Types of Managed Identities
Azure provides two distinct types of managed identities:-
System-Assigned Managed Identity
This identity is automatically created as part of an Azure resource, such as a virtual machine or an Azure App Service. Its lifecycle is intrinsically linked to the resource—when the resource is deleted, the identity is automatically removed as well. -
User-Assigned Managed Identity
This identity is created as an independent Azure resource and can be assigned to one or more Azure services. Since its lifecycle is separate from any individual resource, it requires explicit management and deletion when no longer needed.

System-assigned managed identities are ideal when an identity is needed only for a single resource, while user-assigned managed identities offer flexibility by allowing a single identity to be shared across multiple resources.
When to Use Managed Identities
Managed identities are particularly useful when you need Azure resources—such as virtual machines, App Services, Container Instances, Container Apps, or Azure Kubernetes Service—to access other Azure services securely and without manual credential management. Any service supporting Azure AD (or Microsoft Entra ID) authentication can benefit from this setup.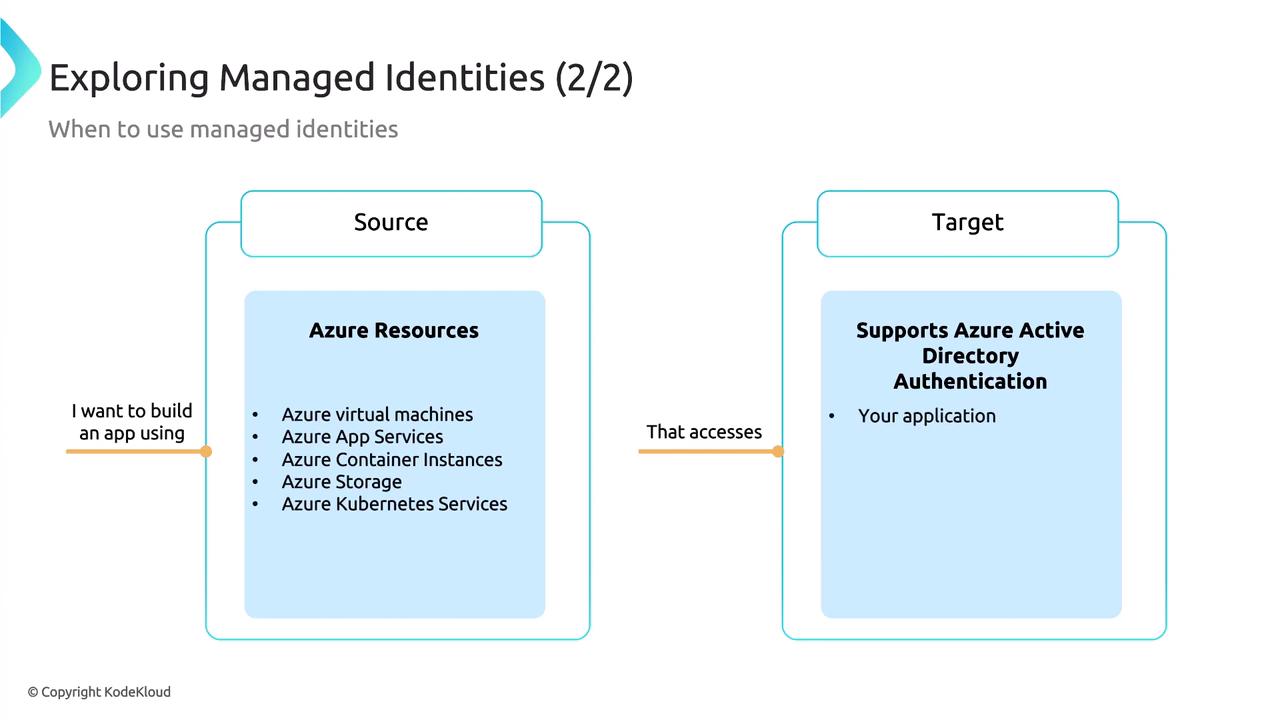
Authentication Flow with Managed Identities
The authentication process with managed identities follows a secure and streamlined flow:- The resource requests a token from Azure AD using its assigned managed identity.
- Azure AD validates the identity and issues a token.
- The resource uses the token to authenticate with the target service that supports Azure AD (or Microsoft Entra ID) authentication.
This authentication flow enhances security by eliminating the need to store and manage credentials, thereby significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access.