What Is CodeQL?
- Code as Data: Parses your application into a queryable database of functions, variables, types, and control flows.
- Custom Queries: Use built-in or bespoke QL queries to find patterns such as SQL injections, cross-site scripting, and buffer overruns.
- Actionable Results: Highlights precise file locations, explains risks, and suggests remediation steps.
For an in-depth overview of CodeQL’s query language, visit the CodeQL QL Reference.
How CodeQL Works
-
Create a CodeQL Database
Index your code into a database for lightning-fast analysis. -
Run Security Queries
Execute predefined or custom queries to uncover vulnerabilities. -
Review Findings
Inspect the output table—each entry includes the file path, line number, and a detailed description. Fix or dismiss alerts as needed.
Tools for Using CodeQL
| Tool | Ideal For | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Command-Line Interface (CLI) | Automation & CI/CD pipelines | Scriptable batch analysis, multi-language support |
| VS Code Extension | Interactive development & debugging | Inline annotations, query editing, DB management |
Integrating CodeQL into Your GitHub Workflow
-
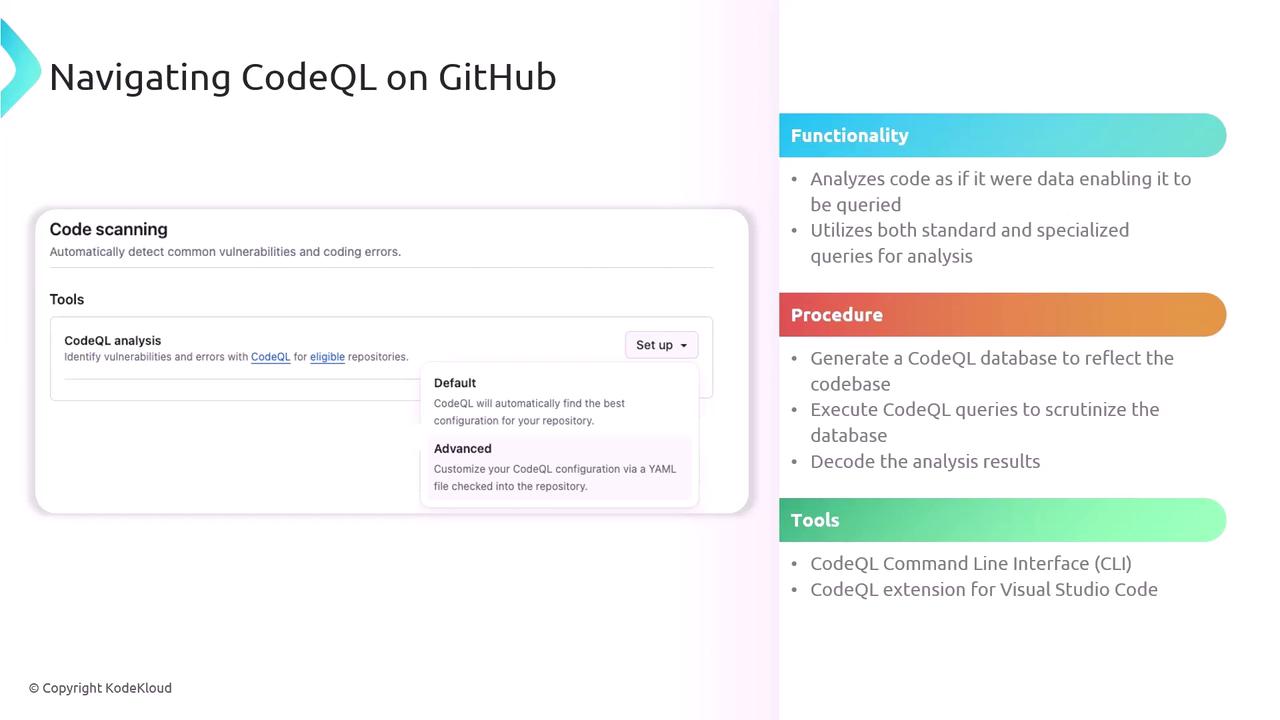
Enable Code Scanning
- Navigate to your repo’s Security → Code scanning.
- Click Set up code scanning and select CodeQL analysis.
-
Choose a Workflow Template
- Default: Covers common languages and queries.
- Advanced: Customize triggers, languages, and query sets.
Be cautious when excluding query packs or paths—omitting critical scans can leave gaps in your security posture.
- Monitor & Triage Alerts
- Check the Security tab for warnings and errors.
- Assign issues to team members, dismiss false positives, or mark fixes directly in the GitHub UI.
- Iterate on your workflow and queries to enhance coverage and accuracy.