In this guide, we’ll show you how to spin up a non-production MongoDB service container alongside your GitHub Actions workflow. By configuring a service container, you isolate test data from your production instance and ensure reliable, repeatable unit tests.
Service containers are Docker containers that run in parallel with your job, providing databases, caches, or other dependencies in an isolated environment.
1. Base Workflow Configuration Here’s our existing workflow using a production MongoDB instance. We need to replace it with a test container:
name : Solar System Workflow on : workflow_dispatch : push : branches : - main - 'feature/*' env : MONGO_URI : mongodb+srv://supercluster.d83jj.mongodb.net/superData MONGO_USERNAME : ${{ vars.MONGO_USERNAME }} MONGO_PASSWORD : ${{ secrets.MONGO_PASSWORD }} jobs : unit-testing : ... code-coverage : ... docker : ...
2. Configuring MongoDB as a Service Container We’ll use the pre-built image siddharth67/mongo-db:non-prod from Docker Hub . Add a services section to your unit-testing job:
jobs : unit-testing : name : Unit Testing runs-on : ubuntu-latest services : mongo-db : image : siddharth67/mongo-db:non-prod ports : - 27017:27017 strategy : matrix : nodejs_version : [ 18 , 20 ] operating_system : [ ubuntu-latest ] exclude : - nodejs_version : 18 operating_system : macos-latest steps : - name : Checkout Repository uses : actions/checkout@v4 - name : Setup Node.js ${{ matrix.nodejs_version }} uses : actions/setup-node@v3 with : node-version : ${{ matrix.nodejs_version }}
Mapping port 27017 on the host to the container lets your tests connect via localhost:27017.
3. Overriding Environment Variables Job-level environment variables override global settings. Point your test suite at the local MongoDB service:
jobs : unit-testing : # ... (services config) env : MONGO_URI : 'mongodb://localhost:27017/superData' MONGO_USERNAME : non-prod-user MONGO_PASSWORD : non-prod-password # ... (strategy & steps)
Job-level env entries take precedence over workflow-level env values.
Commit and push to trigger the updated workflow.
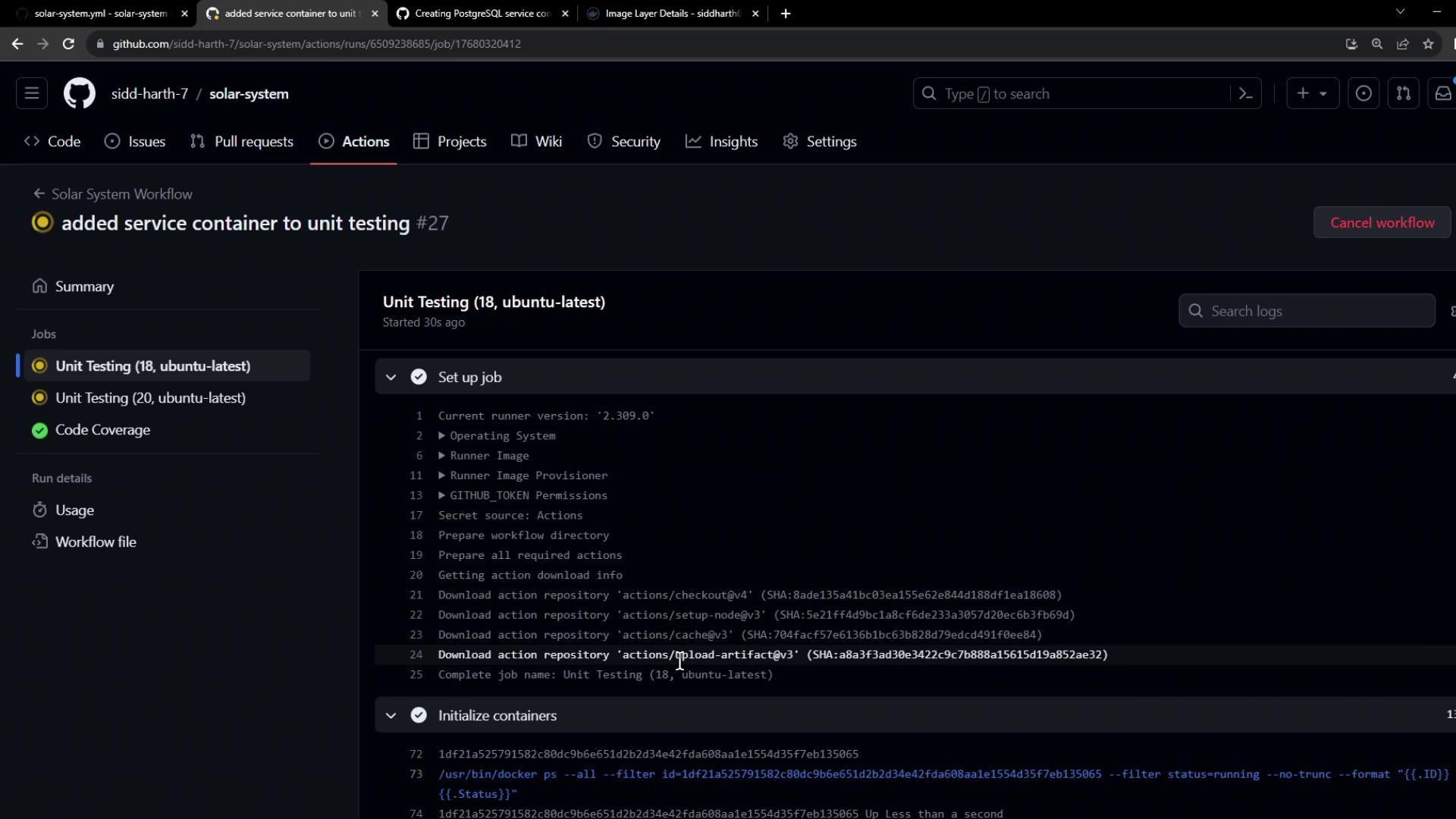
4. Initialization Behind the Scenes During the initialize containers step, GitHub Actions:
Creates an isolated Docker network
Pulls the service image
Launches the container and maps its ports
Waits for any health checks to pass
/usr/bin/docker ps --filter id=... --no-trunc --format "{{.ID}}" /usr/bin/docker inspect --format "{{if .Config.Healthcheck}}{{print .State.Health.Status}}{{end}}"
5. Fixing Connection String Errors If you encounter:
MongoParseError: Invalid connection string
ensure your URI starts with the correct scheme:
env : MONGO_URI : 'mongodb://localhost:27017/superData'
Check for typos and ensure mongodb:// (not mongodb+srv://) when connecting to a local container.
