Common Causes of Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
Zero-day vulnerabilities can occur due to various reasons. A typical example is software bugs—unintentional errors or oversights in code that have not yet been discovered. In addition, vulnerabilities may also stem from hardware flaws or issues within firmware components.
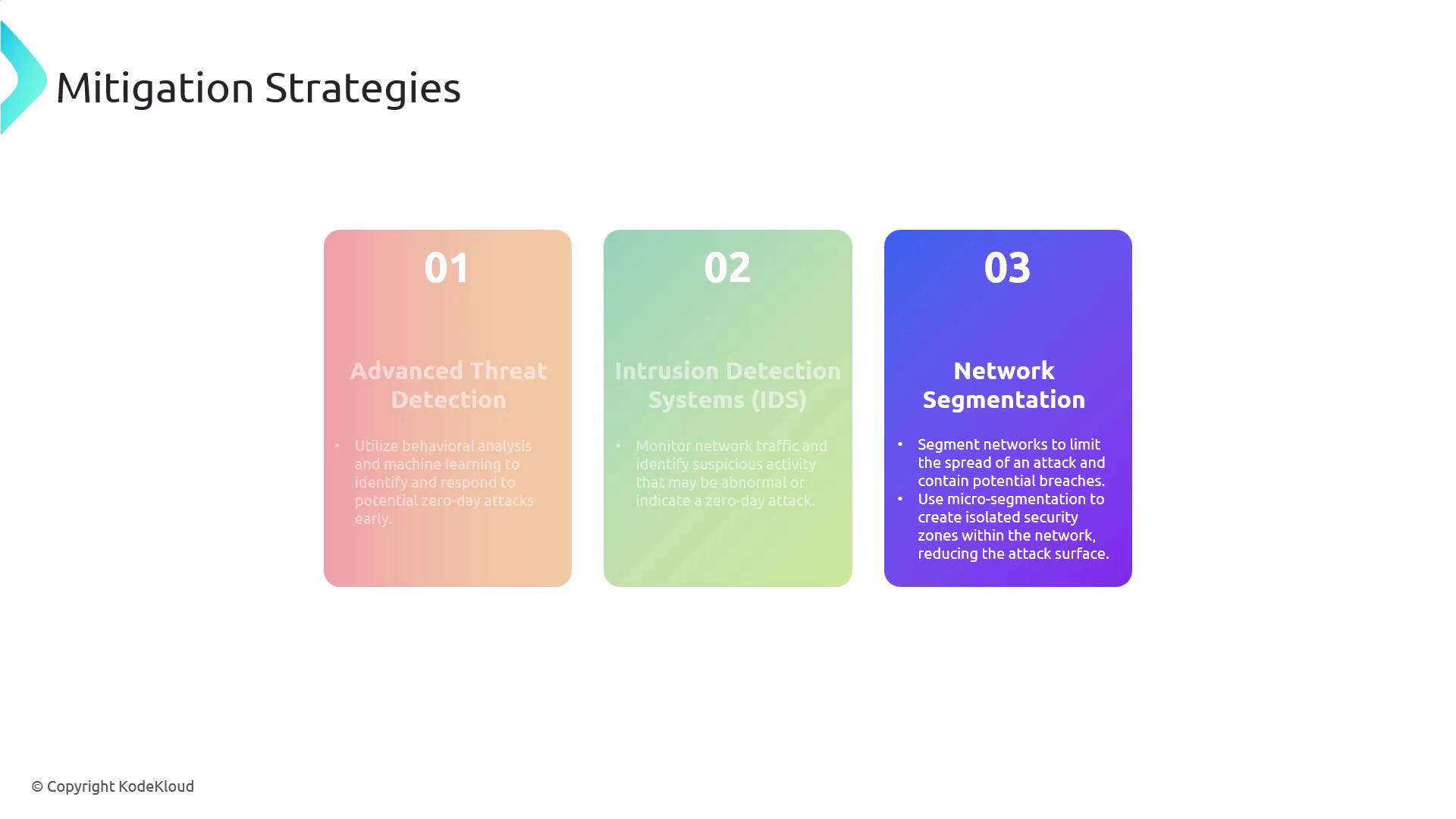
Mitigation Strategies
Although immediate fixes may not be available when a zero-day vulnerability is identified, several proactive measures can be implemented to reduce the risk:-
Advanced Threat Detection:
Utilize behavioral analysis and machine learning tools to detect and respond to suspicious activities that could signal a zero-day attack. Combining this approach with an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) enhances your defenses by monitoring network traffic for anomalous behaviors. -
Network Segmentation:
Dividing your network into smaller, isolated segments limits the spread of an attack. Adopting micro-segmentation techniques can further isolate critical systems, reducing the overall attack surface and improving security posture.
Implementing advanced threat detection, maintaining a robust update and patch management policy, and enforcing network segmentation can significantly decrease the risk and impact of zero-day vulnerabilities.