cowsay, upload it as an artifact in one job, and download it in subsequent jobs within a GitHub Actions workflow. This approach ensures files produced in the build step are available during test and deploy phases.
Table of Contents
- Initial Workflow Setup
- Upload Artifact Action
- Download Artifact Action
- Integrate in Build, Test, and Deploy Jobs
- Inspecting Workflow Results
- Retention and Storage Limits
- Links and References
Initial Workflow Setup
Here’s a basic workflow that installscowsay, generates ASCII art, then idles—without using artifacts yet:
Upload Artifact Action
Use the actions/upload-artifact action to persist files or share them with later jobs. Below is the minimal configuration:
Download Artifact Action
To pull down an artifact in another job, configure actions/download-artifact:Integrate in Build, Test, and Deploy Jobs
1. Build Job
Remove the sleep step and uploaddragon.txt:
2. Test Job
Download the artifact and verify its content:3. Deploy Job
Retrieve the same artifact before deployment:Inspecting Workflow Results
After committing and pushing, view the GitHub Actions tab. You might see a failed test job if something goes wrong: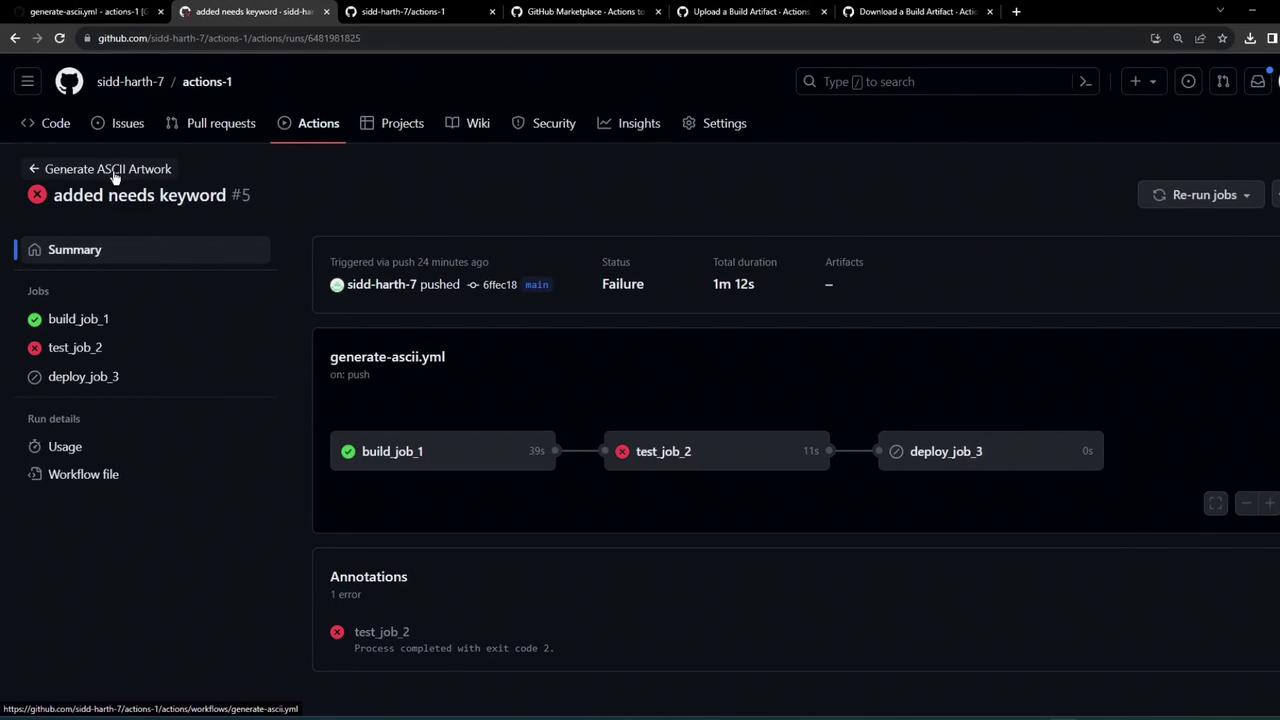
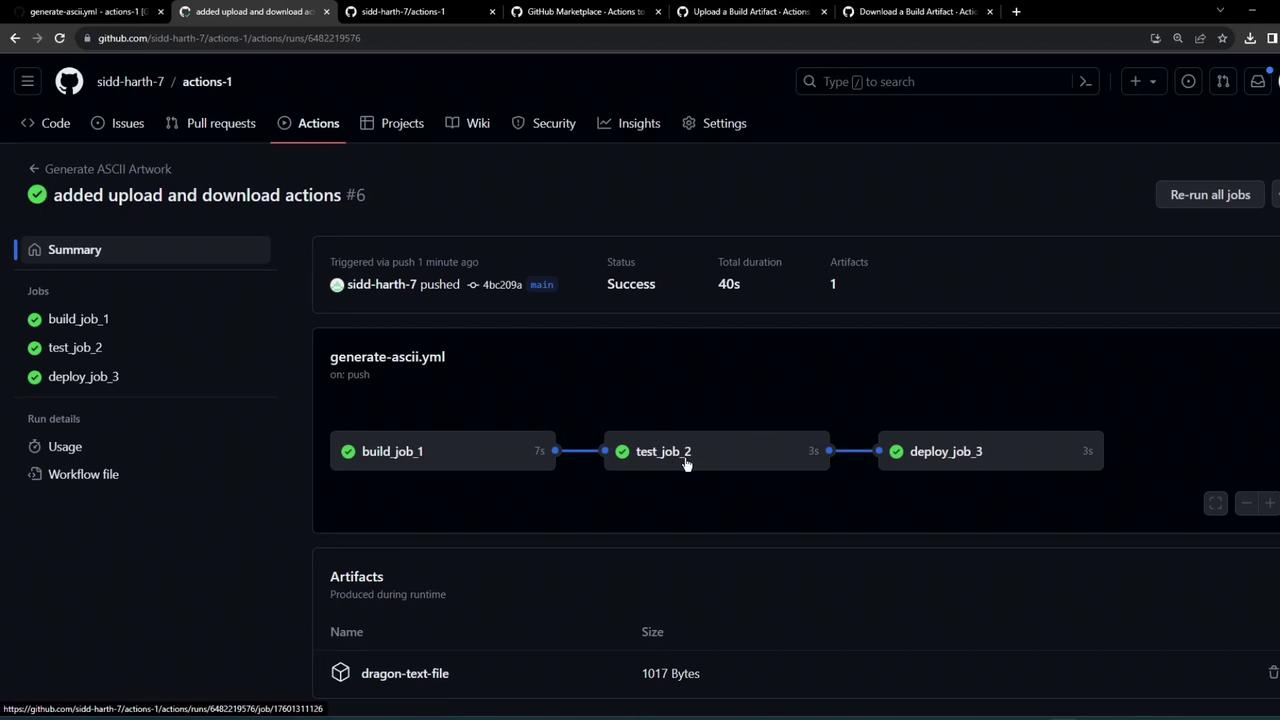
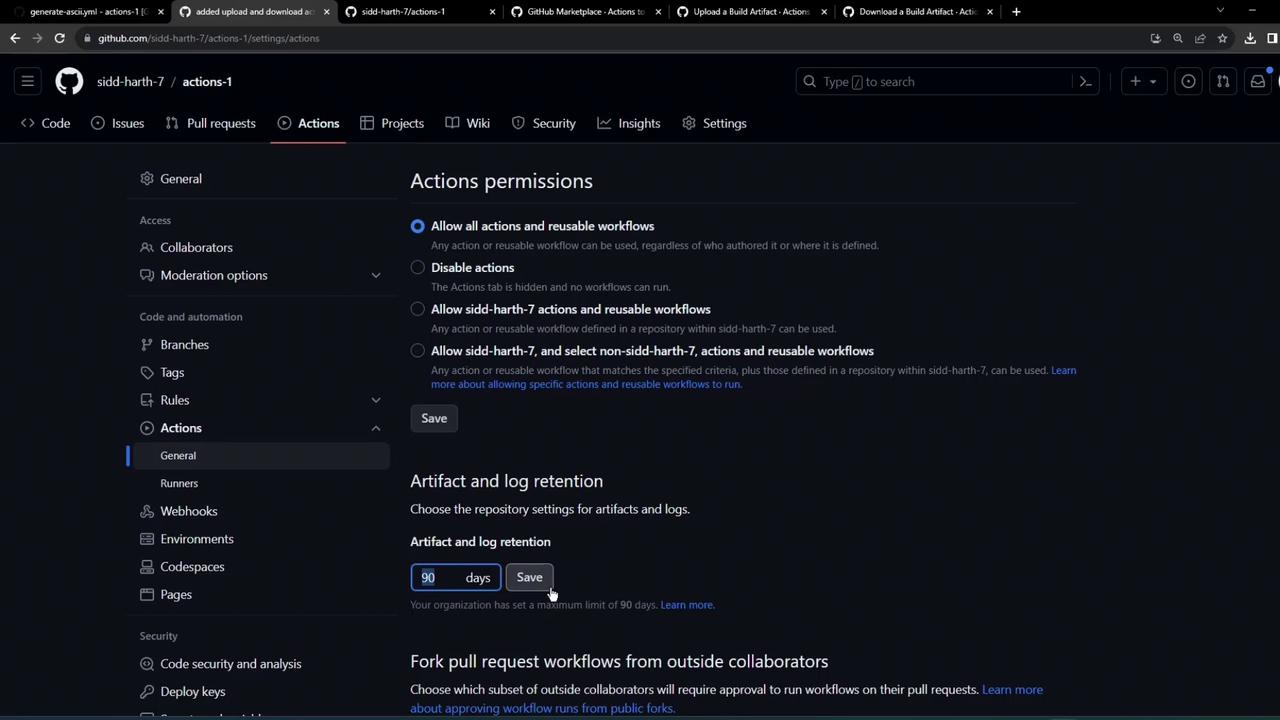
Retention and Storage Limits
By default, artifacts and logs are kept for 90 days. Free-tier repositories can store up to 500 MB in total.| Setting | Default | Max (free tier) |
|---|---|---|
| Artifact retention | 90 days | Configurable |
| Total artifact storage | N/A | 500 MB |
You can adjust retention settings under Repository > Settings > Actions to match your project requirements.
Links and References
- GitHub Actions: Uploading artifacts
- actions/upload-artifact on Marketplace
- actions/download-artifact on Marketplace
By following this pattern, you can persist build outputs (JARs, WARs, binaries) across jobs and ensure a clean, maintainable CI/CD pipeline in GitHub Actions.