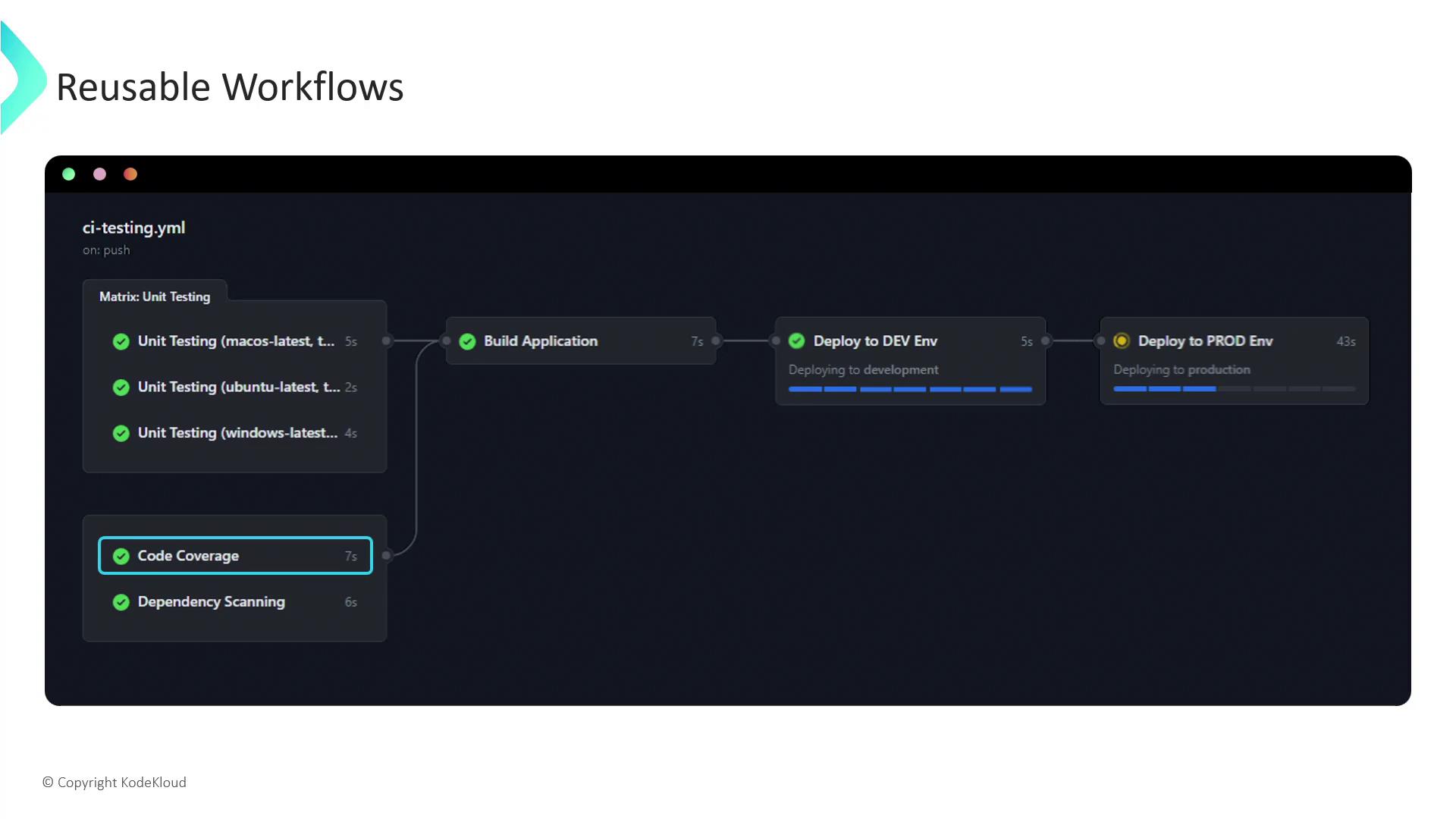
- Unit Testing
- Code Coverage
- Dependency Scanning
- Build
- Deploy to Dev (runs after build succeeds)
- Deploy to Prod (waits for Dev deployment)
Why Use Reusable Workflows?
Imagine your organization maintains services in Java, Python, .NET, Go, and more. While build and test commands differ, deployment steps—like provisioning infrastructure, uploading artifacts, and running smoke tests—tend to be identical. Reusable workflows centralize these shared steps:| Programming Language | Build Tool | Test Tool | Deployment Steps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Java | Maven/Gradle | JUnit/TestNG | Provision → Deploy → Smoke Test → Notify |
| Python | pip/Poetry | pytest | Provision → Deploy → Smoke Test → Notify |
| .NET | dotnet build | xUnit | Provision → Deploy → Smoke Test → Notify |
| Go | go build | go test | Provision → Deploy → Smoke Test → Notify |
| Node.js | npm/ Yarn | Jest/Mocha | Provision → Deploy → Smoke Test → Notify |
1. Extracting the Deployment Job
Let’s say you have a repositoryxyz-org/nodejs-app-repo with .github/workflows/awesome-app.yml:
dev-deploy job into its own reusable workflow file:
The
on: workflow_call trigger makes this workflow callable from other workflows. You can also define inputs, outputs, and secrets under workflow_call for advanced parameterization.2. Calling a Reusable Workflow
Back inawesome-app.yml, replace the inline dev-deploy job with a reference to the reusable workflow:
{owner}/{repo}/{path}@ref:
When calling workflows in private repositories, ensure the caller has appropriate permissions and that any required
secrets: are declared in the called workflow’s workflow_call section.3. Inputs, Outputs, and Secrets
To make your reusable workflows more flexible:- Inputs allow callers to pass parameters (e.g., environment name, version tag).
- Outputs let callers consume results (e.g., artifact URLs, deployment IDs).
- Secrets ensure sensitive data—like cloud credentials—are never exposed.
Benefits of Modular CI/CD with Reusable Workflows
- Consistency: Enforce the same deployment steps across all services.
- Maintainability: Update a single workflow file to propagate changes everywhere.
- Scalability: Easily onboard new projects by referencing prebuilt workflows.
- Security: Centralize and manage secrets in one place.