Defining Intentions with a Service-Intentions Config Entry
The recommended approach for declaring service intentions is to use aservice-intentions config entry. This keeps your intentions version-controlled and declarative.
kind: Must beservice-intentions.name: The upstream service (here,db-01).sources: List of downstream services and their actions (allowordeny).
Modifying an existing intention only impacts new connections. Established sessions continue under the old policy until they’re restarted.
Viewing and Managing Intentions in the UI
- Log in to the Consul UI.
- Click the Intentions tab in the sidebar to see all configured intentions.
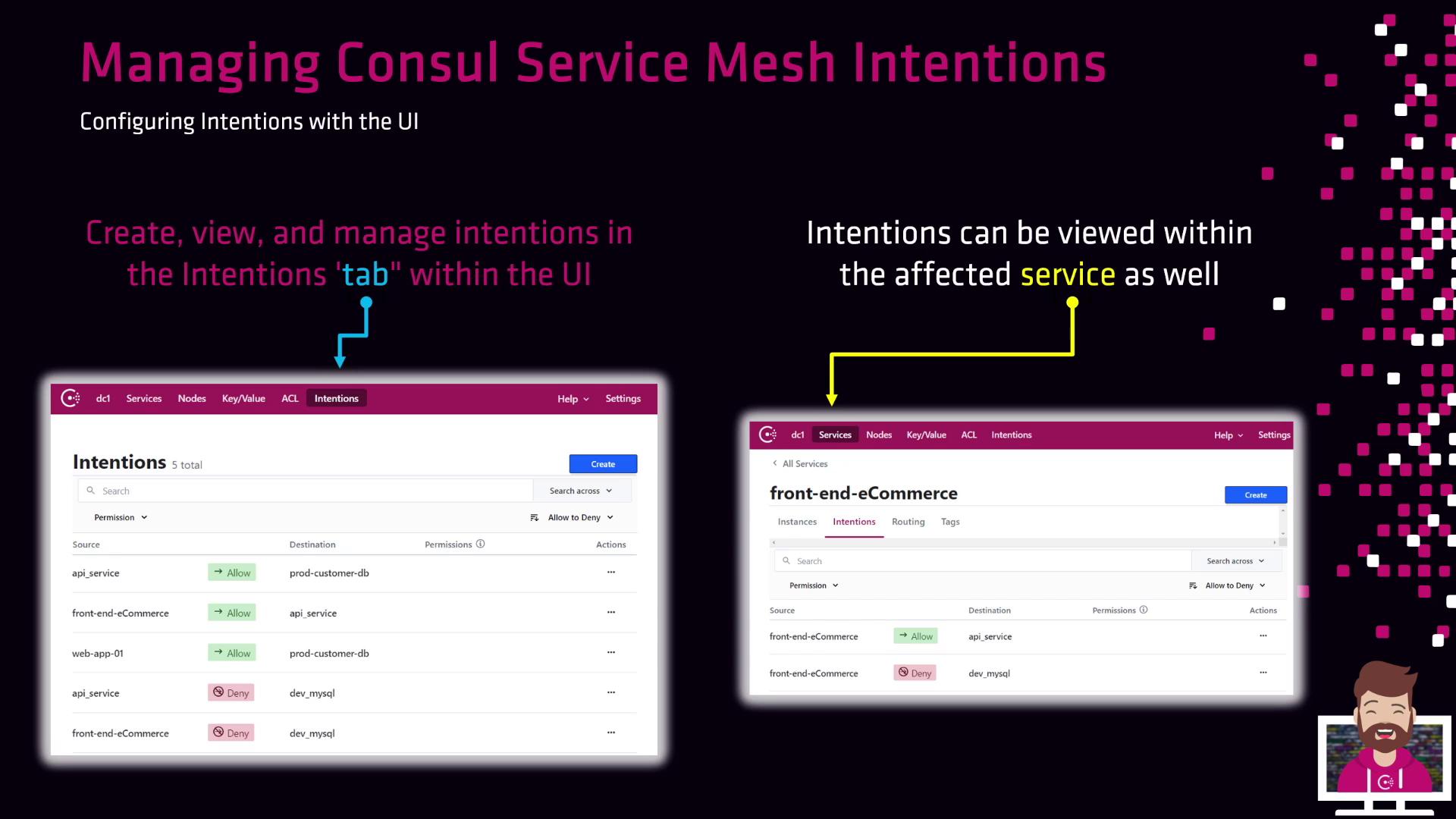
| Source Service | Destination Service | Action |
|---|---|---|
| API service | prod customer DB | allow |
| Web app 01 | customer DB | allow |
| API service, front-end e-commerce | dev MySQL | deny |
- Select the service (e.g., front-end e-commerce).
- Open its Intentions tab.
- Delete or modify any intention directly.
Managing Intentions with the HTTP API
Consul’s HTTP API enables programmatic creation, retrieval, and deletion of intentions. Note that the/v1/connect/intents endpoint was deprecated in v1.9.0 in favor of /v1/connect/intentions/exact.
The
/v1/connect/intents path is deprecated as of Consul v1.9.0. Always use /v1/connect/intentions/exact.Create or Update an Intention
Allowweb-01 to communicate with db-01:
-
Create a
payload.json: -
Send the PUT request:
List and Delete
| Operation | HTTP Method & Endpoint |
|---|---|
| List | GET /v1/connect/intentions |
| Get | GET /v1/connect/intentions/exact?source=<>&destination=<> |
| Delete | DELETE /v1/connect/intentions/exact?source=<>&destination=<> |
Managing Intentions via CLI
Theconsul intention command provides a full suite of subcommands to create, list, inspect, and remove intentions.
Common Commands
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
consul intention create [--deny] <src> <dst> | Create a new intention (default: allow) |
consul intention delete <src> <dst> | Remove an existing intention |
consul intention list | List all intentions |
consul intention get <src> <dst> | Show details of a specific intention |
consul intention check <src> <dst> | Test intent between two services |
consul intention match <src> <dst> | Display the effective intention |
Examples
Omitting
--deny on create defaults to an allow intention.Next, apply these approaches within your own Consul cluster to enforce secure, service-to-service communication.