- Multi-tenant Public Service
- Single-tenant App Service Environment (ASE)
Multi-tenant Public Service
The multi-tenant model is the default option for most App Service plans. In this configuration, multiple tenants share the same underlying infrastructure, and applications are exposed to the public internet. This setup is ideal for hosting scenarios such as blogs or public-facing applications, where efficient resource utilization is key.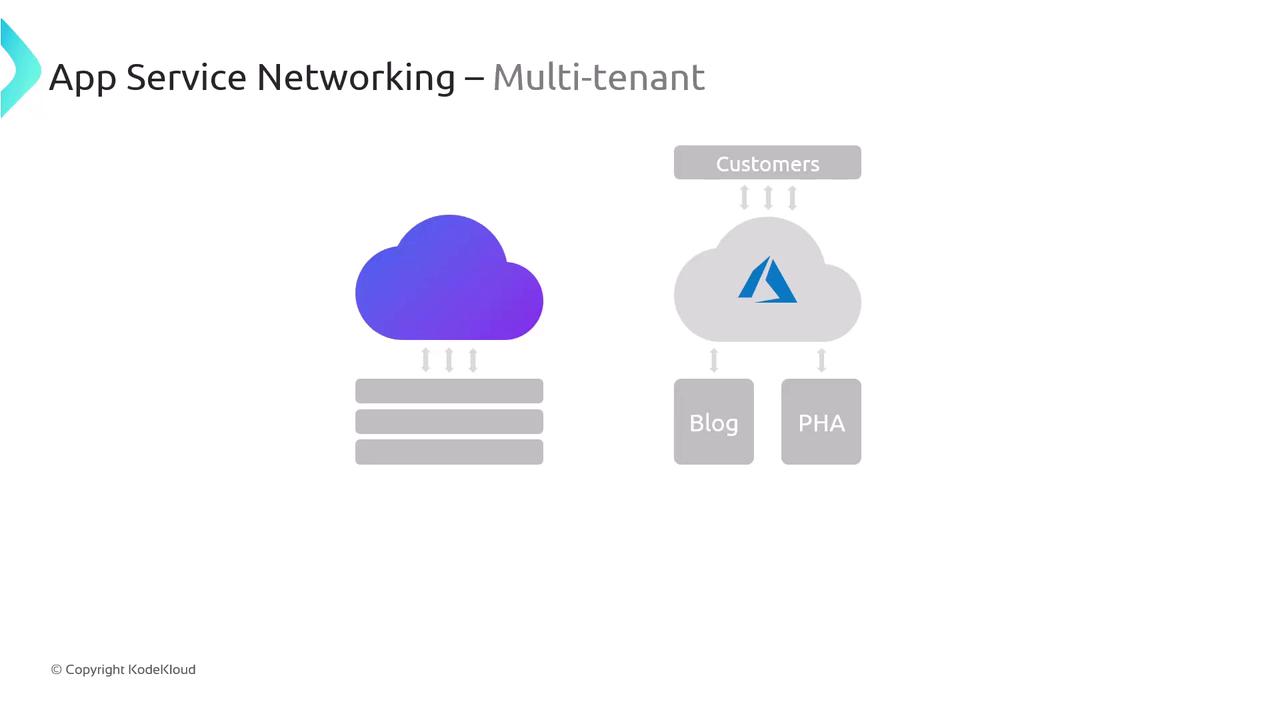
Even though the underlying infrastructure in a multi-tenant environment is shared, your application’s data remains isolated. This model is both cost-effective and efficient.
