dev-deploy job that replaces tokens, creates a MongoDB secret, and applies your manifests.
1. Update the GitHub Actions Workflow
Open.github/workflows/main.yml and add the dev-deploy job:
2. Kubernetes Deployment Manifest
Ensure yourdeployment.yaml in kubernetes/development/ references the secret for environment variables:
3. Repository Variables and Secrets
Configure the following under Settings > Secrets and variables in your GitHub repository.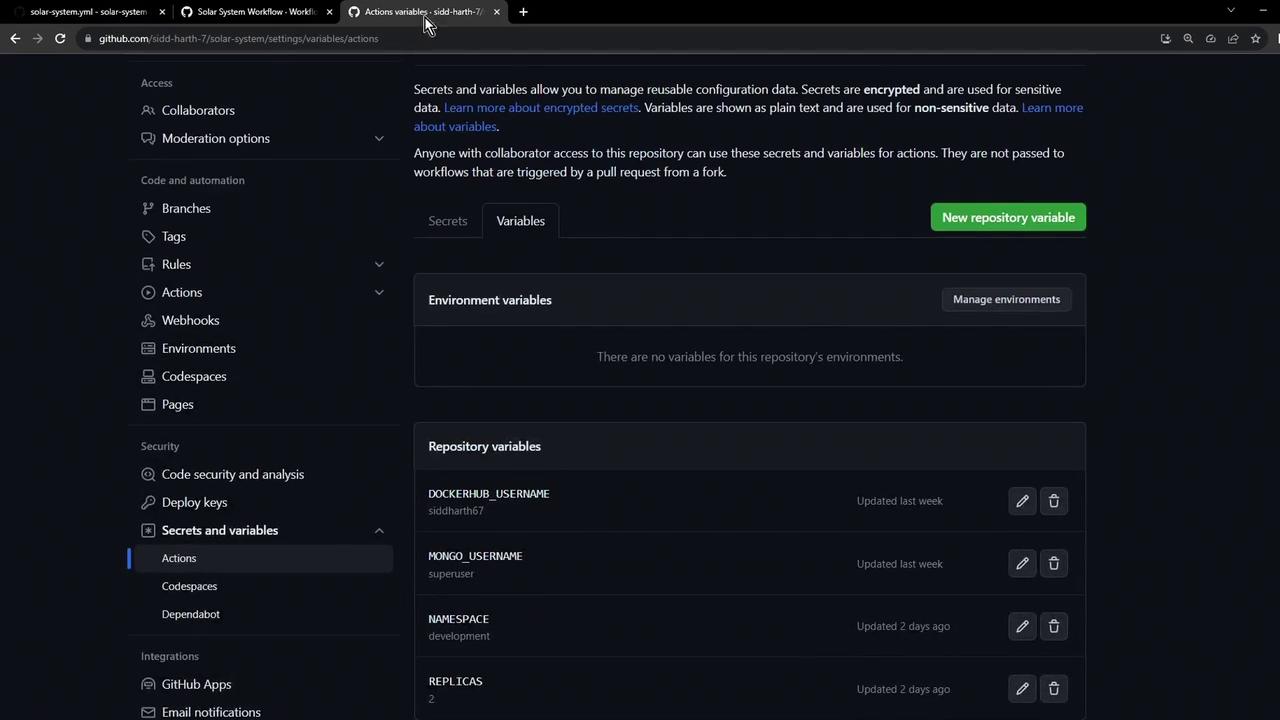
| Variable / Secret | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
MONGO_URI | Environment Variable | MongoDB connection string. |
MONGO_USERNAME | Repository Variable | Username for MongoDB. |
MONGO_PASSWORD | Encrypted Secret | Password for MongoDB. |
NAMESPACE | Repository Variable | Kubernetes namespace (e.g., development). |
REPLICAS | Repository Variable | Number of pod replicas (e.g., 2). |
DOCKERHUB_USERNAME | Repository Variable | Docker Hub account name. |
4. Running the Workflow
Push your changes tomain or any feature/* branch. Then, monitor the pipeline in the Actions tab of your repository.
