Vault Namespaces are available only in Vault Enterprise.
See Enterprise Namespaces Documentation for more details.
See Enterprise Namespaces Documentation for more details.
What Is a Namespace?
A Vault namespace is a child environment inside the root namespace. Each namespace acts like a standalone Vault, offering:- Fully isolated policies, auth methods, and secrets engines
- Delegation of administration to namespace-specific admins
- Centralized cluster management (storage backend, audit devices, upgrades)
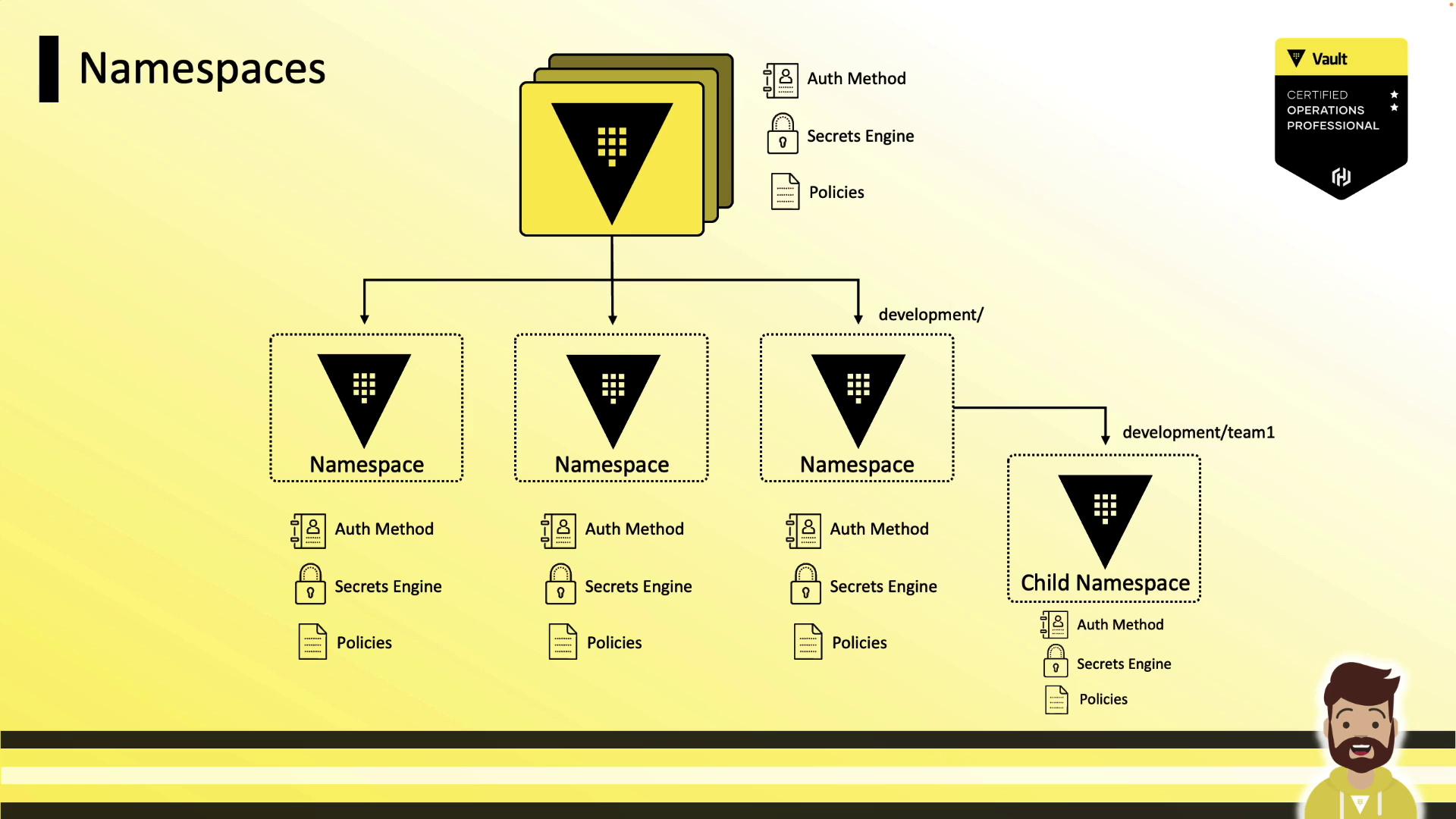
- Hierarchical namespaces, with support for nested child namespaces
- Namespace-scoped tokens (valid only within the issuing namespace)

Namespace Hierarchy
Namespaces are organized in a tree structure under the