- Downloads unit-test and code-coverage artifacts
- Merges them into a directory named after the current commit SHA
- Prepares the reports for upload to an AWS S3 bucket
unit-testingcode-coveragedockerdev-deploydev-integration-testingprod-deployprod-integration-testing
reports-s3, right after code-coverage. It uses needs to depend on both unit-testing and code-coverage.
The artifact
For example,
name in actions/upload-artifact must match the name in actions/download-artifact.For example,
Mocha-Test-Result and Code-Coverage-Result should remain consistent.Previous Jobs: Archiving Artifacts
Below are the essential steps for uploading artifacts in yourunit-testing and code-coverage jobs:
| Job Type | Artifact Name | Path |
|---|---|---|
| Unit Testing | Mocha-Test-Result | test-results.xml |
| Code Coverage | Code-Coverage-Result | coverage/ |
unit-testing
code-coverage
Using
Consider disabling it for stricter enforcement.
continue-on-error: true allows the workflow to proceed even if tests or coverage fail, but you may miss critical failures.Consider disabling it for stricter enforcement.
Workflow Graph and Logs
Once merged, your GitHub Actions graph will show the new AWS S3 – Upload Reports job with arrows fromunit-testing and code-coverage. All upstream jobs complete before reports-s3 starts, and downstream jobs run in parallel.
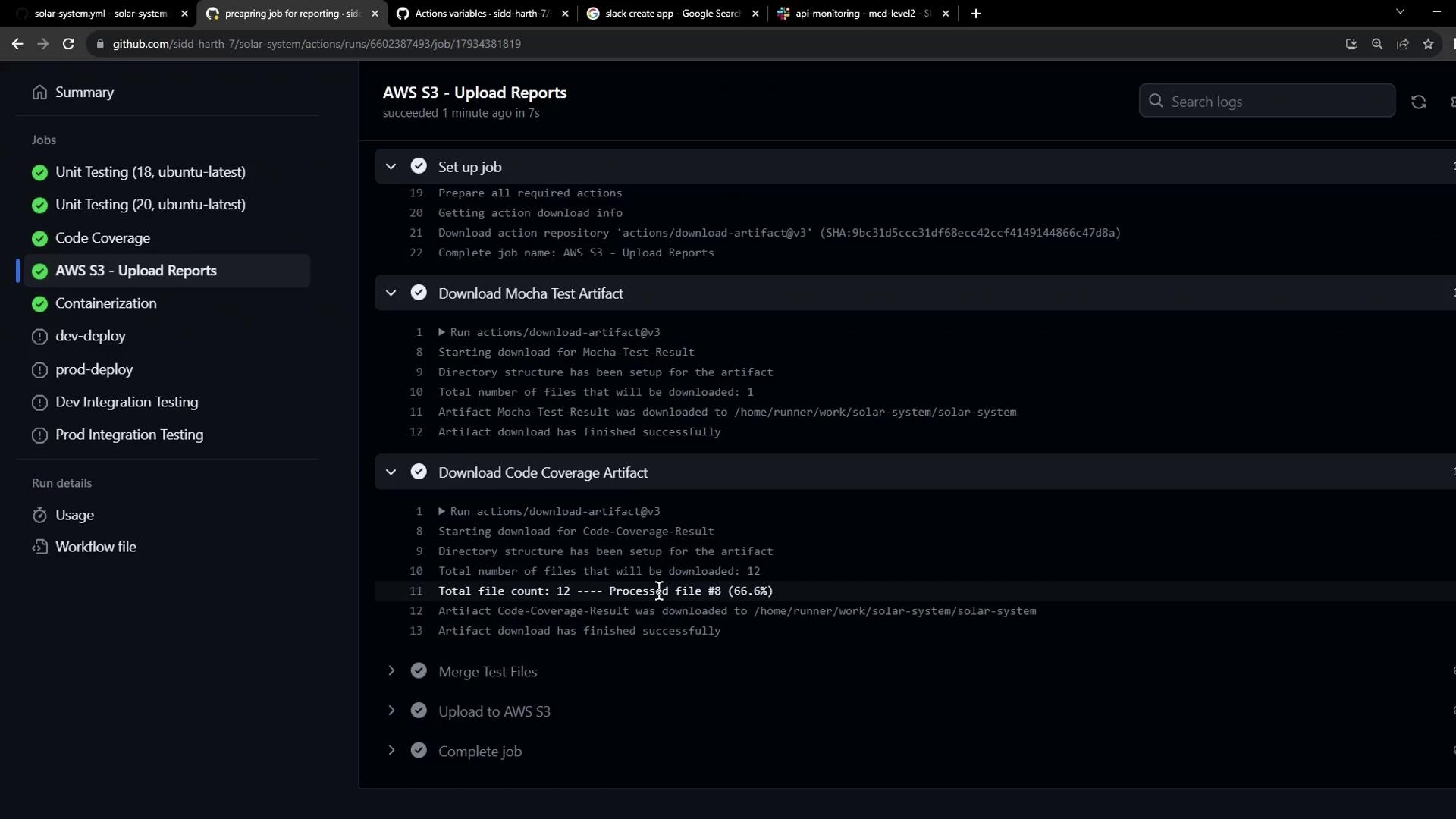
- Download Mocha Test Artifact – via
actions/download-artifact@v3. - Download Code Coverage Artifact – similarly.
- Merge Test Files – creation of
reports-<SHA>and movement ofcobertura-coverage.xmlandtest-results.xml. - Upload to AWS S3 – placeholder echo until we configure an S3 action.
reports-s3 job. Next, we’ll configure the actual AWS S3 upload step.