- Reviewing Enterprise vs. Organization settings
- Creating and renaming runner groups
- Assigning runners to repositories (including public repos)
- Installing a self-hosted runner on Linux
- Running a sample workflow on your new runner
1. Compare Enterprise and Organization Dashboards
First, open two browser tabs side by side: Tab 1: Enterprise Overview
- Enterprise settings live in the left sidebar.
- Organization and user settings appear in the top navigation.
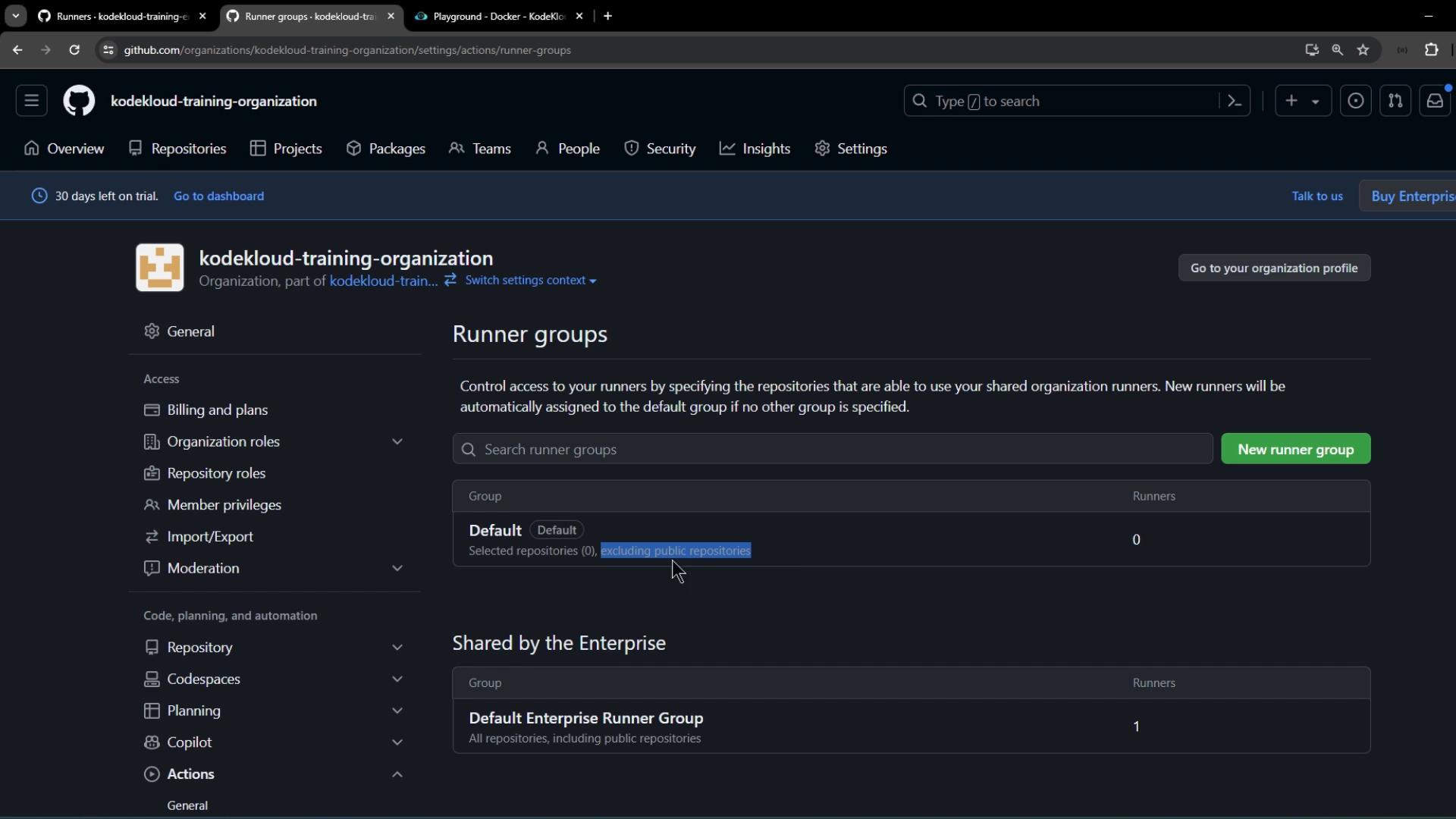
2. View and Rename Organization Runner Groups
- In your organization, navigate to Settings > Actions > Runner groups.