root. You can enable auth methods, secrets engines, and policies at any level—paths and ACLs are always relative to the namespace where they’re defined. This makes policy reuse straightforward.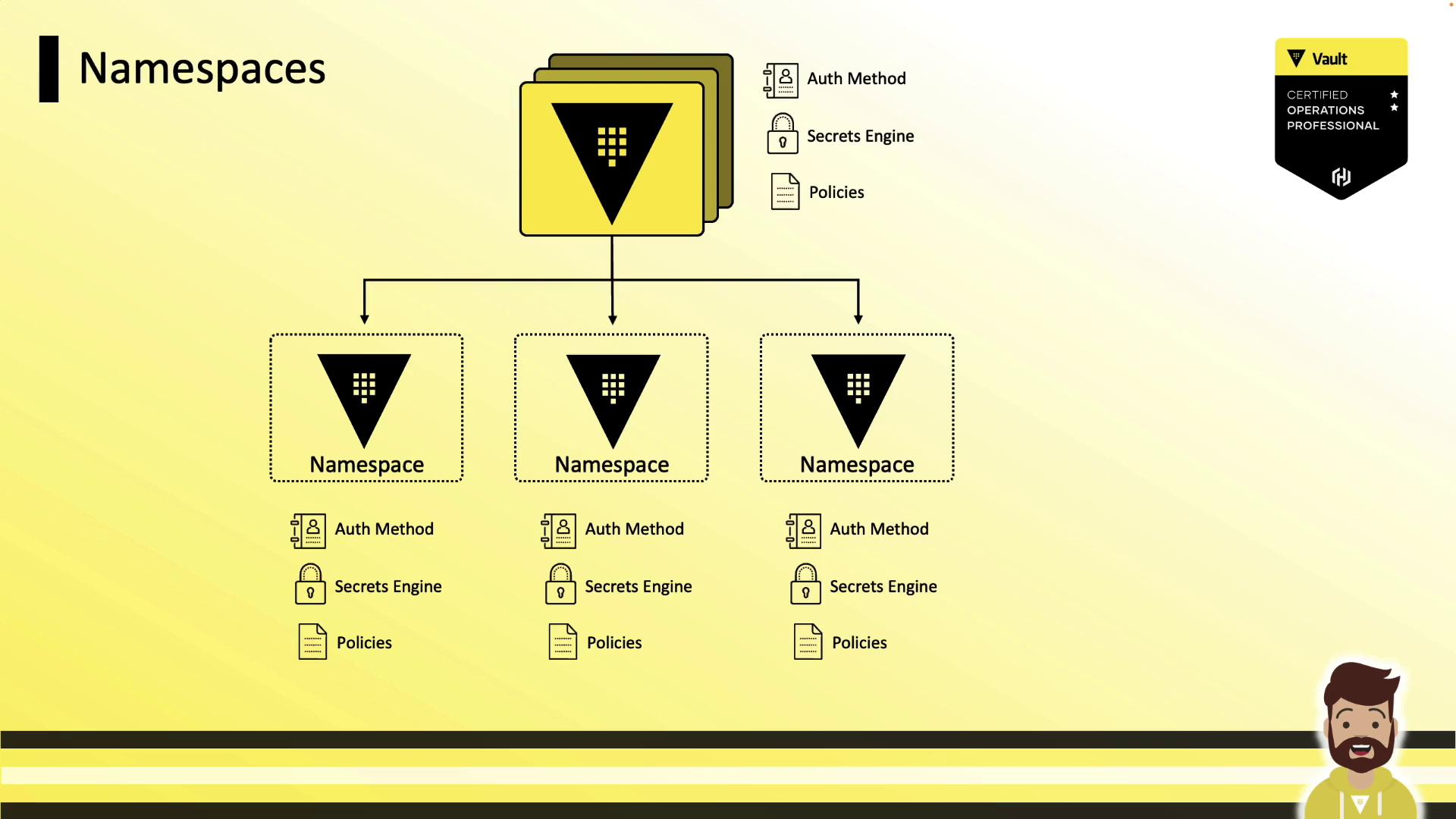
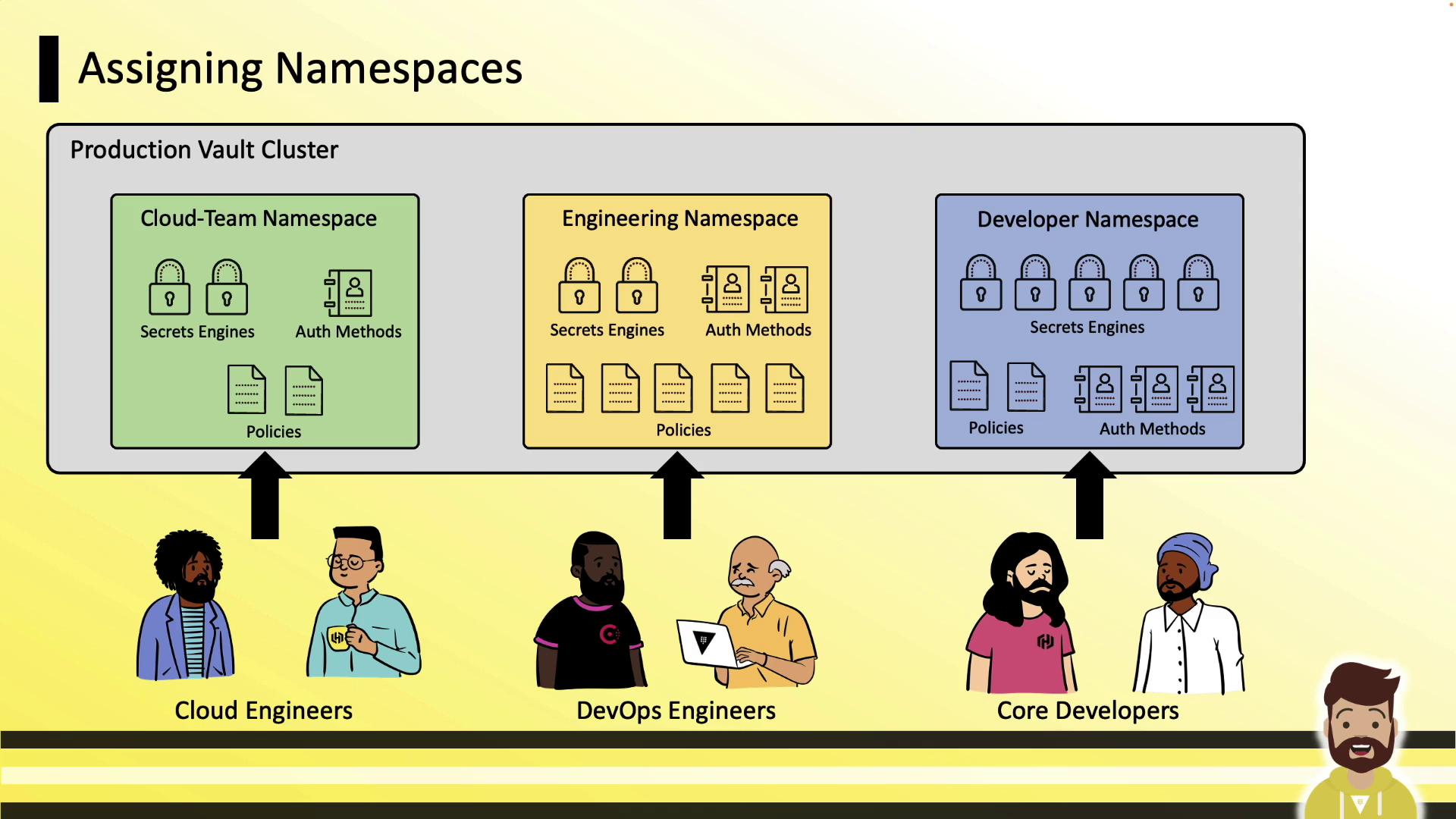
Assigning Namespaces to Teams
In a production Vault cluster, you might create separate namespaces for