What is CI/CD?
CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery.- Continuous Integration is the automated process of building, packaging, and testing your application.
- Continuous Delivery automatically deploys the latest tested code to your production environment, ensuring your live system is always up-to-date.
Automating your deployment process with a CI/CD pipeline not only saves time but also improves consistency and reliability.
Our Current Manual Process
Before implementing a CI/CD pipeline, our workflow involves several manual steps:- Make changes to the code.
- Commit the changes to Git.
- Run Pytest to ensure that changes haven’t broken any functionality.
- Optionally build Docker images if required.
- Deploy the application. This deployment step can range from a simple
git push(as on Heroku) to complex server logins, code pulls, and service restarts.

Note: Although the deployment step is presented as a single action, it often involves multiple sub-steps based on your deployment strategy.
Transition to an Automated CI/CD Pipeline
Implementing a CI/CD pipeline transforms our deployment process by automating critical steps:-
Manual Code Update:
You continue to update the code and commit changes manually. -
Pipeline Trigger:
Each commit triggers the CI/CD pipeline, which manages the remaining tasks automatically. -
Continuous Integration Phase:
- Pull the latest source code.
- Install dependencies as defined in your requirements file.
- Run automated tests using Pytest.
- Optionally build Docker images if your project requires containerization.
-
Continuous Delivery Phase:
- Deploy the updated application or Docker image to production automatically based on your configuration.
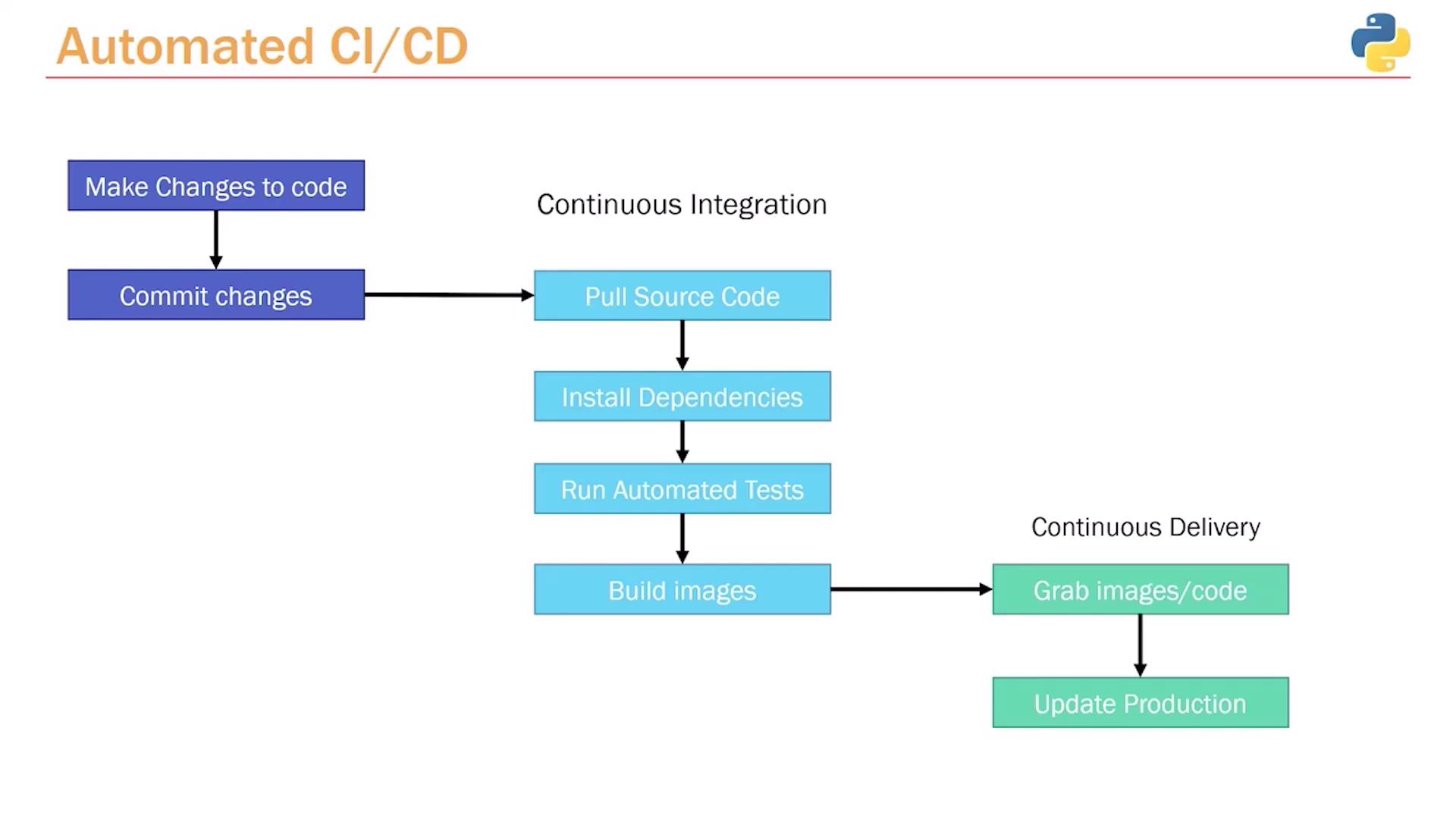
With CI/CD, only the code commit requires manual intervention. The pipeline handles the build, test, and deployment processes seamlessly.
Popular CI/CD Tools
There are several tools available to facilitate CI/CD, including:- Jenkins
- Travis CI
- CircleCI
- GitHub Actions
Understanding CI/CD Tools
A CI/CD tool provides a “runner”—a dedicated computer or virtual machine that executes the commands you specify. This runner carries out instructions as if you were running commands in your local terminal, such as installing packages withpip install or running tests with pytest.
Triggers for these automated tasks can include events like a git push or merge request, or even scheduled times (e.g., nightly builds). Despite its complexity, the CI/CD process is essentially a sequence of simple steps executed automatically.

Example: GitHub Actions Configuration
Below is an example YAML configuration for a GitHub Actions pipeline. This setup instructs the runner to perform the following tasks:- Check out the source code.
- Set up Python 3.9.
- Update pip.
- Install dependencies from the
requirements.txtfile. - Install and run Pytest for testing.