- You’ll see the default runner group:
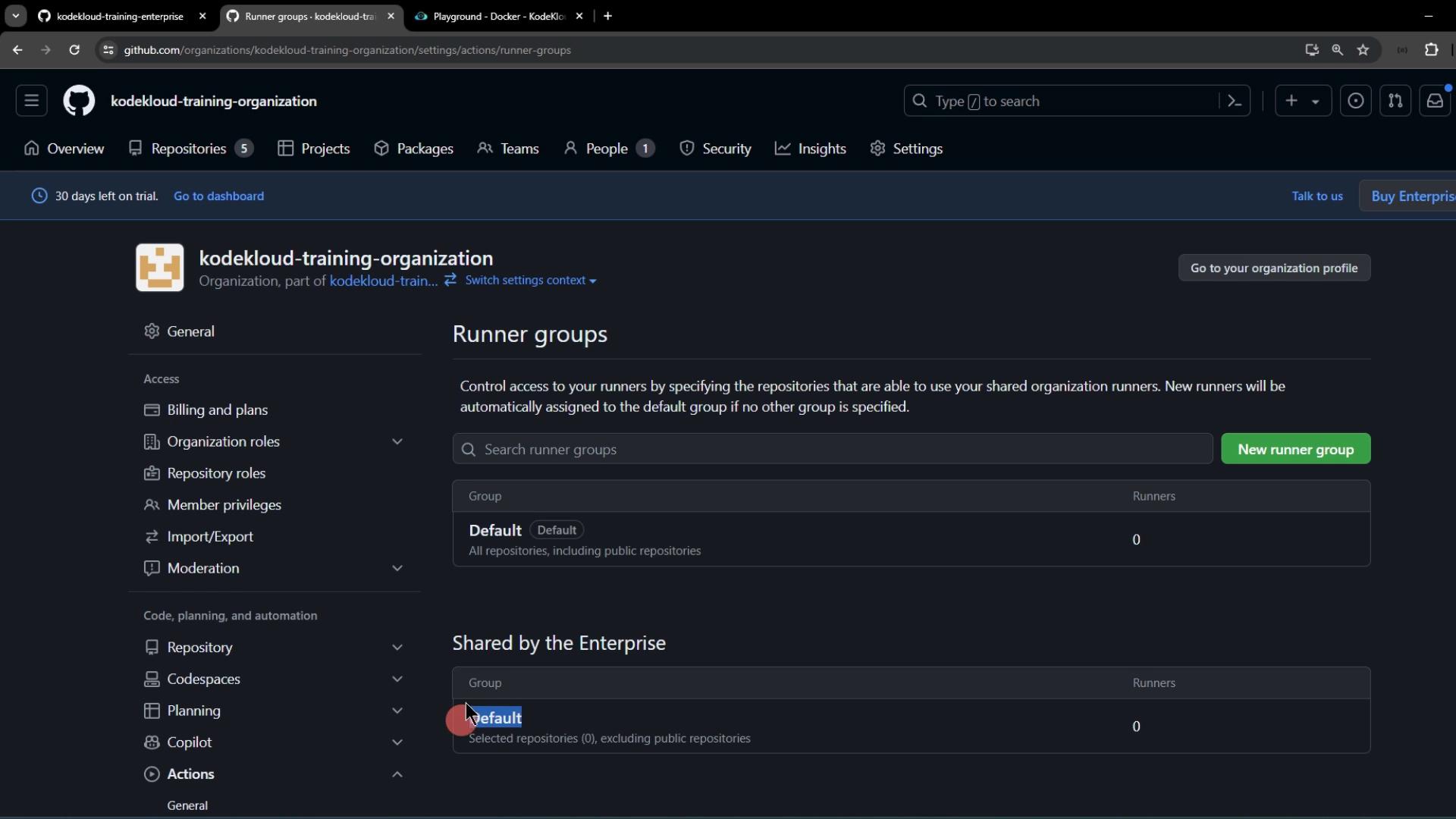
- Click into the default group and observe that public repository support cannot be toggled here:
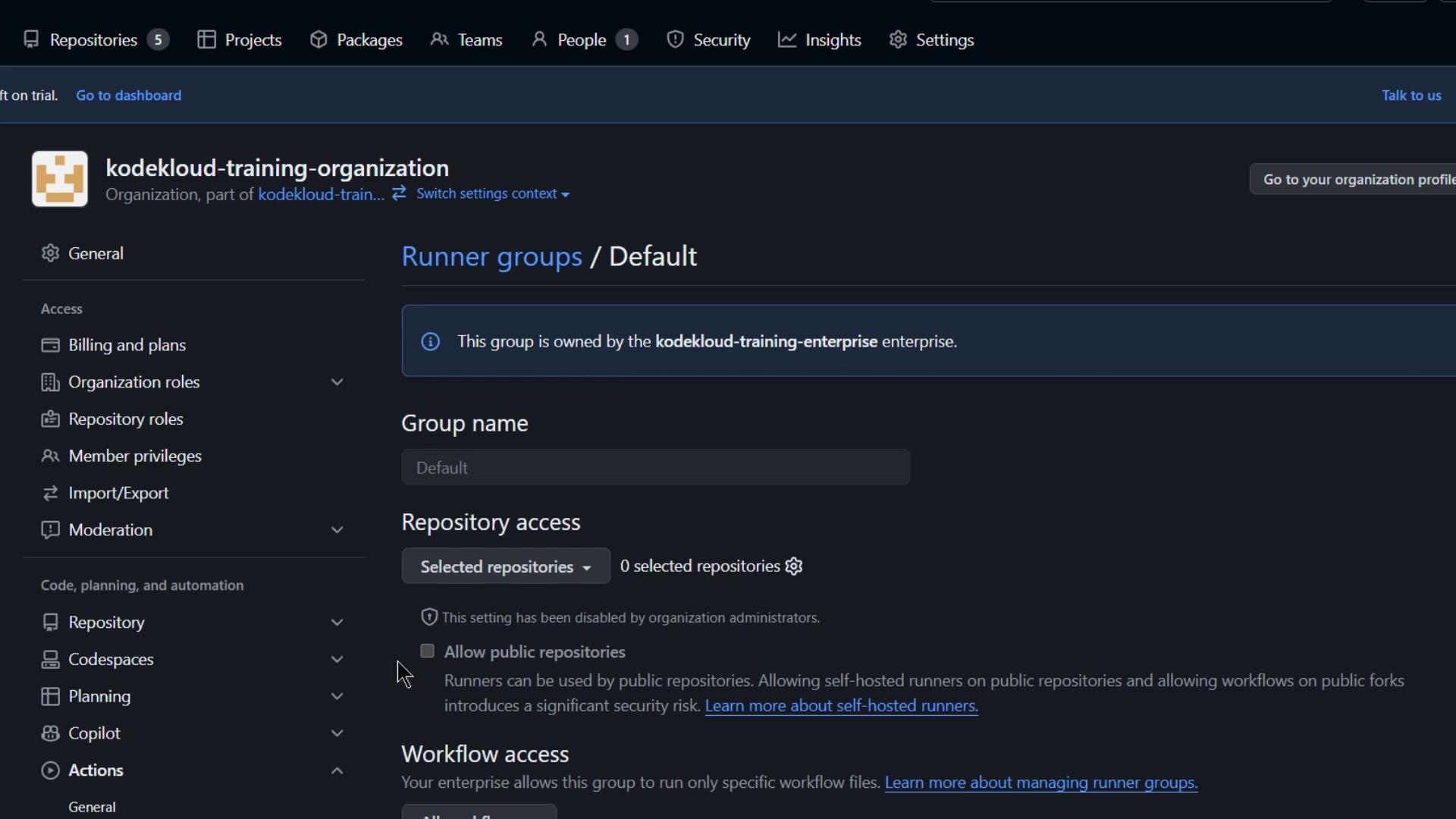
Public repository support for a runner group is only