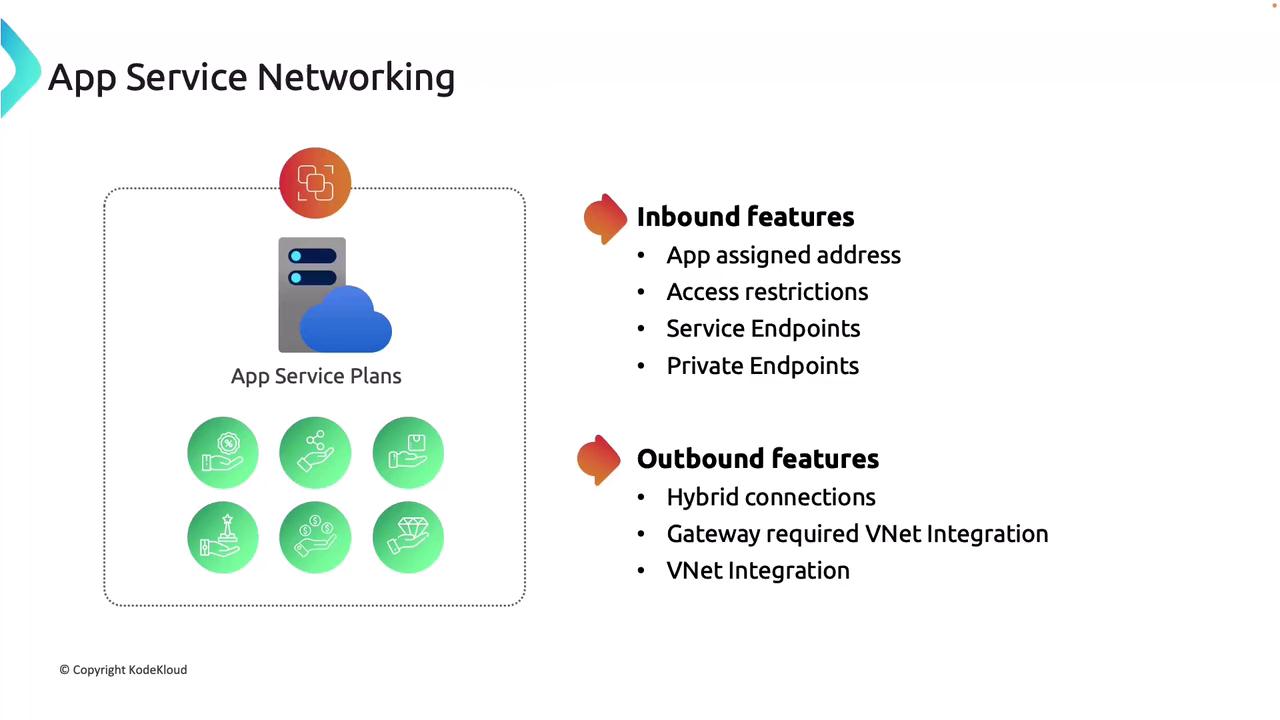
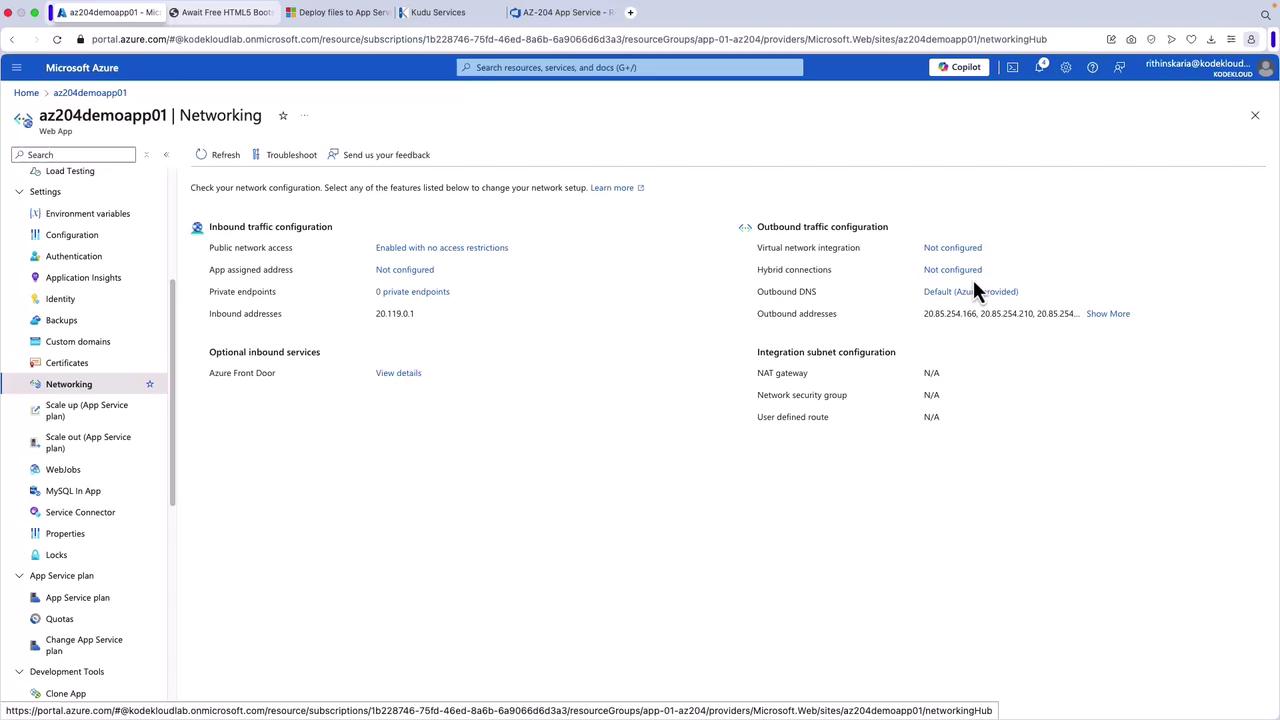
Inbound Networking Features
- App Assigned Address: Each application receives a unique IP address.
