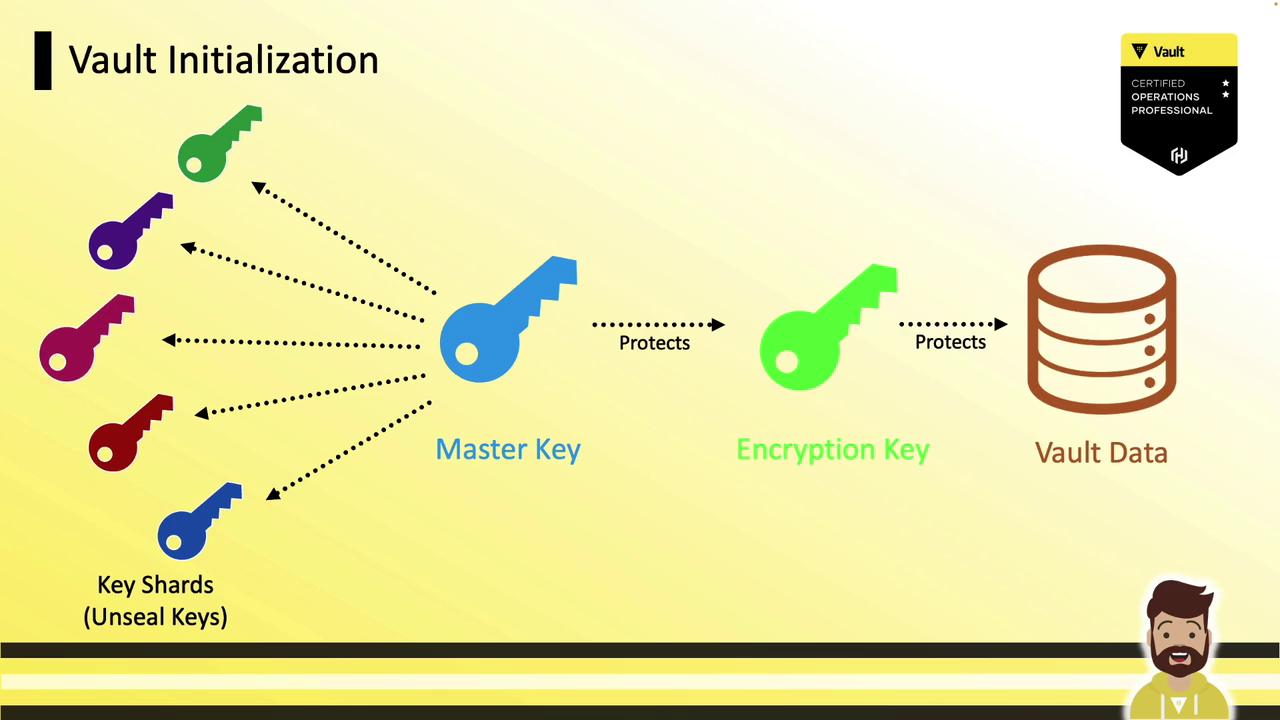
- Generates a master key and splits it into key shares (unseal or recovery keys).
- Creates the initial root token.
Vault Initialization Process
When you runvault operator init, Vault:
- Creates an encryption key for the storage backend.
- Generates a master key to encrypt that storage key.
- Splits the master key into shards (unseal or recovery keys).
- Outputs the shards along with the initial root token.
Distributing Key Shares
A common security practice is to distribute unseal (or recovery) keys to separate, trusted employees. For example, if you configure 5 key shares with a threshold of 3, you give each of five employees one share—any three can reconstruct the master key.
If a single operator runs
vault operator init without encryption, they receive all keys in plaintext. Always encrypt shards when splitting custody.Basic Initialization Options
Customize the number of shares and the reconstruction threshold:| Option | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
-key-shares | Total unseal key shards | -key-shares=5 |
-key-threshold | Shards required to unseal | -key-threshold=3 |
-recovery-shares | Total recovery key shards (auto-unseal) | -recovery-shares=5 |
-recovery-threshold | Shards required for recovery | -recovery-threshold=3 |
These flags adjust only the share count and threshold. They do not encrypt the output.
Encrypting Shares with PGP
To prevent a single operator from holding all key material, encrypt each shard with the recipient’s PGP public key. Provide Vault with each user’s.pub file during initialization.

Unseal Keys with PGP Encryption
Assume five users—Bob, Steve, Stacy, Katie, and Dani—have shared their public PGP keys:Recovery Keys with PGP Encryption
For auto-unseal workflows, encrypt recovery keys similarly:Ensure the count of
-pgp-keys or -recovery-pgp-keys matches the number of shares. Mismatched counts will cause initialization to fail.Encrypting the Root Token
You can also encrypt the initial root token with a PGP public key:Best Practices
- Match the count of PGP keys to the number of shares.
- The order of PGP keys in the command determines the order of encrypted output.
- Store and distribute encrypted shards and the encrypted root token securely.
- Perform a rekey operation if you need to rotate or replace lost key shares.