You can also update to the latest setup-node action:
- name : Setup Node.js ${{ matrix.nodejs_version }} uses : actions/setup-node@v4 with : node-version : ${{ matrix.nodejs_version }}
Push your fixes and rerun the workflow.
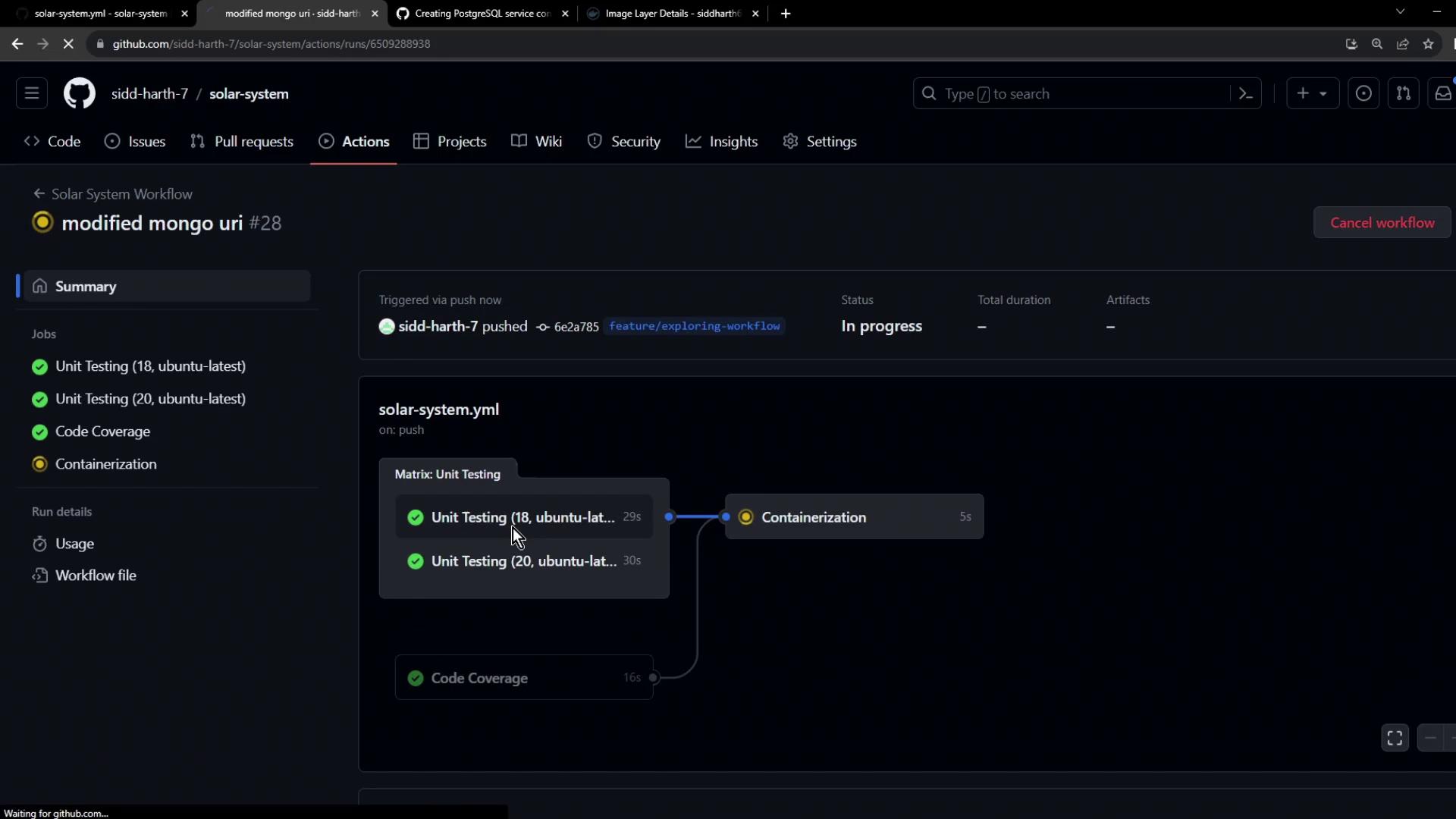
6. Successful Run A successful unit-testing job looks like this:
npm test shell: /usr/bin/bash -e { 0 } env: MONGO_URI: mongodb://localhost:27017/superData MONGO_USERNAME: non-prod-user MONGO_PASSWORD: non-prod-password Solar [email protected] test mocha app-test.js --timeout 10000 --reporter mocha-junit-reporter --exit Server successfully running on port - 3000
Your tests now run against a dedicated non-production MongoDB container, keeping real data safe and test environments reproducible.
References