What Are GitHub Secrets?
GitHub Secrets are encrypted environment variables stored at the repository, environment, or organization level. They enable you to reference sensitive data in your Actions workflows without exposing them in code.| Scope | Description | Ideal for |
|---|---|---|
| Repository secrets | Accessible only in a single repository | Project-specific API keys |
| Environment secrets | Scoped to named environments (e.g., staging, production) | Deployment credentials |
| Organization secrets | Shared across multiple repositories within an organization | Centralized service tokens |
Viewing Secrets and Variables
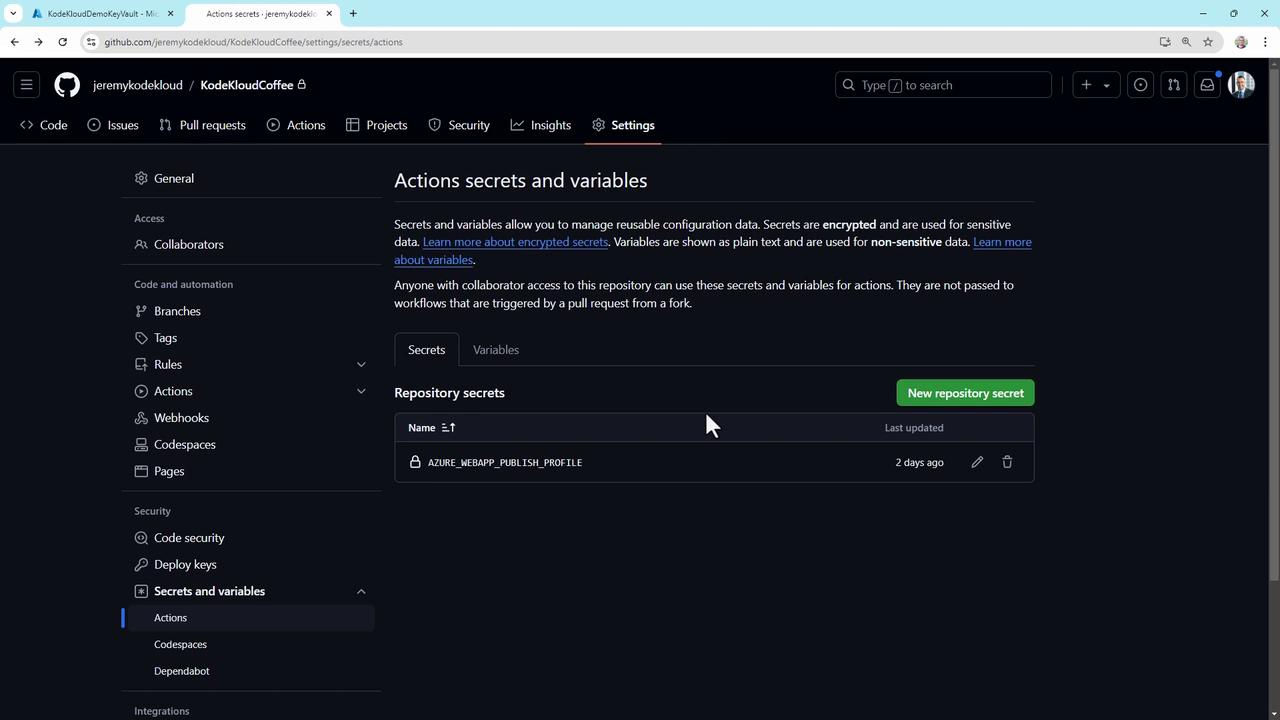
To inspect secrets in a repository:- Navigate to Settings → Secrets and variables.
- Choose Actions, Codespaces, or Dependabot.
