Push-Based Deployment
In a push-based deployment model, an external system—commonly part of a continuous delivery pipeline—initiates the deployment process. For example, a successful commit to a Git repository or an earlier CI pipeline can trigger this process. This external system requires direct read-write access to the Kubernetes cluster, allowing it to push changes into the production environment.When using push-based deployment, you must expose cluster credentials outside of the cluster. Store these credentials securely within your CI/CD system to prevent unauthorized access.
- Encrypt credentials to shield them from exposure.
- Apply strict access controls to limit who can access these credentials.
- Regularly rotate credentials to minimize security risks.
Pull-Based Deployment
In pull-based deployment, changes are applied from within the Kubernetes cluster. An operator running inside the cluster continuously monitors associated Git repositories and Docker registries for updates. When the operator detects a change, it synchronizes the cluster state accordingly.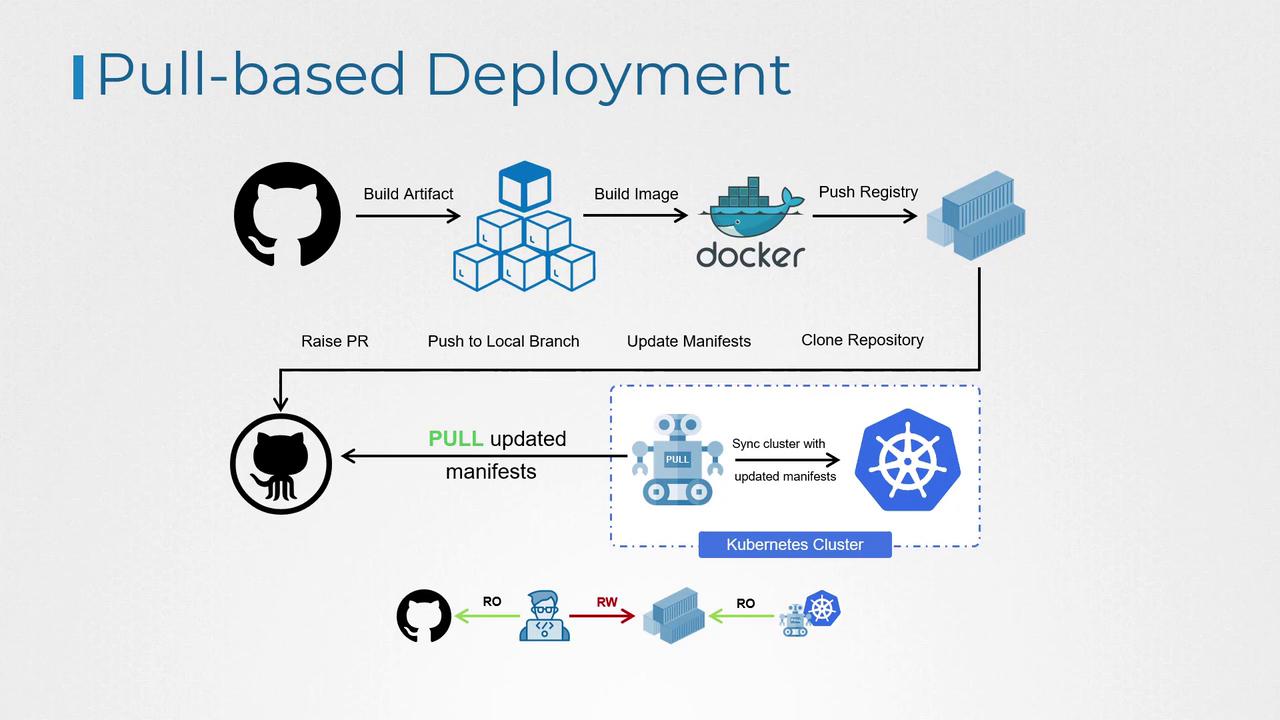
While push-based deployments provide a streamlined process initiated by external systems, they require careful management of sensitive credentials. Conversely, pull-based deployments confine all changes within the cluster, offering a more secure alternative. Choose the deployment strategy that aligns with your organization’s security requirements and operational practices.