- Access Restrictions: Configure rules to restrict app access based on IP addresses or other criteria.
- Service Endpoints and Private Endpoints: Securely connect your apps using service or private endpoints. With private endpoints, your app effectively acquires a private IP from a virtual network even without direct deployment within one.
Outbound Networking Features
- Hybrid Connections: Enable your app to connect to on-premises solutions seamlessly.
- VNet Integration: Securely connect your application to virtual network-based resources, such as internal databases with no public access.
Single-tenant App Service Environment (ASE)
For applications requiring enhanced security and greater isolation, Azure offers the single-tenant App Service Environment (ASE). This model provides dedicated resources and more granular control over networking configurations, making it ideal for applications handling sensitive data or needing to meet compliance standards such as GDPR.
- External Networking: Expose applications to the internet using a public IP address.
- Internal Load Balancer (ILB): Enhance security by setting up applications behind an ILB, making them accessible only within your virtual network—perfect for internal or private applications.
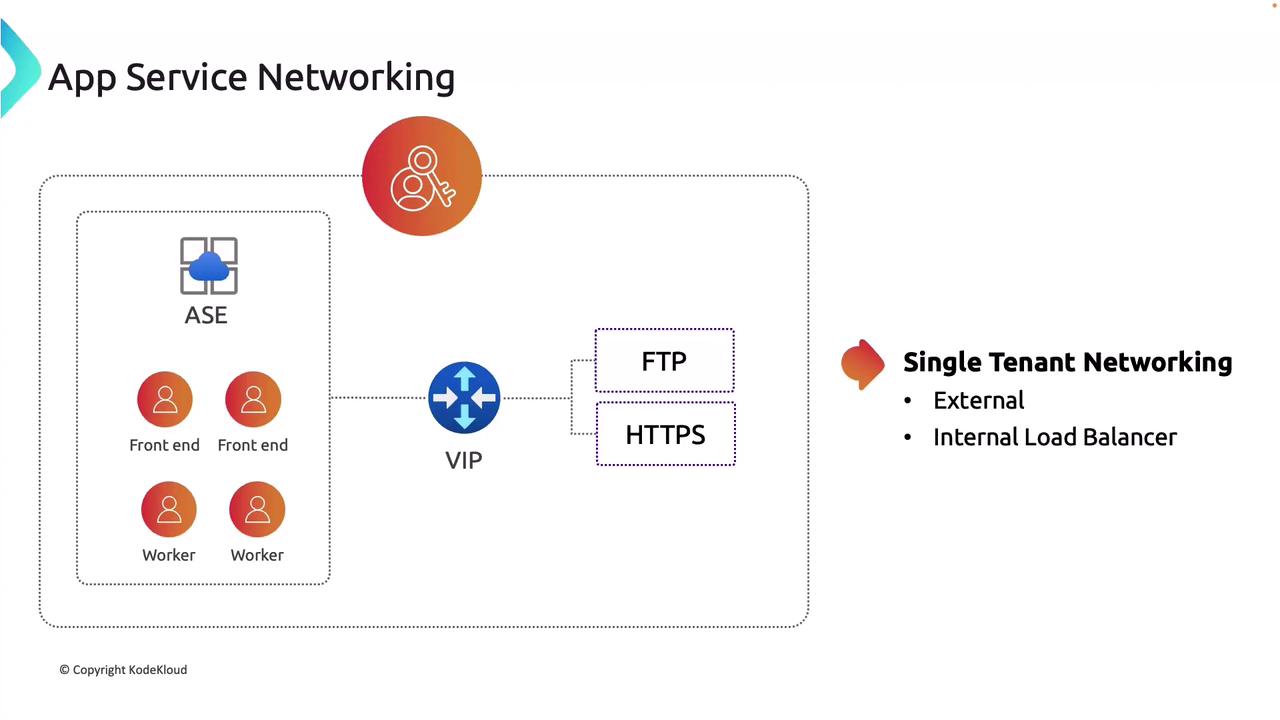
The single-tenant model is typically more expensive. Azure App Service uses an isolated plan to create an ASE.
