docker run vs. Compose, introduce Docker Swarm concepts, and walk through a real-world voting application example—complete with replicas, placement constraints, resource limits, and health checks.
1. Docker Run vs. Docker Compose
When you start with containers, you often usedocker run for each service:
2. Introducing Docker Swarm and Stacks
Docker Swarm enables clustering multiple Docker engines into a single, fault-tolerant Swarm cluster. Instead ofdocker run, you create services:
Docker Stack uses the same Compose file format (v3+), so you can reuse your existing
docker-compose.yml with minimal changes.3. Containers, Services, and Stacks
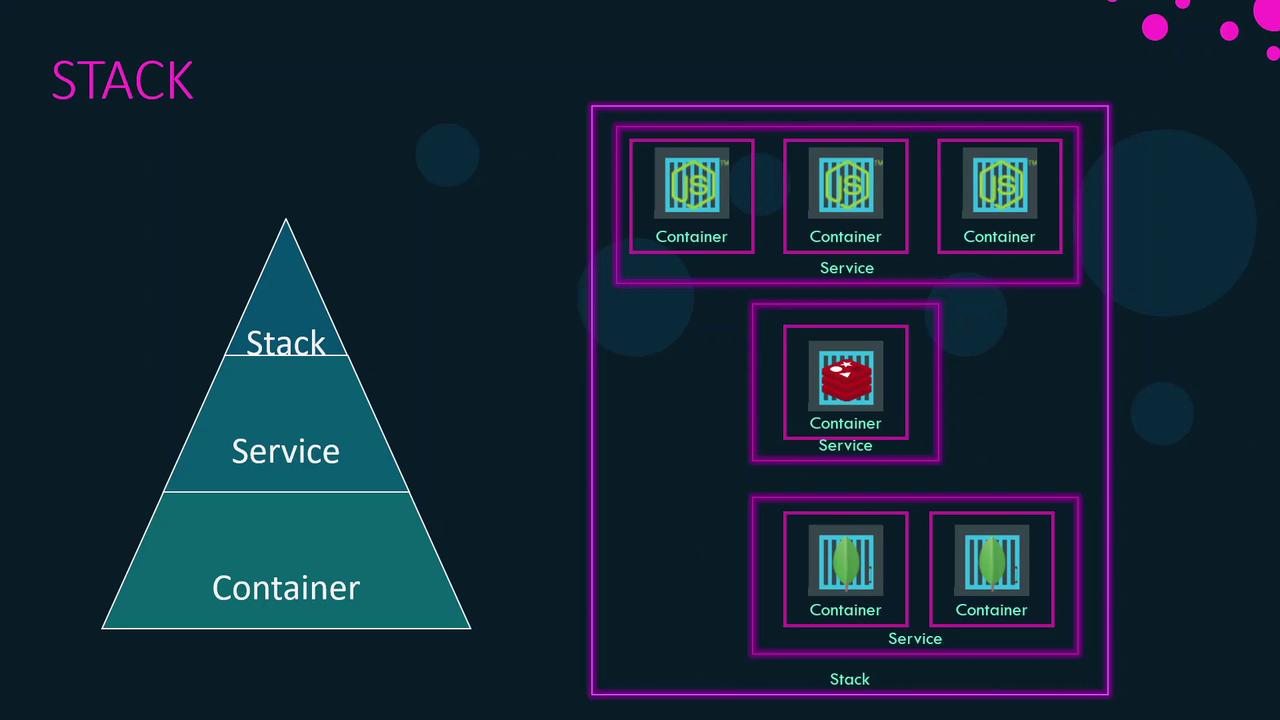
- Container: A running instance of an image, isolated with its dependencies.
- Service: A scalable set of containers of the same image, distributed across Swarm nodes.
- Stack: A collection of related services that define an application.
4. Example: Voting Application
We’ll deploy a simple voting app with Redis, PostgreSQL, vote service, result service, and a worker.4.1 Single-Host Deployment with Docker Compose
4.2 Multi-Node Deployment with Docker Stack
Assume a Swarm with one manager and two workers. Enhance the Compose file with adeploy section for Swarm-specific settings.
4.2.1 Replicas
Scale services by defining replica counts:4.2.2 Placement Constraints
Ensure critical services run only on manager nodes:4.2.3 Resource Limits
Protect node resources by setting CPU and memory limits:4.2.4 Health Checks
Automatically monitor container health:| Field | Description |
|---|---|
test | Command run inside the container to check health (e.g., curl). |
interval | Time between health checks (e.g., 1m30s). |
timeout | Maximum time to wait before marking a check as failed (e.g., 10s). |
retries | Number of consecutive failures before marking unhealthy (e.g., 3). |
start_period | Grace period before starting health checks (e.g., 40s). |
5. Common Stack Commands
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
docker stack deploy --compose-file <file> <name> | Deploy or update a stack |
docker stack ls | List all stacks |
docker stack services <stack_name> | List services within a specific stack |
docker stack ps <stack_name> | List tasks (containers) for a stack |
docker stack rm <stack_name> | Remove an entire stack |
Removing a stack stops and removes all associated services and containers. Use with caution in production environments.