What You’ll Learn
- Overview of the AZ-400 exam
- Exam format, scoring, and timing
- Who should take this exam
- The five core technical domains covered
Exam Overview
| Criteria | Details |
|---|---|
| Number of questions | 40–60 (includes unscored items for research) |
| Question types | Multiple-choice, scenario-based, and hands-on labs |
| Passing score | 700 out of 1,000 (no penalty for incorrect answers) |
| Time limit | 120 minutes |
There’s no penalty for guessing—answer every question. Use official practice tests to gauge your readiness.

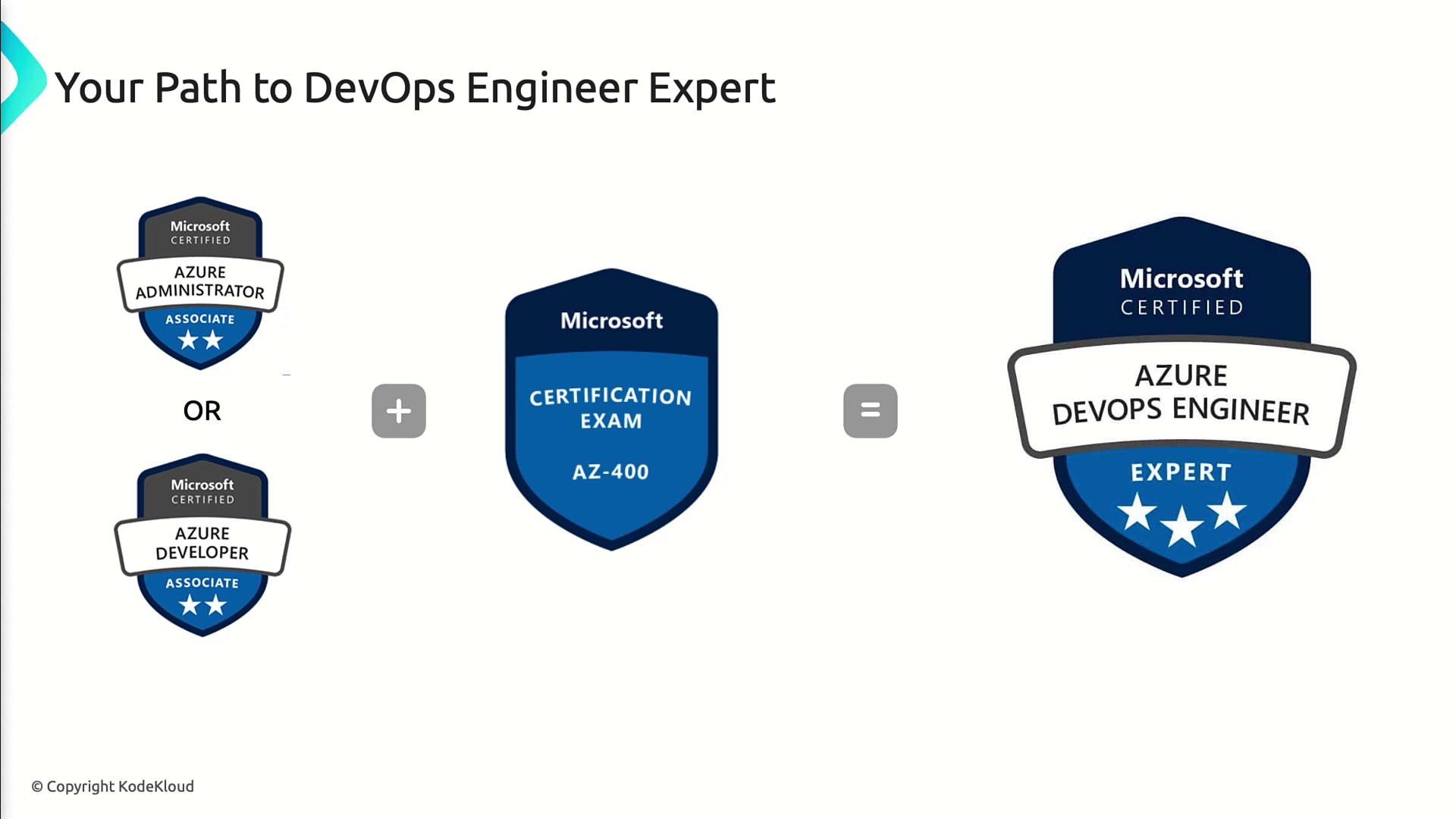
Certification Path
To achieve Azure DevOps Engineer Expert, you must first hold one of these associate-level certificates:- Azure Administrator Associate
- Azure Developer Associate
You can pursue self-study or instructor-led courses. Refer to the official learning path for resources.
Who Should Take AZ-400
This exam is ideal for:- Developers building and deploying applications on Azure
- Site Reliability Engineers (SREs) managing cloud infrastructure
- Azure Administrators integrating DevOps processes

Exam Domains
| Domain | Focus Areas |
|---|---|
| 1. Processes and communications | Agile workflows, collaboration channels, process enforcement |
| 2. Source control | Branching, pull requests, repo policies, pipeline integration |
| 3. Build and release pipelines | CI/CD automation, multi-stage pipelines, environment deployments, artifact management |
| 4. Security and compliance | RBAC, auditing, policy enforcement, compliance in CI/CD |
| 5. Instrumentation | Telemetry, monitoring with Application Insights & Log Analytics, alerts, dashboards |