Configuring Networking in the Azure Portal
The following sections detail how to configure networking settings for your App Service within the Azure portal.Accessing Inbound Traffic Settings
To manage inbound traffic, navigate to the Networking section in the App Service portal. By default, public access is enabled without restrictions. Access restrictions can be configured to allow traffic only from specified IP addresses or virtual networks.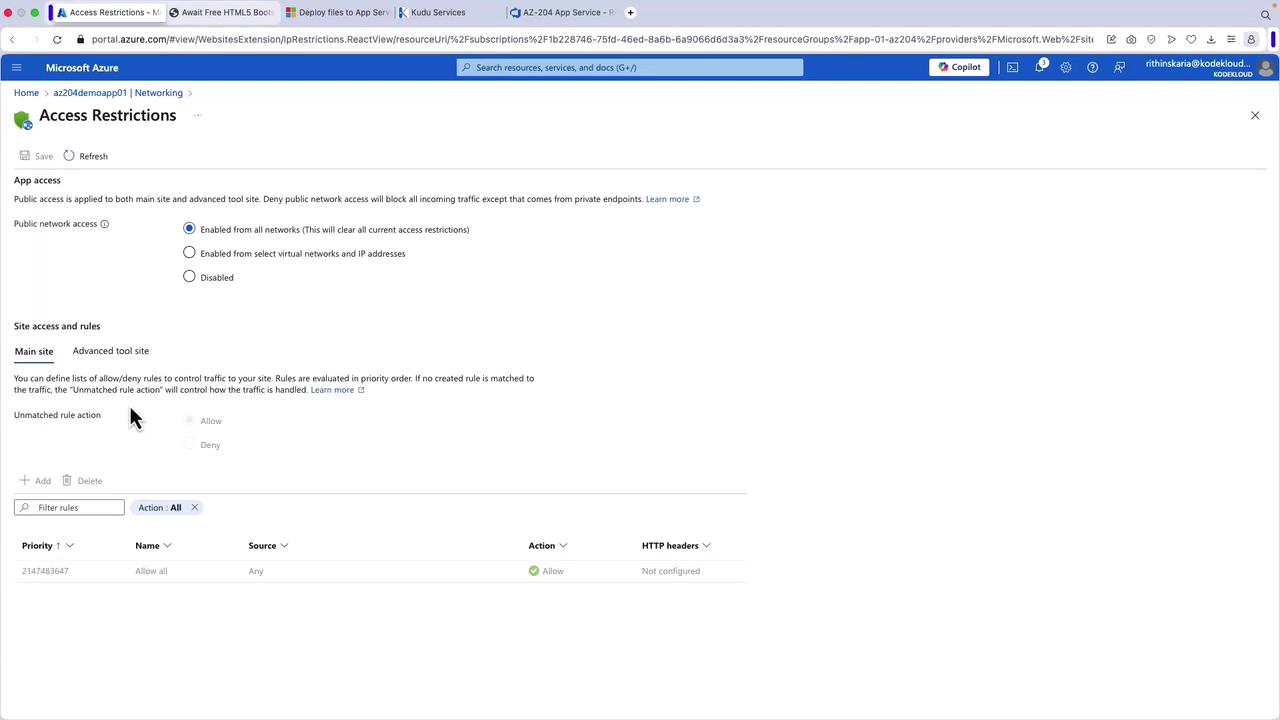