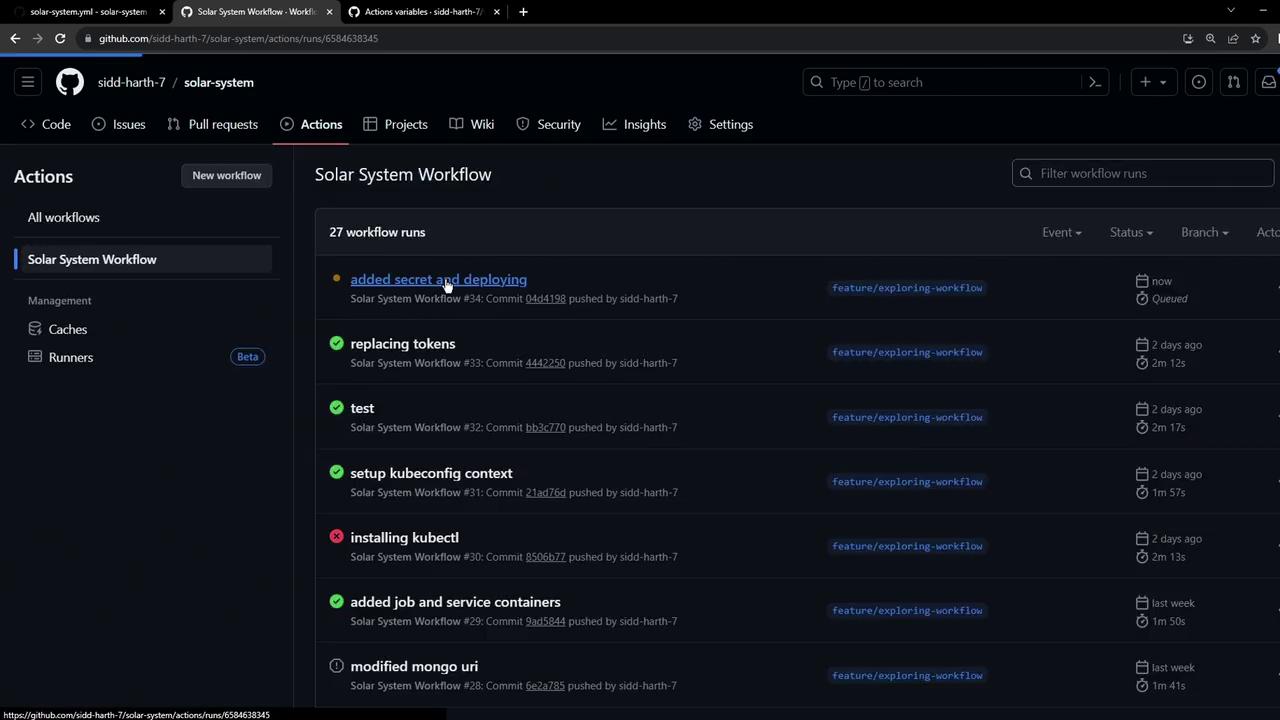
The
dev-deploy job runs after the docker job (and its dependencies: unit-testing and code-coverage). It checks out the repo, replaces tokens, creates the MongoDB secret, and applies the Kubernetes manifests.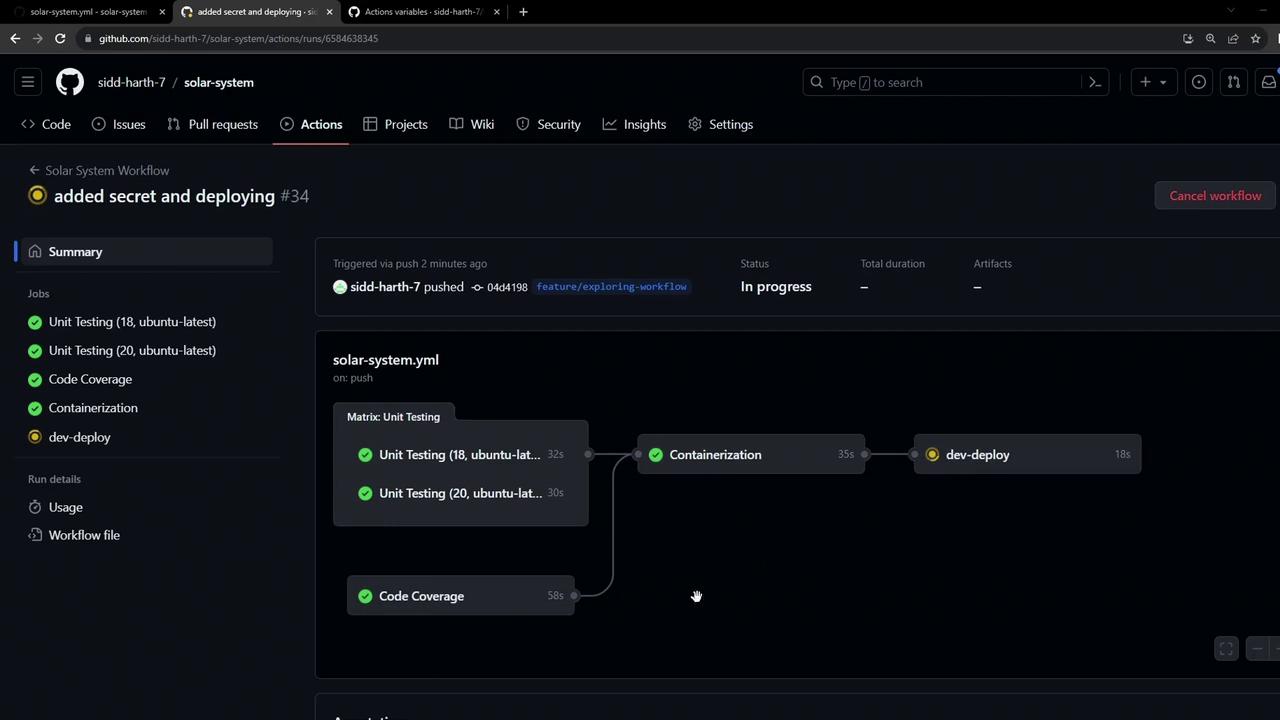
5. Verifying in Kubernetes
Once the workflow succeeds, confirm the resources:mongo-db-credssecret- Deployment and Pods for
solar-system - Service and Ingress resources
6. Accessing the Application
Retrieve and open the ingress endpoint:HOSTNAME in your browser.
If you encounter a self-signed certificate warning, safely accept it to proceed to the application.
This lesson covers creating a Kubernetes secret and deploying to a development cluster via GitHub Actions. Integration testing for this deployment will be addressed in an upcoming article.
Links and References
- [GitHub Actions Documentation][GitHub Actions]
- [GitHub Secrets and Variables][GitHub Secrets and Variables docs]
- [Kubernetes Secrets][Kubernetes Secrets]
- [Kubernetes Ingress][Ingress docs]