Cloud, Engineering, and Developer teams. Each namespace starts empty—no auth methods or engines are enabled by default.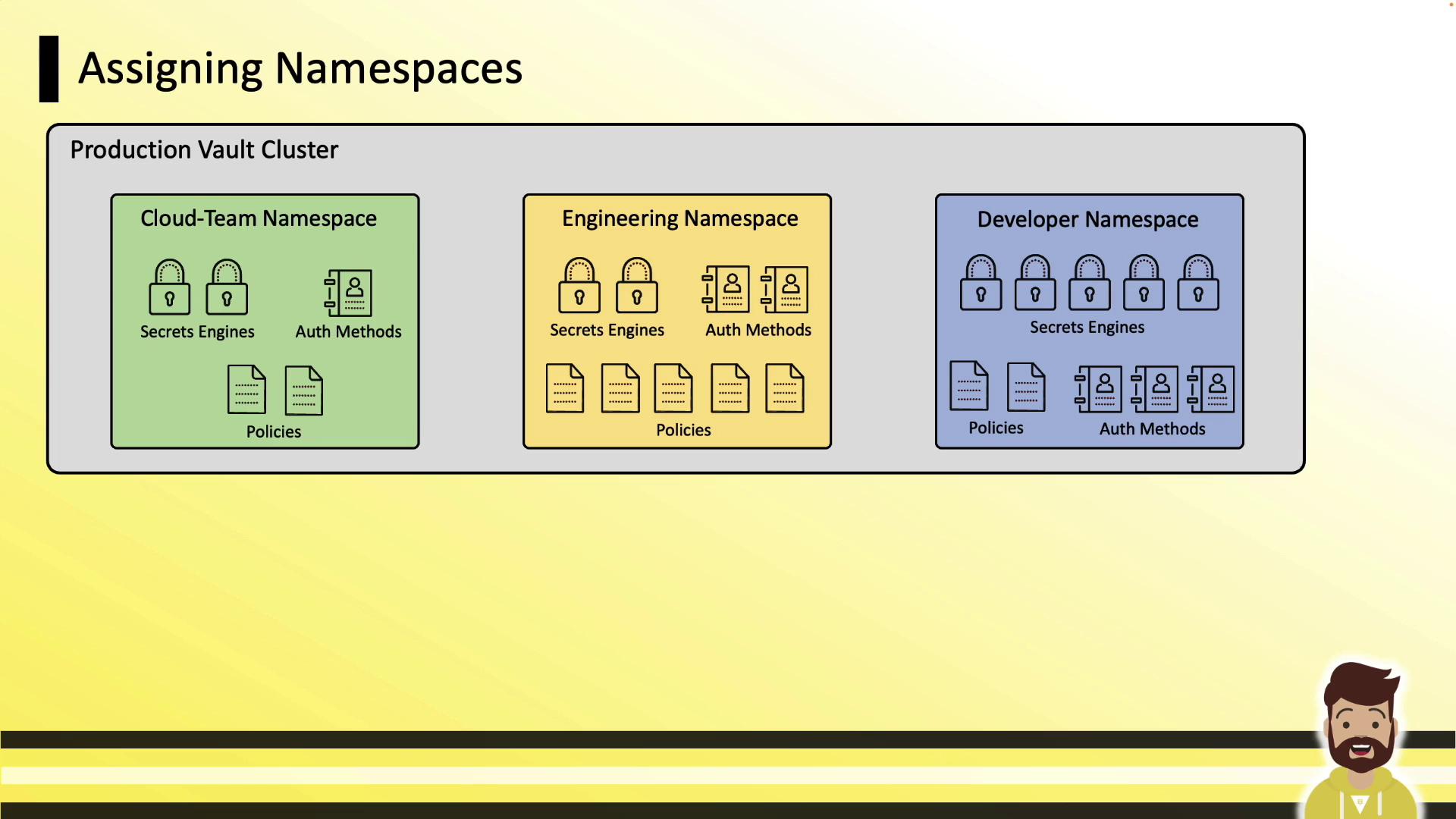
Administrative Delegation
Vault engineers handle cluster-wide tasks (storage backend, root namespace, upgrades). Namespace admins (e.g., developers) gain autonomy to configure auth methods, secrets engines, policies, and tokens—without tickets.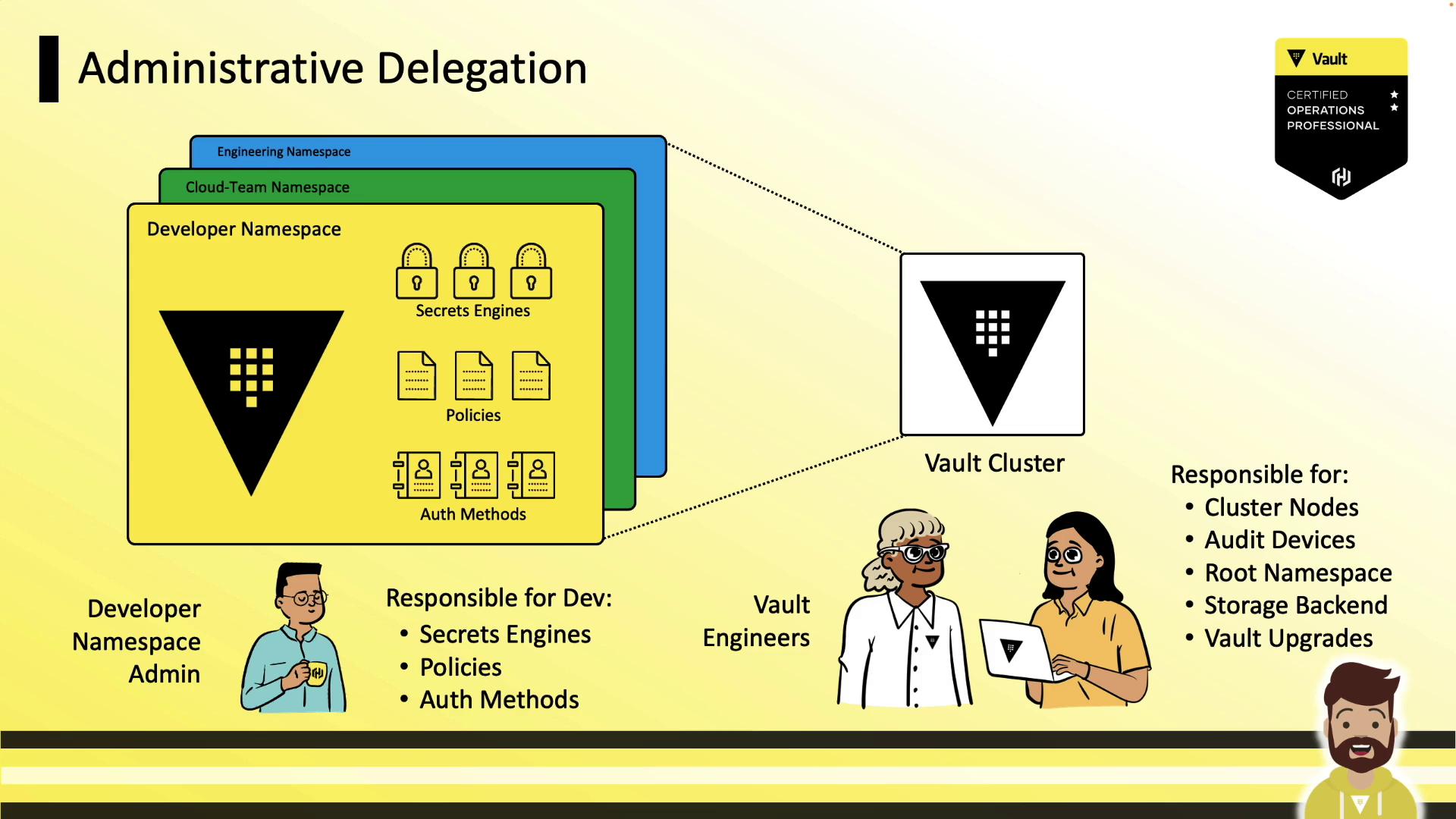
