- Recovering from worker node failures
- Maintaining manager node quorum
- Backing up and restoring Swarm state
1. Worker Node Failure
When a worker node goes offline, Swarm automatically reschedules its tasks to healthy workers. Returning the failed node simply makes it eligible for new tasks; it does not rebalance existing ones by default. To force a rebalance for a specific service:web service, distributing them evenly across available nodes.
2. Manager Node Quorum
Swarm managers rely on Raft consensus. A majority of managers (quorum) must be active to perform administrative tasks. Use the table below to understand different setups:| Cluster Setup | Quorum Required | Impact When a Manager Fails |
|---|---|---|
| Single-manager | 1 | Admin operations stop. Worker tasks keep running. |
| Three-manager | 2 | One failure tolerated. Full functionality remains intact. |
2.1 Scenarios
-
Single manager fails
- Admin operations (adding nodes, updating services) are blocked.
- Worker containers continue serving traffic.
-
Recovery: restart the manager or promote a worker:
-
One of three managers fails
- Quorum (2 of 3) remains.
- Cluster stays fully functional.
- On recovery, the failed manager rejoins automatically if Docker was intact.
-
Two managers fail (no quorum)
- Administrative operations halt completely.
- Options:
- Restore the failed managers.
-
If restoration is impossible, bootstrap a new cluster on the remaining node:
3. Swarm State Storage and Backup
Swarm stores its state in the Raft database at/var/lib/docker/swarm on each manager. Regular backups ensure you can recover from total manager loss.
3.1 Backup Procedure
- On a non-leader manager (to avoid Raft re-election), stop Docker Engine:
- Archive the Swarm data:
- Restart Docker:
While Docker is stopped, the Swarm API is unavailable. Worker containers continue running, but no changes can be made until the engine restarts.
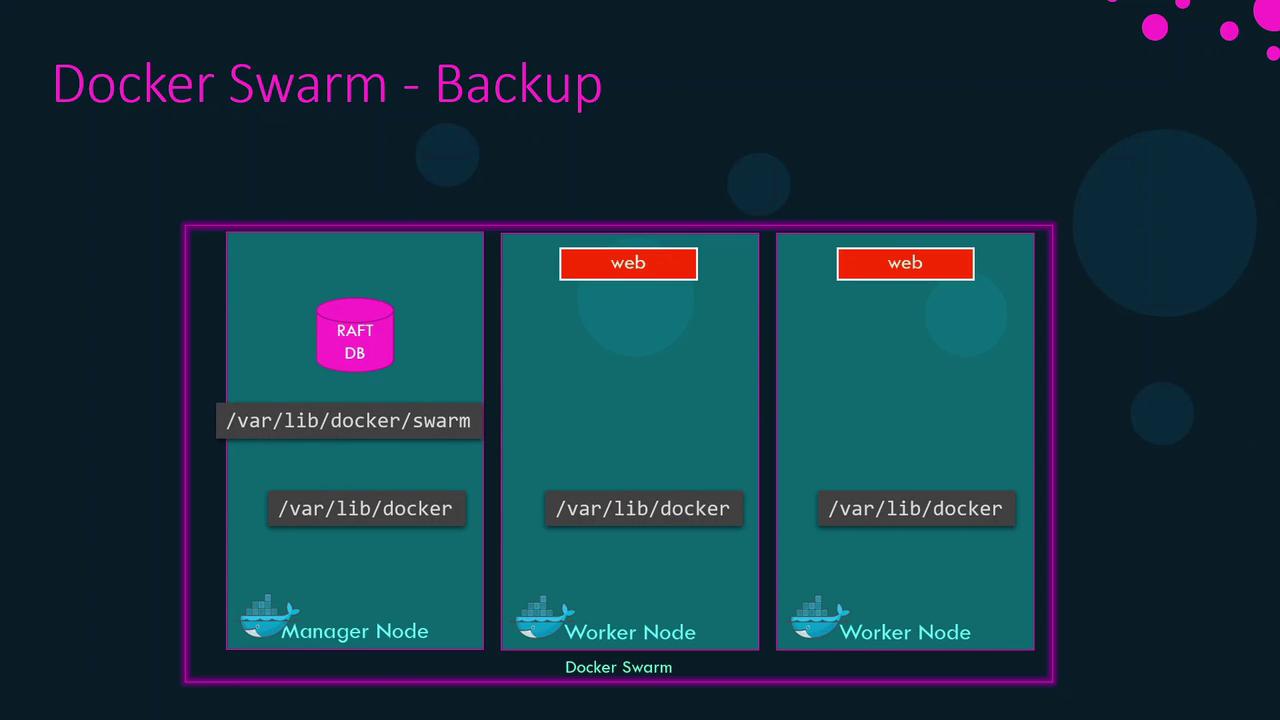
- Raft database (cluster membership, service definitions, overlay networks, configs, secrets)
- Cluster metadata
If auto-locking (Swarm encryption) is enabled, the Raft database is encrypted with an unlock key stored outside
/var/lib/docker/swarm. Securely back up this key in a password manager.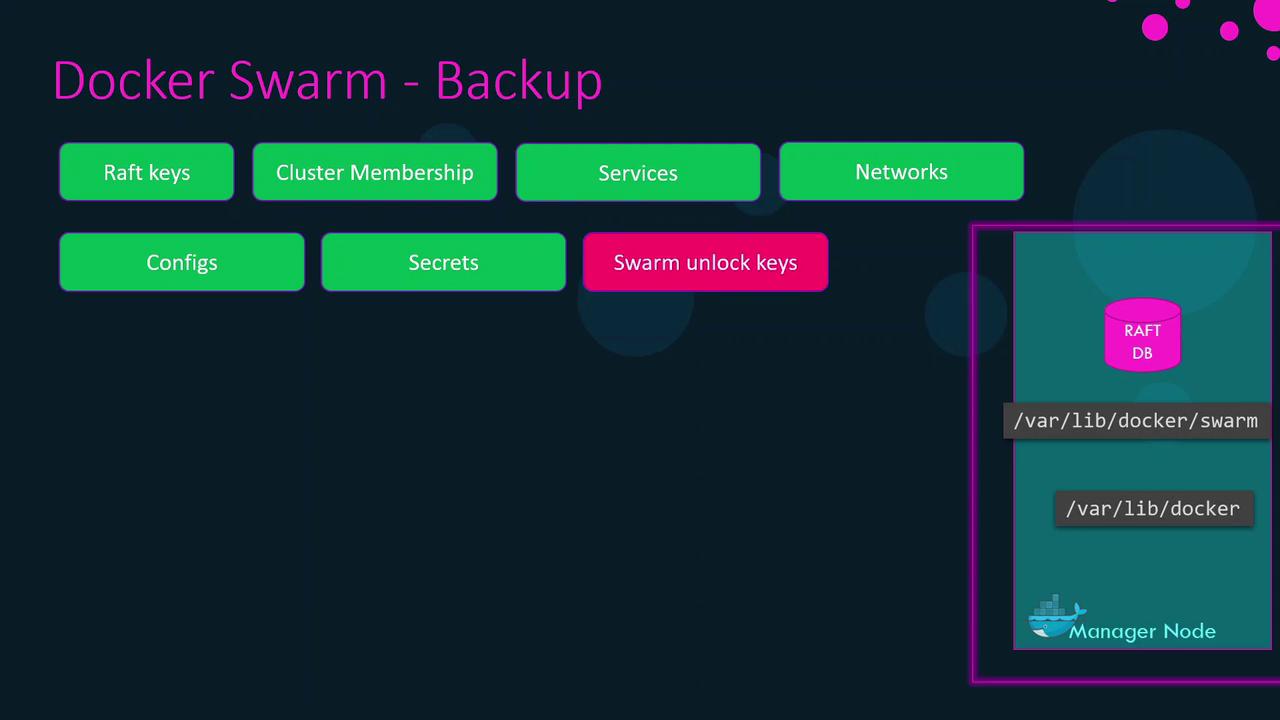
4. Restoring a Swarm from Backup
If all manager nodes are lost, recover your cluster state on a new host:- Install Docker on the new node and stop the engine:
- Ensure
/var/lib/docker/swarmis empty, then extract the backup: - Start Docker:
- Reinitialize Swarm with your restored state:
That completes the Docker Swarm disaster recovery workflow. Strategies for UCP and DTR will be covered in separate articles.