configurable at the enterprise level. You won’t be able to enable it within the organization settings.
3. Configure Enterprise Runner Group Policies
Switch to Enterprise > Policies > Actions > Runner groups: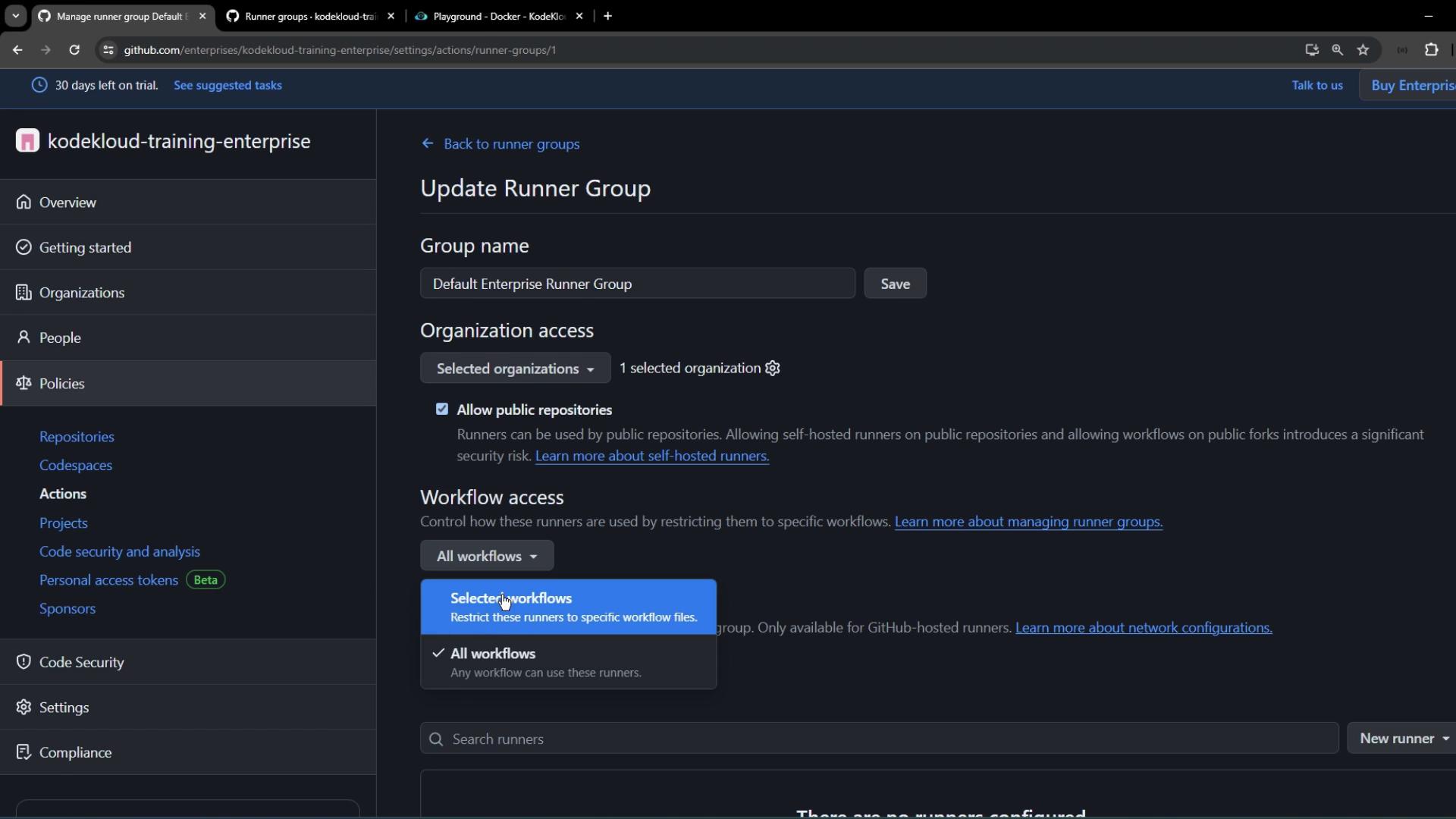
