Understanding persistent storage in AKS is crucial for managing stateful applications effectively. This article explains how persistent storage is integrated and managed within an AKS cluster.
Architecture Overview
An AKS cluster is composed of two major components:-
Azure Managed Control Plane
The control plane hosts the API server, a central component that manages the cluster by orchestrating communication between various components. It handles tasks such as provisioning, scaling, and managing the lifecycle of storage resources. -
Customer Managed Nodes
These nodes run your application workloads (e.g., pods). When pods require persistent data storage, they make a formal request using a Persistent Volume Claim (PVC). This request is processed by the API server to allocate an appropriate Persistent Volume (PV) that maps the storage request to an actual Azure storage resource.
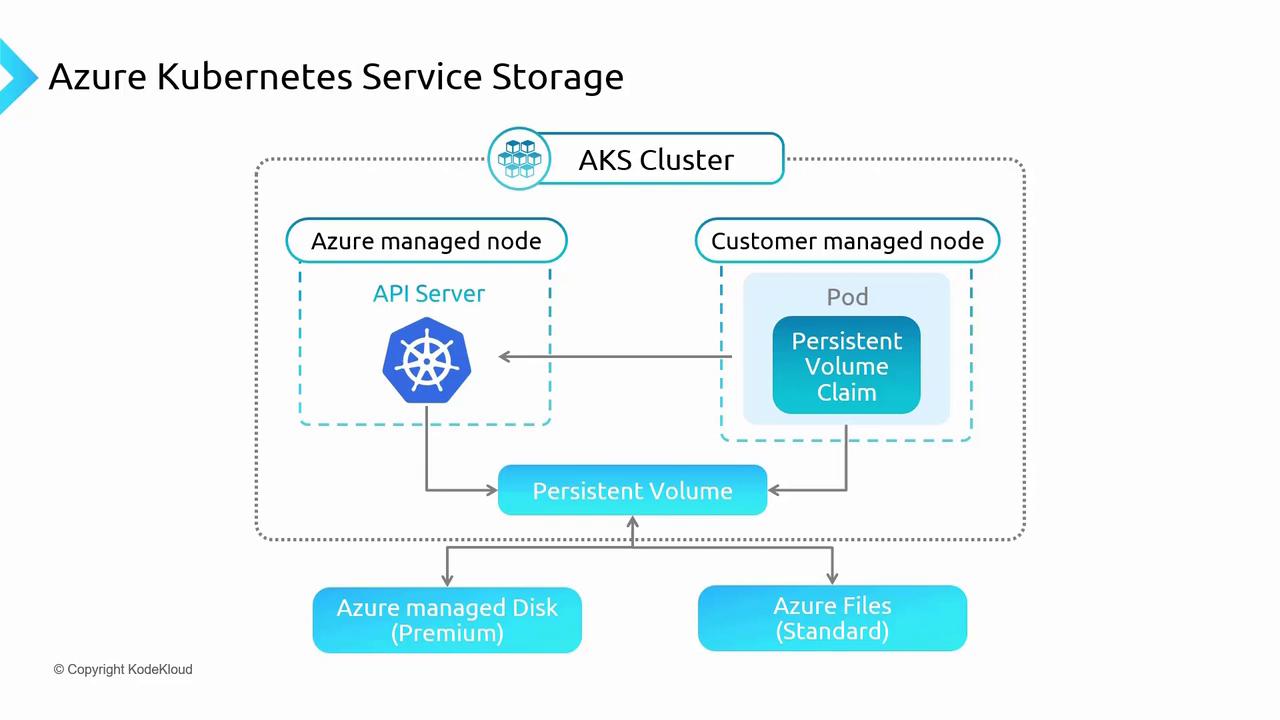
Persistent Storage Backend Options
At the lower part of the architecture diagram, two primary Azure storage backend options are highlighted:-
Azure Managed Disk Premium
Positioned on the left in the diagram, this high-performance storage solution is ideal for data-intensive operations. It offers fast read/write capabilities along with robust security features, including storage service encryption. -
Azure Files
Located on the right in the diagram, Azure Files provides shared storage suitable for applications that require shared content or configuration data. Like Managed Disks, Azure Files ensures comprehensive security when utilized as persistent storage.
Configuring Persistent Storage in AKS
To enable persistent storage within an AKS cluster, you need to define a Storage Class in your Kubernetes manifest (YAML or JSON). In the Storage Class, you specify key details such as:- Storage tier (premium or standard)
- Reclaim policy (determining whether the storage should be retained or deleted once the PVC is released)
By integrating native Azure Storage services as persistent volumes in an AKS cluster, you ensure that your applications benefit from secure, high-performance, and persistent storage. This approach not only supports data durability but also aligns with best practices for managing sensitive workloads by providing data encryption both at rest and in transit.