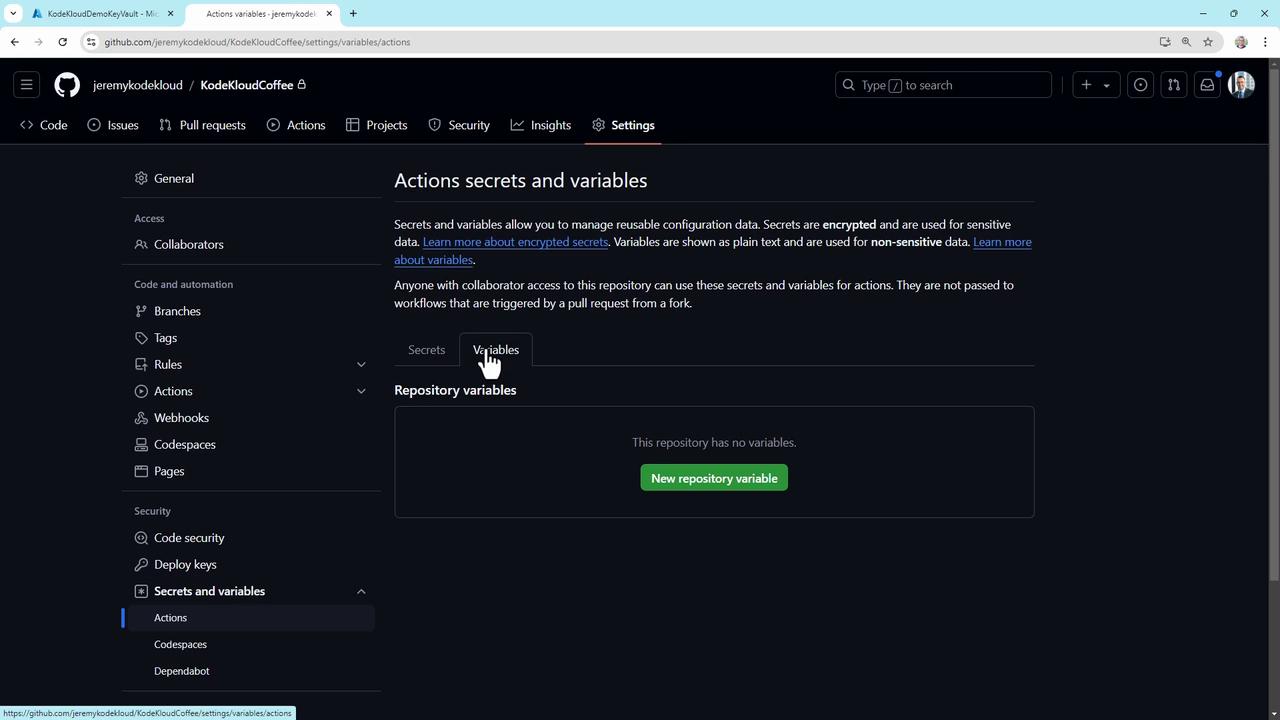
Variables vs. Secrets
- Secrets are encrypted and masked in logs.
- Variables hold non-sensitive data (e.g., server names) and can be updated centrally.
Creating and Updating Repository Secrets
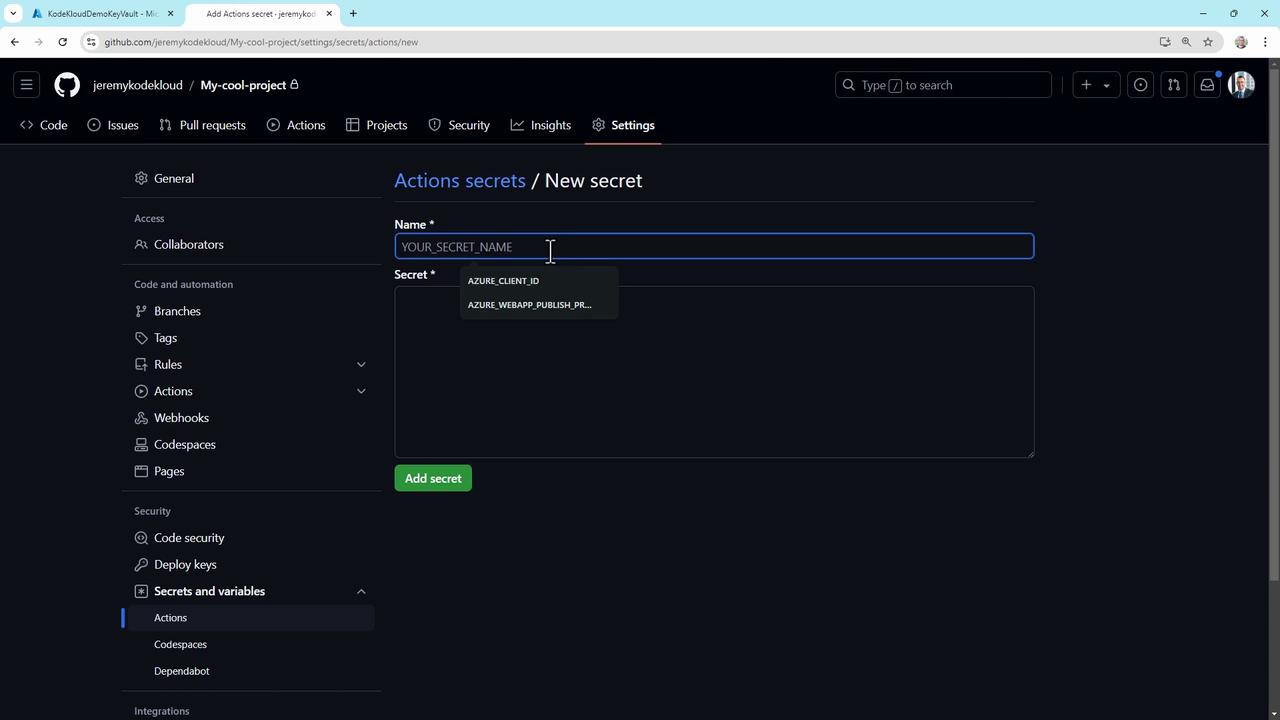
- Go to Settings → Secrets and variables → Actions.
