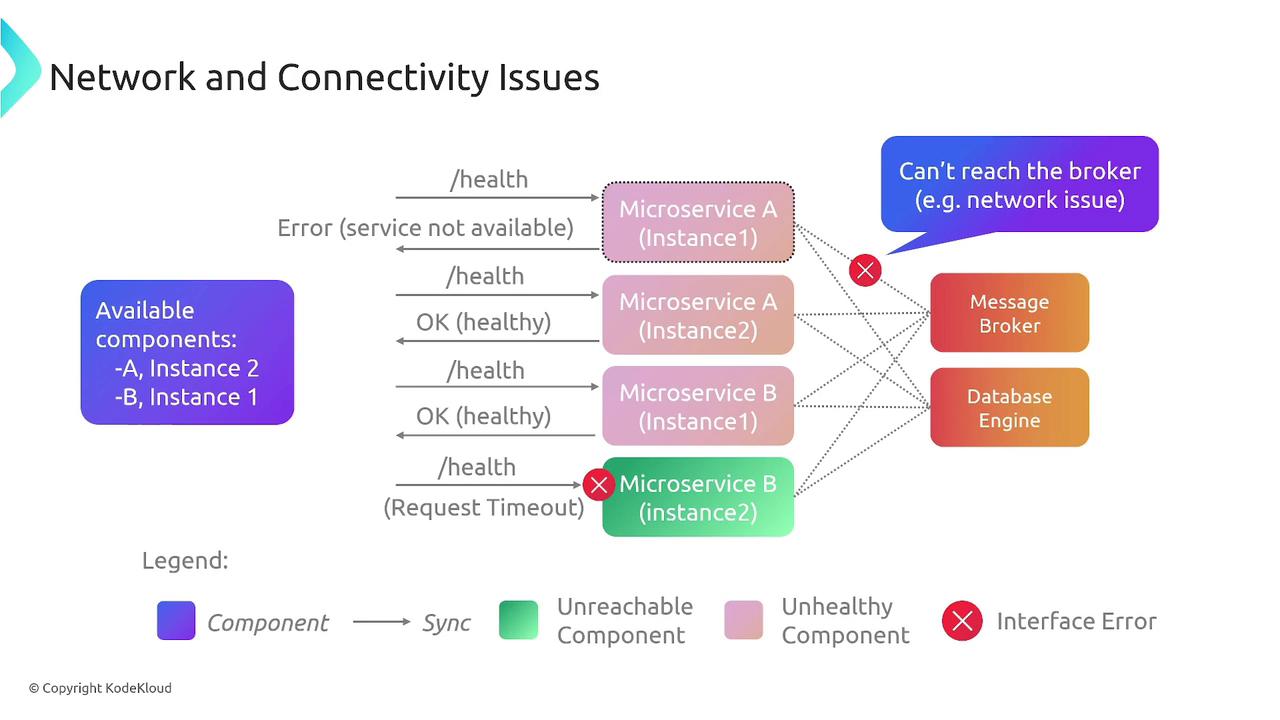
Implement robust monitoring and alerting systems to catch potential connectivity issues before they escalate.