1. Configuring Processes and Communications
- Define Agile boards and work item tracking with Azure Boards
- Automate notifications via Teams, Slack, or email
- Enforce policies for code reviews, test sign-offs, and release approvals
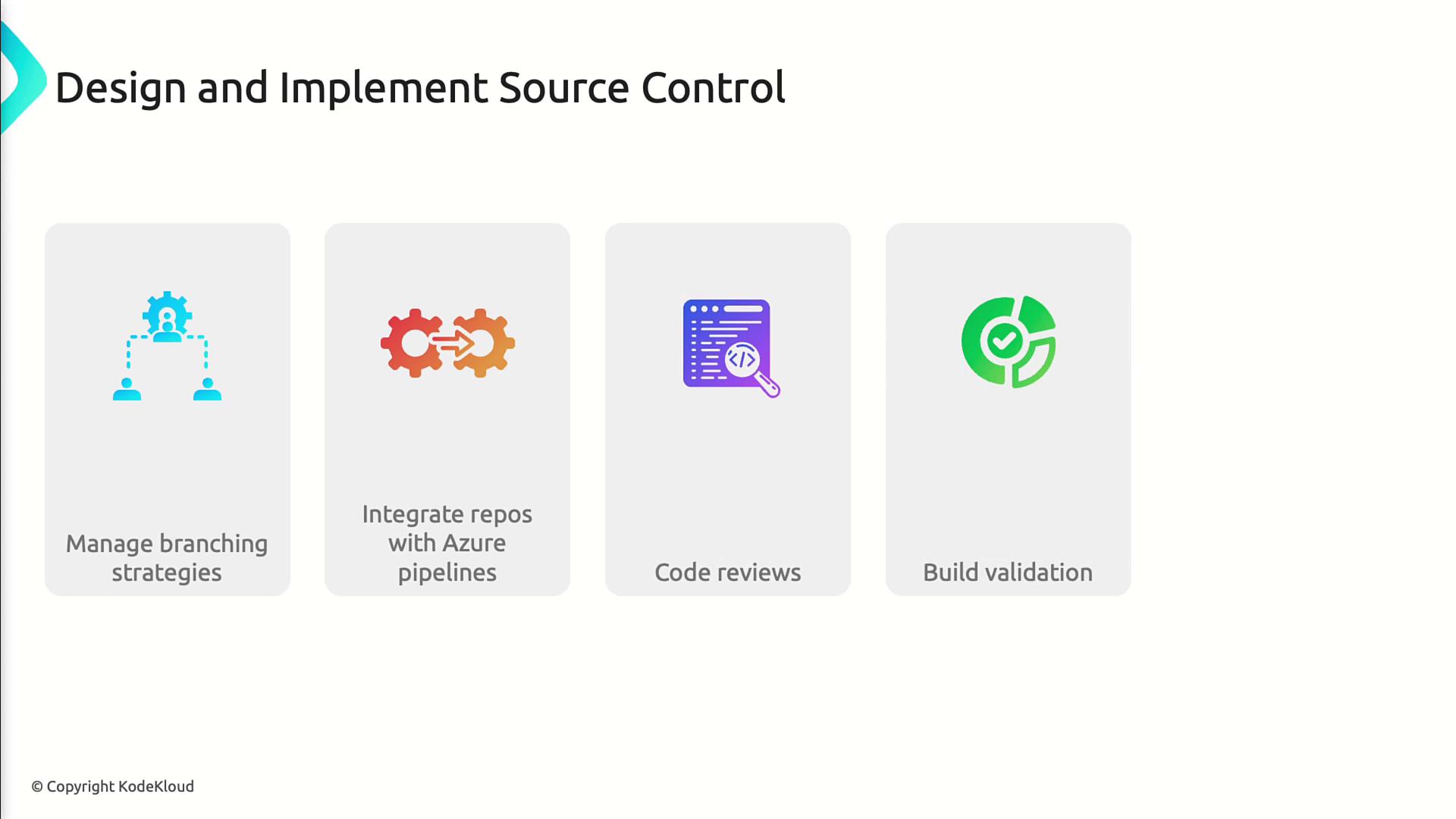
2. Designing and Implementing Source Control
- Manage Git branching strategies (e.g., Feature, GitFlow)
- Integrate Azure Repos with Azure Pipelines
- Enforce pull request policies and build validation
- Configure repository security and permissions
3. Designing and Implementing Build and Release Pipelines
- Automate CI/CD using Azure Pipelines YAML or Classic editor
- Build multi-stage deployments with approvals and gates
- Deploy to Dev, Test, Staging, and Production environments
- Manage packages with Azure Artifacts
- Trigger pipelines via code push, schedules, or REST API

4. Developing a Security and Compliance Plan
- Implement Azure RBAC and resource locks
- Enable audit logs and pipeline security scanning
- Apply compliance configurations using Azure Policy
- Integrate security checks directly into your CI/CD workflows
5. Implementing an Instrumentation Strategy
- Instrument applications with Application Insights telemetry
- Monitor application performance and availability
- Aggregate logs in Log Analytics workspaces
- Configure alerts on key metrics and build custom dashboards