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Group Name | Rename (e.g., default enterprise runner group) |
| Organization Access | Restrict to specific orgs or allow all |
| Repository Access | Choose All, Selected, and include Public repos |
| Workflow File Restrictions | Limit to certain workflow filenames |
4. Assign Runner Group to Organization Repositories
Return to the organization’s Runner groups page and refresh. The renamed enterprise group will appear. Click Add repository access: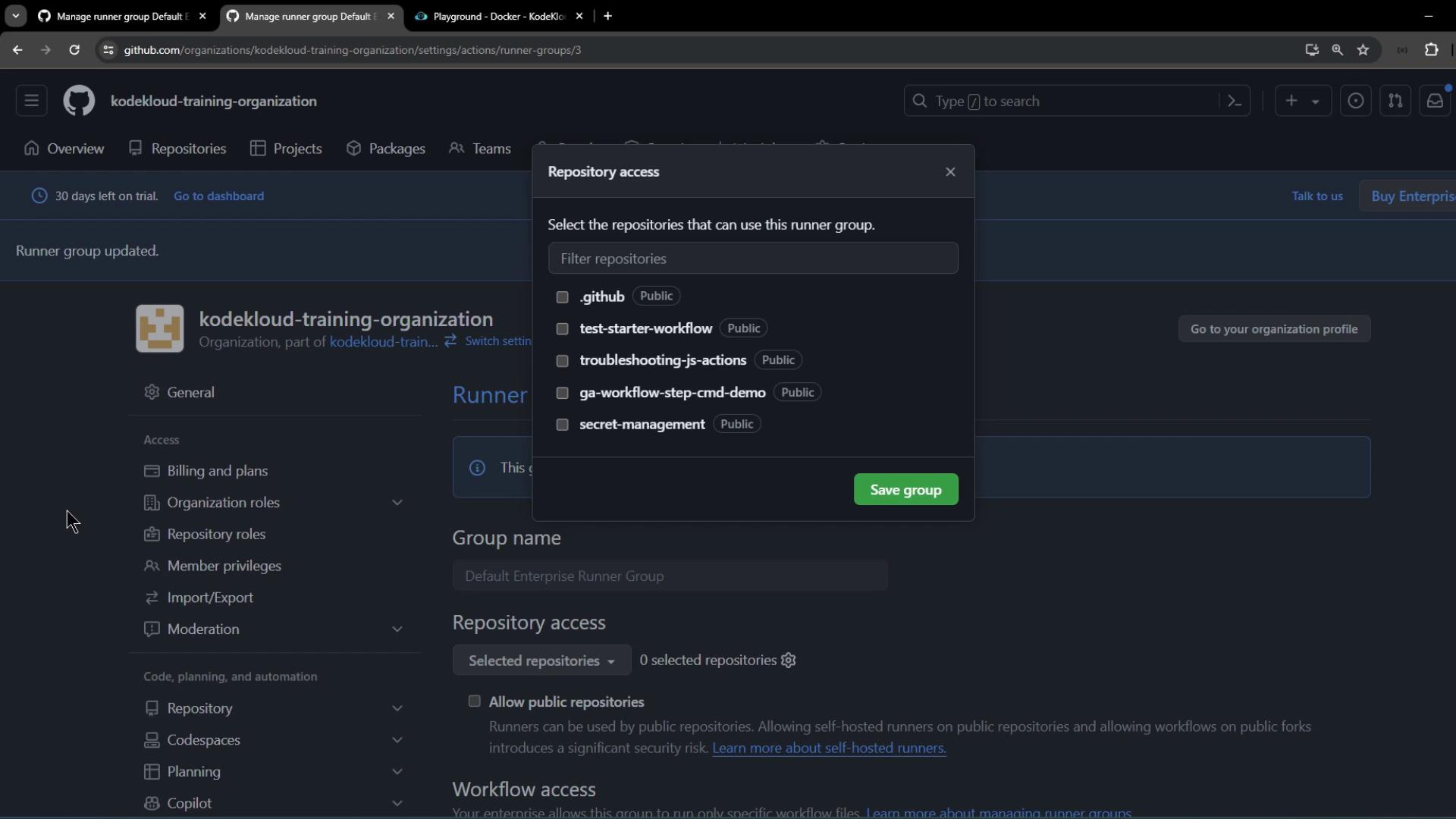
- All repositories
- Include public repositories