- Click New repository secret.
- Enter a Name (e.g.,
API_KEY) and the secret Value. - Click Add secret.
Using Secrets in a Workflow
Add secrets to your workflow YAML to inject them at runtime. Create a file like.github/workflows/hello.yml:
${{ secrets.API_KEY }} retrieves the value securely.
***, while your external endpoint receives the correct token.
Secrets are not exposed to workflows triggered by pull requests from forks. This prevents unauthorized access to your credentials.
Advanced GitHub Secrets Usage
Deploying to Azure with JSON Credentials
Store full JSON service principals in a secret and use them:GitHub automatically masks secrets in Action logs, so your credentials never appear in plaintext.
Automating Secret Rotation
Use a scheduled workflow to rotate keys monthly:Auditing Secret Usage
Log each secret access for compliance:Best Practices for GitHub Secrets
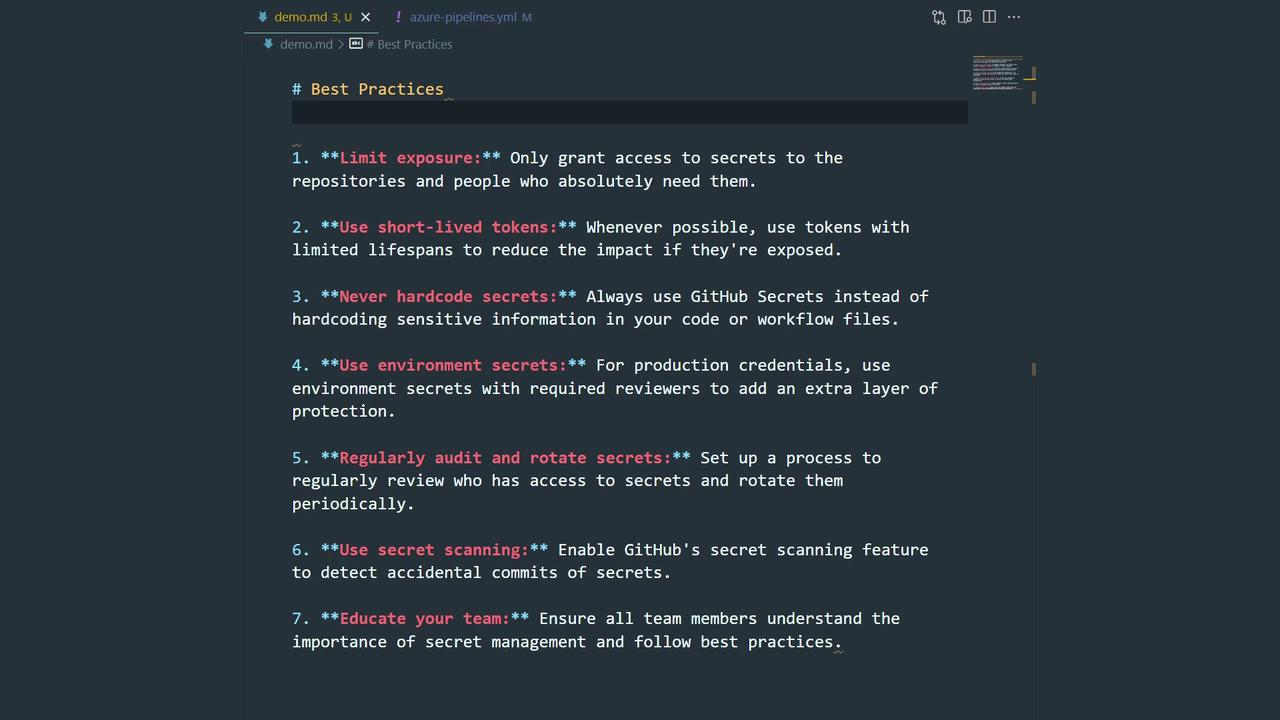
- Limit access with fine-grained permissions.
- Use short-lived tokens or ephemeral credentials.
- Never commit secrets to code or configuration files.
- Require approvals for environment secrets in production.
- Rotate and audit secrets regularly.
- Enable GitHub Secret Scanning.
- Train your team on secure secret handling.