Authenticating to Namespaces
Users authenticate either at the root or directly into child namespaces—wherever relevant auth methods are enabled.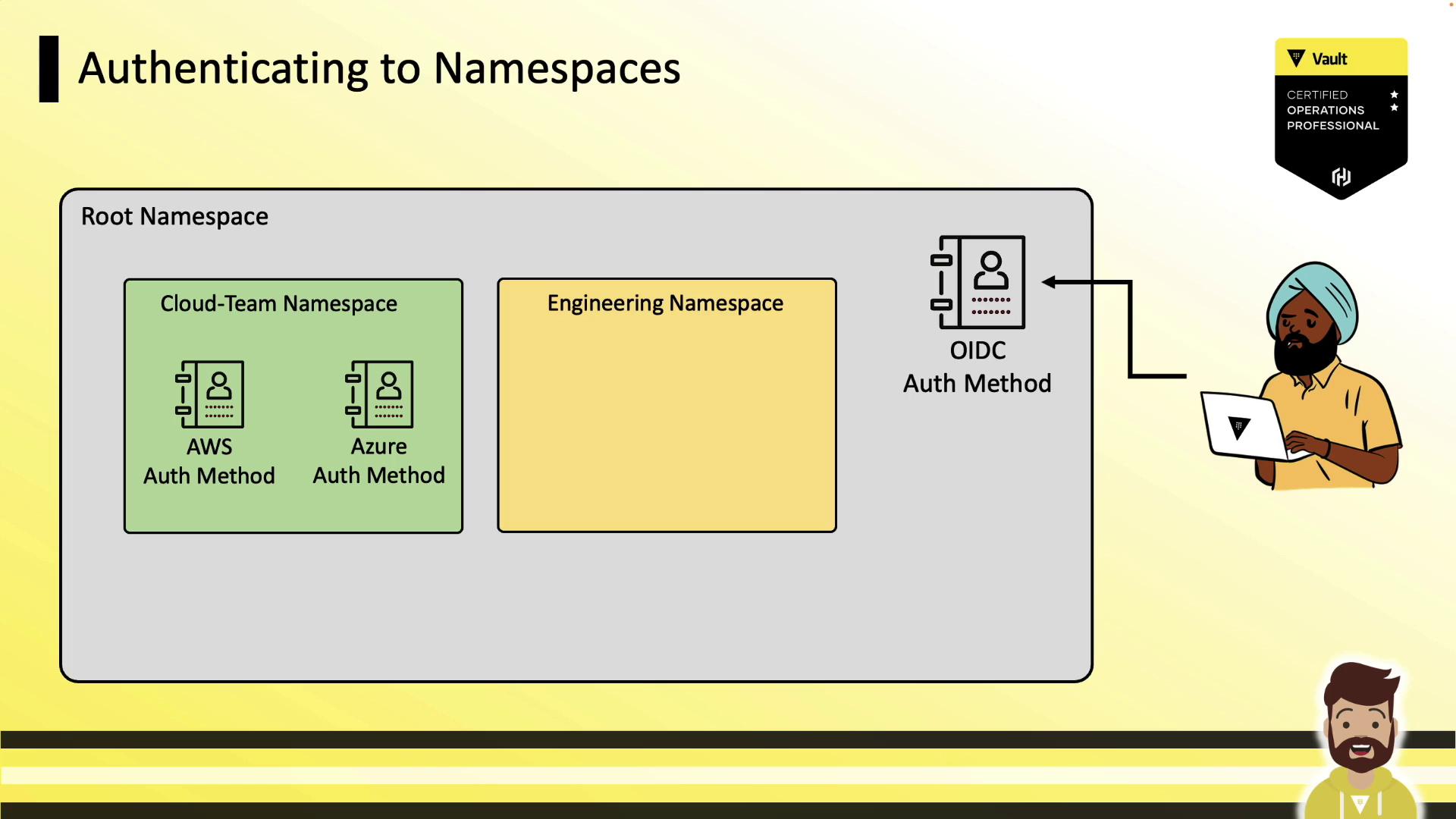
userpass), users can log in directly there:
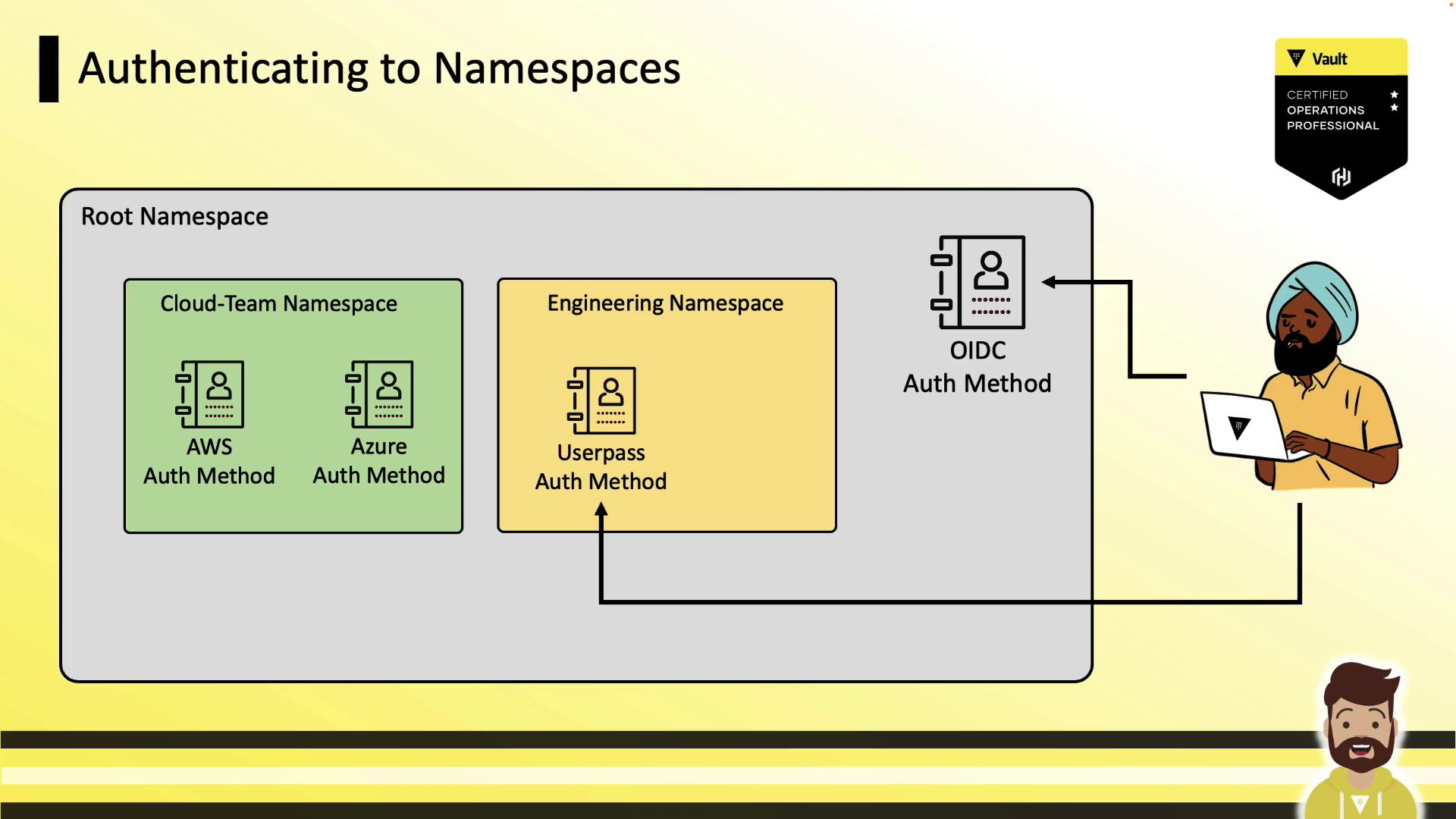
Common Namespace CLI Commands
| Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Create namespace | Create a new namespace | vault namespace create <namespace> |
| List namespaces | List all existing namespaces | vault namespace list |
| Delete namespace | Remove an existing namespace | vault namespace delete <namespace> |
Using an Environment Variable
SetVAULT_NAMESPACE so all CLI requests default to that namespace:
Using the -namespace Flag
Override the namespace for a single command:
Nested Namespace Example
Combine both methods to target child namespaces:Using Namespaces in the API
You can specify namespaces either via a header or in the URL path.| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Header approach | Send X-Vault-Namespace in the request |
| URL path approach | Prefix the endpoint with <namespace>/ |
1. X-Vault-Namespace Header
2. Namespace in the URL Path
v1/development/team-one/kv/data/sql/prod
Writing Policies for Namespaces
Policy paths are relative to their namespace: Insidecloud-team:
cloud-team:
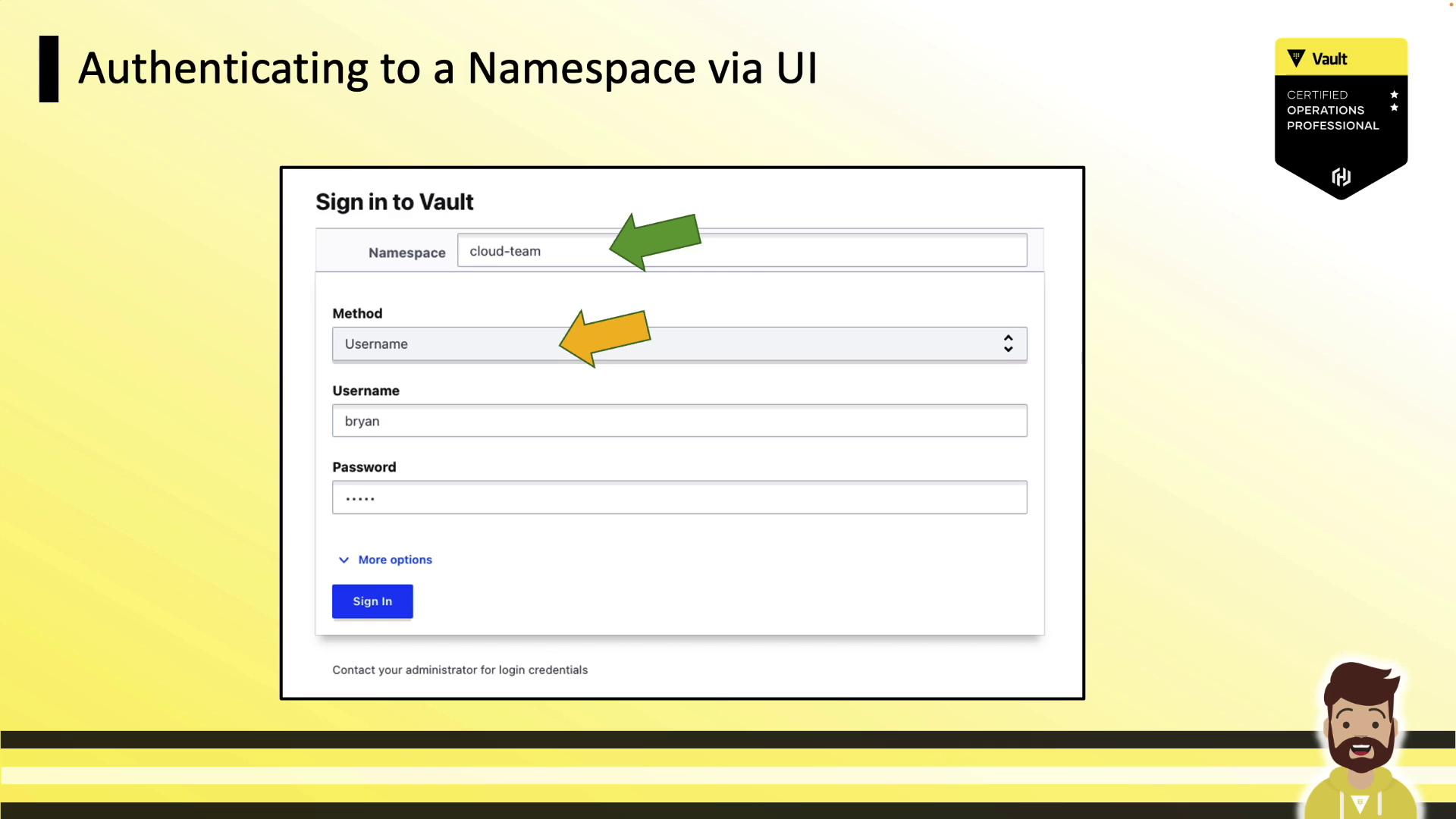
Authenticating via the UI
When signing in, specify your namespace (default isroot), choose the auth method, and enter your credentials: