- Checking runner status in the GitHub UI
- Diagnosing network connectivity
- Reviewing runner application logs
- Monitoring via systemd and journalctl
- Triggering and tracking workflows
- Updating runners and verifying Docker availability
1. Checking Runner Status in the GitHub UI
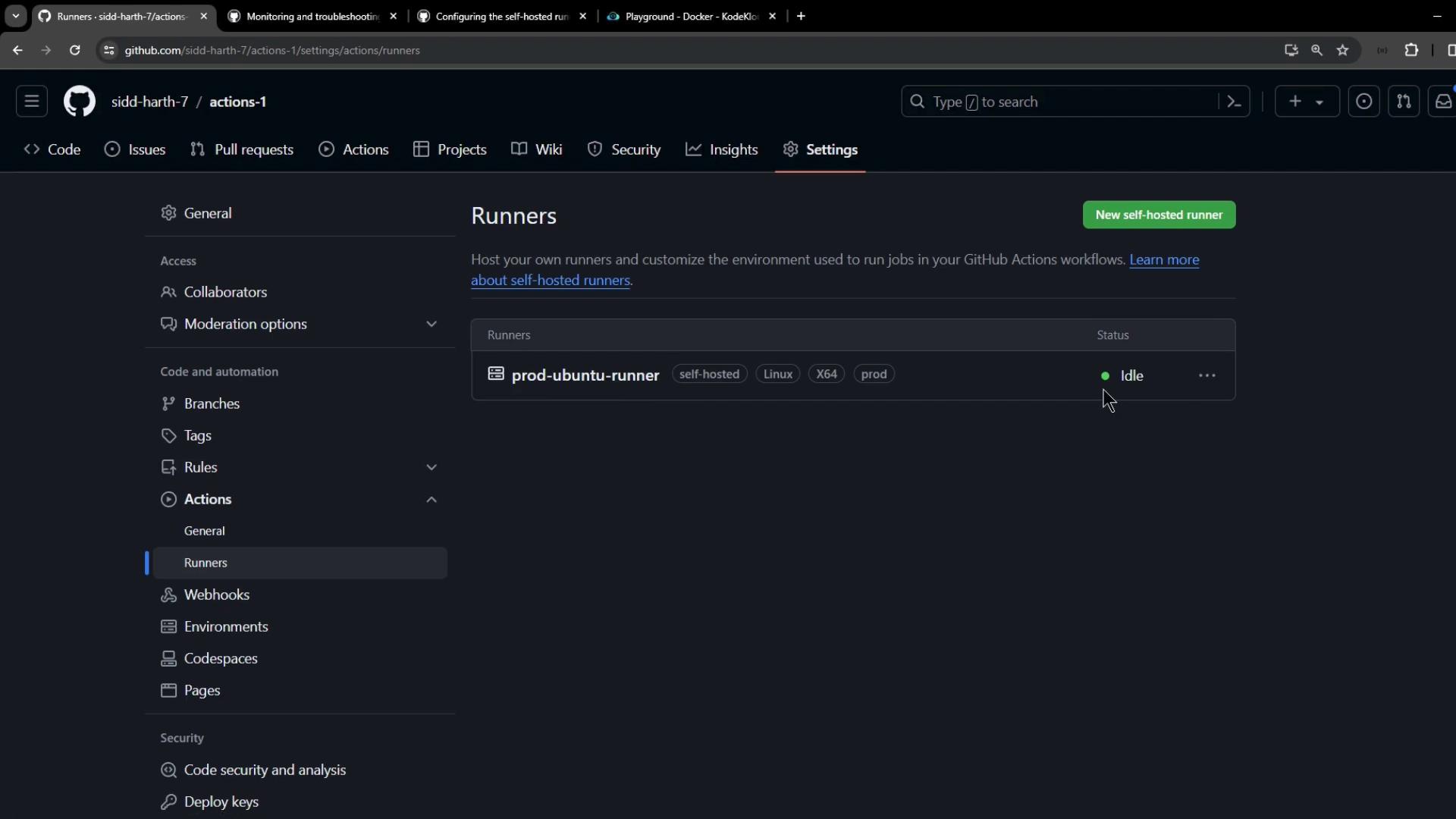
Navigate to Settings > Actions > Runners in your repository (or organization) to see all self-hosted runners, their labels, and their status:
prod:
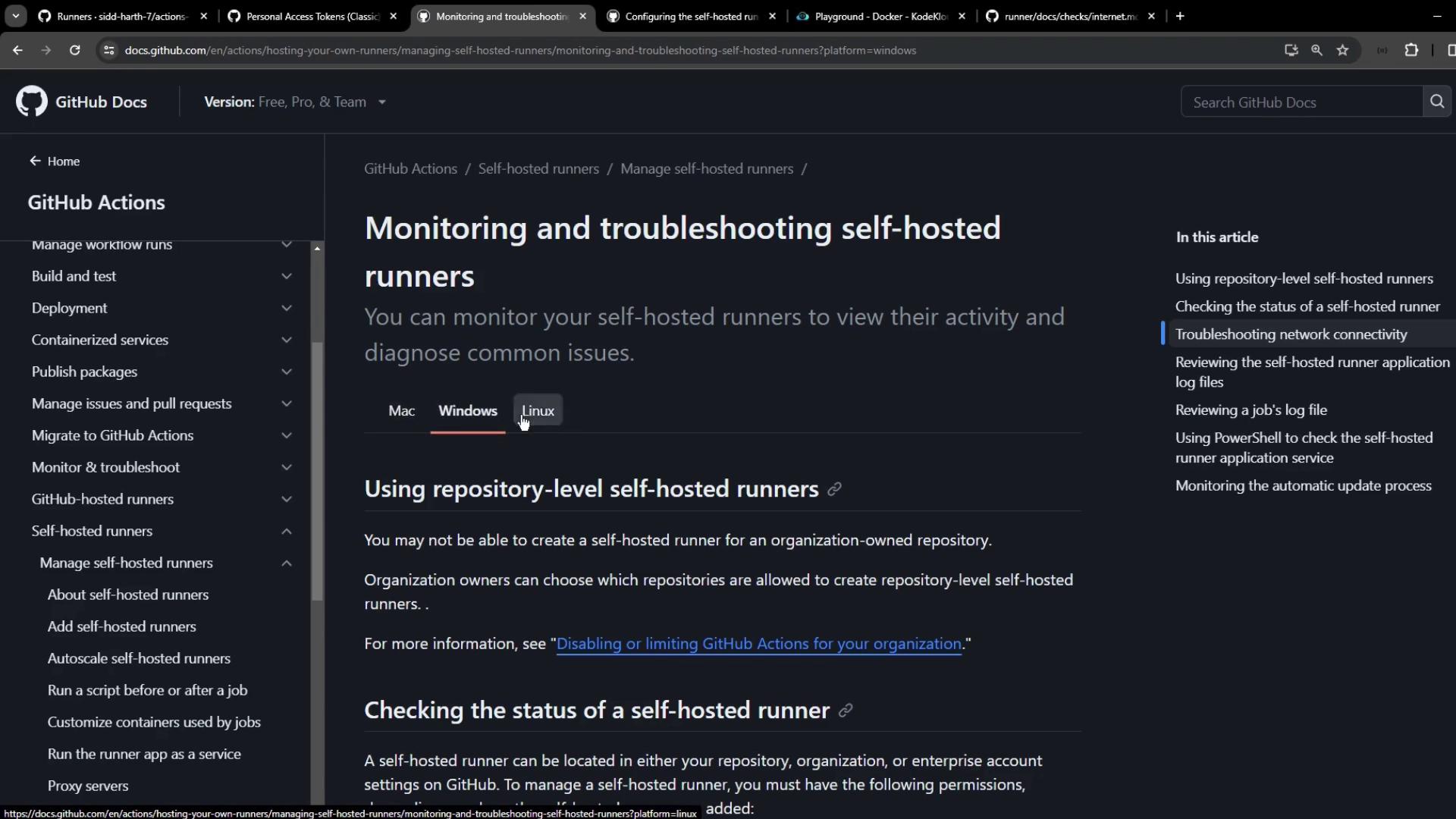
2. Diagnosing Network Connectivity
The runner providesrun.sh with a --check flag to verify connectivity to GitHub services. Run:
Generate a classic personal access token with the
workflow scope under Settings > Developer settings > Personal access tokens.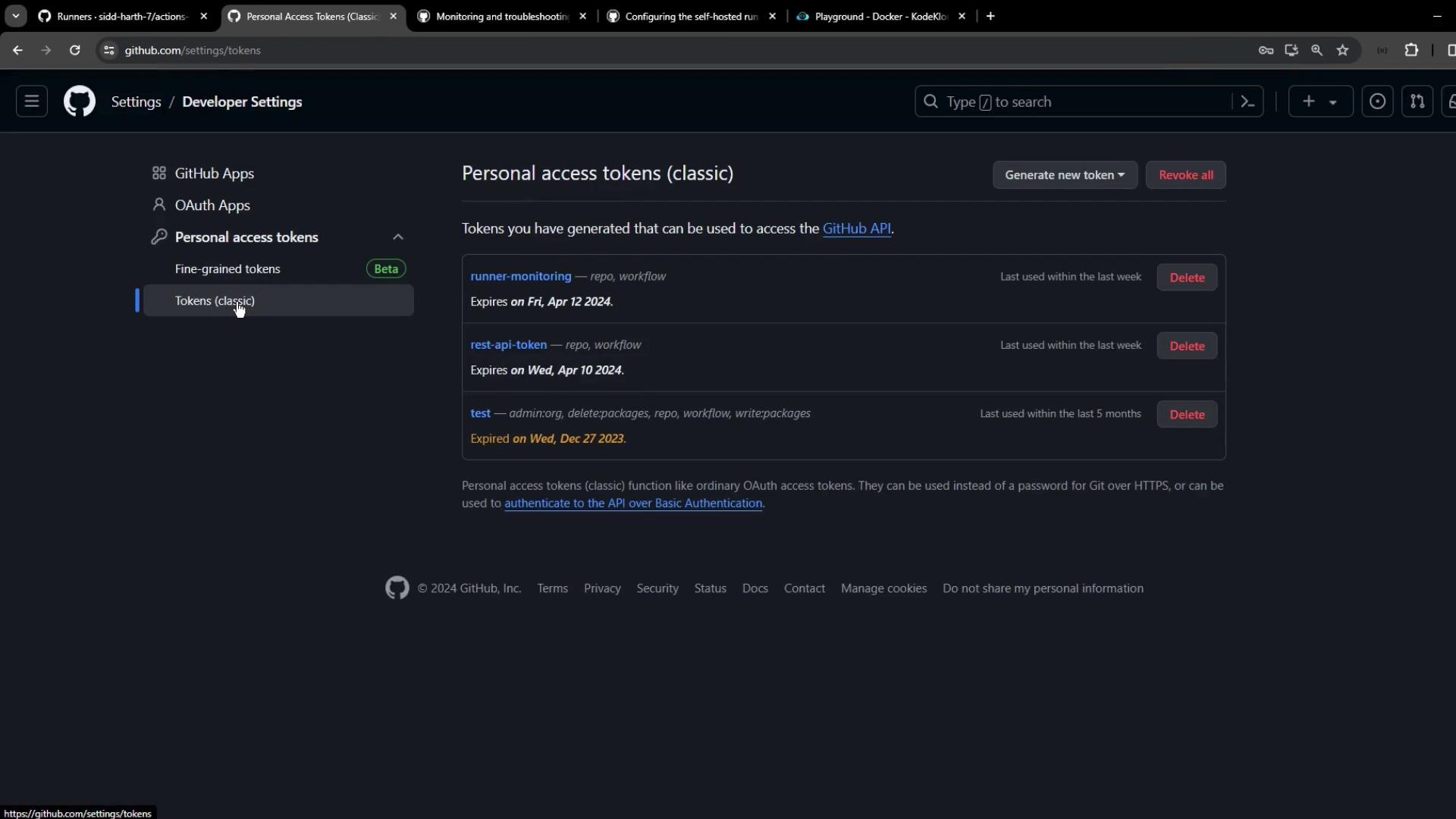
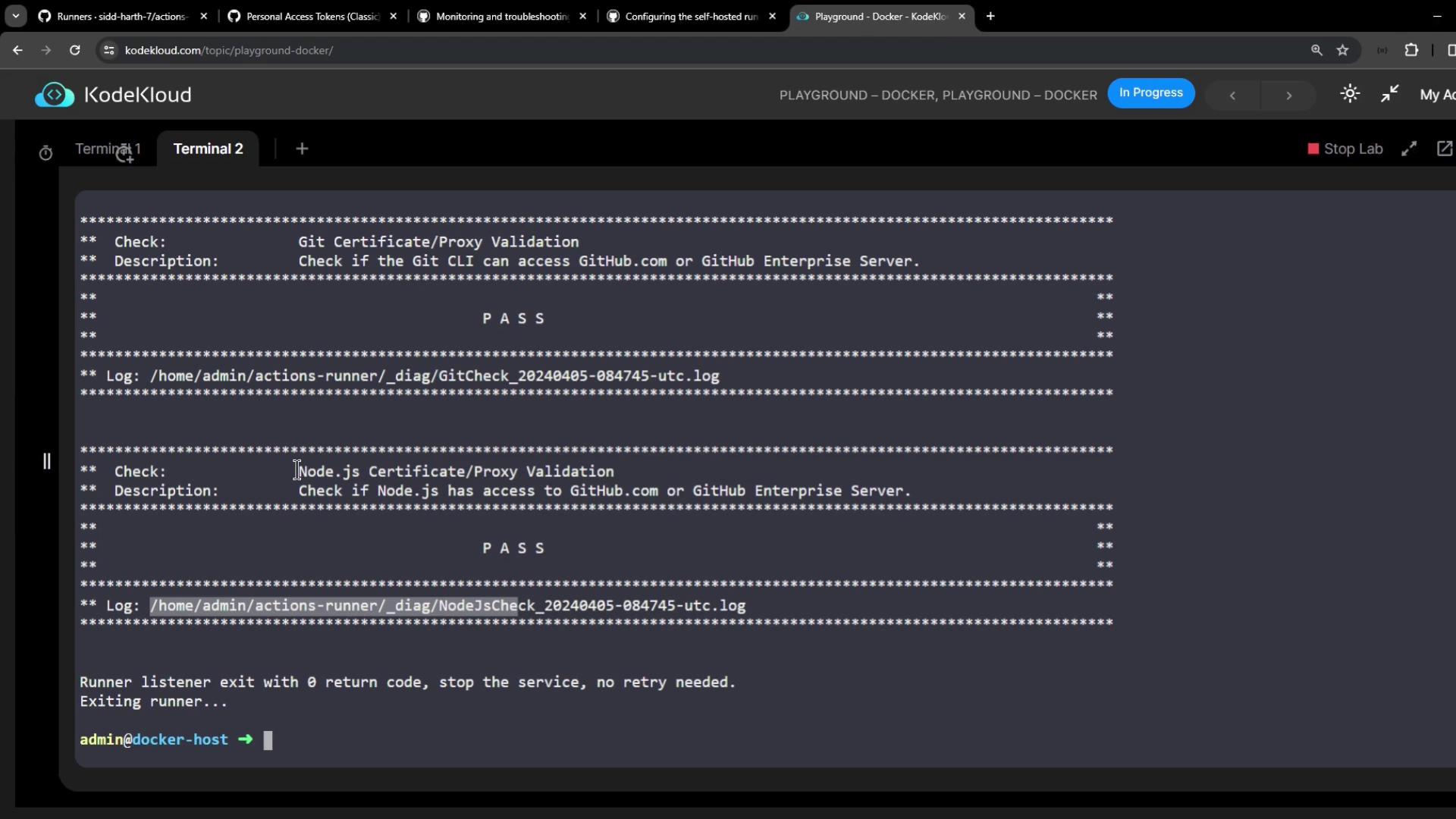
_diag log:
Disabling TLS verification reduces security. Use only for temporary troubleshooting:
3. Reviewing Runner Application Logs
All runner logs reside in the_diag directory of your runner installation:
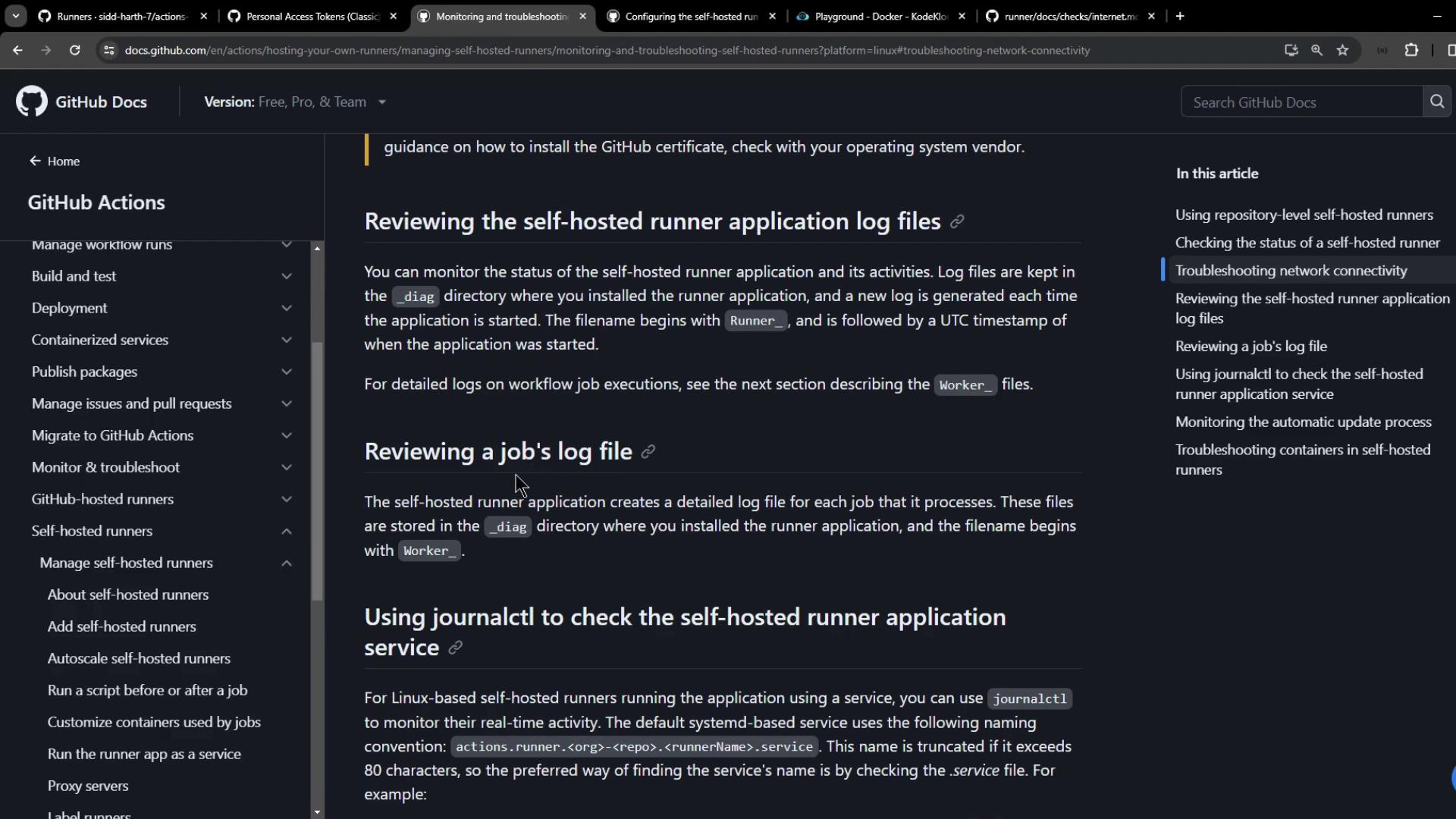
4. Monitoring via systemd and journalctl (Linux)
When installed as a service, manage and view logs usingsystemctl and journalctl. The service name follows:
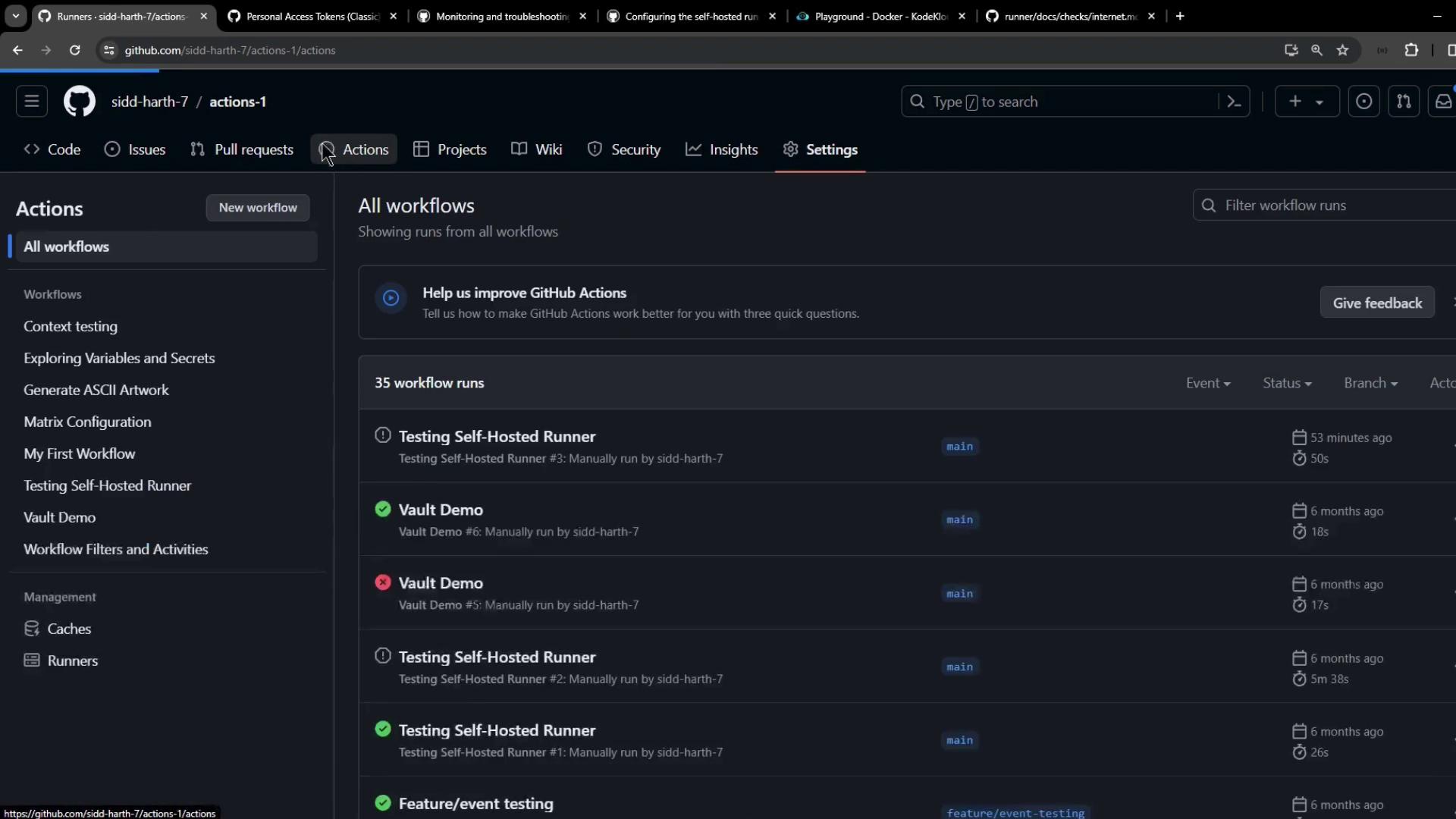
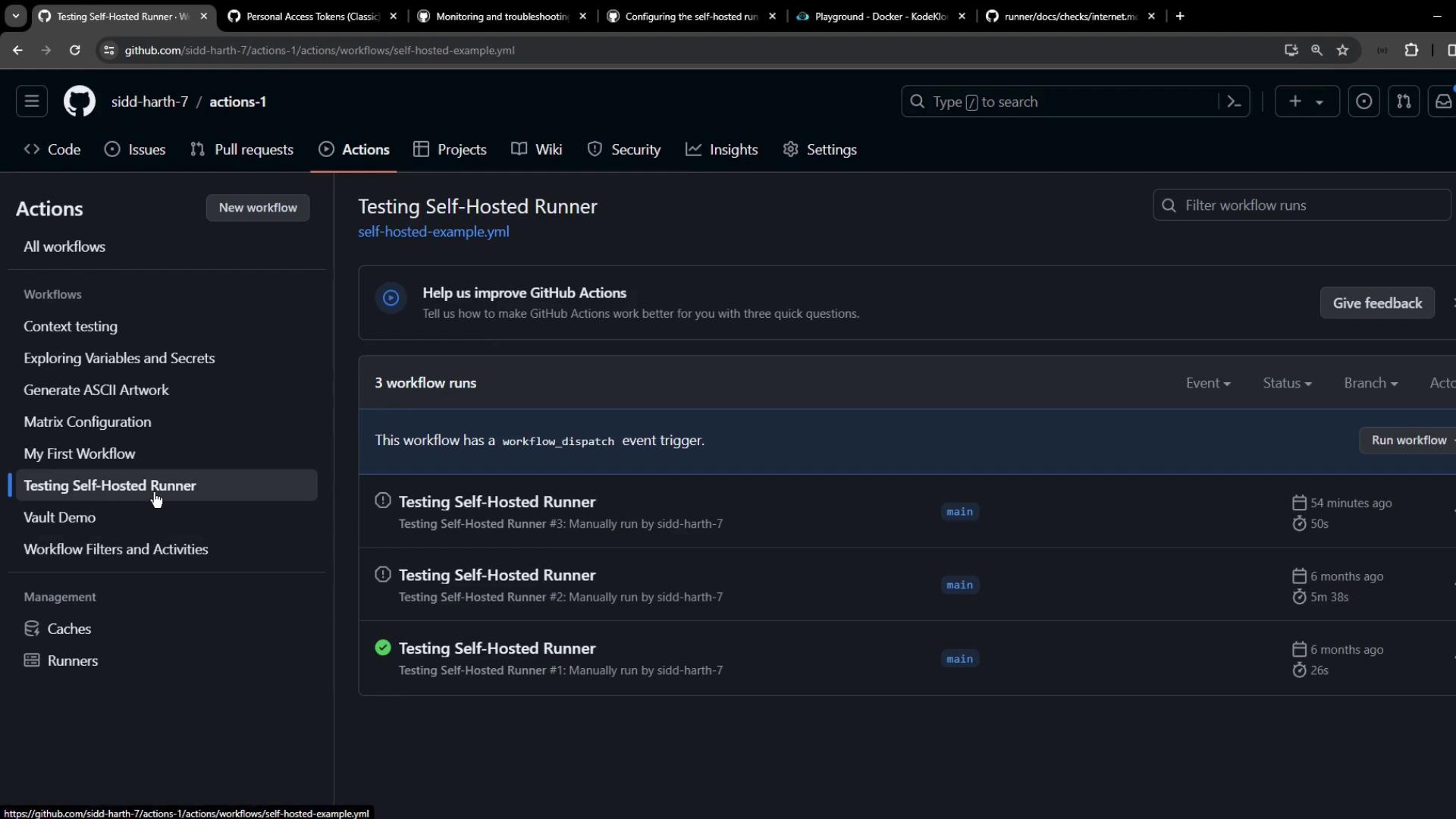
5. Triggering and Tracking a Workflow
Dispatch your workflow (workflow_dispatch) and watch both the service logs and GitHub Actions UI. In the Actions tab, monitor status, duration, and logs:
6. Updating Runners and Verifying Docker
Keep your runner and Docker up-to-date to avoid unexpected failures:| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
./svc.sh remove && ./config.sh --unattended ... | Remove old config and reconfigure runner |
| Follow GitHub’s [runner update guide] | Download and install the latest runner release |
sudo systemctl is-active docker.service | Check Docker service status |
| Issue | Symptom | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| Outdated runner | Workflow errors or deprecation warnings | Update via GitHub runner update guide |
| Missing Docker | FileNotFoundException: 'docker' in logs | Install and start docker.service |
| Network / SSL certificate fail | Connectivity checks fail | Update certificates or set TLS_NO_VERIFY |