- Data Owners
- Data Controllers
- Data Processors
- Data Custodians or Stewards
Effective role designation ensures that data privacy and security measures align with legal regulations and organizational policies.
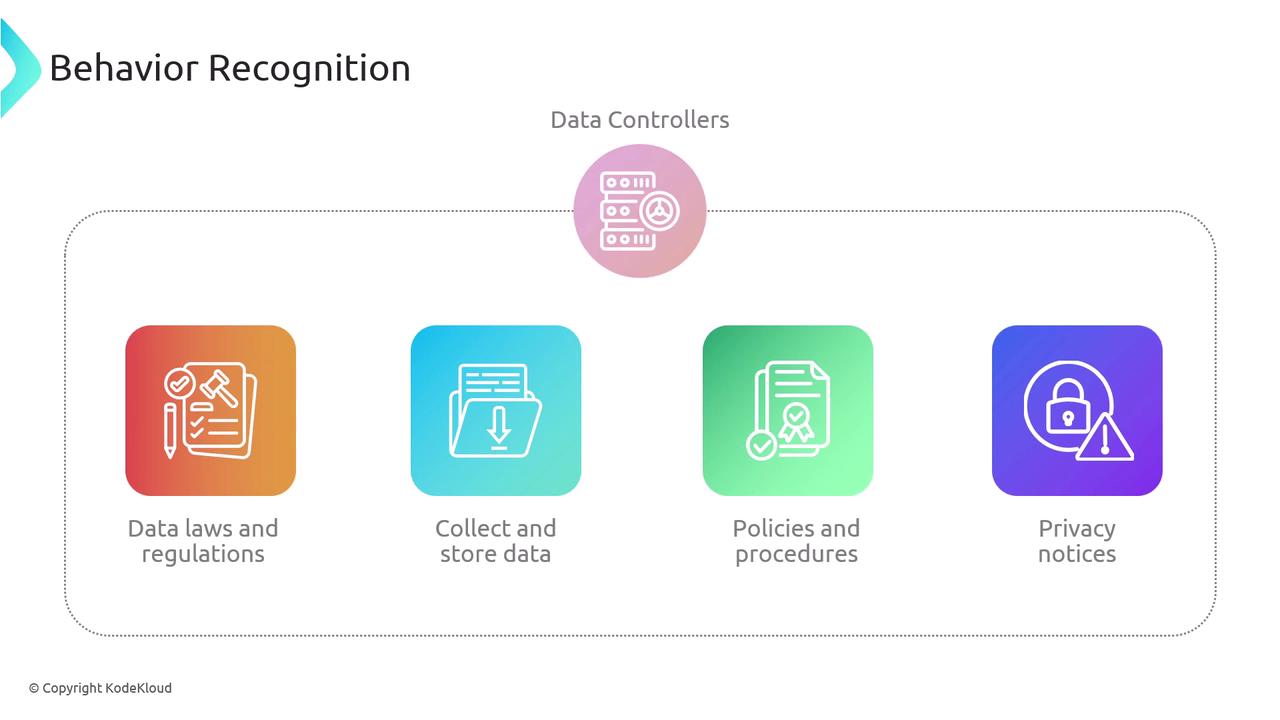
Data Controllers and Data Processors
Legally, a data controller—which may be an individual or organization—is responsible for ensuring compliance with data privacy laws and regulations. As the entity ultimately accountable for the data, the data controller must:- Ensure adherence to data laws and regulations
- Secure consent for data collection and storage
- Implement comprehensive policies and procedures to protect data
- Provide clear privacy notices
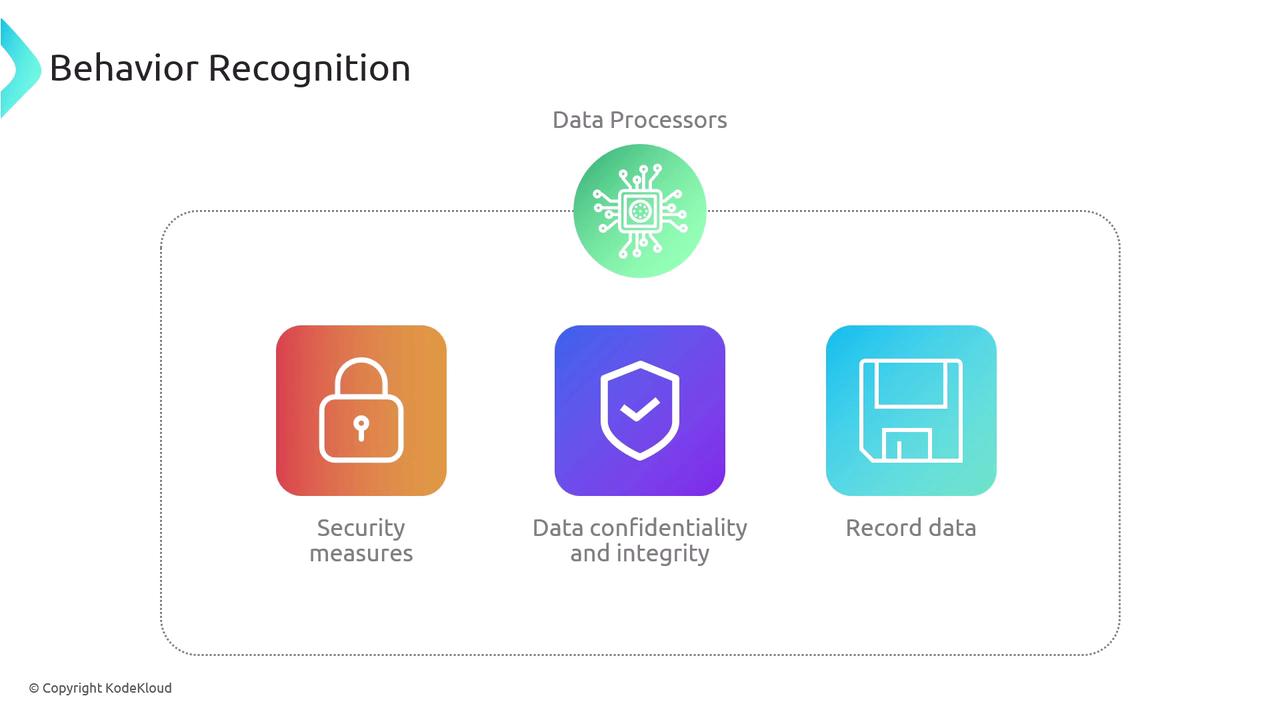
- Implementing robust security measures
- Maintaining data confidentiality and integrity
- Keeping detailed records of all data processing activities
Data Custodians and Data Stewards
The roles of data custodians and data stewards are closely related yet distinct. Data custodians are primarily responsible for managing the technical environment in which data is stored and transmitted. In contrast, data stewards focus on data quality, ensuring its accuracy, and overseeing its proper utilization across the business.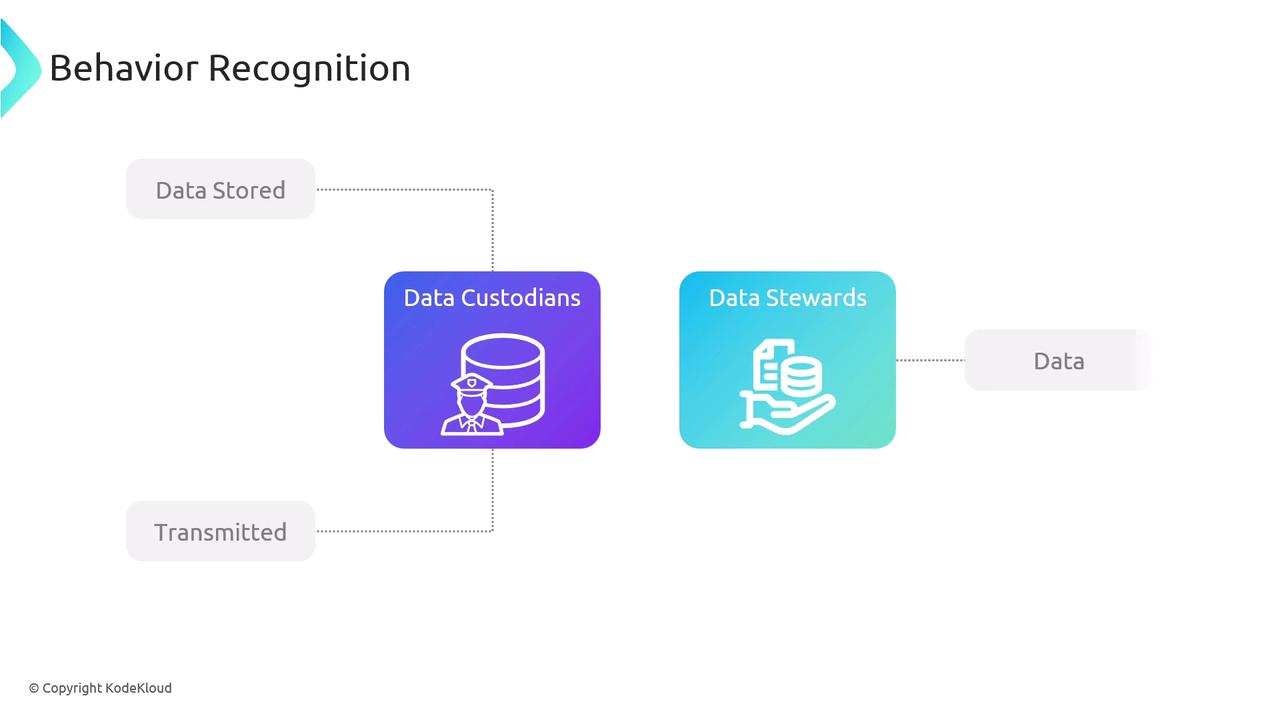
- The data controller (e.g., the HR or payroll department) determines how this data is processed and is accountable for its proper use.
- The data processor is a third-party service engaged to handle payroll processing, implementing robust security measures under the data controller’s directives.
- The data custodian is typically the IT department providing the servers and resources needed to securely store the data, ensuring encryption during data rest and transit.
- The data steward works within the payroll department to verify salary details, manage pay dates, and maintain timesheets accurately.
Data Owners and Data Subjects
Understanding the difference between data ownership and data subjects is imperative for effective data governance:- If personal data is being processed, the individual is recognized as the data subject. Regulations like the GDPR empower data subjects with rights such as the right to be forgotten and the ability to request data removal.
- The data owner is generally the person or department responsible for overseeing the use of that data once provided by the data subject.
Conclusion
In summary, this article has detailed the critical elements of security governance, including:- Policies and procedures for data handling
- Clear delineation of roles and responsibilities among data controllers, processors, custodians, stewards, owners, and subjects
- The importance of maintaining robust data privacy practices in compliance with regulatory requirements