5. Install a Self-Hosted Runner on Linux
In the enterprise settings, go to Policies > Actions > Runners:
enterprise.
Once up, you’ll see logs like:
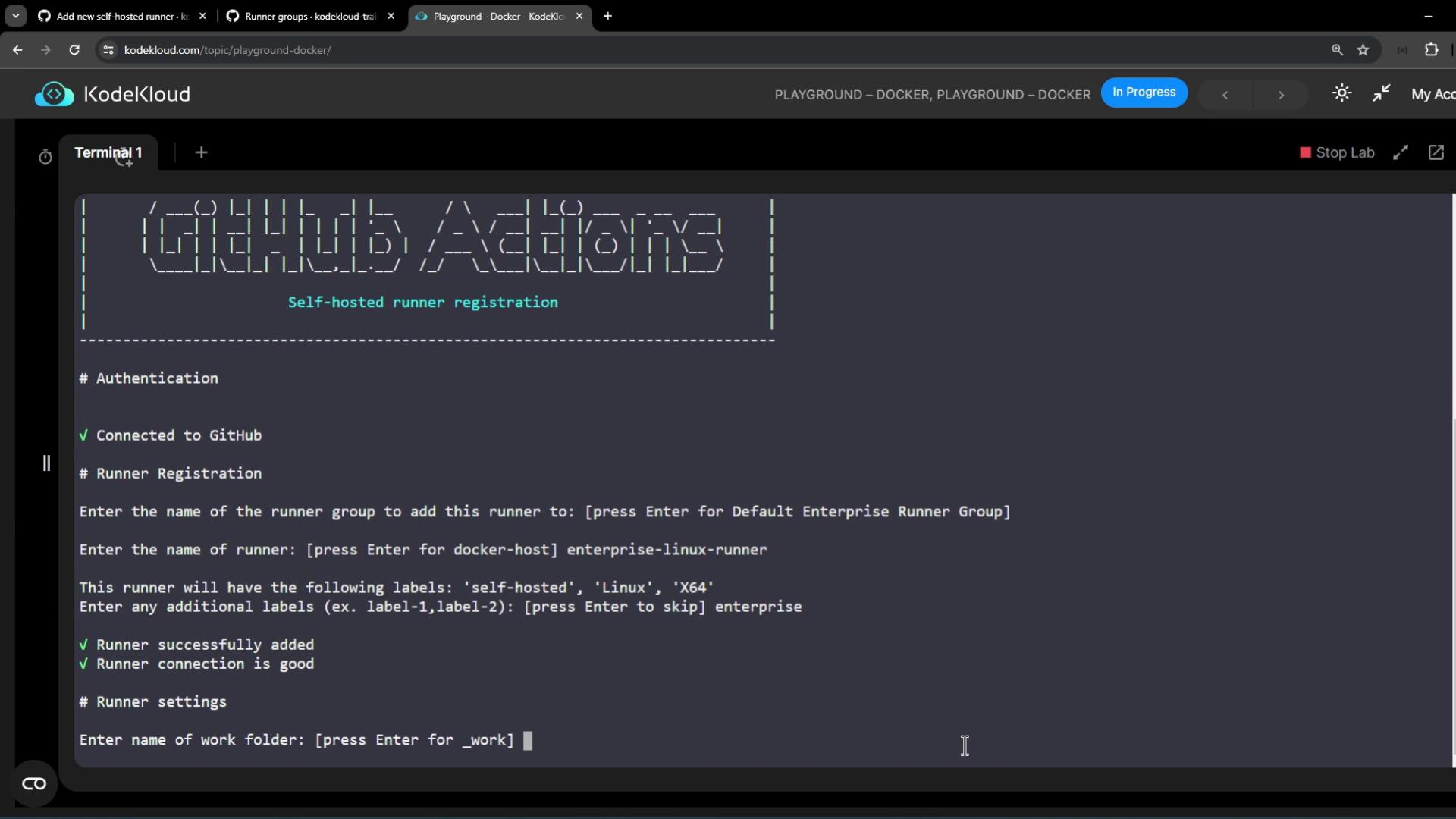
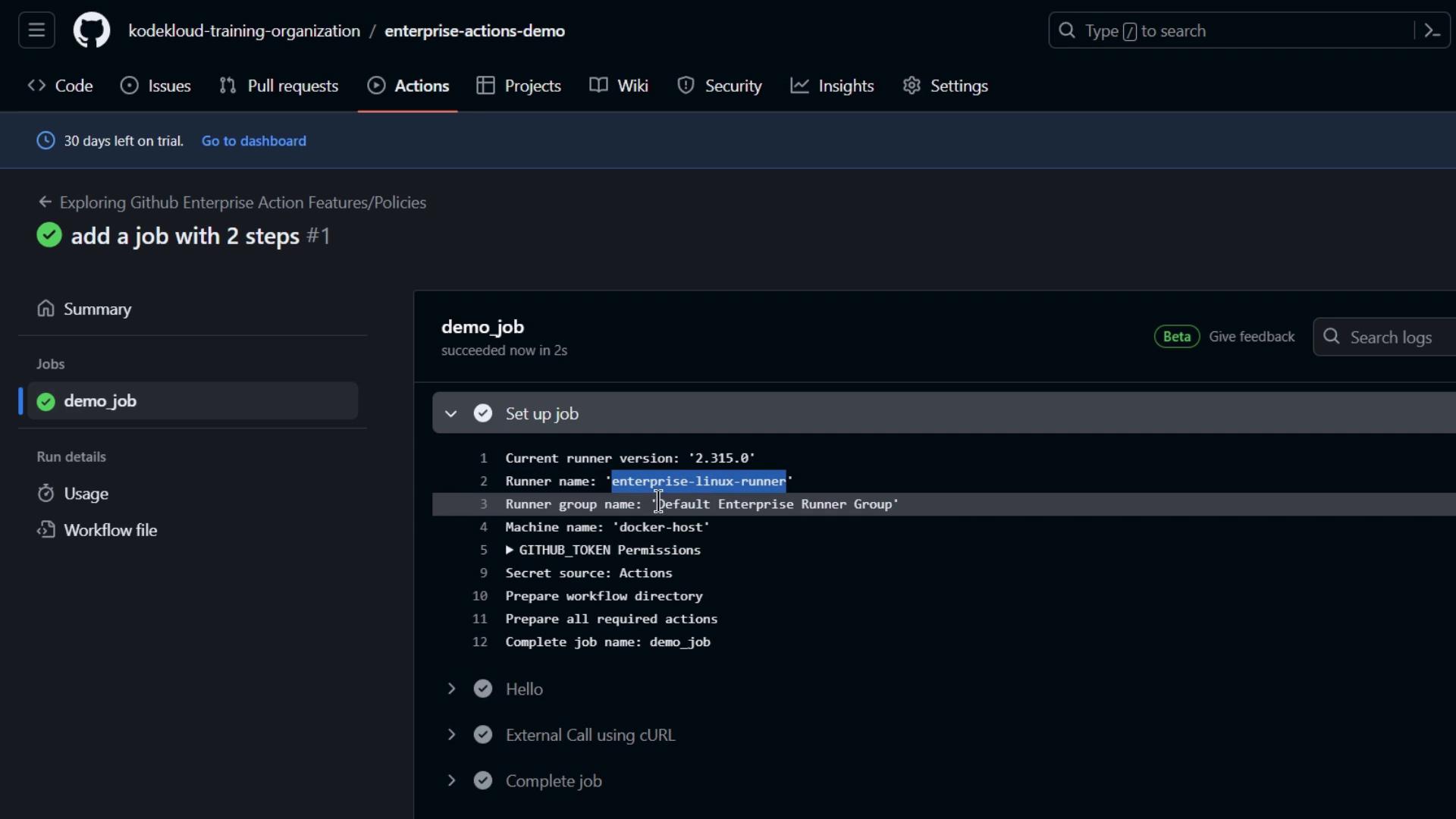
6. Verify Runner Registration
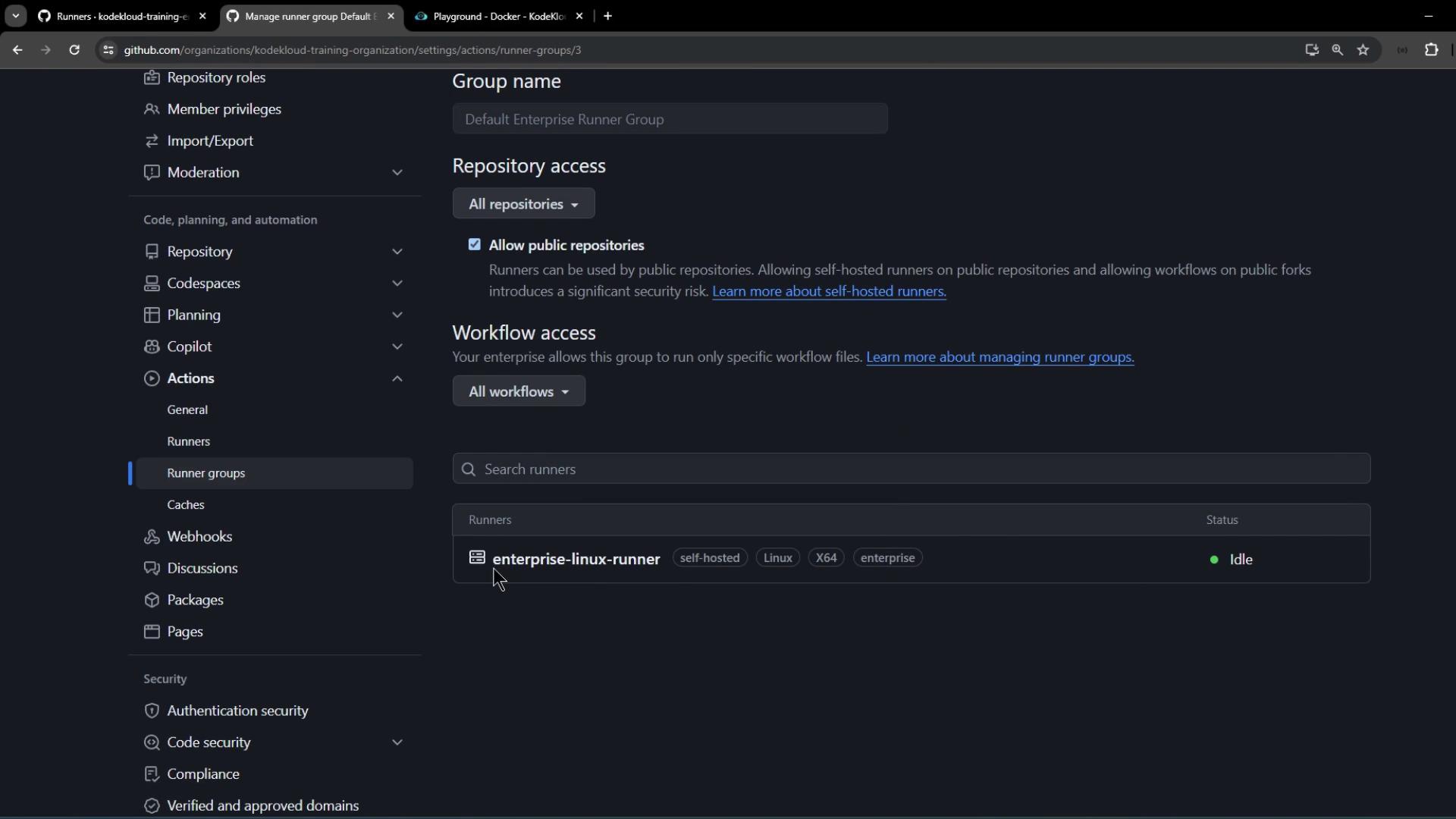
Back in the enterprise’s Runners list, your new self-hosted runner appears with labels and an idle status:
7. Create a New Repository and Workflow
- Disable the organization’s default runner for public repos to enforce enterprise runners.