Scaling Up for Additional Features
Scaling up your App Service plan can unlock additional networking features such as an app assigned IP address or private endpoints. For instance, upgrading from the Basic to the Standard plan can provide these configurations.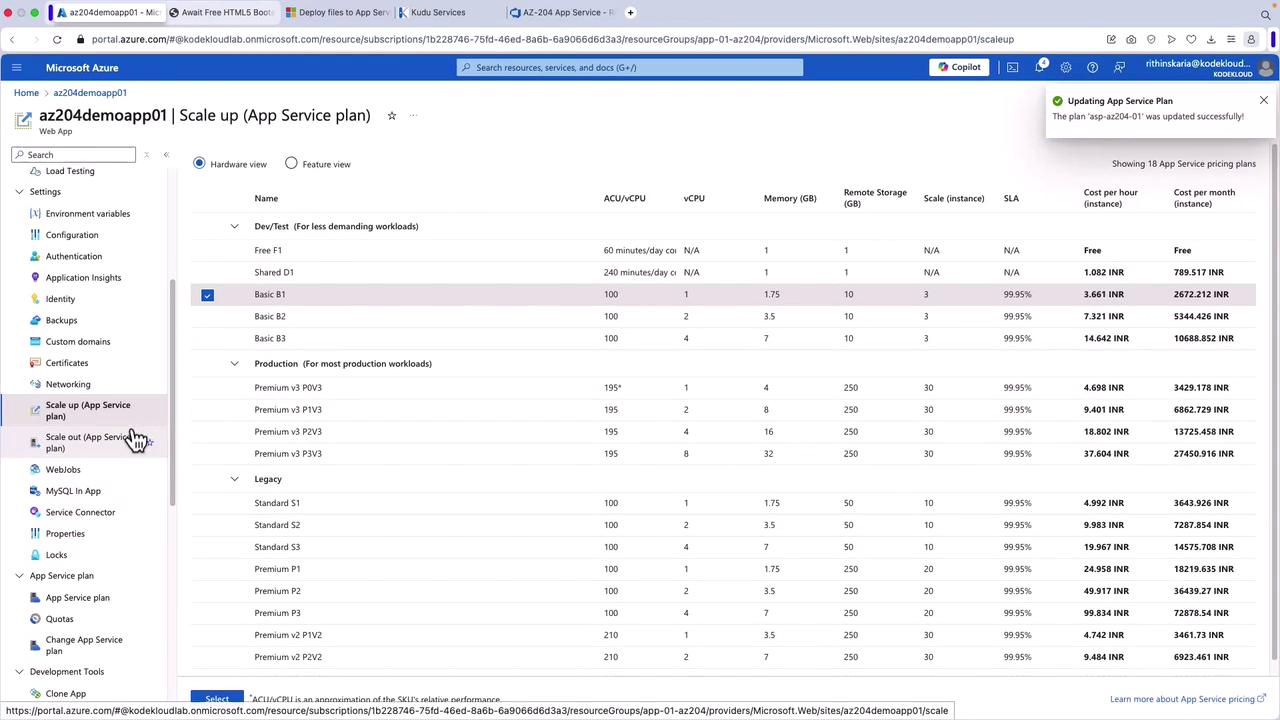
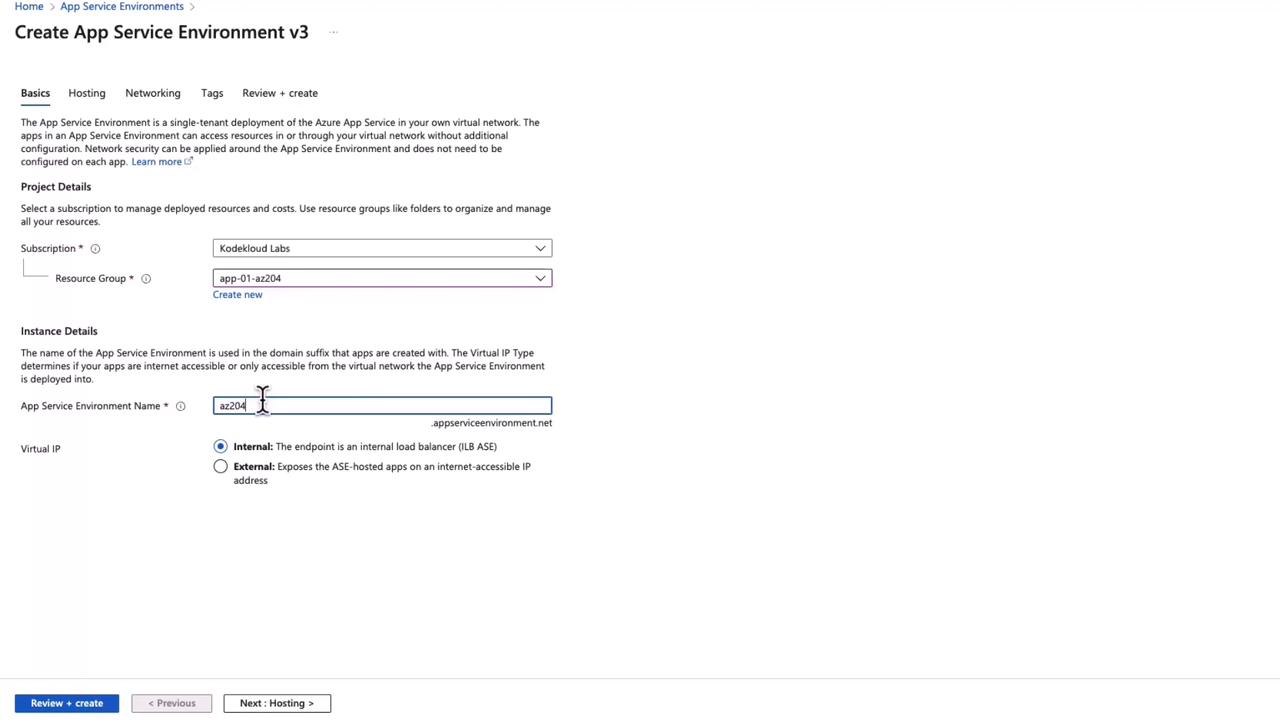
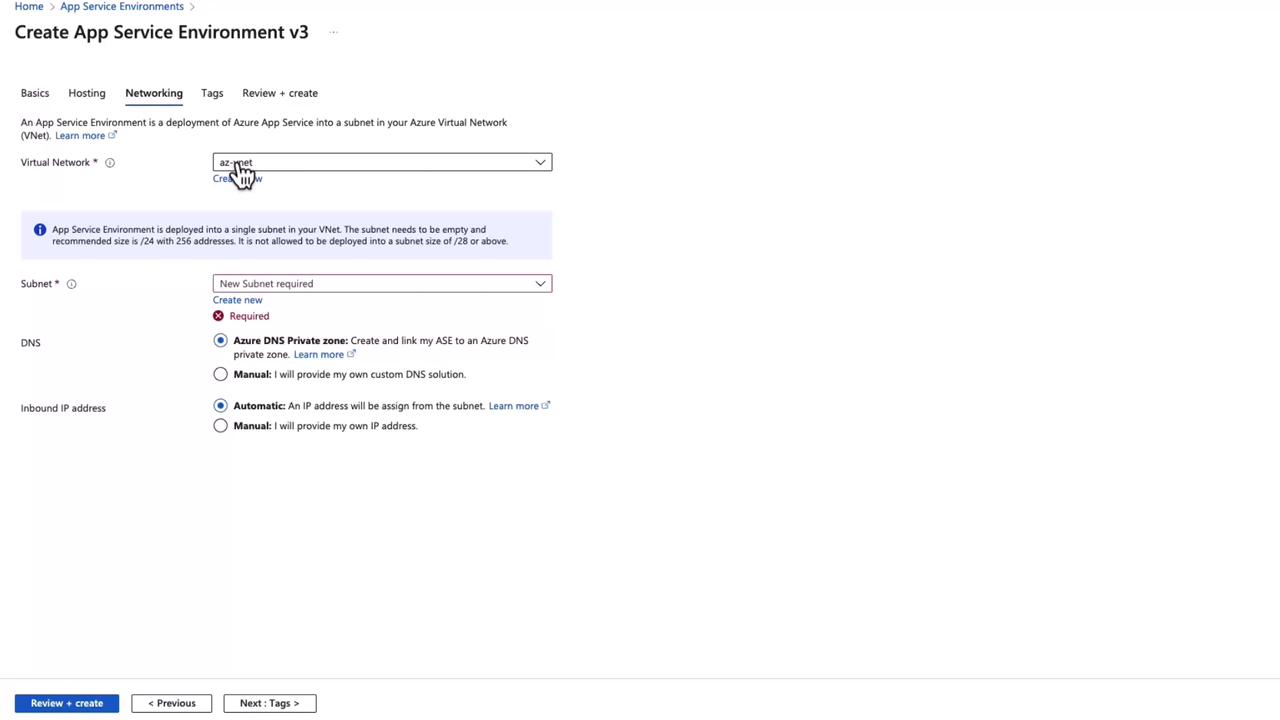
Creating an App Service Environment
To create an App Service Environment in Azure, select the “Add” option within the App Service Environments section. Note that subscription limitations may restrict creation in some cases. In the ASE configuration form, you will notice that the domain name differs from that used in multi-tenant App Services (e.g., appserviceenvironment.net instead of azurewebsites.net). Fill in the necessary details, such as naming the environment and choosing whether the app should be exposed externally or internally (using an internal load balancer).