- Go to Repositories > New repository in your organization:
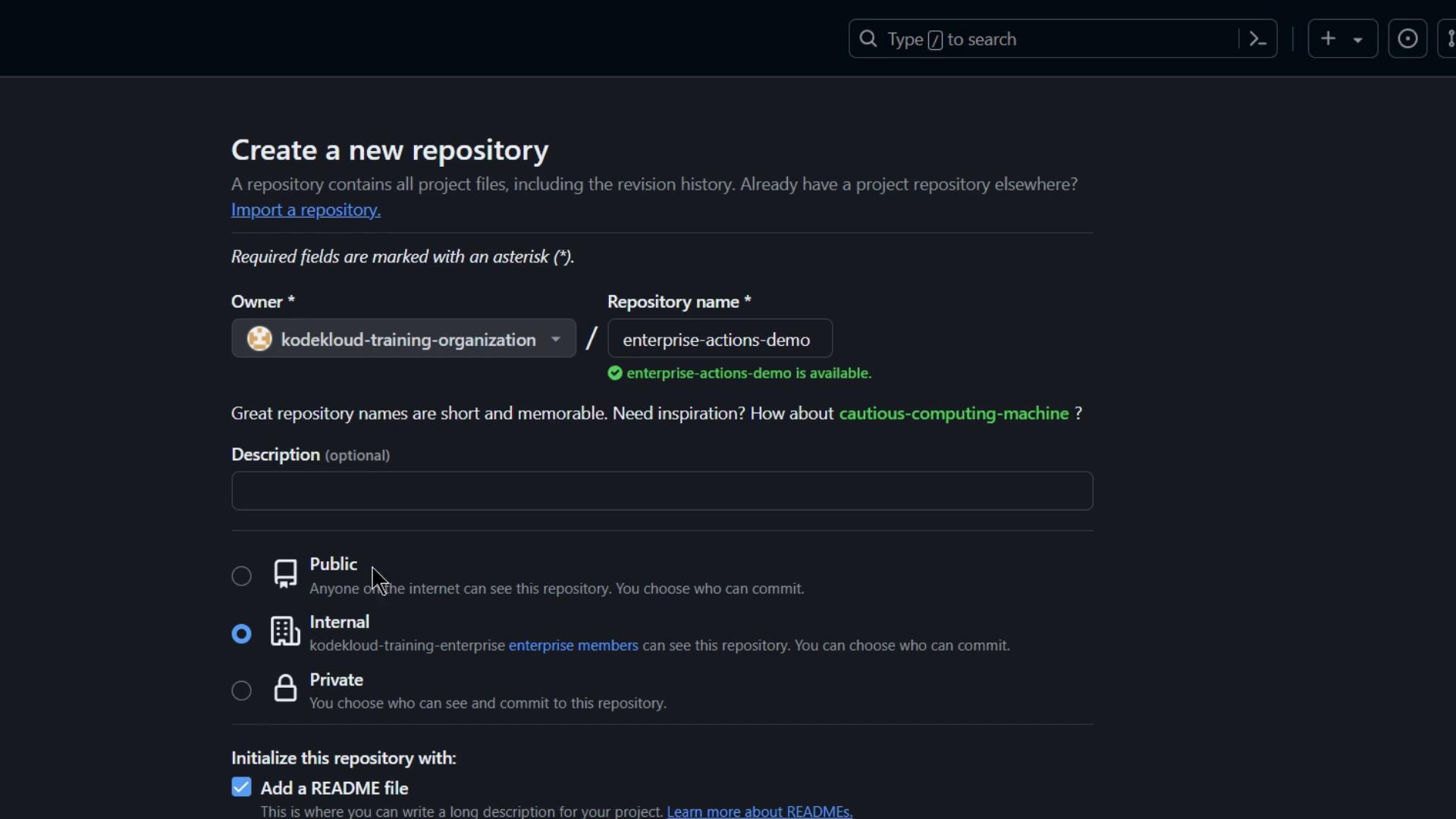
- Initialize with a README and clone locally:
- Add a workflow at
.github/workflows/demo.yaml:
- Commit and push:
8. Review Workflow Execution
Navigate to the repository’s Actions tab. You should seedemo_job queued and running on your self-hosted enterprise runner: